|
SN2 Palmitate
SN2 Palmitate is a structured triglyceride where palmitic acid is bonded to the middle position (sn-2) of the glycerol backbone. Structured triglycerides are achieved through an enzymatic process using vegetable oils. Current usage of structured triglycerides is mainly for infant formula providing a human milk fat substitute. SN2 Palmitate in human milk Fats in human breast milk provides about 50% of the energy needed for the development and growth of a newborn infant. About 98% of the fats provided by human milk are in the form of triglycerides, which themselves are molecules consisting of mixtures of three fatty acids bonded to sn-1, sn-2, and sn-3 positions of a glycerol backbone. The human mammary gland provides the baby with a unique fat composition where the fatty acids arranged in specific combinations, different from the triglycerides in other human tissues and plasma,Breckenridge, W.C., L. Marai, and A. Kuksis, Triglyceride structure of human milk fat. Can J Biochem, 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triglyceride
A triglyceride (TG, triacylglycerol, TAG, or triacylglyceride) is an ester derived from glycerol and three fatty acids (from ''tri-'' and ''glyceride''). Triglycerides are the main constituents of body fat in humans and other vertebrates, as well as vegetable fat. They are also present in the blood to enable the bidirectional transference of adipose fat and blood glucose from the liver, and are a major component of human skin oils. Many types of triglycerides exist. One specific classification focuses on saturated and unsaturated types. Saturated fats have ''no'' C=C groups; unsaturated fats feature one or more C=C groups. Unsaturated fats tend to have a lower melting point than saturated analogues; as a result, they are often liquid at room temperature. Chemical structure Triglycerides are tri-esters consisting of a glycerol bound to three fatty acid molecules. Alcohols have a hydroxyl (HO–) group. Organic acids have a carboxyl (–COOH) group. Alcohols and organ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melting Point
The melting point (or, rarely, liquefaction point) of a substance is the temperature at which it changes state from solid to liquid. At the melting point the solid and liquid phase exist in equilibrium. The melting point of a substance depends on pressure and is usually specified at a standard pressure such as 1 atmosphere or 100 kPa. When considered as the temperature of the reverse change from liquid to solid, it is referred to as the freezing point or crystallization point. Because of the ability of substances to supercool, the freezing point can easily appear to be below its actual value. When the "characteristic freezing point" of a substance is determined, in fact, the actual methodology is almost always "the principle of observing the disappearance rather than the formation of ice, that is, the melting point." Examples For most substances, melting and freezing points are approximately equal. For example, the melting point ''and'' freezing point of mercury is . How ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palmitic Acid
Palmitic acid (hexadecanoic acid in IUPAC nomenclature) is a fatty acid with a 16-carbon chain. It is the most common saturated fatty acid found in animals, plants and microorganisms.Gunstone, F. D., John L. Harwood, and Albert J. Dijkstra. The Lipid Handbook, 3rd ed. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2007. , Its chemical formula is CH3(CH2)14COOH, and its C:D (the total number of carbon atoms to the number of carbon-carbon double-bonds) is 16:0. It is a major component of the oil from the fruit of oil palms ( palm oil), making up to 44% of total fats. Meats, cheeses, butter, and other dairy products also contain palmitic acid, amounting to 50–60% of total fats. Palmitates are the salts and esters of palmitic acid. The palmitate anion is the observed form of palmitic acid at physiologic pH (7.4). Occurrence and production Palmitic acid was discovered by Edmond Frémy in 1840, in saponified palm oil. This remains the primary industrial route for its production, with the triglycerides (fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MUC2
Mucin 2, oligomeric mucus gel-forming, also known as MUC2, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''MUC2'' gene. Function This gene encodes a member of the mucin protein family. The protein encoded by this gene, also called mucin 2, is secreted onto mucosal surfaces. Mucin 2 is particularly prominent in the gut where it is secreted from goblet cells in the epithelial lining into the lumen of the large intestine. There, mucin 2, along with small amounts of related-mucin proteins, polymerizes into a gel of which 80% by weight is oligosaccharide side-chains that are added as post-translational modifications to the mucin proteins. This gel provides an insoluble mucous barrier that serves to protect the intestinal epithelium. Genetics The mucin 2 protein features a central domain containing tandem repeats rich in threonine and proline Proline (symbol Pro or P) is an organic acid classed as a proteinogenic amino acid (used in the biosynthesis of proteins), although it does ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bifidobacteria
''Bifidobacterium'' is a genus of gram-positive, nonmotile, often branched anaerobic bacteria. They are ubiquitous inhabitants of the gastrointestinal tract though strains have been isolated from the vagina and mouth ('' B. dentium'') of mammals, including humans. Bifidobacteria are one of the major genera of bacteria that make up the gastrointestinal tract microbiota in mammals. Some bifidobacteria are used as probiotics. Before the 1960s, ''Bifidobacterium'' species were collectively referred to as ''Lactobacillus bifidus''. History In 1899, Henri Tissier, a French pediatrician at the Pasteur Institute in Paris, isolated a bacterium characterised by a Y-shaped morphology ("bifid") in the intestinal microbiota of breast-fed infants and named it "bifidus". In 1907, Élie Metchnikoff, deputy director at the Pasteur Institute, propounded the theory that lactic acid bacteria are beneficial to human health. Metchnikoff observed that the longevity of Bulgarians was the result ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lactobacilli
The ''Lactobacillaceae'' are a family of lactic acid bacteria. It is the only family in the lactic acid bacteria which includes homofermentative and heterofermentative organisms; in the ''Lactobacillaceae,'' the pathway used for hexose fermentation is a genus-specific trait. ''Lactobacillaceae'' include the homofermentative lactobacilli ''Lactobacillus'', ''Holzapfelia'', ''Amylolactobacillus'', ''Bombilactobacillus'', ''Companilactobacillus'', ''Lapidilactobacillus'', ''Agrilactobacillus'', ''Schleiferilactobacillus'', ''Loigolactobacillus'', ''Lacticaseibacillus'', ''Latilactobacillus'', ''Dellaglioa'', ''Liquorilactobacillus'', ''Ligilactobacillus'', and ''Lactiplantibacillus''; the heterofermentative lactobacilli ''Furfurilactobacillus'', ''Paucilactobacillus'', ''Limosilactobacillus'', ''Fructilactobacillus'', ''Acetilactobacillus'', ''Apilactobacillus'', ''Levilactobacillus'', ''Secundilactobacillus'', and ''Lentilactobacillus,'' which were previously classified in the genus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immune Responses
An immune response is a reaction which occurs within an organism for the purpose of defending against foreign invaders. These invaders include a wide variety of different microorganisms including viruses, bacteria, parasites, and fungi which could cause serious problems to the health of the host organism if not cleared from the body. There are two distinct aspects of the immune response, the innate and the adaptive, which work together to protect against pathogens. The innate branch—the body's first reaction to an invader—is known to be a non-specific and quick response to any sort of pathogen. Components of the innate immune response include physical barriers like the skin and mucous membranes, immune cells such as neutrophils, macrophages, and monocytes, and soluble factors including cytokines and complement. On the other hand, the adaptive branch is the body's immune response which is catered against specific antigens and thus, it takes longer to activate the components involv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inflammation
Inflammation (from la, wikt:en:inflammatio#Latin, inflammatio) is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or Irritation, irritants, and is a protective response involving immune cells, blood vessels, and molecular mediators. The function of inflammation is to eliminate the initial cause of cell injury, clear out necrotic cells and tissues damaged from the original insult and the inflammatory process, and initiate tissue repair. The five cardinal signs are heat, pain, redness, swelling, and Functio laesa, loss of function (Latin ''calor'', ''dolor'', ''rubor'', ''tumor'', and ''functio laesa''). Inflammation is a generic response, and therefore it is considered as a mechanism of innate immune system, innate immunity, as compared to adaptive immune system, adaptive immunity, which is specific for each pathogen. Too little inflammation could lead to progressive tissue destruction by the harmful stimulus (e.g. b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
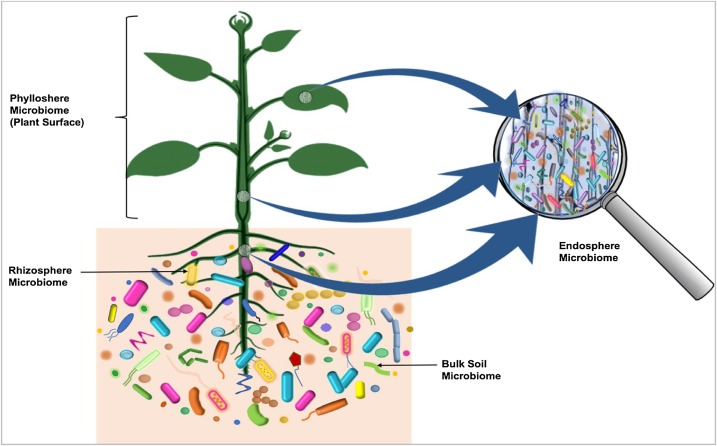
Microflora
Microbiota are the range of microorganisms that may be commensal, symbiotic, or pathogenic found in and on all multicellular organisms, including plants. Microbiota include bacteria, archaea, protists, fungi, and viruses, and have been found to be crucial for immunologic, hormonal, and metabolic homeostasis of their host. The term ''microbiome'' describes either the collective genomes of the microbes that reside in an ecological niche or within the microbes themselves. The microbiome and host emerged during evolution as a synergistic unit from epigenetics and genetic characteristics, sometimes collectively referred to as a holobiont. The presence of microbiota in human and other metazoan guts has been critical for understanding the co-evolution between metazoans and bacteria. Microbiota play key roles in the intestinal immune and metabolic responses via their fermentation product ( short-chain fatty acid), acetate. Introduction All plants and animals, from simple life fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speed Of Sound
The speed of sound is the distance travelled per unit of time by a sound wave as it propagates through an elastic medium. At , the speed of sound in air is about , or one kilometre in or one mile in . It depends strongly on temperature as well as the medium through which a sound wave is propagating. At , the speed of sound in air is about . The speed of sound in an ideal gas depends only on its temperature and composition. The speed has a weak dependence on frequency and pressure in ordinary air, deviating slightly from ideal behavior. In colloquial speech, ''speed of sound'' refers to the speed of sound waves in air. However, the speed of sound varies from substance to substance: typically, sound travels most slowly in gases, faster in liquids, and fastest in solids. For example, while sound travels at in air, it travels at in water (almost 4.3 times as fast) and at in iron (almost 15 times as fast). In an exceptionally stiff material such as diamond, sound travels a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minerals
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid chemical compound with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. (2011): Minerals'; p. 1. In the series ''Geology: Landforms, Minerals, and Rocks''. Rosen Publishing Group. The geological definition of mineral normally excludes compounds that occur only in living organisms. However, some minerals are often biogenic (such as calcite) or are organic compounds in the sense of chemistry (such as mellite). Moreover, living organisms often synthesize inorganic minerals (such as hydroxylapatite) that also occur in rocks. The concept of mineral is distinct from rock, which is any bulk solid geologic material that is relatively homogeneous at a large enough scale. A rock may consist of one type of mineral, or may be an aggregate of two or more different types of minerals, spacially segregated into distinct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
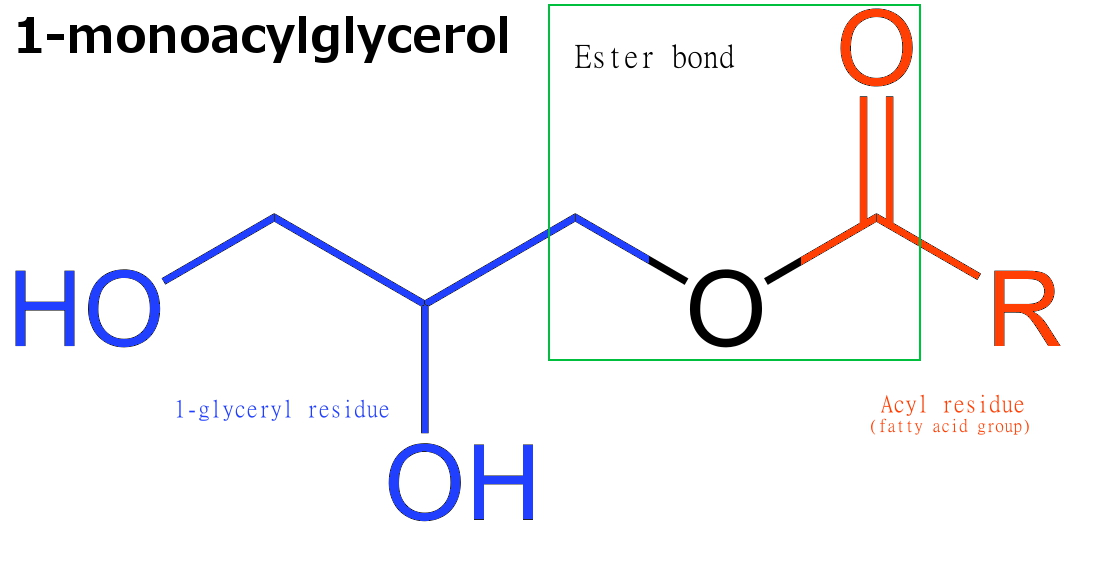
Monoglyceride
Monoglycerides (also: acylglycerols or monoacylglycerols) are a class of glycerides which are composed of a molecule of glycerol linked to a fatty acid via an ester bond. As glycerol contains both primary and secondary alcohol groups two different types of monoglycerides may be formed; 1-monoacylglycerols where the fatty acid is attached to a primary alcohol, or a 2-monoacylglycerols where the fatty acid is attached to the secondary alcohol. Synthesis Monoglycerides are produced both biologically and industrially. They are naturally present at very low levels (0.1-0.2%) in some seed oils such as olive oil, rapeseed oil and cottonseed oil. They are biosynthesized by the enzymatic hydrolysis of triglycerides by lipoprotein lipase and the enzymatic hydrolysis of diglycerides by diacylglycerol lipase; or as an intermediate in the alkanoylation of glycerol to form fats. Several monoglycerides are pharmacologically active (e.g. 2-oleoylglycerol, 2-arachidonoylglycerol). Industrial p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_-_filtered.jpg)