|
Sammeda śikhara
Shri Sammet Shikharji () is a pilgrimage site in Giridih district, Jharkhand, India. It is located on Parasnath hill, the highest mountain in the state of Jharkhand. It is the most important Jain Tirtha (pilgrimage site) by both Digambara and Śvētāmbara, for it is the place where twenty of the twenty-four Jain tirthankaras along with many other monks attained Moksha. Etymology ''Shikharji'' means the "venerable peak". The site is also called Sammet Śikhar "peak of concentration." because it is a place where twenty of twenty-four Tirthankaras attained Moksha through meditation. The word "Parasnath" is derived from Parshvanatha, the twenty-third Jain Tirthankara, who was one of those who is believed to have attained Moksha at the site. Geography Shikarji is located in an inland part of rural east India. It lies on NH-2, the Delhi-Kolkata highway in a section called the Grand Trunk road Shikharji rises to making it the highest mountain in Jharkhand state. Jain traditi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jainism
Jainism ( ), also known as Jain Dharma, is an Indian religions, Indian religion. Jainism traces its spiritual ideas and history through the succession of twenty-four tirthankaras (supreme preachers of ''Dharma''), with the first in the current time cycle being Rishabhadeva, whom the tradition holds to have lived millions of years ago, the twenty-third ''tirthankara'' Parshvanatha, whom historians date to the 9th century BCE, and the twenty-fourth ''tirthankara'' Mahāvīra, Mahavira, around 600 BCE. Jainism is considered to be an eternal ''dharma'' with the ''tirthankaras'' guiding every time cycle of the Jain cosmology, cosmology. The three main pillars of Jainism are ''Ahimsa in Jainism, ahiṃsā'' (non-violence), ''anekāntavāda'' (non-absolutism), and ''aparigraha'' (asceticism). Jain monks, after positioning themselves in the sublime state of soul consciousness, take five main vows: ''ahiṃsā'' (non-violence), ''satya'' (truth), ''Achourya, asteya'' (not stealing), ''b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Girnar
Girnar is an ancient hill in Junagadh, Gujarat, India. Geology Mount Girnar is a major igneous plutonic complex which intruded into the basalts towards the close of the Deccan Trap period. The rock types identified in this complex are gabbros (tholeiitic and alkalic), diorites, lamprophyres, alkali-syenites and rhyolites. The parent gabbroic magma is shown to have given rise in sequence to diorites, lamprophyres and alkali-syenites. The rhyolite, though earlier considered a product of differentiation, is now believed to be an independent magma without any genetic link with the gabbro and its variants. History Fourteen of Ashoka's Major Rock Edicts, dating to circa 250 BCE, are inscribed on a large boulder that is housed in a small building located outside the town of Junagadh on Saurashtra peninsula in the state of Gujarat, India. It is located on Girnar Taleti road, at about 2 km (1.2 mi) far from Uperkot Fort easterly, some 2 km before Girnar Taleti. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akbar
Abu'l-Fath Jalal-ud-din Muhammad Akbar (25 October 1542 – 27 October 1605), popularly known as Akbar the Great ( fa, ), and also as Akbar I (), was the third Mughal emperor, who reigned from 1556 to 1605. Akbar succeeded his father, Humayun, under a regent, Bairam Khan, who helped the young emperor expand and consolidate Mughal domains in India. A strong personality and a successful general, Akbar gradually enlarged the Mughal Empire to include much of the Indian subcontinent. His power and influence, however, extended over the entire subcontinent because of Mughal military, political, cultural, and economic dominance. To unify the vast Mughal state, Akbar established a centralised system of administration throughout his empire and adopted a policy of conciliating conquered rulers through marriage and diplomacy. To preserve peace and order in a religiously and culturally diverse empire, he adopted policies that won him the support of his non-Muslim subjects. Eschewing t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an early-modern empire that controlled much of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries. Quote: "Although the first two Timurid emperors and many of their noblemen were recent migrants to the subcontinent, the dynasty and the empire itself became indisputably Indian. The interests and futures of all concerned were in India, not in ancestral homelands in the Middle East or Central Asia. Furthermore, the Mughal empire emerged from the Indian historical experience. It was the end product of a millennium of Muslim conquest, colonization, and state-building in the Indian subcontinent." For some two hundred years, the empire stretched from the outer fringes of the Indus river basin in the west, northern Afghanistan in the northwest, and Kashmir in the north, to the highlands of present-day Assam and Bangladesh in the east, and the uplands of the Deccan Plateau in South India. Quote: "The realm so defined and governed was a vast territory of some , rang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
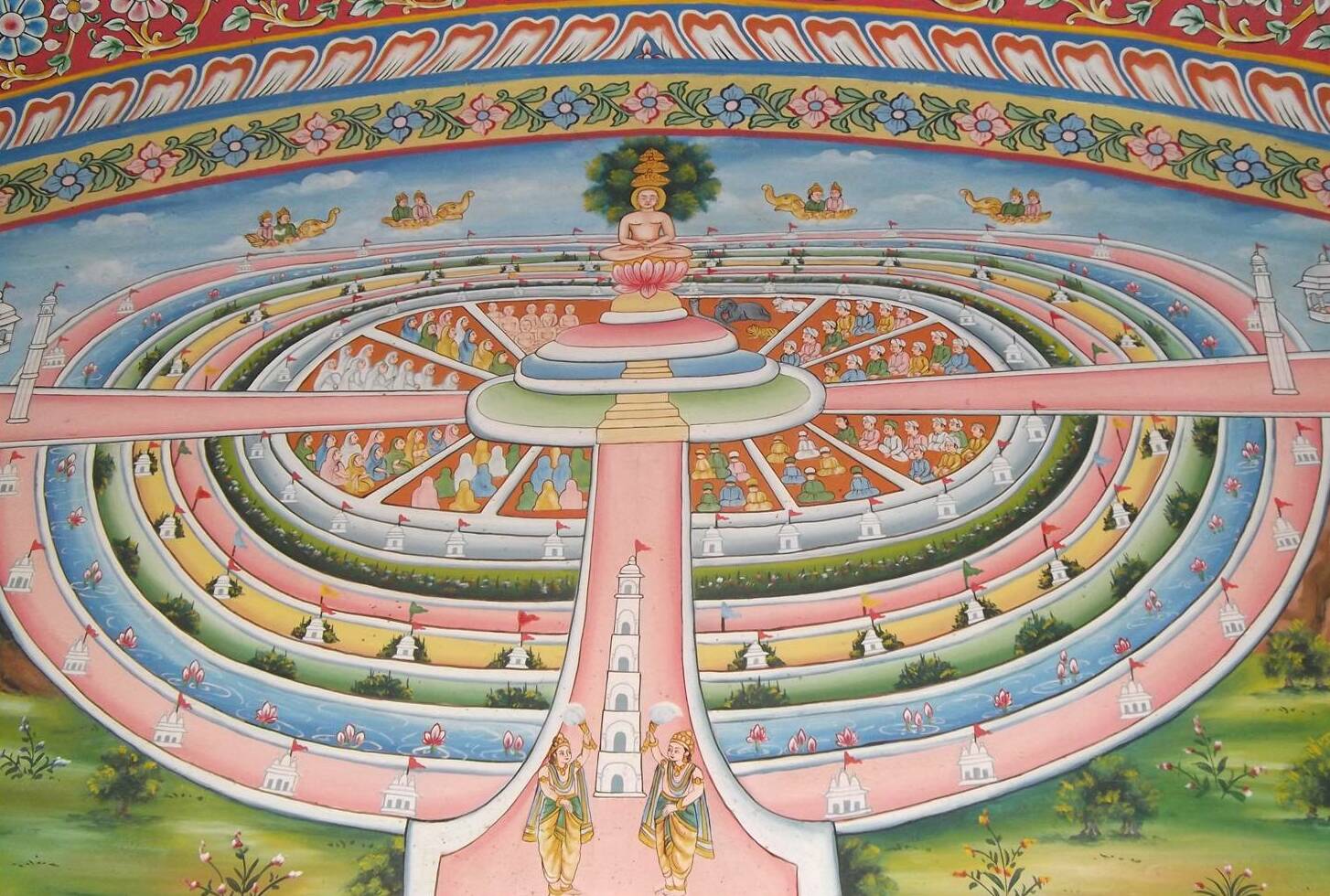
Samavasarana
In Jainism, Samavasarana or Samosharana ("Refuge to All") is the divine preaching hall of the Tirthankara, stated to have more than 20,000 stairs in it. The word ''samavasarana'' is derived from two words, ''sama'', meaning general and ''avasara'', meaning opportunity. It is an important feature in Jain art. The Samavasarana seems to have replaced the original Jain stupa as an object of worship. Samavasarana Hall In samavasarana hall, the ''tirthankara'' sits on a throne without touching it (about two inches above it). Around the tirthankara sit the ''ganadharas'' (chief disciples). Living beings sit in the following order: *In the first hall, ascetics *In the second hall, one class of deva ladies *In the third hall, ''aryikas'' (nuns) and laywomen *In the next three halls, three other classes of deva ladies *In the next four halls, the four classes of devas (heavenly beings) *Men, in the eleventh hall *Animals, in the last hall According to Jain texts, there would be four w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vaghela Dynasty
The Vaghela dynasty were an offshoot vassal clan connected to the Chaulukya (Solanki) dynasty, ruling Gujarat in the 13th century CE. Their capital was Dholka. They were the last Hindu dynasty to rule Gujarat before the Muslim conquest of the region. Early members of the Vaghela family served the Chaulukyas in the 12th century CE, and claimed to be a branch of that dynasty. In the 13th century, during the reign of the weak Chaulukya king Bhima II, the Vaghela general Lavanaprasada and his son Viradhavala gained a large amount of power in the kingdom, although they continued to nominally acknowledge Chaulukya suzerainty. In the mid-1240s, Viradhavala's son Visaladeva usurped the throne, and his successors ruled Gujarat until Karna Vaghela was defeated by Nusrat Khan of the Delhi Sultanate in 1304 CE, and lost Gujarat. Origin The Vaghelas usurped power from the Chaulukya dynasty. According to the 14th century chronicler Merutunga, the earliest known member of the Vaghel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vastupala
Vastupāla (died 1240 CE) was a prime minister of the Vāghelā king Vīradhavala and his successor Vīsaladeva, who ruled in present-day Gujarat region of India, in the early 13th century. Although he served in an administrative and military capacity, he was also a patron of art, literature and public works. He, together with his brother Tejapāla, assisted in the restoration of peace in the kingdom, and served in a number of campaigns against Lāṭa, Godraha, Kutch and the Delhi Sultanate. The brothers were instrumental in the construction of the , Luniga-vasahi temple on Mount Abu and the Vastupala-vihara on Girnar. Ancestry and family Vastupala and his brother Tejapala were born to a Pragavata, or Porwad as they are known today, Jain family in Anahilavada Patan (modern day Patan, Gujarat). Vijayasenasuri, a Jain monk of Nagendra Gachchha, was their clan guru. Extensive information on their ancestry has been drawn from literary works and inscriptions: in ''Naranarayanana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kalpa Sūtra
The ''Kalpa Sūtra'' ( sa, कल्पसूत्र) is a Jain text containing the biographies of the Jain Tirthankaras, notably Parshvanatha and Mahavira. Traditionally ascribed to Bhadrabahu, which would place it in the 4th century BCE, it was probably put in writing 980 or 993 years after the ''Nirvana'' (''Moksha'') of Mahavira. History Within the six sections of the Jain literary corpus belonging to the Svetambara school, it is classed as one of the Cheda Sūtras. This Sutra contains detailed life histories and, from the mid-15th century, was frequently illustrated with miniature painting. The oldest surviving copies are written on paper in western India in the 14th century. The Kalpa Sutra is ascribed to Bhadrabahu, traditionally said to have composed it some 150 years after the ''Nirvāṇa'' (samadhi) of Mahavira. It was compiled probably during the reign of Dhruvasena, 980 or 993 years after Mahavira's death. Importance The book is read and illustrated in an eigh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jnatrdharmakathah
''Jnātrdhārmakathāh'' is the sixth of the 12 Jain āgamas said to be promulgated by Māhavīra himself. Jnātrdhārmakathāh translated as "Stories of Knowledge and Righteousness" is said to have been composed by Ganadhara Sudharmaswami as per the Śvetámbara tradition. Subject matter of the Agama It contains a series of narratives, from which morals about results of following the religious path are drawn. The Eighth Chapter gives the story of Lord Mallinath Mallinatha (Prakrit ''Mallinātha'', "Lord of jasmine or seat") was the 19th tīrthaṅkara "ford-maker" of the present ''avasarpiṇī'' age in Jainism. Jain texts indicate Mālliṇātha was born at Mithila into the Ikshvaku dynasty to ... the nineteenth Tirthankara. English translations Popular English Translations are :- Illustrated SRI JNATADHARMAKATHANGA SUTRA in 2 volumes Prakrit Gatha - Hindi exposition - English exposition and Appendices Ed. by Pravartaka Amar Muni, Shrichand Surana Saras, Eng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brahmacharya
''Brahmacharya'' (; sa, ब्रह्मचर्य ) is a concept within Indian religions that literally means to stay in conduct within one's own Self. In Yoga, Hinduism, Buddhism and Jainism it generally refers to a lifestyle characterized by sexual continence or complete abstinence. In the Hindu, Jain, and Buddhist monastic traditions, ''brahmacharya'' implies, among other things, the mandatory renunciation of sex and marriage. It is considered necessary for a monk's spiritual practice. Western notions of the religious life as practiced in monastic settings mirror these characteristics. Etymology The word ''brahmacharya'' stems from two Sanskrit roots: #''Brahma'' (Devanagari: ब्रह्म) meaning one's own Self, ultimate unchanging reality, absolute consciousness, much discussed in the Upanishads. Brahma is also the Vedic God of creation, no different from the Self or Atman. (''Ayam Ātmā Brahma (अयम् आत्मा ब्रह्म) The Self ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
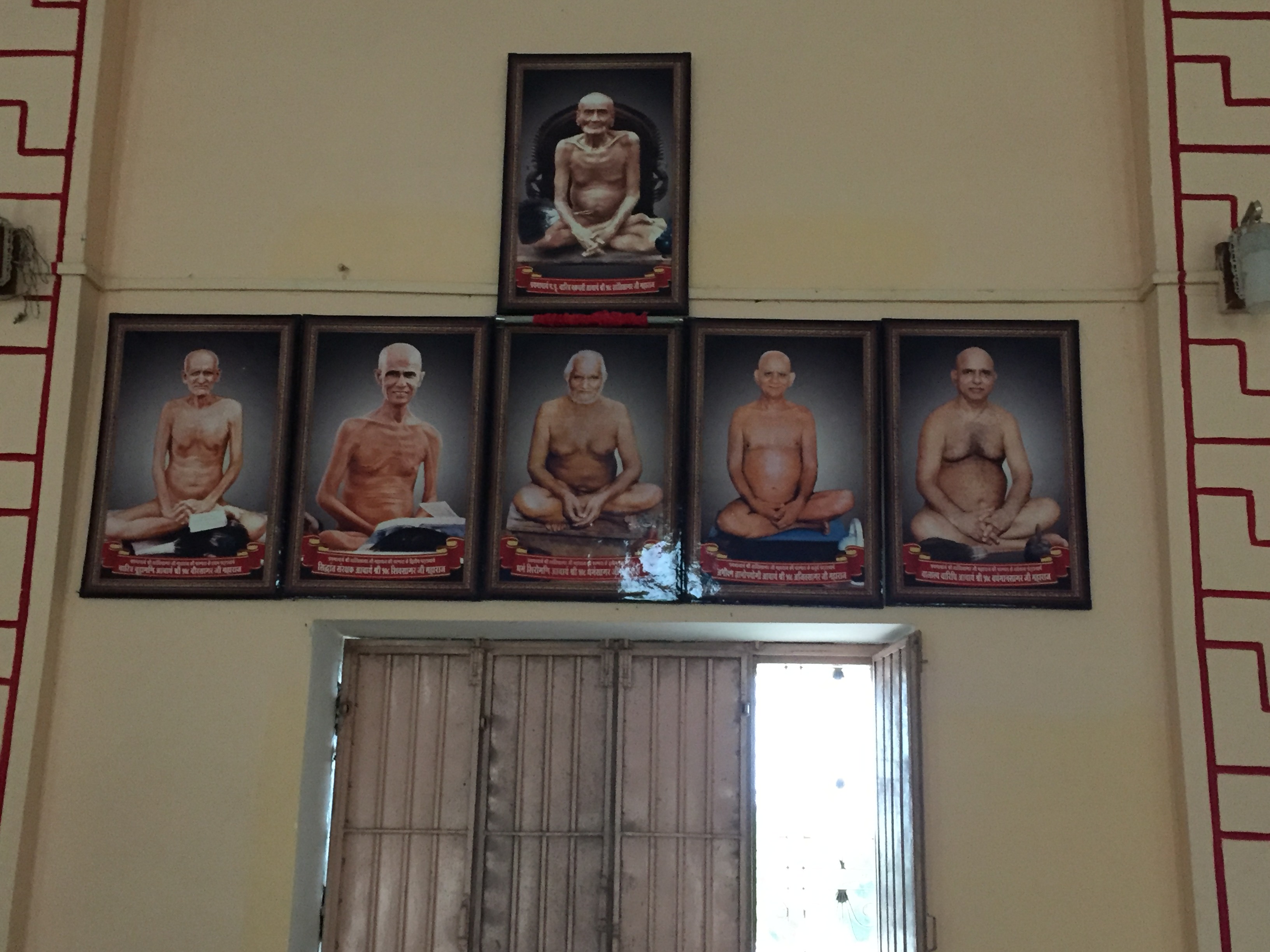
Acharya Shantisagar
Acharya Shri Shantisagar (1872–1955) was an Indian monk of the Digambara school of the Jain faith. He was the first Acharya (preceptor) and a leader of his sect in the 20th century. Shanti Sagar ji revived the teaching and practice of traditional Digambara practices in North India. He was lustrated as a kshullaka into the Sangha (holy order) by Devappa (Devakirti) Swami. He took his ailaka deeksha (religious vows) before an image of the Tirthankara Neminatha. In about 1920, Shantisagar became a full muni (monk) of the Digambara sect of Jainism. In 1922, at Yarnal village, Belgaum district, Karnataka, he was given the name "Shanti Sagara" ("Ocean of Peace"). Early life Shantisagar ji were born in 1872 near Bhoj village, Belgavi district Karnataka, India. His father either worked as a farmer or was employed in the clothing business. At age eighteen, having read religious texts and undergone several pilgrimages, Shantisagar Ji decided to dedicate his life to a religious order. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.png)



