|
S2 (Munich)
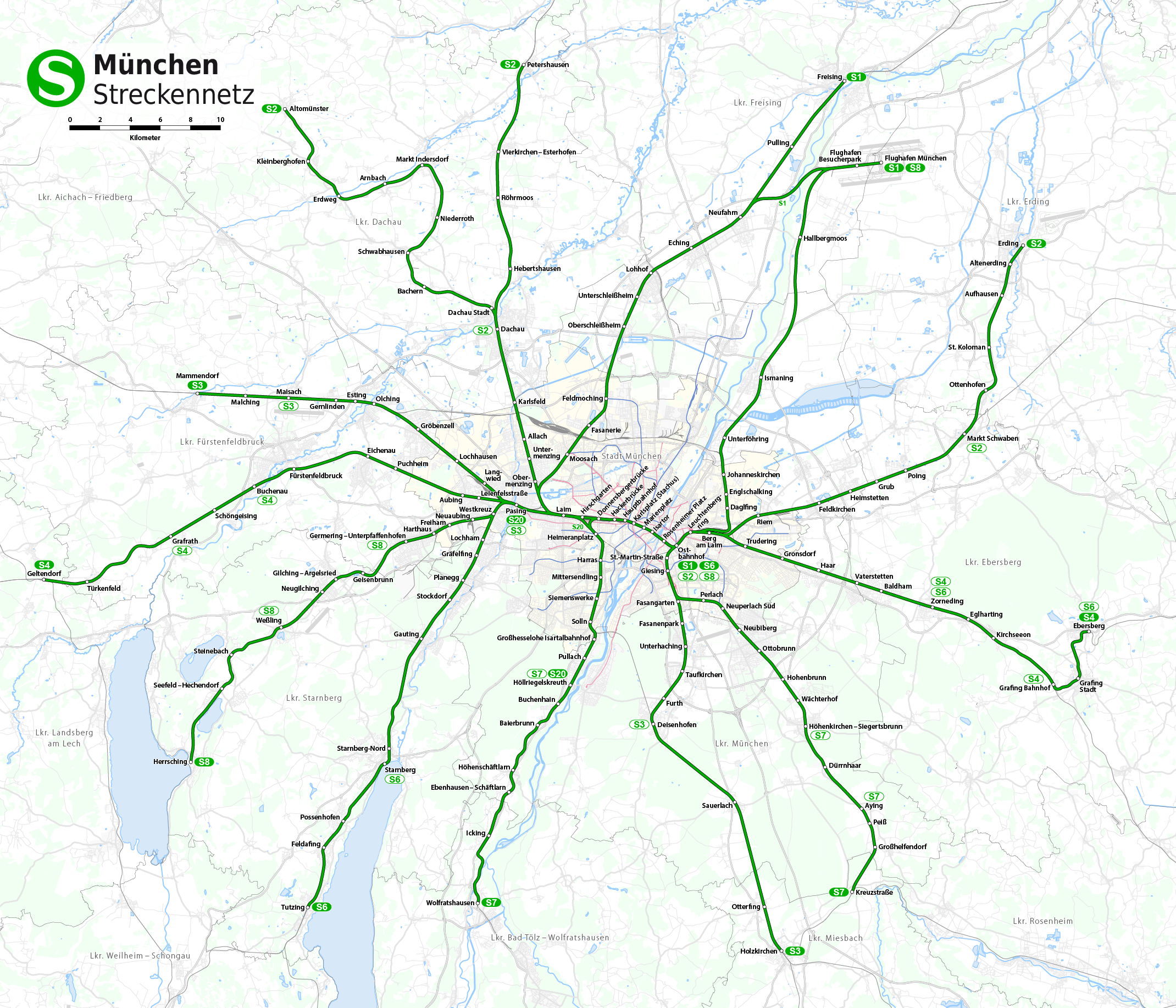
The S2 is a service on the Munich S-Bahn network. It is operated by DB Regio Bayern. It runs from Petershausen station to Erding station via Dachau, Laim, central Munich, Munich East and Markt Schwaben. The line is operated at 20-minute intervals between Dachau and Markt Schwaben. One train an hour continues from Dachau to Altomünster and the other two continue from Dachau to Petershausen so that the gap between trains alternates between 20 and 40 minutes between Dachau to Petershausen. Similarly only two out of three continue from Markt Schwaben to Erding, creating a similar varying gap between trains. It is operated using class 423 four-car electrical multiple units, usually as two coupled sets. In the evenings and on Sundays they generally run as single sets. Extra peak hour services are operated between Dachau and Altomünster, using class 420 four-car electrical multiple units (this is the only place this class operates on the Munich S-Bahn network), creating a 30-minute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Munich S-Bahn
The Munich S-Bahn (german: S-Bahn München) is an electric rail transit system in Munich, Germany. "S-Bahn" is the German abbreviation for ''Stadtschnellbahn'' (literally, "urban rapid rail"), and the Munich S-Bahn exhibits characteristics of both rapid transit and commuter rail systems. The Munich S-Bahn network is operated by S-Bahn München, a subsidiary of DB Regio Bayern, which is itself a subsidiary of the German national railway company, Deutsche Bahn. It is integrated into the Munich Transport and Tariff Association (''Münchner Verkehrs- und Tarifverbund'', MVV) and interconnected throughout the city with the locally owned Munich U-Bahn. Today, the S-Bahn covers most of the populated area of the Munich metropolitan area of about 2.7 million inhabitants. The Munich S-Bahn was established on 28 May 1972. It was intended as part of the scheme to provide an adequate transport system during the 1972 Summer Olympics held in Munich by connecting the pre-existing suburban rail s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dachau Station
Dachau station (german: Dachau Bahnhof) is a station in the Bavarian town of Dachau on the Munich S-Bahn network. It is classified by Deutsche Bahn as a category 3 station and it has five platform tracks. It is served daily by about 190 trains operated by Deutsche Bahn, including 150 S-Bahn trains. Dachau station is on the Nuremberg–Munich high-speed railway and is the beginning of the Dachau–Altomünster railway. Dachau Stadt (town) station is on the Dachau–Altomünster Railway. Location Dachau station is located southeast of the town of Dachau. The station building is located to the west of the tracks and has the address of Bahnhofplatz 1. Frühlingstraße runs to the west of the station, while Langhammerstraße runs west from the Bahnhofplatz (station forecourt). To the east of the tracks is Obere Moosschwaigestraße where there is a park-and-ride area. Schleißheimer Straße passes under the tracks to the north of the station. Augustenfelder Straße runs through a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Markt Schwaben–Erding Railway
The Markt Schwaben–Erding railway is a 13.63 km-long branch line in Upper Bavaria in Germany and now part of line S 2 of the Munich S-Bahn. Erding made an unsuccessful bid for the Munich–Mühldorf railway to run through the town; instead it was built a few kilometres south of the town. Other suggested links (to Freising, Passau or Rosenheim) were rejected by the railway board. On 8 March 1869, it was announced that the town would be connected to the railway network by a secondary railway (then called a ''Vizinalbahn'' in Bavaria) from Schwaben (now Markt Schwaben) to Erding. The contract for the construction of this railway was signed on 9 May 1870 by the town of Erding and the Head Office of the Royal Transport Institution (german: Generaldirektion der königlichen Verkehrsanstalten). The line was opened on 16 November 1872. The line branches off the Munich East–Mühldorf line in Markt Schwaben and runs to the north. The next stop is Ottenhofen station. Wifling s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Bavarian State Railways
The Royal Bavarian State Railways (''Königliche Bayerische Staats-Eisenbahnen'' or ''K.Bay.Sts.B.'') was the state railway company for the Kingdom of Bavaria. It was founded in 1844. The organisation grew into the second largest of the German state railways (after that of the Prussian state railways) with a railway network of 8,526 kilometres (including the Palatinate Railway or ''Pfalzbahn'') by the end of the First World War. Following the abdication of the Bavarian monarchy at the end of the First World War, the 'Royal' title was dropped and on 24 April 1920 the Bavarian State Railway (''Bayerische Staatseisenbahn''), as it was now called, was merged into the newly formed German Reich Railways Authority or Deutsche Reichseisenbahnen as the Bavarian Group Administration (''Gruppenverwaltung Bayern''). The management of the Bavarian railway network was divided into four Reichsbahn divisions: Augsburg, Munich, Nuremberg and Regensburg. The former Palatinate Railway formed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Munich–Mühldorf Railway
The Munich–Mühldorf railway is a 74 .8 km long main line in the German state of Bavaria, which opened on 1 May 1871. It runs from Munich East station via Markt Schwaben and Dorfen to Mühldorf. The travel time between Munich East and Mühldorf is currently about an hour. The track is one of the 18 bottlenecks with capacity problems identified under the ''Bundesschienenwegeausbaugesetz'' (Federal Railway Infrastructure Development Act) of 1993. In particular the section between Markt Schwaben and Ampfing is one of the busiest single-track lines in Germany. About 3 million tonnes is handled on this single-track, non-electrified route; this is more than one percent of Germany's total rail freight task and in 2015 it will probably be more than two percent. Current operations The 21.1 km of line between Munich East and Markt Schwaben is double track and electrified. Between München-Riem West junction and Markt Schwaben the Munich S-Bahn does not have separate tracks and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Munich–Augsburg Railway Company
The Munich–Augsburg Railway Company (''München-Augsburger Eisenbahn-Gesellschaft''), the second private railway company in Bavaria, built the Munich–Augsburg line between 1838 and 1840. It was nationalised in 1846 and became part of the Royal Bavarian State Railways, subsequently forming part of the Bavarian Maximilian’s Railway built between 1851 and 1854. Foundation and Construction of the Railway After the opening of the first private railway in Bavaria, the Bavarian Ludwig Railway from Nuremberg to Fürth on 7 December 1835, local committees for the construction of railway lines grew up all over Bavaria. The two committees in Augsburg and Munich soon united and had a civil servant draw up a route proposal. The task of carrying out the detailed planning and construction was given to the engineer, Paul Camille Denis, who had just completed the Nuremberg-Fürth line. After the state had issued the "Basic Regulations for All Railway Statutes in Bavaria" (''Fundamentalbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Munich–Augsburg Railway
The Munich–Augsburg line connects Munich and Augsburg in the German state of Bavaria. It was built by the Munich-Augsburg Railway Company and opened in 1840. It was nationalised in 1846 and extended to Ulm in 1854. The line between Augsburg and Munich is a major traffic axis and part of the Magistrale for Europe from Budapest through Vienna to Paris. History The line was built by the Munich-Augsburg Railway Company (German: ''München-Augsburg Eisenbahn-Gesellschaft'') and opened in 1839 and 1840. The Munich-Augsburg Railway Company was nationalised on 1 June 1846 and taken over by the Royal Bavarian State Railways (''Königlich Bayerische Staats-Eisenbahnen''). The line became part of Bavarian Maximilian’s Railway (''Bayerische Maximiliansbahn'') and was extended to Ulm on 1 May 1854. After the nationalisation of the line in 1846 a new Augsburg station was built at Rosenauberg along with new rail facilities in nearby Oberhausen. The old stations at the ''Roten Tor'' ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trunk Line (Munich S-Bahn)
The Munich S-Bahn (german: S-Bahn München) is an electric rail transit system in Munich, Germany. "S-Bahn" is the German abbreviation for ''Stadtschnellbahn'' (literally, "urban rapid rail"), and the Munich S-Bahn exhibits characteristics of both rapid transit and commuter rail systems. The Munich S-Bahn network is operated by S-Bahn München, a subsidiary of DB Regio Bayern, which is itself a subsidiary of the German national railway company, Deutsche Bahn. It is integrated into the Munich Transport and Tariff Association (''Münchner Verkehrs- und Tarifverbund'', MVV) and interconnected throughout the city with the locally owned Munich U-Bahn. Today, the S-Bahn covers most of the populated area of the Munich metropolitan area of about 2.7 million inhabitants. The Munich S-Bahn was established on 28 May 1972. It was intended as part of the scheme to provide an adequate transport system during the 1972 Summer Olympics held in Munich by connecting the pre-existing suburban rail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Munich Central Station
Munich ( ; german: München ; bar, Minga ) is the capital and most populous city of the German state of Bavaria. With a population of 1,558,395 inhabitants as of 31 July 2020, it is the third-largest city in Germany, after Berlin and Hamburg, and thus the largest which does not constitute its own state, as well as the 11th-largest city in the European Union. The city's metropolitan region is home to 6 million people. Straddling the banks of the River Isar (a tributary of the Danube) north of the Bavarian Alps, Munich is the seat of the Bavarian administrative region of Upper Bavaria, while being the most densely populated municipality in Germany (4,500 people per km2). Munich is the second-largest city in the Bavarian dialect area, after the Austrian capital of Vienna. The city was first mentioned in 1158. Catholic Munich strongly resisted the Reformation and was a political point of divergence during the resulting Thirty Years' War, but remained physically ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
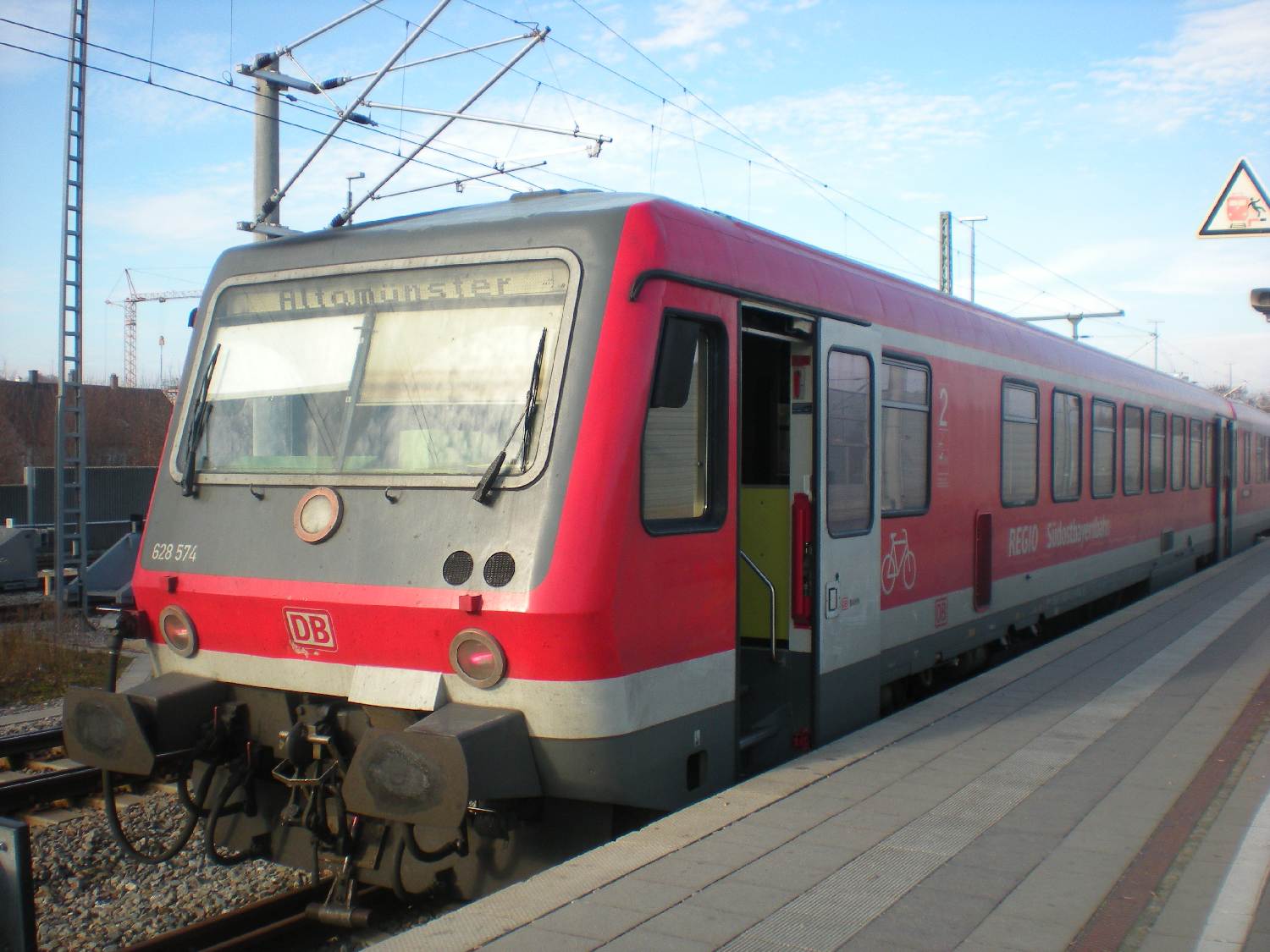
Dachau–Altomünster Railway
The Dachau–Altomünster railway, also called the Bummerl, Bockerl or Ludwig Thoma Railway, is a railway in the German state of Bavaria. It is part of the Munich S-Bahn network and is integrated within the Münchner Verkehrs- und Tarifverbund (Munich Transport and Tariff Association, MVV) as line S2. The branch line connects the town of Dachau on the Nuremberg–Munich high-speed railway with Altomünster. Markt Indersdorf is an important stop. Until its electrification in 2014, it was the only non-electrified line of the Munich S-Bahn and was designated as ''line A''. History At the beginning of the year 1900 it was decided to build a railway line from the Munich–Ingolstadt line (now part of the Nuremberg–Munich high-speed line) for the development of the hinterland of Dachau. There were two option for the route: connecting Altomünster via Schwabhausen and Erdweg from Dachau station or connecting Markt Indersdorf from Hebertshausen. The respective municipalities could n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Bavarian Eastern Railway Company
The Royal Bavarian Eastern Railway Company (''Königlich privilegirte Actiengesellschaft der bayerischen Ostbahnen'') or Bavarian Ostbahn was founded in 1856. Within just two decades it built an extensive railway network in the eastern Bavarian provinces of Upper Palatinate (''Oberpfalz'') and Lower Bavaria (''Niederbayern'') that had previously been largely undisturbed by the railway. Much of this network is still important for local and long distance rail traffic operated by the Deutsche Bahn today. Foundation The construction of the Bavarian state railway network had concentrated, during the first decade, on the 3 major lines: Ludwig's South-North Railway, Ludwig's Western Railway and the Bavarian Maximilian's Railway. At that point the majority of the Bavarian State Parliament rejected any further expansion of the state railway network due to the state's financial situation and the fact that railway operations were still largely unprofitable in those days. As a result, la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuremberg–Munich High-speed Railway
The Nuremberg–Munich high-speed railway line is a high-speed railway running between the two largest cities in Bavaria, Germany: Nuremberg and Munich. The northern section, between Nuremberg and Ingolstadt, is a track built between 1998 and 2006. It is in length with nine tunnels (total length: ). In order to minimize damage to the environment, it runs for the most part right next to Bundesautobahn 9. The southern section, between Ingolstadt and Munich, is 19th-century track. Its southern section has been upgraded for up to . Between 2010 and 2013, further upgrades to the midsection of the track will be done. The minimum speed on the Munich-Ingolstadt section should then be , with in the middle and 200 km/h in the southern section. Both long-distance and regional services operate on the line. Intercity-Express trains reach the tracks' 300 km/h speed-limit. InterCity and RegionalExpress trains travel at a maximum speed of 200 km/h. The Allersberg-Express, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)


