|
Saccharic Acid
Saccharic acid, also called glucaric acid, is a chemical compound with the formula C6H10O8. It is derived by oxidizing a sugar such as glucose with nitric acid. at NIST The salts of saccharic acid are called saccharates or glucarates. See also * * * * * |
Chemical Compound
A chemical compound is a chemical substance composed of many identical molecules (or molecular entities) containing atoms from more than one chemical element held together by chemical bonds. A molecule consisting of atoms of only one element is therefore not a compound. A compound can be transformed into a different substance by a chemical reaction, which may involve interactions with other substances. In this process, bonds between atoms may be broken and/or new bonds formed. There are four major types of compounds, distinguished by how the constituent atoms are bonded together. Molecular compounds are held together by covalent bonds; ionic compounds are held together by ionic bonds; intermetallic compounds are held together by metallic bonds; coordination complexes are held together by coordinate covalent bonds. Non-stoichiometric compounds form a disputed marginal case. A chemical formula specifies the number of atoms of each element in a compound molecule, using ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxidizing
Redox (reduction–oxidation, , ) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of substrate change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or a decrease in the oxidation state. There are two classes of redox reactions: * ''Electron-transfer'' – Only one (usually) electron flows from the reducing agent to the oxidant. This type of redox reaction is often discussed in terms of redox couples and electrode potentials. * ''Atom transfer'' – An atom transfers from one substrate to another. For example, in the rusting of iron, the oxidation state of iron atoms increases as the iron converts to an oxide, and simultaneously the oxidation state of oxygen decreases as it accepts electrons released by the iron. Although oxidation reactions are commonly associated with the formation of oxides, other chemical species can serve the same function. In hydrogenation, C=C (and other) bonds a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monosaccharide
Monosaccharides (from Greek '' monos'': single, '' sacchar'': sugar), also called simple sugars, are the simplest forms of sugar and the most basic units (monomers) from which all carbohydrates are built. They are usually colorless, water- soluble, and crystalline solids. Contrary to their name (sugars), only some monosaccharides have a sweet taste. Most monosaccharides have the formula (though not all molecules with this formula are monosaccharides). Examples of monosaccharides include glucose (dextrose), fructose (levulose), and galactose. Monosaccharides are the building blocks of disaccharides (such as sucrose and lactose) and polysaccharides (such as cellulose and starch). The table sugar used in everyday vernacular is itself a disaccharide sucrose comprising one molecule of each of the two monosaccharides D-glucose and D-fructose. Each carbon atom that supports a hydroxyl group is chiral, except those at the end of the chain. This gives rise to a number of isome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
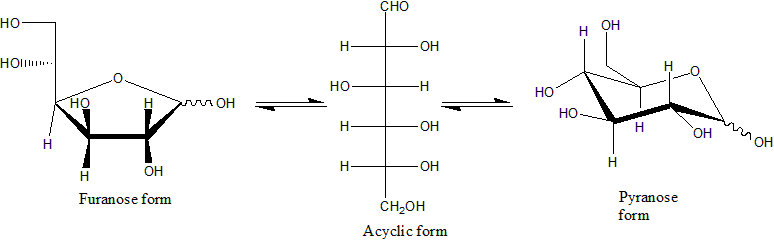
Glucose
Glucose is a simple sugar with the molecular formula . Glucose is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. Glucose is mainly made by plants and most algae during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, using energy from sunlight, where it is used to make cellulose in cell walls, the most abundant carbohydrate in the world. In energy metabolism, glucose is the most important source of energy in all organisms. Glucose for metabolism is stored as a polymer, in plants mainly as starch and amylopectin, and in animals as glycogen. Glucose circulates in the blood of animals as blood sugar. The naturally occurring form of glucose is -glucose, while -glucose is produced synthetically in comparatively small amounts and is less biologically active. Glucose is a monosaccharide containing six carbon atoms and an aldehyde group, and is therefore an aldohexose. The glucose molecule can exist in an open-chain (acyclic) as well as ring (cyclic) fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitric Acid
Nitric acid is the inorganic compound with the formula . It is a highly corrosive mineral acid. The compound is colorless, but older samples tend to be yellow cast due to decomposition into oxides of nitrogen. Most commercially available nitric acid has a concentration of 68% in water. When the solution contains more than 86% , it is referred to as ''fuming nitric acid''. Depending on the amount of nitrogen dioxide present, fuming nitric acid is further characterized as red fuming nitric acid at concentrations above 86%, or white fuming nitric acid at concentrations above 95%. Nitric acid is the primary reagent used for nitration – the addition of a nitro group, typically to an organic molecule. While some resulting nitro compounds are shock- and thermally-sensitive explosives, a few are stable enough to be used in munitions and demolition, while others are still more stable and used as pigments in inks and dyes. Nitric acid is also commonly used as a strong oxidizing age ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saccharide
In organic chemistry, a carbohydrate () is a biomolecule consisting of carbon (C), hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) atoms, usually with a hydrogen–oxygen atom ratio of 2:1 (as in water) and thus with the empirical formula (where ''m'' may or may not be different from ''n''), which does not mean the H has covalent bonds with O (for example with , H has a covalent bond with C but not with O). However, not all carbohydrates conform to this precise stoichiometric definition (e.g., uronic acids, deoxy-sugars such as fucose), nor are all chemicals that do conform to this definition automatically classified as carbohydrates (e.g. formaldehyde and acetic acid). The term is most common in biochemistry, where it is a synonym of saccharide (), a group that includes sugars, starch, and cellulose. The saccharides are divided into four chemical groups: monosaccharides, disaccharides, oligosaccharides, and polysaccharides. Monosaccharides and disaccharides, the smallest (lower molecular wei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disaccharides
A disaccharide (also called a double sugar or ''biose'') is the sugar formed when two monosaccharides are joined by glycosidic linkage. Like monosaccharides, disaccharides are simple sugars soluble in water. Three common examples are sucrose, lactose, and maltose. Disaccharides are one of the four chemical groupings of carbohydrates (monosaccharides, disaccharides, oligosaccharides, and polysaccharides). The most common types of disaccharides—sucrose, lactose, and maltose—have 12 carbon atoms, with the general formula C12H22O11. The differences in these disaccharides are due to atomic arrangements within the molecule. The joining of monosaccharides into a double sugar happens by a condensation reaction, which involves the elimination of a water molecule from the functional groups only. Breaking apart a double sugar into its two monosaccharides is accomplished by hydrolysis with the help of a type of enzyme called a disaccharidase. As building the larger sugar ejects a water ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monosaccharides
Monosaccharides (from Greek '' monos'': single, '' sacchar'': sugar), also called simple sugars, are the simplest forms of sugar and the most basic units ( monomers) from which all carbohydrates are built. They are usually colorless, water- soluble, and crystalline solids. Contrary to their name (sugars), only some monosaccharides have a sweet taste. Most monosaccharides have the formula (though not all molecules with this formula are monosaccharides). Examples of monosaccharides include glucose (dextrose), fructose (levulose), and galactose. Monosaccharides are the building blocks of disaccharides (such as sucrose and lactose) and polysaccharides (such as cellulose and starch). The table sugar used in everyday vernacular is itself a disaccharide sucrose comprising one molecule of each of the two monosaccharides D-glucose and D-fructose. Each carbon atom that supports a hydroxyl group is chiral, except those at the end of the chain. This gives rise to a numbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mucic Acid
Mucic acid, C6H10O8 or HOOC-(CHOH)4-COOH (also known as galactaric or meso-galactaric acid) is an aldaric acid obtained by nitric acid oxidation of galactose or galactose-containing compounds such as lactose, dulcite, quercite, and most varieties of gum. Properties Mucic acid forms a crystalline powder, which melts at 210–230 °C. It is insoluble in alcohol, and nearly insoluble in cold water. Due to the symmetry in the molecule, it is optically inactive even though it has chiral carbon atoms (i.e., it is a meso compound). Reactions When heated with pyridine to 140 °C, it is converted into allomucic acid. When digested with fuming hydrochloric acid for some time it is converted into αα′ furfural dicarboxylic acid while on heating with barium sulfide it is transformed into a thiophene carboxylic acid. The ammonium salt yields on dry distillation carbon dioxide, ammonia, pyrrol and other substances. The acid when fused with caustic alkalis yields oxalic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gluconic Acid
Gluconic acid is an organic compound with molecular formula C6H12O7 and condensed structural formula HOCH2(CHOH)4COOH. It is one of the 16 stereoisomers of 2,3,4,5,6-pentahydroxyhexanoic acid. In aqueous solution at neutral pH, gluconic acid forms the gluconate ion. The salts of gluconic acid are known as "gluconates". Gluconic acid, gluconate salts, and gluconate esters occur widely in nature because such species arise from the oxidation of glucose. Some drugs are injected in the form of gluconates. Chemical structure The chemical structure of gluconic acid consists of a six-carbon chain, with five hydroxyl groups positioned in the same way as in the open-chained form of glucose, terminating in a carboxylic acid group. In aqueous solution, gluconic acid exists in equilibrium with the cyclic ester glucono delta-lactone. Production Gluconic acid preparation was first reported by Hlasiwetz and Habermann in 1870 and involved the chemical oxidation of glucose. In 1880, Boutro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isosaccharinic Acid
Isosaccharinic acid (ISA) is a six-carbon sugar acid which is formed by the action of calcium hydroxide on lactose and other carbohydrates. It is of interest because it may form in intermediate-level nuclear waste stores when cellulose is degraded by the calcium hydroxide in cements such as Portland cement. The calcium salt of the alpha form of ISA is very crystalline and quite insoluble in cold water, but in hot water it is soluble. ISA is thought to form by means of a series of reactions in which calcium ions acting as lewis acids catalyze two of the three steps. The first step is likely to be a rearrangement of the reducing sugar end of the cellulose (or lactose) into a keto sugar, the second step is likely to be a reaction similar to the base catalyzed dehydration which often occurs after an aldol reaction. In this second step an alkoxide (derived from a sugar) takes the role of the hydroxide leaving group, this second step is not likely to require the lewis acidity of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sugar Acids
A Sugar acid or acidic sugar is a monosaccharide with a carboxyl group at one end or both ends of its chain. Main classes of sugar acids include: * Aldonic acids, in which the aldehyde group (−CHO) located at the initial end ( position 1) of an aldose is oxidized. * Ulosonic acids, in which the −CH2(OH) group at the initial end of a 2- ketose is oxidized creating an α- ketoacid. * Uronic acids, in which the −CH2(OH) group at the terminal end of an aldose or ketose is oxidized. * Aldaric acids, in which both ends (−CHO and −CH2(OH)) of an aldose are oxidized. Examples Examples of sugar acids include: * Aldonic acids ** Glyceric acid (3C) ** Xylonic acid (5C) ** Gluconic acid (6C) ** Ascorbic acid (6C, unsaturated lactone) * Ulosonic acids ** Neuraminic acid (5-amino-3,5-dideoxy-D- ''glycero''-D- ''galacto''-non-2-ulosonic acid) ** Ketodeoxyoctulosonic acid (KDO or 3-deoxy-D- ''manno''-oct-2-ulosonic acid) * Uronic acids ** Glucuronic acid (6C) ** Galacturonic acid (6C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |