|
Sacred Relic Of St. George
The sacred relic of Saint George was one of the most famous of relics, after the True Cross and Holy Lance, and was the arm of the Saint George (d. 303), ordered killed by the Roman Emperor Diocletian for his failure to renounce his faith in Christ. George, a secondary patron saint of the First Crusade, played a significant role and provided other relics, as the occupation of his tomb at Lydda (now Lod, Israel) marked the first Latin bishop of Jerusalem as well as a service to ask for his intervention. The arm was given to the abbey of Anchin by Robert of Jerusalem (Robert II of Flanders) at some time during the Jerusalem campaign. Later, in northern Syria, Gerbault, a priest from Lille, and a companion (name unknown), who travelled with the army of Robert's, while foraging for food, came upon a monastery, where, according to custom, they were well received and fed. Gerbault, apparently forgetting his vows and the kind nature of his hosts, had his eyes on relics that might be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
True Cross
The True Cross is the cross upon which Jesus was said to have been crucified, particularly as an object of religious veneration. There are no early accounts that the apostles or early Christians preserved the physical cross themselves, although protective use of the sign of the cross was common by at least the 2nd century. Post-Nicene historians such as Socrates of Constantinople relate that Helena, the mother of the Roman emperor ConstantineI, travelled to the Holy Land in the years 326–328, founding churches and establishing relief agencies for the poor. The late 4th-century historians Gelasius of Caesarea and Tyrannius Rufinus claimed that while there she discovered the hiding place of three crosses that were believed to have been used at the crucifixion of Jesus and the two thieves, St. Dismas and Gestas, executed with him. To one cross was affixed the titulus bearing Jesus's name, but according to Rufinus, Helena was not sure until a miracle revealed that this was t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
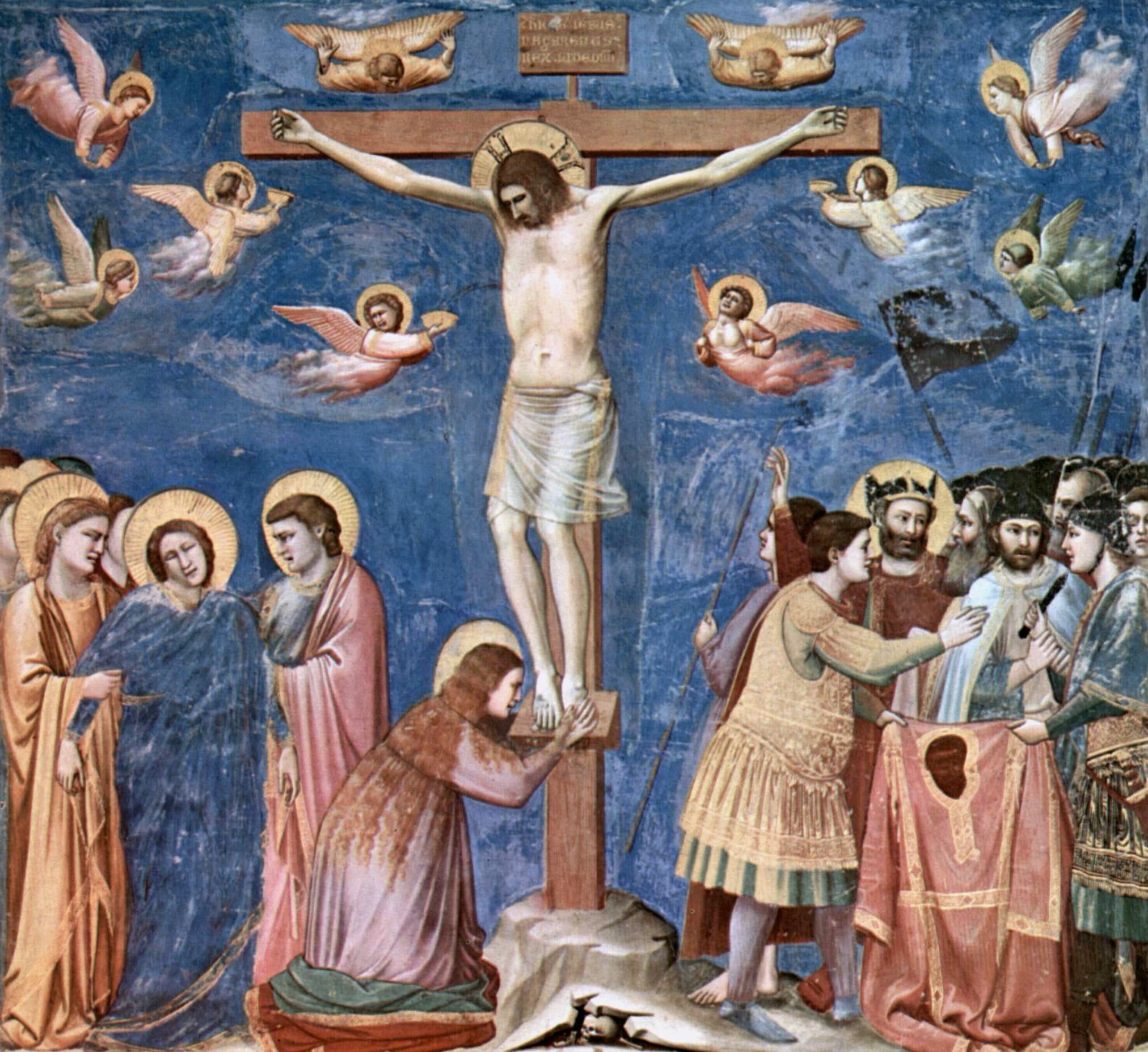
Holy Lance
The Holy Lance, also known as the Lance of Longinus (named after Saint Longinus), the Spear of Destiny, or the Holy Spear, is the lance that pierced the side of Jesus as he hung on the cross during his crucifixion. Biblical references The lance ( el, λόγχη, ) is mentioned in the Gospel of John, but not the Synoptic Gospels. The gospel states that the Romans planned to break Jesus' legs, a practice known as , which was a method of hastening death during a crucifixion. Because it was the eve of the Sabbath (Friday sundown to Saturday sundown), the followers of Jesus needed to "entomb" him because of Sabbath laws. Just before they did so, they noticed that Jesus was already dead and that there was no reason to break his legs ("and no bone will be broken"). To make sure that he was dead, a Roman soldier (named in extra-Biblical tradition as Longinus) stabbed him in the side. Liturgical re-enactments The phenomenon of blood and water was considered a miracle by Origen. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
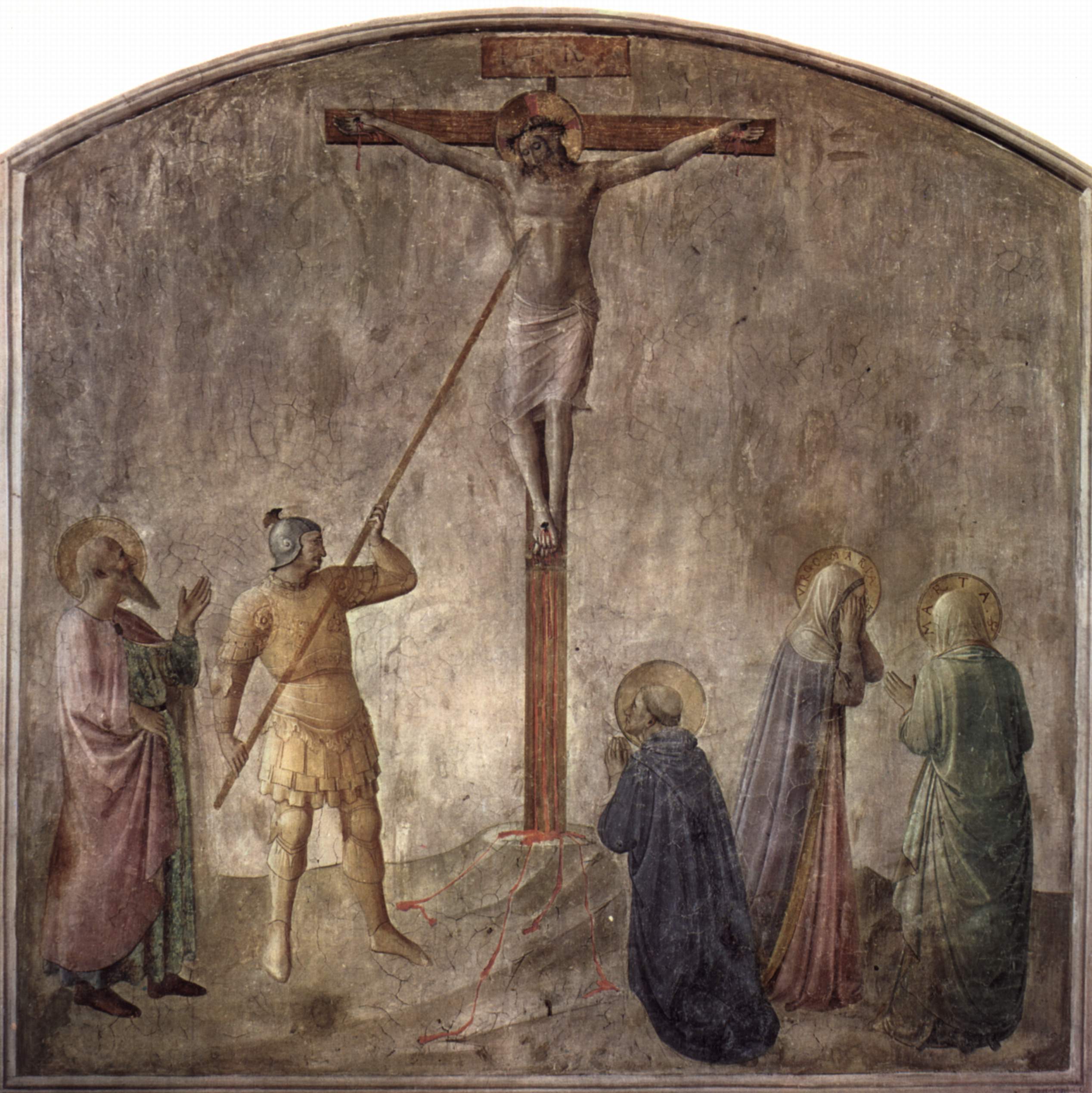
Saint George
Saint George (Greek: Γεώργιος (Geórgios), Latin: Georgius, Arabic: القديس جرجس; died 23 April 303), also George of Lydda, was a Christian who is venerated as a saint in Christianity. According to tradition he was a soldier in the Roman army. Saint George was a soldier of Cappadocian Greek origin and member of the Praetorian Guard for Roman emperor Diocletian, who was sentenced to death for refusing to recant his Christian faith. He became one of the most venerated saints and megalomartyrs in Christianity, and he has been especially venerated as a military saint since the Crusades. He is respected by Christians, Druze, as well as some Muslims as a martyr of monotheistic faith. In hagiography, as one of the Fourteen Holy Helpers and one of the most prominent military saints, he is immortalized in the legend of Saint George and the Dragon. His memorial, Saint George's Day, is traditionally celebrated on 23 April. Historically, the countries of England, Ukrai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diocletian
Diocletian (; la, Gaius Aurelius Valerius Diocletianus, grc, Διοκλητιανός, Diokletianós; c. 242/245 – 311/312), nicknamed ''Iovius'', was Roman emperor from 284 until his abdication in 305. He was born Gaius Valerius Diocles to a family of low status in the Roman province of Dalmatia. Diocles rose through the ranks of the military early in his career, eventually becoming a cavalry commander for the army of Emperor Carus. After the deaths of Carus and his son Numerian on a campaign in Persia, Diocles was proclaimed emperor by the troops, taking the name Diocletianus. The title was also claimed by Carus's surviving son, Carinus, but Diocletian defeated him in the Battle of the Margus. Diocletian's reign stabilized the empire and ended the Crisis of the Third Century. He appointed fellow officer Maximian as ''Augustus'', co-emperor, in 286. Diocletian reigned in the Eastern Empire, and Maximian reigned in the Western Empire. Diocletian delegated further on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Crusade
The First Crusade (1096–1099) was the first of a series of religious wars, or Crusades, initiated, supported and at times directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The objective was the recovery of the Holy Land from Islamic rule. While Jerusalem had been under Muslim rule for hundreds of years, by the 11th century the Seljuk takeover of the region threatened local Christian populations, pilgrimages from the West, and the Byzantine Empire itself. The earliest initiative for the First Crusade began in 1095 when Byzantine emperor Alexios I Komnenos requested military support from the Council of Piacenza in the empire's conflict with the Seljuk-led Turks. This was followed later in the year by the Council of Clermont, during which Pope Urban II supported the Byzantine request for military assistance and also urged faithful Christians to undertake an armed pilgrimage to Jerusalem. This call was met with an enthusiastic popular response across all social classes in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
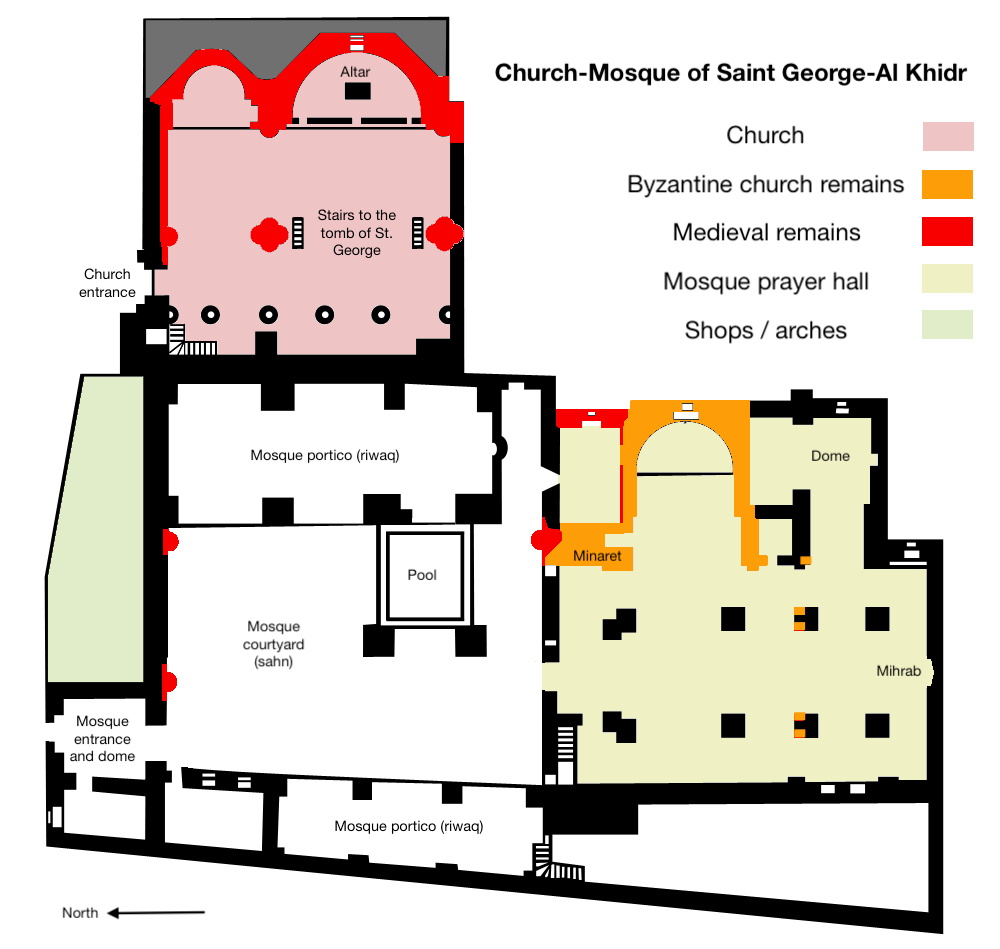
Church Of Saint George, Lod
The Church of Saint George and the Mosque of Al-Khidr are two houses of worship from Lod, Israel, built next to each other on top of and embedding the remains of Byzantine- and Crusader-period predecessors of the current church building. The Church of Saint George ( ar, كنيسة القديس جيورجوس or كنيسة مار جريس, he, כנסיית גאורגיוס הקדוש קוטל הדרקון, "Church of Saint George, slayer of the dragon") is a 19th-century Greek Orthodox church commemorating the fourth-century Christian martyr Saint George. The current 19th-century church is a based on a partially rebuilt Crusader-period church, which had itself been built over the remains and footprint of a Byzantine-period predecessor. (pp. 9 ff, se9 The Mosque of El-Khidr is a 13th-century ( |
Latin Patriarchate Of Jerusalem
The Latin Patriarchate of Jerusalem ( la, Patriarchatus Latinus Hierosolymitanus) is the Latin Catholic ecclesiastical patriarchate in Jerusalem, officially seated in the Church of the Holy Sepulchre. It was originally established in 1099, with the Kingdom of Jerusalem encompassing the territories in the Holy Land newly conquered by the First Crusade. From 1374 to 1847 it was a titular see, with the patriarchs of Jerusalem being based at the Basilica di San Lorenzo fuori le Mura in Rome. A resident Latin patriarch was re-established in 1847 by Pius IX. The Latin patriarch of Jerusalem is now the archbishop of Latin Church Catholics of the Archdiocese of Jerusalem with jurisdiction for all Latin Catholics in Israel, Palestine, Jordan and Cyprus. The Latin patriarch of Jerusalem also holds the office of grand prior of the Order of the Holy Sepulchre. The office of Latin patriarch of Jerusalem became vacant on 24 June 2016, and the patriarchate was managed by Archbishop Pierbattis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anchin Abbey
Anchin Abbey was a Benedictine monastery founded in 1079 in the commune of Pecquencourt in what is now the Nord department of France. Geography Aquicintum then Aquacignium , Anchin (or Chisho ) is an island of 25 hectares, part of the territory of Pecquencourt and surrounded by marshes, the river Scarpe and the stream of Bouchart. History ''Aquicintum'', later ''Aquacignium'' and then Anchin (or ''Enchin''), was a 25 hectare island forming part of the territory of Pecquencourt, between the ''marais'', the river Scarpe and the Bouchart brook. The hermit and confessor Gordaine built his hermitage on the island in the 8th century) and is sometimes considered the abbey's founder: an anonymous 17th-century painting in the church of Saint-Gilles at Pecquencourt shows his miracles. In 1096 the abbey was the site of a large tournament, the ''Tournoi d'Anchin'', at which 300 knights from Ostrevent, Hainaut, Cambrésis and Artois fought. An important cultural centre from the 11t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert II Of Flanders
Robert II, Count of Flanders (c. 1065 – 5 October 1111) was Count of Flanders from 1093 to 1111. He became known as Robert of Jerusalem (''Robertus Hierosolimitanus'') or Robert the Crusader after his exploits in the First Crusade. Early life Robert was the eldest son of Robert I of Flanders (also known as Robert the Frisian) and Gertrude of Saxony. His father, hoping to place the cadet branch (or "Baldwinite" branch) of Flanders over the county, began to associate him with his rule around 1086. From 1085 to 1091 he was regent of the county while his father was away on pilgrimage to the Holy Land. First Crusade After becoming count in 1093, Robert joined the First Crusade, launched by Pope Urban II in 1095. He made his wife, Clementia of Burgundy, regent in Flanders, and formed the army of Robert the Crusader that followed the retinue of his kinsman Godfrey of Bouillon, Duke of Lower Lorraine. After reaching Constantinople, the crusaders were obliged to swear an oath of fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Army Of Robert The Crusader
Robert II of Flanders' army was formed shortly after that of his kinsman Godfrey of Bouillon, arriving in Constantinople considerably later.Runciman, S. (1949)The First Crusaders' Journey across the Balkan Peninsula ''Byzantion'', 19, 207–221. His wife Clementia of Burgundy was regent of Flanders in his absence. The known members of the army, mostly Flemish, included the ones listed below, as reported in histories of the First Crusade. Unless otherwise noted, references are to the on-line database of Riley-Smith, et al., and the hyperlinks therein provide details including original sources. The names below are also referenced in the Riley-Smith tome, Appendix I: Preliminary List of Crusaders. Those references are not shown unless they appear elsewhere in the text of the book. Articles that are hyperlinked to a more detailed article in this encyclopædia rely on the latter for references. Household of Robert Among those from Robert’s household included the following: * En ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chronique De Saint-Pierre-le-Vif De Sens
The ''Chronicle of Saint-Pierre-le-Vif of Sens'' ( la, Chronicon Sancti Petri Vivi Senonensis, french: Chronique de Saint-Pierre-le-Vif de Sens) is an anonymous Latin chronicle written at the Abbey of Saint-Pierre-le-Vif in Sens between about 1100 and 1125 with continuations added into the 13th century. The original work was attributed to a monk named Clarius by Dom Victor Cottron in 1650, but this is not now accepted. It is, however, sometimes still labeled the ''Chronique dite de Clarius'' ("Chronicle said to be of Clarius"). The ''Chronicle'' is mainly a history of the abbey and of the city of Sens.Régis Rech"Chronicon S. Petri Vivi" in Graeme Dunphy and Cristian Bratu (eds.), ''Encyclopedia of the Medieval Chronicle'' (Brill, online 2016), accessed 21 June 2019. The ''Chronicle'' is divided into four sections. The first is a universal history inspired by Hugh of Flavigny and, through him, by Eusebius of Caesarea and Jerome. This covers the period from the birth of Jesus to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lambert Of Ardres
Lambert of Ardres (active 1194–1203) was a chronicler in the twelfth-century Kingdom of France, from on the frontiers of the County of Flanders. Cyriel Moeyaert, "Aarde (Ardres), Lambert van (Lambertus Ardensis)", '' Nationaal Biografisch Woordenboek'', vol. 16 (2002), 1-3. By 1194, Lambert was the parish priest of Ardres. He was related to the Counts of Guînes, for whom he wrote a ''Historia comitum Ghisnensium'', begun around 1196 and left unfinished in 1203. It is a mixture of history and folklore. It also contains a contemporary description of a donjon. A chapter of Georges Duby's ''The Knight, The Lady, and the Priest'' is dedicated to Lambert's ''Historia''. Lambert's ''Historia'' has been published in a number of editions: * Godfrey de Ménilglaise (ed.), ''Chronique de Guines et d'Ardres par Lambert, curé d'Ardres'' (Paris, 1855). * Johannes Heller (ed.), "Lamberti ardensis historia comitum Ghisnensium", in ''Monumenta Germaniae Historica The ''Monumenta Germaniae H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |