|
Saltovo-Mayaki
Saltovo-Mayaki or Saltovo-Majaki is the name given by archaeologists to the early medieval culture of the Pontic steppe region roughly between the Don and the Dnieper Rivers, flourishing roughly between the years of 700 and 950. History Saltovo-Mayaki influence was strong in the area of the Volyntsevo culture to the northwest of the main Saltovo-Mayaki territory. There is no consensus as to what ethnicity to assign to this culture, if any at all.https://publicera.kb.se/csa/article/download/1117/1072/1294 Characteristics The Saltovo-Mayaki material culture was "fairly uniform" across the various tribes. Ethnicity Their culture was a melting pot of Onogur, Khazar, Pecheneg, Magyar, Alan, and Slavic influences. Genetics A genetic study published in ''Nature'' in May 2018 examined three males of the Saltovo-Mayaki culture buried in Belgorod Oblast, Russia between ca. 700 AD and 900 AD. The sample of Y-DNA extracted belonged to haplogroup R1. The three samples of mtDNA Mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
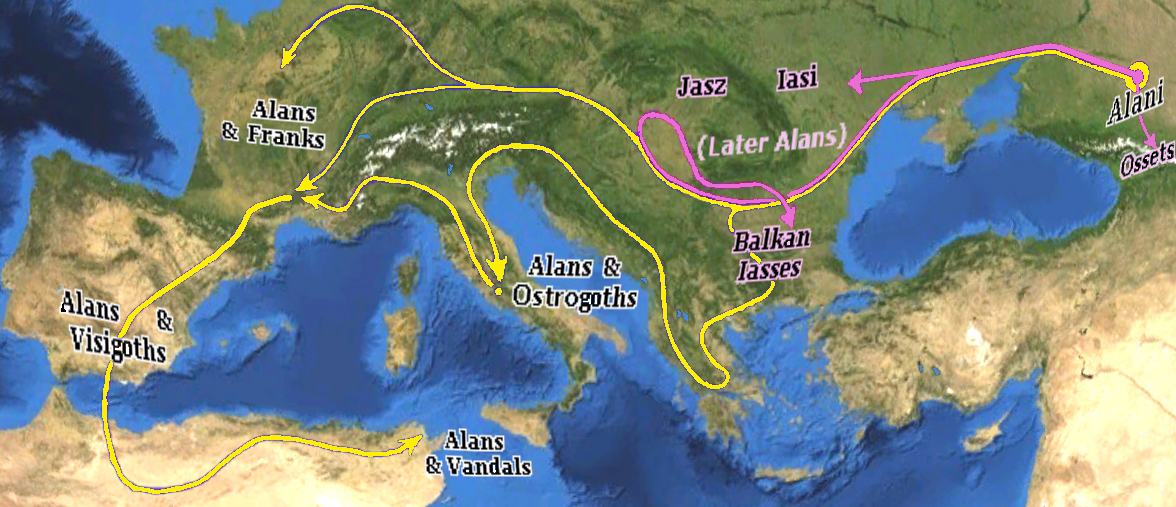
Alans
The Alans (Latin: ''Alani'') were an ancient and medieval Iranian nomadic pastoral people of the North Caucasus – generally regarded as part of the Sarmatians, and possibly related to the Massagetae. Modern historians have connected the Alans with the Central Asian Yancai of Chinese sources and with the Aorsi of Roman sources. Having migrated westwards and becoming dominant among the Sarmatians on the Pontic–Caspian steppe, the Alans are mentioned by Roman sources in the . At that time they had settled the region north of the Black Sea and frequently raided the Parthian Empire and the Caucasian provinces of the Roman Empire. From the Goths broke their power on the Pontic Steppe. Upon the Hunnic defeat of the Goths on the Pontic Steppe around , many of the Alans migrated westwards along with various Germanic tribes. They crossed the Rhine in 406CE along with the Vandals and Suebi, settling in Orléans and Valence. Around 409 CE they joined the Vandals and Suebi in cro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volyntsevo Culture
Volyntsevo culture is an archaeological culture of the early Middle Ages (8th to 9th centuries), located between the Dnieper and the Don rivers. In the west, the territory of the Volyntsevo monuments reaches the right bank of Dnieper in the Kyiv area. identified the culture, and named it after the village of in Sumy Oblast of Central Ukraine, which he excavated in 1948-1950. Monuments The type site of Volyntsevo, itself, is an open settlement and cemetery situated in a valley and surrounded by bogs. The best known archaeological monuments of Volyntsevo culture are: Bytytsia and Novotroitske settlements on the Psel River, the burial from Rylsk, Russia (Kursk Oblast), the settlement of Volyntseve, the Oleksandrivka settlement near Chernihiv, Obukhiv, and Khodosivka near Kyiv. In Kyiv, layers of the Volyntsevo culture of the middle of the 8th to early 9th century were found on Starokyivsky Hill and under the northern gallery of the Church of the Tithes. The culture is identif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khazars
The Khazars ; he, כּוּזָרִים, Kūzārīm; la, Gazari, or ; zh, 突厥曷薩 ; 突厥可薩 ''Tūjué Kěsà'', () were a semi-nomadic Turkic people that in the late 6th-century CE established a major commercial empire covering the southeastern section of modern European Russia, southern Ukraine, Crimea, and Kazakhstan. They created what for its duration was the most powerful polity to emerge from the break-up of the Western Turkic Khaganate. Astride a major artery of commerce between Eastern Europe and Western Asia, Southwestern Asia, Khazaria became one of the foremost trading empires of the Early Middle Ages, early medieval world, commanding the western March (territory), marches of the Silk Road and playing a key commercial role as a crossroad between China, the Middle East and Kievan Rus'. For some three centuries (c. 650–965) the Khazars dominated the vast area extending from the Volga-Don steppes to the eastern Crimea and the northern Caucasus. Khazari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magyars
Hungarians, also known as Magyars ( ; hu, magyarok ), are a nation and ethnic group native to Hungary () and historical Hungarian lands who share a common culture, history, ancestry, and language. The Hungarian language belongs to the Uralic language family. There are an estimated 15 million ethnic Hungarians and their descendants worldwide, of whom 9.6 million live in today's Hungary. About 2–3 million Hungarians live in areas that were part of the Kingdom of Hungary before the Treaty of Trianon in 1920 and are now parts of Hungary's seven neighbouring countries, Slovakia, Ukraine, Romania, Serbia, Croatia, Slovenia, and Austria. Significant groups of people with Hungarian ancestry live in various other parts of the world, most of them in the United States, Canada, Germany, France, the United Kingdom, Chile, Brazil, Australia, and Argentina. Hungarians can be divided into several subgroups according to local linguistic and cultural characteristics; subgroups with distinct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caftan MET DT1115
A kaftan or caftan (; fa, خفتان, ) is a variant of the robe or tunic. Originating in Asia, it has been worn by a number of cultures around the world for thousands of years. In Russian usage, ''kaftan'' instead refers to a style of men's long suit with tight sleeves. It may be made of wool, cashmere, silk, or cotton, and may be worn with a sash. Popular during the time of the Ottoman Empire, detailed and elaborately designed garments were given to ambassadors and other important guests at the Topkapı Palace. Variations of the kaftan were inherited by cultures throughout Asia and were worn by individuals in Russia (North Asia, Eastern Europe and formerly Central Asia), Southwest Asia and Northern Africa. Styles, uses, and names for the kaftan vary from culture to culture. The kaftan is often worn as a coat or as an overdress, usually having long sleeves and reaching to the ankles. In regions with a warm climate, it is worn as a light-weight, loose-fitting garment. In some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haplogroup I (mtDNA)
Haplogroup I is a human mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) haplogroup. It is believed to have originated about 21,000 years ago, during the Last Glacial Maximum (LGM) period in West Asia (; ; ). The haplogroup is unusual in that it is now widely distributed geographically, but is common in only a few small areas of East Africa, West Asia and Europe. It is especially common among the El Molo and Rendille peoples of Kenya, various regions of Iran, the Lemko people of Slovakia, Poland and Ukraine, the island of Krk in Croatia, the department of Finistère in France and some parts of Scotland and Ireland. Origin Haplogroup I is a descendant (subclade) of haplogroup N1a1b and sibling of haplogroup N1a1b1 . It is believed to have arisen somewhere in West Asia between 17,263 and 24,451 years before present (BP) , with coalescence age of 20.1 thousand years ago . It has been suggested that its origin may be in Iran or more generally the Near East . It has diverged to at least seven distinct clad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Cultures Of Eastern Europe
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. Archaeology is distinct from palaeontology, which is the study of fossil remains. Archaeology is particularly important for learning about prehistoric societies, for which, by definition, there are no written records. Prehistory includes over 99% of the human past, from the Paleolithic until the advent o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medieval Russia
Kievan Rusʹ, also known as Kyivan Rusʹ ( orv, , Rusĭ, or , , ; Old Norse: ''Garðaríki''), was a state in Eastern and Northern Europe from the late 9th to the mid-13th century.John Channon & Robert Hudson, ''Penguin Historical Atlas of Russia'' (Penguin, 1995), p.14–16.Kievan Rus Encyclopædia Britannica Online. Encompassing a variety of polities and peoples, including East Slavic, Norse, and Finnic, it was ruled by the , foun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeology Of Russia
Russian archaeology begins in the Russian Empire in the 1850s and becomes Soviet archaeology in the early 20th century. The journal ''Sovetskaya arkheologiya'' is published from 1957. Archaeologists Sites major archaeological cultures and sites in Russia ** Kermek ( :ru:Кермек (стоянка)) ** Bogatyri/Sinyaya Balka ( :ru:Богатыри/Синяя балка) ** Palaeolithic site Kostyonki **Sungir Sungir (, sometimes spelled Sunghir) is an Upper Paleolithic archaeological site in Russia and one of the earliest records of modern ''Homo sapiens'' in Eurasia. It is situated about two hundred kilometres east of Moscow, on the outskirts of Vlad ... **Yana Rhinoceros Horn Site, Yana RHS (:ru:Янская стоянка) **Afontova Gora *Mal'ta–Buret' culture (Upper Paleolithic) *Khvalynsk culture (Eneolithic) *Fatyanovo–Balanovo culture (Chalcolithic) *Novotitorovka culture (Early Bronze Age) *Maykop culture (Early Bronze Age) **Maykop kurgan *Yamna culture *Afa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeology Of Ukraine
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. Archaeology is distinct from palaeontology, which is the study of fossil remains. Archaeology is particularly important for learning about prehistoric societies, for which, by definition, there are no written records. Prehistory includes over 99% of the human past, from the Paleolithic until the adve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Middle Ages
The Early Middle Ages (or early medieval period), sometimes controversially referred to as the Dark Ages, is typically regarded by historians as lasting from the late 5th or early 6th century to the 10th century. They marked the start of the Middle Ages of European history, following the decline of the Western Roman Empire, and preceding the High Middle Ages ( 11th to 13th centuries). The alternative term ''late antiquity'', for the early part of the period, emphasizes elements of continuity with the Roman Empire, while ''Early Middle Ages'' is used to emphasize developments characteristic of the earlier medieval period. The period saw a continuation of trends evident since late classical antiquity, including population decline, especially in urban centres, a decline of trade, a small rise in average temperatures in the North Atlantic region and increased migration. In the 19th century the Early Middle Ages were often labelled the ''Dark Ages'', a characterization based on t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medieval Ukraine
#Prehistory, Prehistoric Ukraine, as a part of the Pontic–Caspian steppe, Pontic steppe in Eastern Europe, played an important role in Eurasian cultural contacts, including the spread of the Chalcolithic, the Bronze Age, Indo-European migrations and the domestication of the horse.(Link does not exist anymore) Part of Scythia in antiquity and settled by the Greuthungi and Getae in the Migration Period, migration period, Ukraine is also the site of early Slavs, early Slavic expansion, and enters written history with the establishment of the medieval state of Kievan Rus', which emerged as a powerful nation in the Middle Ages but disintegrated by the mid-12th century. During the 14th and 15th centuries, present-day Ukrainian territories came under the rule of four external powers: the Golden Horde, the Crimean Khanate, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland. The latter two would then merge into the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth following the Union o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)

