|
Samarium Hexaboride
Samarium hexaboride (SmB6) is an intermediate-valence compound where samarium is present both as Sm2+ and Sm3+ ions at the ratio 3:7. It belongs to a class of Kondo insulators. At temperatures above 50 K its properties are typical of a Kondo metal, with metallic electrical conductivity characterized by strong electron scattering, whereas at low temperatures, it behaves as a non-magnetic insulator with a narrow band gap of about 4–14 meV. The cooling-induced metal-insulator transition in SmB6 is accompanied by a sharp increase in thermal conductivity, peaking at about 15 K. The reason for this increase is that electrons do not contribute to thermal conductivity at low temperatures, which is instead dominated by phonons. The decrease in electron concentration reduced the rate of electron-phonon scattering. Some research claims that it may be a topological insulator. Other researchers found no evidence of topological surface states. The increasing electrical resistance with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samarium
Samarium is a chemical element with symbol Sm and atomic number 62. It is a moderately hard silvery metal that slowly oxidizes in air. Being a typical member of the lanthanide series, samarium usually has the oxidation state +3. Compounds of samarium(II) are also known, most notably the monoxide SmO, monochalcogenides SmS, SmSe and SmTe, as well as samarium(II) iodide. The last compound is a common reducing agent in chemical synthesis. Samarium has no significant biological role, and some samarium salts are slightly toxic. Samarium was discovered in 1879 by French chemist Paul-Émile Lecoq de Boisbaudran and named after the mineral samarskite from which it was isolated. The mineral itself was named after a Russian mine official, Colonel Vassili Samarsky-Bykhovets, who thus became the first person to have a chemical element named after him, albeit indirectly. Though classified as a rare-earth element, samarium is the 40th most abundant element in Earth's crust and more common than ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ions
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge. The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convention. The net charge of an ion is not zero because its total number of electrons is unequal to its total number of protons. A cation is a positively charged ion with fewer electrons than protons while an anion is a negatively charged ion with more electrons than protons. Opposite electric charges are pulled towards one another by electrostatic force, so cations and anions attract each other and readily form ionic compounds. Ions consisting of only a single atom are termed atomic or monatomic ions, while two or more atoms form molecular ions or polyatomic ions. In the case of physical ionization in a fluid (gas or liquid), "ion pairs" are created by spontaneous molecule collisions, where each generated pair consists of a free electron and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
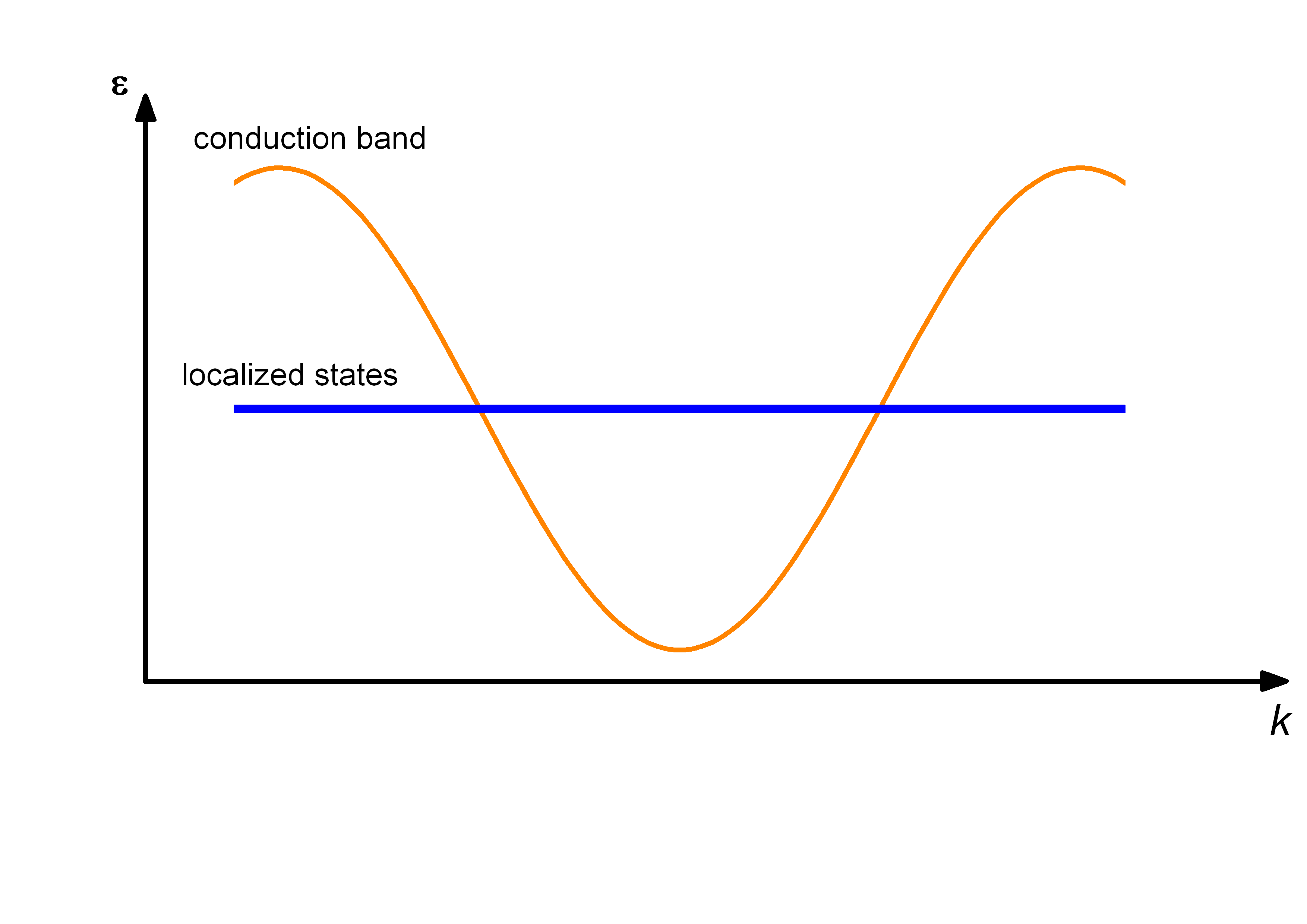
Kondo Insulator
In solid-state physics, Kondo insulators (also referred as Kondo semiconductors and heavy fermion semiconductors) are understood as materials with strongly correlated electrons, that open up a narrow band gap (in the order of 10 meV) at low temperatures with the chemical potential lying in the gap, whereas in heavy fermion materials the chemical potential is located in the conduction band. The band gap opens up at low temperatures due to hybridization of localized electrons (mostly f-electrons) with conduction electrons, a correlation effect known as the Kondo effect. As a consequence, a transition from metallic behavior to insulating behavior is seen in resistivity measurements. The band gap could be either direct or indirect. Most studied Kondo insulators are FeSi, Ce3Bi4Pt3, SmB6, YbB12, and CeNiSn, although there are over a dozen known Kondo insulators. Historical overview In 1969, Menth ''et al.'' found no magnetic ordering in SmB6 down to 0.35 K and a change from metal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
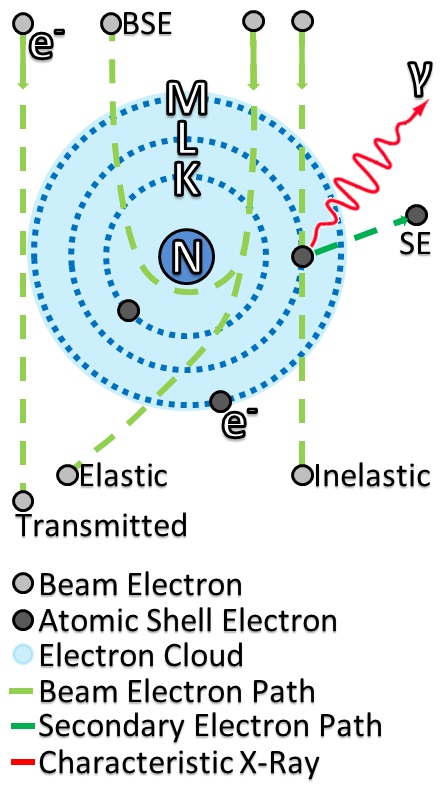
Electron Scattering
Electron scattering occurs when electrons are deviated from their original trajectory. This is due to the electrostatic forces within matter interaction or, if an external magnetic field is present, the electron may be deflected by the Lorentz force. This scattering typically happens with solids such as metals, semiconductors and insulators; and is a limiting factor in integrated circuits and transistors. The application of electron scattering is such that it can be used as a high resolution microscope for hadronic systems, that allows the measurement of the distribution of charges for nucleons and nuclear structure. The scattering of electrons has allowed us to understand that protons and neutrons are made up of the smaller elementary subatomic particles called quarks. Electrons may be scattered through a solid in several ways: *Not at all: no electron scattering occurs at all and the beam passes straight through. *Single scattering: when an electron is scattered just once. *Plu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Band Gap
In solid-state physics, a band gap, also called an energy gap, is an energy range in a solid where no electronic states can exist. In graphs of the electronic band structure of solids, the band gap generally refers to the energy difference (in electron volts) between the top of the valence band and the bottom of the conduction band in insulators and semiconductors. It is the energy required to promote a valence electron bound to an atom to become a conduction electron, which is free to move within the crystal lattice and serve as a charge carrier to conduct electric current. It is closely related to the HOMO/LUMO gap in chemistry. If the valence band is completely full and the conduction band is completely empty, then electrons cannot move within the solid because there are no available states. If the electrons are not free to move within the crystal lattice, then there is no generated current due to no net charge carrier mobility. However, if some electrons transfer from th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermal Conductivity
The thermal conductivity of a material is a measure of its ability to conduct heat. It is commonly denoted by k, \lambda, or \kappa. Heat transfer occurs at a lower rate in materials of low thermal conductivity than in materials of high thermal conductivity. For instance, metals typically have high thermal conductivity and are very efficient at conducting heat, while the opposite is true for insulating materials like Rockwool or Styrofoam. Correspondingly, materials of high thermal conductivity are widely used in heat sink applications, and materials of low thermal conductivity are used as thermal insulation. The reciprocal of thermal conductivity is called thermal resistivity. The defining equation for thermal conductivity is \mathbf = - k \nabla T, where \mathbf is the heat flux, k is the thermal conductivity, and \nabla T is the temperature gradient. This is known as Fourier's Law for heat conduction. Although commonly expressed as a scalar, the most general form of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phonon
In physics, a phonon is a collective excitation in a periodic, Elasticity (physics), elastic arrangement of atoms or molecules in condensed matter physics, condensed matter, specifically in solids and some liquids. A type of quasiparticle, a phonon is an excited state in the quantum mechanical Quantization (physics), quantization of the mode of vibration, modes of vibrations for elastic structures of interacting particles. Phonons can be thought of as quantized sound waves, similar to photons as quantized light waves. The study of phonons is an important part of condensed matter physics. They play a major role in many of the physical properties of condensed matter systems, such as thermal conductivity and electrical conductivity, as well as in models of neutron scattering and related effects. The concept of phonons was introduced in 1932 by Soviet Union, Soviet physicist Igor Tamm. The name ''phonon'' comes from the Ancient Greek language, Greek word (), which translates to ''so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
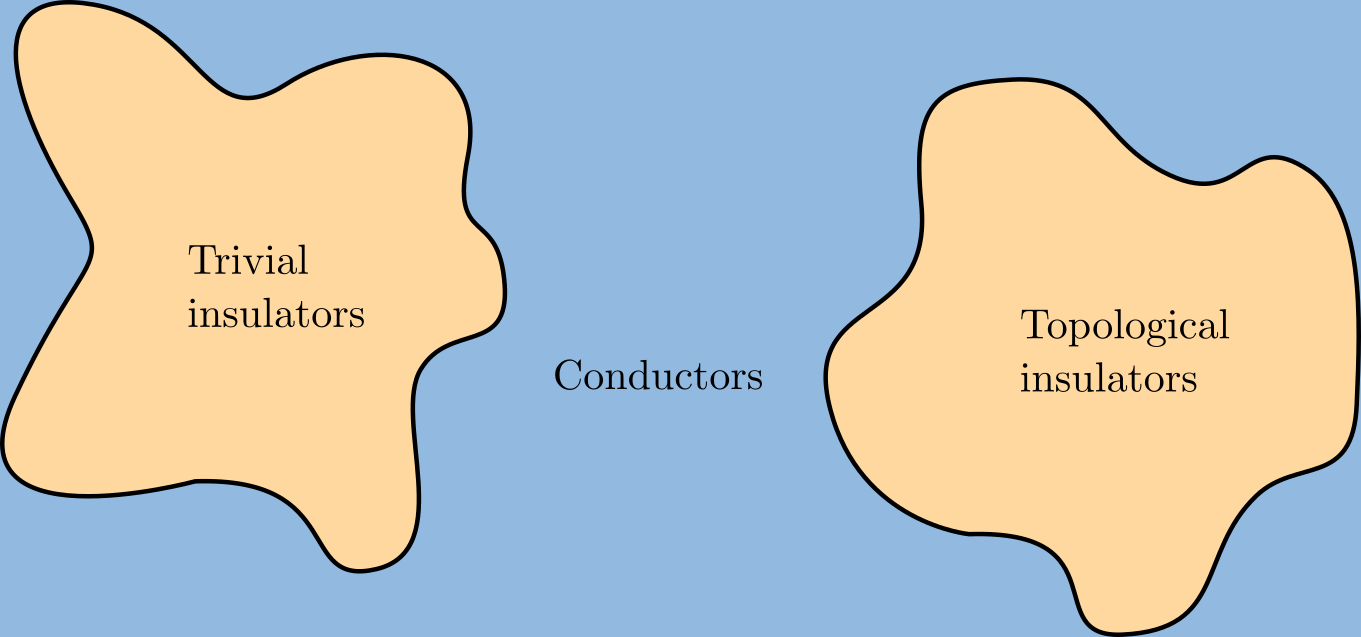
Topological Insulator
A topological insulator is a material whose interior behaves as an electrical insulator while its surface behaves as an electrical conductor, meaning that electrons can only move along the surface of the material. A topological insulator is an insulator for the same reason a "trivial" (ordinary) insulator is: there exists an energy gap between the valence and conduction bands of the material. But in a topological insulator, these bands are, in an informal sense, "twisted", relative to a trivial insulator. The topological insulator cannot be continuously transformed into a trivial one without untwisting the bands, which closes the band gap and creates a conducting state. Thus, due to the continuity of the underlying field, the border of a topological insulator with a trivial insulator (including vacuum, which is topologically trivial) is forced to support a conducting state. Since this results from a global property of the topological insulator's band structure, local (symmetry- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical Review X
''Physical Review X'' is a peer-reviewed open access scientific journal published by the American Physical Society covering all branches of pure, applied, and interdisciplinary physics. It carefully applies highly selective editorial standards and aims to attract, select, and publish papers that are exceptional in originality, substance, and significance. It is part of the ''Physical Review'' family of journals. The lead editors are Jean-Michel Raimond of the Université Pierre-et-Marie-Curie and M. Cristina Marchetti of University of California, Santa Barbara. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal had a 2021 impact factor of 14.417. History The journal was announced in January 2011 and began publishing papers in August 2011. An early editorial outlined the journal's publishing philosophy. The first editor was Jorge Pullin Jorge Pullin (; born 1963 in Argentina) is an American theoretical physicist known for his work on black hole collisions and quantum grav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fermi Surface
In condensed matter physics, the Fermi surface is the surface in reciprocal space which separates occupied from unoccupied electron states at zero temperature. The shape of the Fermi surface is derived from the periodicity and symmetry of the crystalline lattice and from the occupation of electronic energy bands. The existence of a Fermi surface is a direct consequence of the Pauli exclusion principle, which allows a maximum of one electron per quantum state. The study of the Fermi surfaces of materials is called fermiology. Theory Consider a spin-less ideal Fermi gas of N particles. According to Fermi–Dirac statistics, the mean occupation number of a state with energy \epsilon_i is given by :\langle n_i\rangle =\frac, where, *\left\langle n_i\right\rangle is the mean occupation number of the i^ state *\epsilon_i is the kinetic energy of the i^ state *\mu is the chemical potential (at zero temperature, this is the maximum kinetic energy the particle can have, i.e. Fermi ene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Absolute Zero
Absolute zero is the lowest limit of the thermodynamic temperature scale, a state at which the enthalpy and entropy of a cooled ideal gas reach their minimum value, taken as zero kelvin. The fundamental particles of nature have minimum vibrational motion, retaining only quantum mechanical, zero-point energy-induced particle motion. The theoretical temperature is determined by extrapolating the ideal gas law; by international agreement, absolute zero is taken as −273.15 degrees on the Celsius scale (International System of Units), Note: The triple point of water is 0.01 °C, not 0 °C; thus 0 K is −2890.15 °C, not −273.16 °C. which equals −459.67 degrees on the Fahrenheit scale ( United States customary units or Imperial units). The corresponding Kelvin and Rankine temperature scales set their zero points at absolute zero by definition. It is commonly thought of as the lowest temperature possible, but it is not the lowest ''enthalpy'' state poss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |