|
Salpn Ligand
} Salpn is the common name for a chelating ligand, properly called ''N'',''N''-bis(salicylidene)-1,2-propanediamine, used as a motor oil additive. The molecular structure of pure (metal-free) salpn, sometimes denoted H2(salpn) or salpnH2, can be described as the salen ligand with a methyl group attached to the ethylene group, ethylene bridge that links the two nitrogen atoms. As in the case of salen compound, the actual ligand is usually the conjugate base salpn2-, the Valence (chemistry), divalent anion that result from the metal-free compound by the loss of two hydroxyl protons. This dianion is commonly denoted "(salpn)" in formulas of metal complexes. The abbreviation "salpn" is also sometimes used for the structural isomer N,N'-bis(salicylidene)-1,3-diaminopropane, ''N'',''N''-bis(salicylidene)-1,3-diaminopropane and its conjugate base,K. Rajender Reddy, M. V. Rajasekharan, and J.-P. Tuchagues (1998): "Synthesis, Structure, and Magnetic Properties of Mn(salpn)N3, a Helic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chelating
Chelation is a type of bonding of ions and molecules to metal ions. It involves the formation or presence of two or more separate coordinate bonds between a Denticity, polydentate (multiple bonded) ligand and a single central metal atom. These ligands are called chelants, chelators, chelating agents, or sequestering agents. They are usually organic compounds, but this is not a necessity, as in the case of zinc and its use as a maintenance therapy to prevent the absorption of copper in people with Wilson's disease. Chelation is useful in applications such as providing nutritional supplements, in chelation therapy to remove toxic metals from the body, as contrast medium, contrast agents in MRI, MRI scanning, in manufacturing using homogeneous catalysts, in chemical water treatment to assist in the removal of metals, and in fertilizers. Chelate effect The chelate effect is the greater affinity of chelating ligands for a metal ion than that of similar nonchelating (monodentate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salicylaldehyde
Salicylic aldehyde (2-hydroxybenzaldehyde) is the organic compound with the formula (C7 H6 O2) C6H4CHO-2-OH. Along with 3-hydroxybenzaldehyde and 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde, it is one of the three isomers of hydroxybenzaldehyde. This colorless oily liquid has a bitter almond odor at higher concentration. Salicylaldehyde is a key precursor to a variety chelating agents, some of which are commercially important. Production Salicylaldehyde is prepared from phenol Phenol (also called carbolic acid) is an aromatic organic compound with the molecular formula . It is a white crystalline solid that is volatile. The molecule consists of a phenyl group () bonded to a hydroxy group (). Mildly acidic, it req ... and chloroform by heating with sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide in a Reimer–Tiemann reaction: : Alternatively, it is produced by condensation of phenol or its derivatives with formaldehyde to give hydroxybenzyl alcohol, which is oxidized to the aldehyde. Salicylald ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schiff Bases
In organic chemistry, a Schiff base (named after Hugo Schiff) is a compound with the general structure ( = alkyl or aryl, but not hydrogen). They can be considered a sub-class of imines, being either secondary ketimines or secondary aldimines depending on their structure. The term is often synonymous with azomethine which refers specifically to secondary aldimines (i.e. where R' ≠ H). A number of special naming systems exist for these compounds. For instance a Schiff base derived from an aniline, where is a phenyl or a substituted phenyl, can be called an ''anil'', while bis-compounds are often referred to as salen-type compounds. The term Schiff base is normally applied to these compounds when they are being used as ligands to form coordination complexes with metal ions. Such complexes occur naturally, for instance in corrin, but the majority of Schiff bases are artificial and are used to form many important catalysts, such as Jacobsen's catalyst. Synthesis Schiff b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
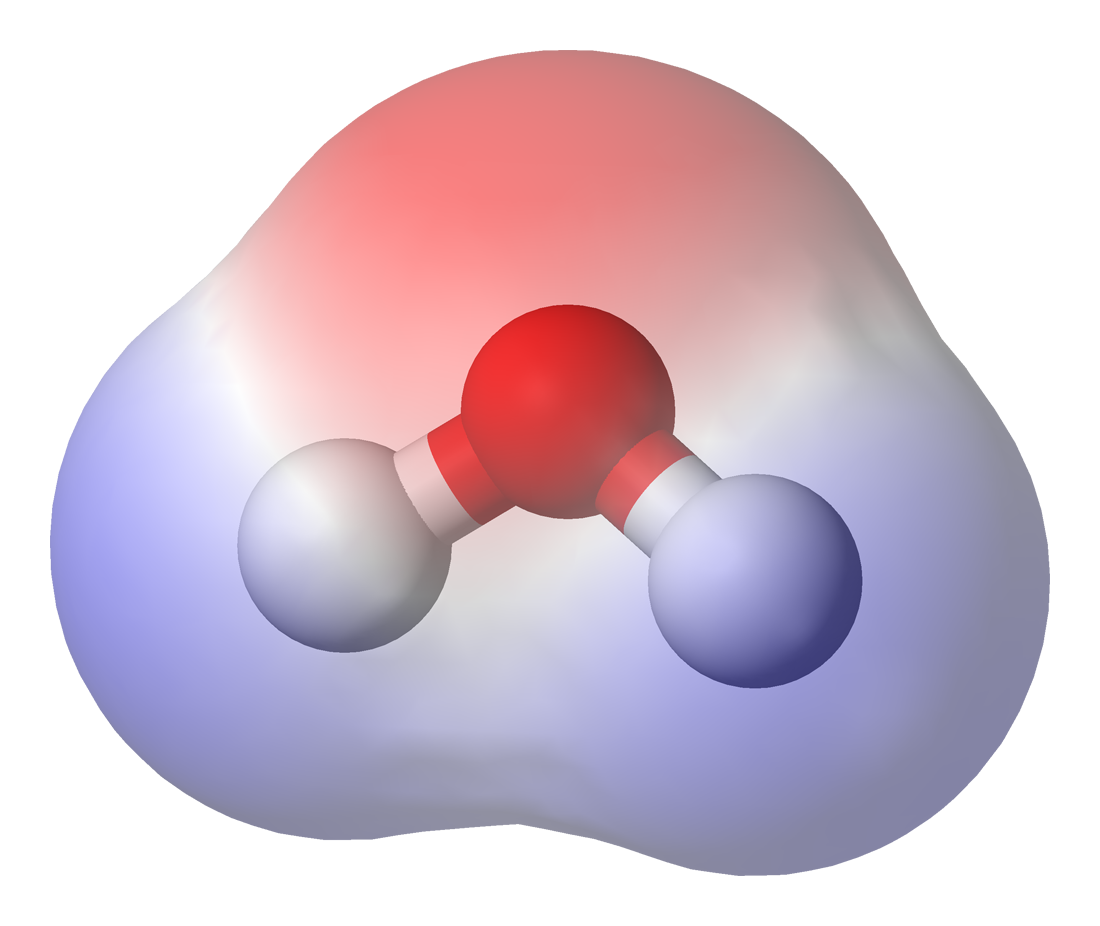
Polarity (chemistry)
In chemistry, polarity is a separation of electric charge leading to a molecule or its chemical groups having an electric dipole moment, with a negatively charged end and a positively charged end. Polar molecules must contain one or more polar bonds due to a difference in electronegativity between the bonded atoms. Molecules containing polar bonds have no molecular polarity if the bond dipoles cancel each other out by symmetry. Polar molecules interact through dipole–dipole intermolecular forces and hydrogen bonds. Polarity underlies a number of physical properties including surface tension, solubility, and melting and boiling points. Polarity of bonds Not all atoms attract electrons with the same force. The amount of "pull" an atom exerts on its electrons is called its electronegativity. Atoms with high electronegativitiessuch as fluorine, oxygen, and nitrogenexert a greater pull on electrons than atoms with lower electronegativities such as alkali metals and alkaline ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Square Planar Molecular Geometry
The square planar molecular geometry in chemistry describes the stereochemistry (spatial arrangement of atoms) that is adopted by certain chemical compounds. As the name suggests, molecules of this geometry have their atoms positioned at the corners. Examples Numerous compounds adopt this geometry, examples being especially numerous for transition metal complexes. The noble gas compound XeF4 adopts this structure as predicted by VSEPR theory. The geometry is prevalent for transition metal complexes with d8 configuration, which includes Rh(I), Ir(I), Pd(II), Pt(II), and Au(III). Notable examples include the anticancer drugs cisplatin tCl2(NH3)2and carboplatin. Many homogeneous catalysts are square planar in their resting state, such as Wilkinson's catalyst and Crabtree's catalyst. Other examples include Vaska's complex and Zeise's salt. Certain ligands (such as porphyrins) stabilize this geometry. Splitting of d-orbitals A general d-orbital splitting diagram for square planar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catalysis
Catalysis () is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed in the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recycles quickly, very small amounts of catalyst often suffice; mixing, surface area, and temperature are important factors in reaction rate. Catalysts generally react with one or more reactants to form intermediates that subsequently give the final reaction product, in the process of regenerating the catalyst. Catalysis may be classified as either homogeneous, whose components are dispersed in the same phase (usually gaseous or liquid) as the reactant, or heterogeneous, whose components are not in the same phase. Enzymes and other biocatalysts are often considered as a third category. Catalysis is ubiquitous in chemical industry of all kinds. Estimates are that 90% of all commercially produced chemical products involve catalysts at some s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nickel
Nickel is a chemical element with symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal. Pure nickel is chemically reactive but large pieces are slow to react with air under standard conditions because a passivation layer of nickel oxide forms on the surface that prevents further corrosion. Even so, pure native nickel is found in Earth's crust only in tiny amounts, usually in ultramafic rocks, and in the interiors of larger nickel–iron meteorites that were not exposed to oxygen when outside Earth's atmosphere. Meteoric nickel is found in combination with iron, a reflection of the origin of those elements as major end products of supernova nucleosynthesis. An iron–nickel mixture is thought to compose Earth's outer and inner cores. Use of nickel (as natural meteoric nickel–iron alloy) has been traced as far back as 3500 BCE. Nickel was first isolated and classified as an e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromium
Chromium is a chemical element with the symbol Cr and atomic number 24. It is the first element in group 6. It is a steely-grey, lustrous, hard, and brittle transition metal. Chromium metal is valued for its high corrosion resistance and hardness. A major development in steel production was the discovery that steel could be made highly resistant to corrosion and discoloration by adding metallic chromium to form stainless steel. Stainless steel and chrome plating (electroplating with chromium) together comprise 85% of the commercial use. Chromium is also greatly valued as a metal that is able to be highly polished while resisting tarnishing. Polished chromium reflects almost 70% of the visible spectrum, and almost 90% of infrared light. The name of the element is derived from the Greek word χρῶμα, ''chrōma'', meaning color, because many chromium compounds are intensely colored. Industrial production of chromium proceeds from chromite ore (mostly FeCr2O4) to produce ferro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron
Iron () is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from la, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in front of oxygen (32.1% and 30.1%, respectively), forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust. In its metallic state, iron is rare in the Earth's crust, limited mainly to deposition by meteorites. Iron ores, by contrast, are among the most abundant in the Earth's crust, although extracting usable metal from them requires kilns or furnaces capable of reaching or higher, about higher than that required to smelt copper. Humans started to master that process in Eurasia during the 2nd millennium BCE and the use of iron tools and weapons began to displace copper alloys, in some regions, only around 1200 BCE. That event is considered the transition from the Bronze Age to the Iron A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orange color. Copper is used as a conductor of heat and electricity, as a building material, and as a constituent of various metal alloys, such as sterling silver used in jewelry, cupronickel used to make marine hardware and coins, and constantan used in strain gauges and thermocouples for temperature measurement. Copper is one of the few metals that can occur in nature in a directly usable metallic form ( native metals). This led to very early human use in several regions, from circa 8000 BC. Thousands of years later, it was the first metal to be smelted from sulfide ores, circa 5000 BC; the first metal to be cast into a shape in a mold, c. 4000 BC; and the first metal to be purposely alloyed with another metal, tin, to create ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coordination Compound
A coordination complex consists of a central atom or ion, which is usually metallic and is called the ''coordination centre'', and a surrounding array of bound molecules or ions, that are in turn known as ''ligands'' or complexing agents. Many metal-containing compounds, especially those that include transition metals (elements like titanium that belong to the Periodic Table's d-block), are coordination complexes. Nomenclature and terminology Coordination complexes are so pervasive that their structures and reactions are described in many ways, sometimes confusingly. The atom within a ligand that is bonded to the central metal atom or ion is called the donor atom. In a typical complex, a metal ion is bonded to several donor atoms, which can be the same or different. A polydentate (multiple bonded) ligand is a molecule or ion that bonds to the central atom through several of the ligand's atoms; ligands with 2, 3, 4 or even 6 bonds to the central atom are common. These compl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metal Deactivator
Metal deactivators, or metal deactivating agents (MDA) are fuel additives and oil additives used to stabilize fluids by deactivating (usually by sequestrant, sequestering) metal ions, mostly introduced by the action of naturally occurring acids in the fuel and acids generated in lubricants by oxidative processes with the metallic parts of the systems. Fuels desulfurized by copper sweetening also contain a significant trace amounts of copper. Metal deactivators inhibit the catalytic effects of such ions, especially copper, retarding the formation of gummy residues (e.g. gels containing copper mercaptide). Even concentrations of copper as low as 0.1 ppm can have detrimental effects. An example of a metal deactivator used for gasoline and jet fuels is salpn. It is used in turbine and jet fuels, Diesel fuel, diesel, heating oil, and grease (lubricant), greases. It is approved for military and commercial aviation fuels. Benzotriazole and its various derivatives are also common in lubric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |