|
SPARC Enterprise
The SPARC Enterprise series is a range of UNIX server computers based on the SPARC V9 architecture. It was co-developed by Sun Microsystems and Fujitsu, announced on June 1st, 2004 and introduced in 2007. They were marketed and sold by Sun Microsystems (later Oracle Corporation, after their acquisition of Sun), Fujitsu, and Fujitsu Siemens Computers under the common brand of "SPARC Enterprise", superseding Sun's Sun Fire and Fujitsu's PRIMEPOWER server product lines. Codename is APL (Advanced Product Line). Since 2010, servers based on new SPARC CMT processors (SPARC T3 and later) have been branded as Oracle's SPARC T-Series servers, the "SPARC Enterprise" brand being dropped. Fujitsu continued to sell SPARC T-Series as their SPARC Enterprise product line until December 2015. Fujitsu rebranded the product line to "SPARC Servers" since SPARC M10 released in 2013 and continued to sell SPARC M-Series and T-Series with their new brand. Model range SPARC64 processor based models ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UNIX
Unix (; trademarked as UNIX) is a family of multitasking, multiuser computer operating systems that derive from the original AT&T Unix, whose development started in 1969 at the Bell Labs research center by Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie, and others. Initially intended for use inside the Bell System, AT&T licensed Unix to outside parties in the late 1970s, leading to a variety of both academic and commercial Unix variants from vendors including University of California, Berkeley ( BSD), Microsoft ( Xenix), Sun Microsystems (SunOS/ Solaris), HP/ HPE (HP-UX), and IBM ( AIX). In the early 1990s, AT&T sold its rights in Unix to Novell, which then sold the UNIX trademark to The Open Group, an industry consortium founded in 1996. The Open Group allows the use of the mark for certified operating systems that comply with the Single UNIX Specification (SUS). Unix systems are characterized by a modular design that is sometimes called the " Unix philosophy". According to this p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reliability, Availability And Serviceability (computer Hardware)
Reliability, availability and serviceability (RAS), also known as reliability, availability, and maintainability (RAM), is a computer hardware engineering term involving reliability engineering, high availability, and serviceability design. The phrase was originally used by International Business Machines ( IBM) as a term to describe the robustness of their mainframe computers. Computers designed with higher levels of RAS have many features that protect data integrity and help them stay available for long periods of time without failure This data integrity and uptime is a particular selling point for mainframes and fault-tolerant systems. Definitions While RAS originated as a hardware-oriented term, systems thinking has extended the concept of reliability-availability-serviceability to systems in general, including software. * ''Reliability'' can be defined as the probability that a system will produce correct outputs up to some given time ''t''. Reliability is enhanced by f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solaris 10
Solaris is a proprietary Unix operating system originally developed by Sun Microsystems. After the Sun acquisition by Oracle in 2010, it was renamed Oracle Solaris. Solaris superseded the company's earlier SunOS in 1993, and became known for its scalability, especially on SPARC systems, and for originating many innovative features such as DTrace, ZFS and Time Slider. Solaris supports SPARC and x86-64 workstations and servers from Oracle and other vendors. Solaris was registered as compliant with the Single UNIX Specification until 29 April 2019. Historically, Solaris was developed as proprietary software. In June 2005, Sun Microsystems released most of the codebase under the CDDL license, and founded the OpenSolaris open-source project. With OpenSolaris, Sun wanted to build a developer and user community around the software. After the acquisition of Sun Microsystems in January 2010, Oracle decided to discontinue the OpenSolaris distribution and the development model. In Augu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UltraSPARC T2
Sun Microsystems' UltraSPARC T2 microprocessor is a multithreading, multi-core CPU. It is a member of the SPARC family, and the successor to the UltraSPARC T1. The chip is sometimes referred to by its codename, Niagara 2. Sun started selling servers with the T2 processor in October 2007. New features The T2 is a commodity derivative of the UltraSPARC series of microprocessors, targeting Internet workloads in computers, storage and networking devices. The processor, manufactured in 65 nm, is available with eight CPU cores, and each core is able to handle eight threads concurrently. Thus the processor is capable of processing up to 64 concurrent threads. Other new features include: * Speed bump for each thread, which increased the frequency from 1.2 GHz to 1.6 GHz * One PCI Express port (x8 1.0) vs. the T1's JBus interface * Two Sun Neptune 10 Gigabit Ethernet ports (embedded into the T2 processor) with packet classification and filtering * L2 cache size increased to 4 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UltraSPARC T1
Sun Microsystems' UltraSPARC T1 microprocessor, known until its 14 November 2005 announcement by its development codename "Niagara", is a Multithreading (computer architecture), multithreading, Multi-core processor, multicore central processing unit, CPU. Designed to lower the energy consumption of server (computing)#Hardware, server computers, the CPU typically uses 72 watt, W of power at 1.4 GHz. Afara Websystems pioneered a radical thread-heavy SPARC design. The company was purchased by Sun, and the intellectual property became the foundation of the CoolThreads line of processors, starting with the T1. The T1 is a new-from-the-ground-up SPARC microprocessor implementation that conforms to thUltraSPARC Architecture 2005 specificationand executes the full SPARC V9 instruction set. Sun has produced two previous multicore processors (UltraSPARC IV and IV+), but UltraSPARC T1 was its first microprocessor that is both multicore ''and'' multithreaded. Security was built-in from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard Performance Evaluation Corporation
The Standard Performance Evaluation Corporation (SPEC) is an American non-profit corporation that aims to "produce, establish, maintain and endorse a standardized set" of performance benchmarks for computers. SPEC was founded in 1988. SPEC benchmarks are widely used to evaluate the performance of computer systems; the test results are published on the SPEC website. SPEC evolved into an umbrella organization encompassing four diverse groups; Graphics and Workstation Performance Group (GWPG), the High Performance Group (HPG), the Open Systems Group (OSG) and the newest, the Research Group (RG). Structure * The Open Systems Group (OSG) * The High-Performance Group (HPG) * The Graphics and Workstation Performance Group (GWPG) * SPEC Research Group (RG) Membership Membership in SPEC is open to any interested company or entity that is willing to commit to SPEC's standards. It allows: * Participation in benchmark development * Participation in review of results * Complimentary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transaction Processing Performance Council
In online transaction processing (OLTP), information systems typically facilitate and manage transaction-oriented applications. This is contrasted with online analytical processing. The term "transaction" can have two different meanings, both of which might apply: in the realm of computers or database transactions it denotes an atomic change of state, whereas in the realm of business or finance, the term typically denotes an exchange of economic entities (as used by, e.g., Transaction Processing Performance Council or commercial transactions.) OLTP may use transactions of the first type to record transactions of the second. OLTP has also been used to refer to processing in which the system responds immediately to user requests. An automated teller machine (ATM) for a bank is an example of a commercial transaction processing application. Online transaction processing applications have high throughput and are insert- or update-intensive in database management. These applications are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oracle Database
Oracle Database (commonly referred to as Oracle DBMS, Oracle Autonomous Database, or simply as Oracle) is a multi-model database management system produced and marketed by Oracle Corporation. It is a database commonly used for running online transaction processing (OLTP), data warehousing (DW) and mixed (OLTP & DW) database workloads. Oracle Database is available by several service providers on-prem, on-cloud, or as a hybrid cloud installation. It may be run on third party servers as well as on Oracle hardware ( Exadata on-prem, on Oracle Cloud or at Cloud at Customer). History Larry Ellison and his two friends and former co-workers, Bob Miner and Ed Oates, started a consultancy called Software Development Laboratories (SDL) in 1977. SDL developed the original version of the Oracle software. The name ''Oracle'' comes from the code-name of a CIA-funded project Ellison had worked on while formerly employed by Ampex. Releases and versions Oracle products follow a cus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
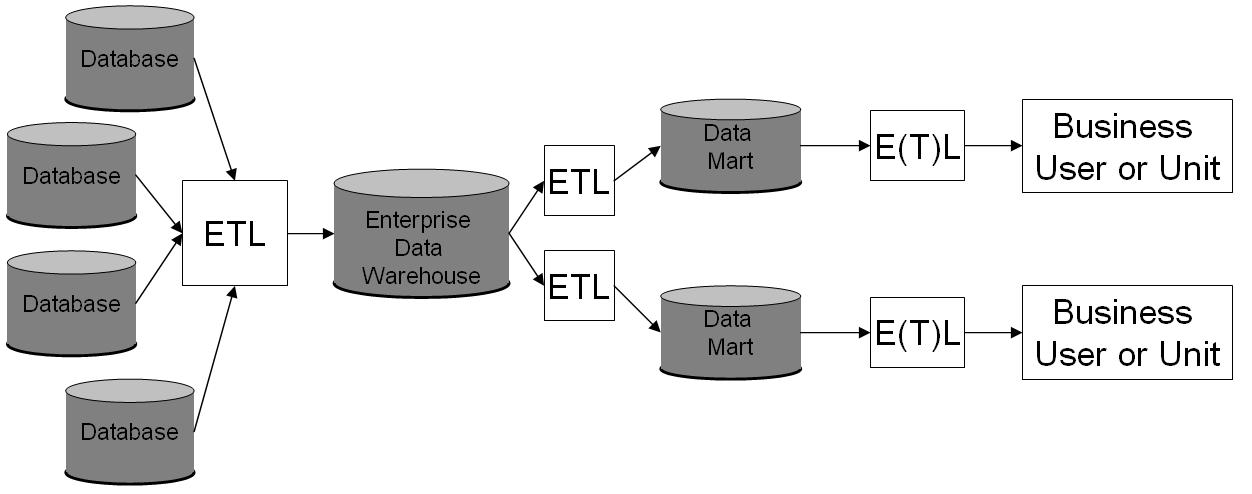
Data Warehousing
In computing, a data warehouse (DW or DWH), also known as an enterprise data warehouse (EDW), is a system used for reporting and data analysis and is considered a core component of business intelligence. DWs are central repositories of integrated data from one or more disparate sources. They store current and historical data in one single place that are used for creating analytical reports for workers throughout the enterprise. The data stored in the warehouse is uploaded from the operational systems (such as marketing or sales). The data may pass through an operational data store and may require data cleansing for additional operations to ensure data quality before it is used in the DW for reporting. Extract, transform, load (ETL) and extract, load, transform (ELT) are the two main approaches used to build a data warehouse system. ETL-based data warehousing The typical extract, transform, load (ETL)-based data warehouse uses staging, data integration, and access layers t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supercomputer
A supercomputer is a computer with a high level of performance as compared to a general-purpose computer. The performance of a supercomputer is commonly measured in floating-point operations per second (FLOPS) instead of million instructions per second (MIPS). Since 2017, there have existed supercomputers which can perform over 1017 FLOPS (a hundred quadrillion FLOPS, 100 petaFLOPS or 100 PFLOPS). For comparison, a desktop computer has performance in the range of hundreds of gigaFLOPS (1011) to tens of teraFLOPS (1013). Since November 2017, all of the world's fastest 500 supercomputers run on Linux-based operating systems. Additional research is being conducted in the United States, the European Union, Taiwan, Japan, and China to build faster, more powerful and technologically superior exascale supercomputers. Supercomputers play an important role in the field of computational science, and are used for a wide range of computationally intensive tasks in v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |