|
Sakuranetin
Sakuranetin is a flavan-on, the 7-methoxy derivative of naringenin, found in Polymnia fruticosa and rice, where it acts as a phytoalexin against spore germination of '' Pyricularia oryzae''. Glycosides Sakuranin is the 5-O- glucoside of sakuranetin. Metabolism ; biosynthesis Naringenin 7-O-methyltransferase uses naringenin to yield sakuranetin, with S-adenosyl-methionine as the methyl donor. ; biodegradation In compounds like 7-methoxylated flavanones like sakuranetin, demethylation followed by sulfation occur in model organism ''Cunninghamella elegans ''Cunninghamella elegans'' is a species of fungus in the genus ''Cunninghamella'' found in soil. It can be grown in Sabouraud dextrose broth, a liquid medium used for cultivation of yeasts and molds from liquid which are normally sterile. As o ...''. References Aromatase inhibitors O-methylated flavanones Phytoalexins {{aromatic-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phytoalexin
Phytoalexins are antimicrobial substances, some of which are antioxidative as well. They are defined, not by their having any particular chemical structure or character, but by the fact that they are defensively synthesized ''de novo'' by plants that produce the compounds rapidly at sites of pathogen infection. In general phytoalexins are broad spectrum inhibitors; they are chemically diverse, and different chemical classes of compounds are characteristic of particular plant taxa. Phytoalexins tend to fall into several chemical classes, including terpenoids, glycosteroids and alkaloids, however the term applies to any phytochemicals that are induced by microbial infection. Function Phytoalexins are produced in plants to act as toxins to the attacking organism. They may puncture the cell wall, delay maturation, disrupt metabolism or prevent reproduction of the pathogen in question. Their importance in plant defense is indicated by an increase in susceptibility of plant tissue t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flavanone
The flavanones, a type of flavonoids, are various aromatic, colorless ketones derived from flavone that often occur in plants as glycosides. List of flavanones * Blumeatin * Butin * Eriodictyol * Hesperetin * Hesperidin * Homoeriodictyol * Isosakuranetin * Naringenin * Naringin * Pinocembrin * Poncirin * Sakuranetin * Sakuranin * Sterubin Sterubin (7-methoxy-3',4',5-trihydroxyflavanone) is a bitter-masking flavanone extracted from Yerba Santa (''Eriodictyon californicum'') a plant growing in America. Sterubin is one of the four flavanones identified by Symrise in this plant whic ... * Pinostrobin Metabolism The enzyme chalcone isomerase uses a chalcone-like compound to produce a flavanone. Flavanone 4-reductase is an enzyme that uses (2''S'')- flavan-4-ol and NADP+ to produce (2''S'')-flavanone, NADPH, and H+. Synthesis Numerous methods exist for the enantioselective chemical and biochemical synthesis of flavanones and related compounds. References Exte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnaporthe Grisea
''Magnaporthe grisea'', also known as rice blast fungus, rice rotten neck, rice seedling blight, blast of rice, oval leaf spot of graminea, pitting disease, ryegrass blast, Johnson spot, neck blast, wheat blast, and Imochi ( Japanese:稲熱) is a plant-pathogenic fungus and model organism that causes a serious disease affecting rice. It is now known that ''M. grisea'' consists of a cryptic species complex containing at least two biological species that have clear genetic differences and do not interbreed. Complex members isolated from '' Digitaria'' have been more narrowly defined as ''M. grisea''. The remaining members of the complex isolated from rice and a variety of other hosts have been renamed ''Magnaporthe oryzae'', within the same ''M. grisea'' complex. Confusion on which of these two names to use for the rice blast pathogen remains, as both are now used by different authors. Members of the ''Magnaporthe grisea'' complex can also infect other agriculturally important cer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sakuranin
Sakuranin is a flavanone The flavanones, a type of flavonoids, are various aromatic, colorless ketones derived from flavone that often occur in plants as glycosides. List of flavanones * Blumeatin * Butin * Eriodictyol * Hesperetin * Hesperidin * Homoeriodictyol * ..., a type of flavonoid. It is the ''O''- glucoside of sakuranetin. It can be found in '' Prunus sp.''Flavonoids of Various Prunus Species. IV. The Flavonoids in the Wood of Prunus donarium var. spontanea. Masao Hasegawa and Teruo Shirato, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1955, 77 (13), pages 3557–3558, References External links * O-methylated flavanones Flavanone glycosides Phenol glucosides {{phenol-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glucoside
A glucoside is a glycoside that is derived from glucose. Glucosides are common in plants, but rare in animals. Glucose is produced when a glucoside is hydrolysed by purely chemical means, or decomposed by fermentation or enzymes. The name was originally given to plant products of this nature, in which the other part of the molecule was, in the greater number of cases, an aromatic aldehydic or phenolic compound (exceptions are Jinigrin and Jalapin or Scammonin). It has now been extended to include synthetic ethers, such as those obtained by acting on alcoholic glucose solutions with hydrochloric acid, and also the polysaccharoses, e.g. cane sugar, which appear to be ethers also. Although glucose is the most common sugar present in glucosides, many are known which yield rhamnose or iso-dulcite; these may be termed pentosides. Much attention has been given to the non-sugar parts (aglyca) of the molecules; the constitutions of many have been determined, and the compounds synt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
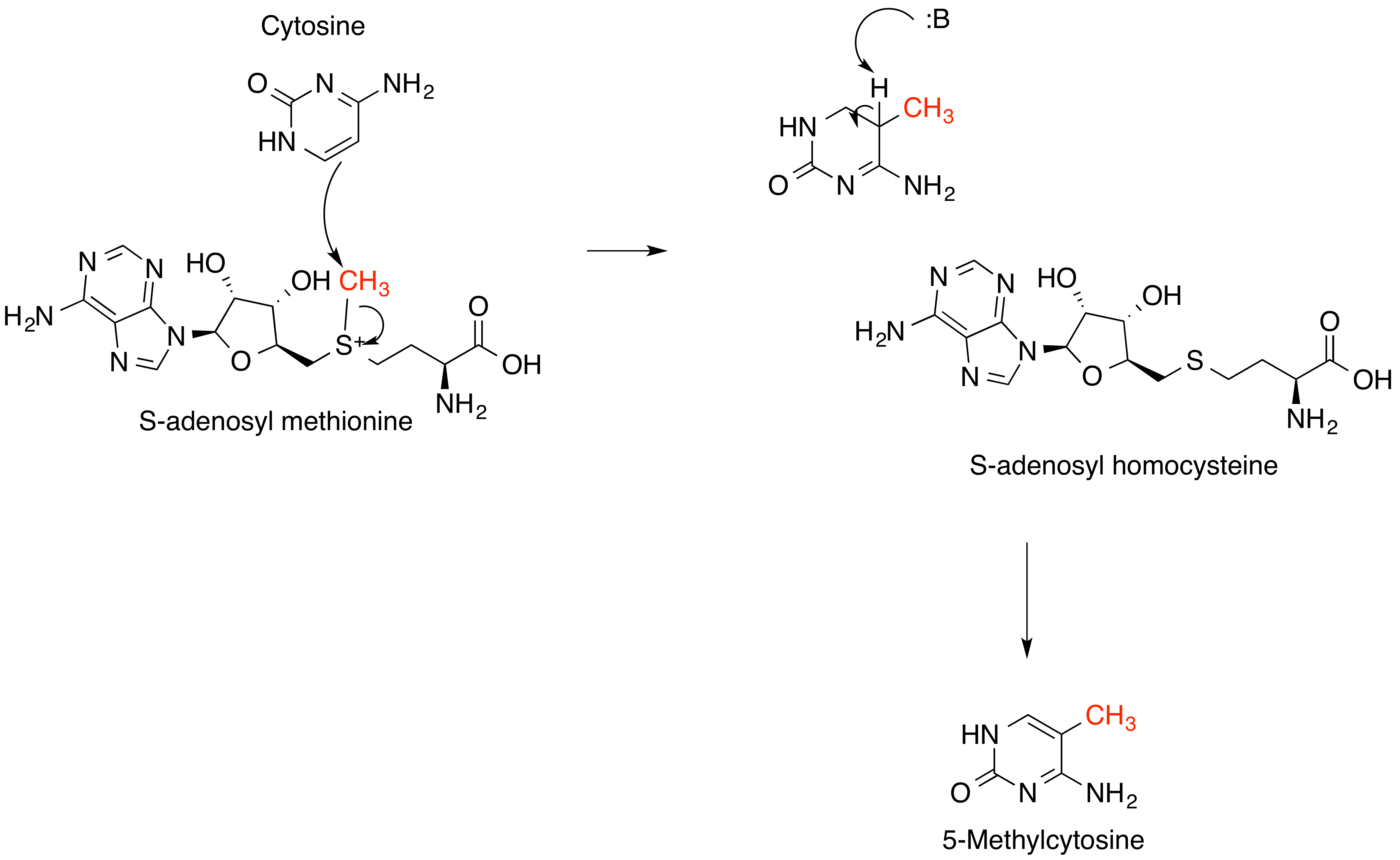
Naringenin 7-O-methyltransferase
Naringenin 7-''O''-methyltransferase (, ''NOMT'') (full systematic name ''S-adenosyl-L-methionine:(2S)-5,7,4'-trihydroxyflavanone 7-''O''-methyltransferase'') is a methyltransferase isolated from rice, which catalyzes the biosynthesis of sakuranetin. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction: : S-adenosyl-L-methionine + (2S)- naringenin \rightleftharpoons S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine + (2S)- sakuranetin While the enzyme is not present in healthy rice leaves, it can be induced by treatment with ultraviolet radiation Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nanometer, nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 Hertz, PHz) to 400 nm (750 Hertz, THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than ..., jasmonic acid and copper chloride. References External links * {{Portal bar, Biology, border=no EC 2.1.1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naringenin
Naringenin is a flavorless, colorless flavanone, a type of flavonoid. It is the predominant flavanone in grapefruit, and is found in a variety of fruits and herbs. Structure Naringenin has the skeleton structure of a flavanone with three hydroxy groups at the 4', 5, and 7 carbons. It may be found both in the aglycol form, naringenin, or in its glycosidic form, naringin, which has the addition of the disaccharide neohesperidose attached via a glycosidic linkage at carbon 7. Like the majority of flavanones, naringenin has a single chiral center at carbon 2, although the optical purity is variable. Racemization of S(-)-naringenin has been shown to occur fairly quickly. Sources and bioavailability Naringenin and its glycoside has been found in a variety of herbs and fruits, including grapefruit, bergamot, sour orange, tart cherries, tomatoes, cocoa, Greek oregano, water mint, as well as in beans. Ratios of naringenin to naringin vary among sources, as do enantiomeric ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
S-adenosyl-methionine
''S''-Adenosyl methionine (SAM), also known under the commercial names of SAMe, SAM-e, or AdoMet, is a common cosubstrate involved in methyl group transfers, transsulfuration, and aminopropylation. Although these anabolic reactions occur throughout the body, most SAM is produced and consumed in the liver. More than 40 methyl transfers from SAM are known, to various substrates such as nucleic acids, proteins, lipids and secondary metabolites. It is made from adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and methionine by methionine adenosyltransferase. SAM was first discovered by Giulio Cantoni in 1952. In bacteria, SAM is bound by the SAM riboswitch, which regulates genes involved in methionine or cysteine biosynthesis. In eukaryotic cells, SAM serves as a regulator of a variety of processes including DNA, tRNA, and rRNA methylation; immune response; amino acid metabolism; transsulfuration; and more. In plants, SAM is crucial to the biosynthesis of ethylene, an important plant hormone and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demethylation
Demethylation is the chemical process resulting in the removal of a methyl group (CH3) from a molecule. A common way of demethylation is the replacement of a methyl group by a hydrogen atom, resulting in a net loss of one carbon and two hydrogen atoms. The counterpart of demethylation is methylation. In biochemistry In biochemical systems, the process of demethylation is catalyzed by demethylases. These enzymes oxidize N-methyl groups, which occur in histones and some forms of DNA: :R2N-CH3 + O → R2N-H + CH2O One such oxidative enzyme family is the cytochrome P450. Alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent hydroxylases are active for demethylation of DNA, operating by a similar pathway. These reactions exploit the weak C-H bond adjacent to amines. In particular, 5-methylcytosines in DNA can be demethylated by TET enzymes as illustrated in the figure. TET enzymes are dioxygenases in the family of alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent hydroxylases. A TET enzyme is an alpha-ketoglut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfation
Sulfation is the chemical reaction that entails the addition of SO3 group. In principle, many sulfations would involve reactions of sulfur trioxide (SO3). In practice, most sulfations are effected less directly. Regardless of the mechanism, the installation of a sulfate-like group on a substrate leads to substantial changes. Sulfation in industry Sulfation of calcium oxides Sulfation is a process used to remove "sulfur" from the combustion of fossil fuels. The goal is to minimize the pollution by the combusted gases. Combustion of sulfur-containing fuels releases sulfur dioxide, which, in the atmosphere, oxidizes to the equivalent of sulfuric acid, which is corrosive. To minimize the problem, the combustion is often conducted in the presence of calcium oxide or calcium carbonate, which, directly or indirectly, bind sulfur dioxide and some oxygen to give calcium sulfate. The net reaction is: :CaO + SO2 → CaSO3 :CaSO3 + 1/2 O2 → CaSO4 or the net reaction is su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cunninghamella Elegans
''Cunninghamella elegans'' is a species of fungus in the genus ''Cunninghamella'' found in soil. It can be grown in Sabouraud dextrose broth, a liquid medium used for cultivation of yeasts and molds from liquid which are normally sterile. As opposed to '' C. bertholletiae'', it is not a human pathogen, with the exception of two documented patients. Description ''Cunninghamella elegans'' is a filamentous fungus that produces purely gray colonies. Electron microscopy studies show that the conidia are covered with spines. Use as a fungal organism capable of xenobiotics metabolism ''Cunninghamella elegans'' is able to degrade xenobiotics. It has a variety of enzymes of phases I (modification enzymes acting to introduce reactive and polar groups into their substrates) and II (conjugation enzymes) of the xenobiotic metabolism, as do mammals. Cytochrome P450 monooxygenase, aryl sulfotransferase, glutathione S-transferase, UDP-glucuronosyltransferase, UDP-glucosyltransferase a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aromatase Inhibitors
Aromatase inhibitors (AIs) are a class of drugs used in the treatment of breast cancer in postmenopausal women and in men, and gynecomastia in men. They may also be used off-label to reduce estrogen conversion when supplementing testosterone exogenously. They may also be used for chemoprevention in women at high risk for breast cancer. Aromatase is the enzyme that catalyzes a key aromatization step in the synthesis of estrogen. It converts the enone ring of androgen precursors such as testosterone, to a phenol, completing the synthesis of estrogen. As such, AIs are estrogen synthesis inhibitors. Because hormone-positive breast and ovarian cancers are dependent on estrogen for growth, AIs are taken to either block the production of estrogen or block the action of estrogen on receptors. Medical uses Cancer In contrast to premenopausal women, in whom most of the estrogen is produced in the ovaries, in postmenopausal women estrogen is mainly produced in peripheral tissues ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |