|
Isosaccharinic Acid
Isosaccharinic acid (ISA) is a six-carbon sugar acid which is formed by the action of calcium hydroxide on lactose and other carbohydrates. It is of interest because it may form in intermediate-level nuclear waste stores when cellulose is degraded by the calcium hydroxide in cements such as Portland cement. The calcium salt (chemistry), salt of the alpha form of ISA is very crystalline and quite insoluble in cold water, but in hot water it is soluble. ISA is thought to form by means of a series of reactions in which calcium ions acting as lewis acids catalyze two of the three steps. The first step is likely to be a rearrangement of the reducing sugar end of the cellulose (or lactose) into a keto sugar, the second step is likely to be a reaction similar to the base catalyzed dehydration which often occurs after an aldol reaction. In this second step an alkoxide (derived from a sugar) takes the role of the hydroxide leaving group, this second step is not likely to require the lewis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sugar Acid
A Sugar acid or acidic sugar is a monosaccharide with a carboxyl group at one end or both ends of its chain. Main classes of sugar acids include: * Aldonic acids, in which the aldehyde group (−CHO) located at the initial end ( position 1) of an aldose is oxidized. * Ulosonic acids, in which the −CH2(OH) group at the initial end of a 2-ketose is oxidized creating an α-ketoacid. * Uronic acids, in which the −CH2(OH) group at the terminal end of an aldose or ketose is oxidized. * Aldaric acids, in which both ends (−CHO and −CH2(OH)) of an aldose are oxidized. Examples Examples of sugar acids include: * Aldonic acids ** Glyceric acid (3C) ** Xylonic acid (5C) ** Gluconic acid (6C) ** Ascorbic acid (6C, unsaturated lactone) * Ulosonic acids ** Neuraminic acid (5-amino-3,5-dideoxy-D- ''glycero''-D- ''galacto''-non-2-ulosonic acid) ** Ketodeoxyoctulosonic acid (KDO or 3-deoxy-D- ''manno''-oct-2-ulosonic acid) * Uronic acids ** Glucuronic acid (6C) ** Galacturonic acid (6C) * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzilic Acid Rearrangement
The benzilic acid rearrangement is formally the 1,2-rearrangement of 1,2-diketones to form α- hydroxy–carboxylic acids using a base. This reaction receives its name from the reaction of benzil with potassium hydroxide to form benzilic acid. First performed by Justus von Liebig in 1838, it is the first reported example of a rearrangement reaction.Nerve Agent Precursors: Benzilic acid and Methyl Benzilate , Factsheets on Chemical and Biological Warfare Agents, Chemical precursors. It has become a classic reaction in organic synthesis and has been reviewed many times before. It can be viewed as an intramolecular |
Chirality
Chirality is a property of asymmetry important in several branches of science. The word ''chirality'' is derived from the Greek (''kheir''), "hand", a familiar chiral object. An object or a system is ''chiral'' if it is distinguishable from its mirror image; that is, it cannot be superimposed onto it. Conversely, a mirror image of an ''achiral'' object, such as a sphere, cannot be distinguished from the object. A chiral object and its mirror image are called ''enantiomorphs'' (Greek, "opposite forms") or, when referring to molecules, '' enantiomers''. A non-chiral object is called ''achiral'' (sometimes also ''amphichiral'') and can be superposed on its mirror image. The term was first used by Lord Kelvin in 1893 in the second Robert Boyle Lecture at the Oxford University Junior Scientific Club which was published in 1894: Human hands are perhaps the most recognized example of chirality. The left hand is a non-superimposable mirror image of the right hand; no matter ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetone Acetal
Acetone (2-propanone or dimethyl ketone), is an organic compound with the formula . It is the simplest and smallest ketone (). It is a colorless, highly volatile and flammable liquid with a characteristic pungent odour. Acetone is miscible with water and serves as an important organic solvent in its own right, in industry, home, and laboratory. About 6.7 million tonnes were produced worldwide in 2010, mainly for use as a solvent and production of methyl methacrylate (and from that PMMA) as well as bisphenol A.Acetone World Petrochemicals report, January 2010Stylianos Sifniades, Alan B. Levy, "Acetone" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2005. It is a common building block in |
Acid
In computer science, ACID ( atomicity, consistency, isolation, durability) is a set of properties of database transactions intended to guarantee data validity despite errors, power failures, and other mishaps. In the context of databases, a sequence of database operations that satisfies the ACID properties (which can be perceived as a single logical operation on the data) is called a ''transaction''. For example, a transfer of funds from one bank account to another, even involving multiple changes such as debiting one account and crediting another, is a single transaction. In 1983, Andreas Reuter and Theo Härder coined the acronym ''ACID'', building on earlier work by Jim Gray who named atomicity, consistency, and durability, but not isolation, when characterizing the transaction concept. These four properties are the major guarantees of the transaction paradigm, which has influenced many aspects of development in database systems. According to Gray and Reuter, the IBM Informa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetone
Acetone (2-propanone or dimethyl ketone), is an organic compound with the formula . It is the simplest and smallest ketone (). It is a colorless, highly volatile and flammable liquid with a characteristic pungent odour. Acetone is miscible with water and serves as an important organic solvent in its own right, in industry, home, and laboratory. About 6.7 million tonnes were produced worldwide in 2010, mainly for use as a solvent and production of methyl methacrylate (and from that PMMA) as well as bisphenol A.Acetone World Petrochemicals report, January 2010Stylianos Sifniades, Alan B. Levy, "Acetone" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2005. It is a common building block in |
Alcohol (chemistry)
In chemistry, an alcohol is a type of organic compound that carries at least one hydroxyl () functional group bound to a saturated carbon atom. The term ''alcohol'' originally referred to the primary alcohol ethanol (ethyl alcohol), which is used as a drug and is the main alcohol present in alcoholic drinks. An important class of alcohols, of which methanol and ethanol are the simplest examples, includes all compounds which conform to the general formula . Simple monoalcohols that are the subject of this article include primary (), secondary () and tertiary () alcohols. The suffix ''-ol'' appears in the IUPAC chemical name of all substances where the hydroxyl group is the functional group with the highest priority. When a higher priority group is present in the compound, the prefix ''hydroxy-'' is used in its IUPAC name. The suffix ''-ol'' in non-IUPAC names (such as paracetamol or cholesterol) also typically indicates that the substance is an alcohol. However, some compou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carboxylic Acid
In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group () attached to an R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is or , with R referring to the alkyl, alkenyl, aryl, or other group. Carboxylic acids occur widely. Important examples include the amino acids and fatty acids. Deprotonation of a carboxylic acid gives a carboxylate anion. Examples and nomenclature Carboxylic acids are commonly identified by their trivial names. They at oftentimes have the suffix ''-ic acid''. IUPAC-recommended names also exist; in this system, carboxylic acids have an ''-oic acid'' suffix. For example, butyric acid (C3H7CO2H) is butanoic acid by IUPAC guidelines. For nomenclature of complex molecules containing a carboxylic acid, the carboxyl can be considered position one of the parent chain even if there are other substituents, such as 3-chloropropanoic acid. Alternately, it can be named as a "carboxy" or "carboxylic acid" substituent on another ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ester
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an oxoacid (organic or inorganic) in which at least one hydroxyl group () is replaced by an alkoxy group (), as in the substitution reaction of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. Glycerides are fatty acid esters of glycerol; they are important in biology, being one of the main classes of lipids and comprising the bulk of animal fats and vegetable oils. Esters typically have a pleasant smell; those of low molecular weight are commonly used as fragrances and are found in essential oils and pheromones. They perform as high-grade solvents for a broad array of plastics, plasticizers, resins, and lacquers, and are one of the largest classes of synthetic lubricants on the commercial market. Polyesters are important plastics, with monomers linked by ester moieties. Phosphoesters form the backbone of DNA molecules. Nitrate esters, such as nitroglycerin, are known for their explosive properties. '' Nomenclature Etymology Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
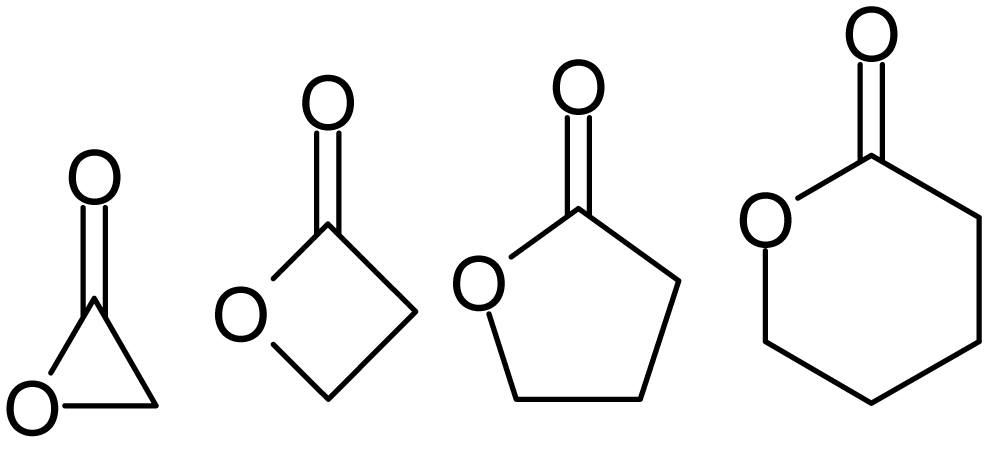
Lactone
Lactones are cyclic carboxylic esters, containing a 1-oxacycloalkan-2-one structure (), or analogues having unsaturation or heteroatoms replacing one or more carbon atoms of the ring. Lactones are formed by intramolecular esterification of the corresponding hydroxycarboxylic acids, which takes place spontaneously when the ring that is formed is five- or six-membered. Lactones with three- or four-membered rings (α-lactones and β-lactones) are very reactive, making their isolation difficult. Special methods are normally required for the laboratory synthesis of small-ring lactones as well as those that contain rings larger than six-membered. Nomenclature Lactones are usually named according to the precursor acid molecule (''aceto'' = 2 carbon atoms, ''propio'' = 3, ''butyro'' = 4, ''valero'' = 5, ''capro'' = 6, etc.), with a ''-lactone'' suffix and a Greek letter prefix that specifies the number of carbon atoms in the heterocycle — that is, the distance between the relevant -OH ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5-hydroxymethylfurfural
Hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF), also 5-(hydroxymethyl)furfural, is an organic compound formed by the dehydration of reducing sugars. It is a white low-melting solid (although commercial samples are often yellow) which is highly soluble in both water and organic solvents. The molecule consists of a furan ring, containing both aldehyde and alcohol functional groups. HMF can form in sugar-containing food, particularly as a result of heating or cooking. Its formation has been the topic of significant study as HMF was regarded as being potentially carcinogenic to humans. However, so far in vivo genotoxicity was negative. No relevance for humans concerning carcinogenic and genotoxic effects can be derived. HMF is classified as a food improvement agent and is primarily being used in the food industry in form of a food additive as a biomarker as well as a flavoring agent for food products. It is also produced industrially on a modest scale as a carbon-neutral feedstock for the production o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |