|
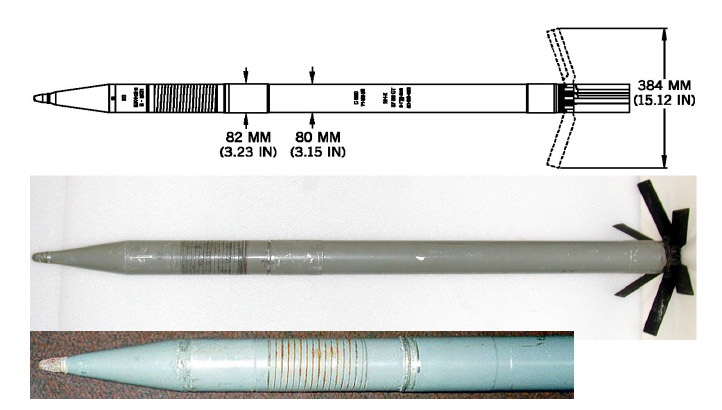
S-8 (rocket)
The S-8 is a rocket weapon developed by the Soviet Air Force for use by military aircraft. It remains in service with the Russian Air Force and various export customers. Developed in the 1970s, the S-8 is an 80 mm (3.1 in) rocket used by fighter bombers and helicopters. The system entered service in 1984 and is produced in a variety of subtypes with different warheads, including HEAT anti-armor, high-explosive fragmentation, smoke, and incendiary, as well as the specialized S-8BM runway-destroying munition and the S-8DM fuel-air explosive variants. Each rocket is between 1.5 meters (4 ft 11 in) and 1.7 meters (5 ft 7 in) long and weighs between 11.3 kg (25 lb) and 15.2 kg (33.5 lb), depending on warhead and fuse. Range is 2 to 4 kilometers (1.3 to 2.6 mi). The S-8 is generally carried in the B series of rocket pods, carrying either seven or 20 rockets. In 2018, the Russian Aerospace Forces took delivery and completed state tests of se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
S-8 KOM 80 Mm Rocket
S8, S-8, or S 8 may refer to: Routes * S8 (Berlin), a S-Bahn line in Berlin, Germany * S8 (Milan suburban railway network) * S8 (Munich) * Expressway S8 (Poland) * S8 (RER Vaud) * S8 (Rhine-Main S-Bahn) * S8 (Rhine-Ruhr S-Bahn) in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany * S8 (ZVV), a S-Bahn line in the cantons of Zürich and Zug in Switzerland * Short S.8 Calcutta, British transport flying boat * Stagecoach Gold bus route S8, a bus route in Oxfordshire, England * S8, a line in the Brussels Regional Express Network * Line S8 (Nanjing Metro) Other uses * S8 (classification), for disabled swimmers * S-8 (rocket), a Russian air-to-surface missile * S8: Keep container dry, a safety phrase in chemistry * Samsung Galaxy S8, a smartphone by Samsung * Samsung Galaxy Tab S8, a tablet computer by Samsung * Octasulfur, the main allotrope of sulfur, having the formula S8 * Audi S8, German car {{Letter-NumberCombDisambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
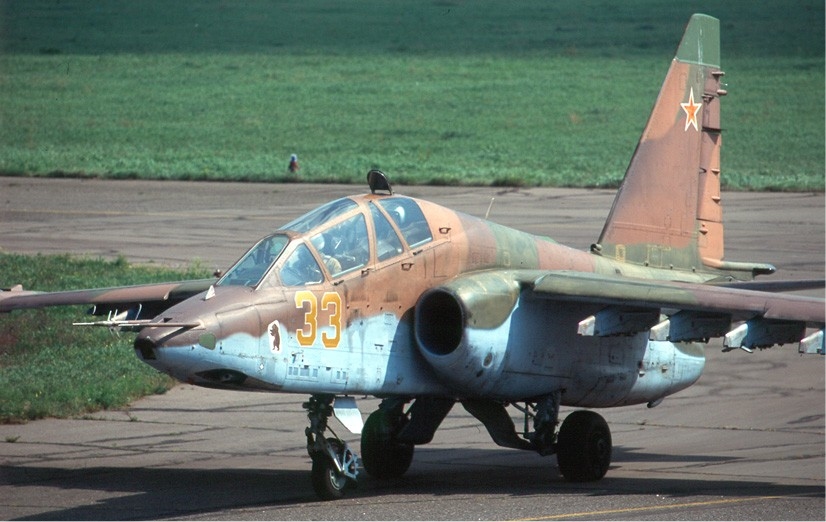
Sukhoi Su-25
The Sukhoi Su-25 ''Grach'' (russian: Грач ('' rook''); NATO reporting name: Frogfoot) is a subsonic, single-seat, twin-engine jet aircraft developed in the Soviet Union by Sukhoi. It was designed to provide close air support for Soviet Ground Forces. The first prototype made its maiden flight on 22 February 1975. After testing, the aircraft went into series production in 1978 in Tbilisi in the Georgian Soviet Socialist Republic. Early variants included the Su-25UB two-seat trainer, the Su-25BM for target-towing, and the Su-25K for export customers. Some aircraft were upgraded to the Su-25SM standard in 2012. The Su-25T and the Su-25TM (also known as the Su-39) were further developments, not produced in significant numbers. The Su-25, and the Su-34, were the only armoured, fixed-wing aircraft in production in 2007.Gordon and Dawes 2004. Su-25s are in service with Russia, other CIS members, and export customers. Production of the Su-25 ended in 2017 in Russia and 201 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ugroza
Ugroza (russian: Угроза, meaning "menace") is a precision-guided weapons system developed by the Russian Federation. It is an upgrade for standard Russian "dumb" rockets, including the S-5, S-8, and S-13 rockets. The system upgrades the "dumb" rockets with laser guidance, very significantly increasing their accuracy. It requires a laser target designator, from either an airborne or land based source, to "paint" a target. Circular error probable (CEP) is about 0.8 to 1.8 m, while maximum ranges of rockets varies from the rockets used 1.5–8 km. Ugroza allows rockets to be ripple-fired up to 7 at a time. The notable novelty is that the system does not use aerodynamic flight control (e.g. tail fins), but impulse steering with mini-thrusters. It has been dubbed as the Russian concept of impulse corrections (RCIC). The concept has been demonstrated by Ametech (russian: Аметех - Автоматизация и механизация технологий) on 1999 MAKS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
S-13 Rocket
The S-13 is a 122 mm calibre unguided rocket weapon developed by the Soviet Air Force for use by military aircraft. It remains in service with the Russian Air Force and some other countries. Development The S-13 rocket was developed in the 1970s to meet requirements for a penetrating weapon capable of cratering runways and penetrating hardened aircraft shelters, bunkers and pillboxes, to fill a gap between 80 mm and 240 mm rockets and fulfill a role similar to the 127 mm Zuni rocket. The S-13 is conventional in layout, with a solid rocket motor and folding tail fins that provide stability after launch. The first trials were in 1973, but it was introduced only in 1983. S-13 rockets are shot from 5-tube launchers B-13L, that can be carried by most of Soviet and Russian attack and new fighter aircraft, like Sukhoi Su-17/20/22, Sukhoi Su-24, Sukhoi Su-25, Sukhoi Su-27, MiG-23BN, MiG-27, MiG-29. B-13L1 launcher is used by helicopters such as Mil Mi-24, Mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
S-5 Rocket
The S-5 (first designated ARS-57) is a rocket weapon developed by the Soviet Air Force and used by military aircraft against ground area targets. It is in service with the Russian Air Force and various export customers. It is based on a German design from World War 2.Comeback for Russia’s Unguided Rockets ''Aviation International News''. 24 October 2019. It is produced in a variety of sub-types with different s, including anti-armour (S-5K), high-explosive |
YouTube
YouTube is a global online video sharing and social media platform headquartered in San Bruno, California. It was launched on February 14, 2005, by Steve Chen, Chad Hurley, and Jawed Karim. It is owned by Google, and is the second most visited website, after Google Search. YouTube has more than 2.5 billion monthly users who collectively watch more than one billion hours of videos each day. , videos were being uploaded at a rate of more than 500 hours of content per minute. In October 2006, YouTube was bought by Google for $1.65 billion. Google's ownership of YouTube expanded the site's business model, expanding from generating revenue from advertisements alone, to offering paid content such as movies and exclusive content produced by YouTube. It also offers YouTube Premium, a paid subscription option for watching content without ads. YouTube also approved creators to participate in Google's AdSense program, which seeks to generate more revenue for both parties. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Mil Mi-24 Variants
The Soviet and later Russian Mil Mi-24 helicopter has been produced in many variants, as described below. History In 1966, Soviet aircraft designer Mikhail Mil created a mock-up design of a new helicopter (derived from the Mil Mi-8) which was made with the intent of fulfilling both the role of a close air support aircraft as well as being able to transport infantry into combat. This prototype design was designated the V-24, and in 1968 a directive was given to proceed with the development of the helicopter. The Mi-24 went from the drawing board to the first test-flights in less than eighteen months, with the first models being delivered to the Soviet Armed Forces for evaluation in 1971. As a result of the speedy development, the initial Mi-24 variants had a number of problems: lateral roll, weapon sighting issues, and a limited field of view for the pilot. A later redesign of the Mi-24's front section solved most of these problems. List of variants ;A-10: Designation given to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flechette
A flechette ( ) is a pointed steel projectile with a vaned tail for stable flight. The name comes from French , "little arrow" or "dart", and sometimes retains the acute accent in English: fléchette. They have been used as ballistic weapons since World War I. Delivery systems and methods of launching flechettes vary, from a single shot, to thousands in a single explosive round. The use of flechettes as antipersonnel weapons has been controversial. Air-dropped During World War I, flechettes were dropped from aircraft to attack infantry and were able to pierce helmets. Later the U.S. used Lazy Dog bombs, which are small, unguided kinetic projectiles typically about in length, in diameter, and weighing about . The weapons were designed to be dropped from an aircraft. They contained no explosive charge but as they fell they developed significant kinetic energy making them lethal and able to easily penetrate soft cover such as jungle canopy, several inches of sand or light ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
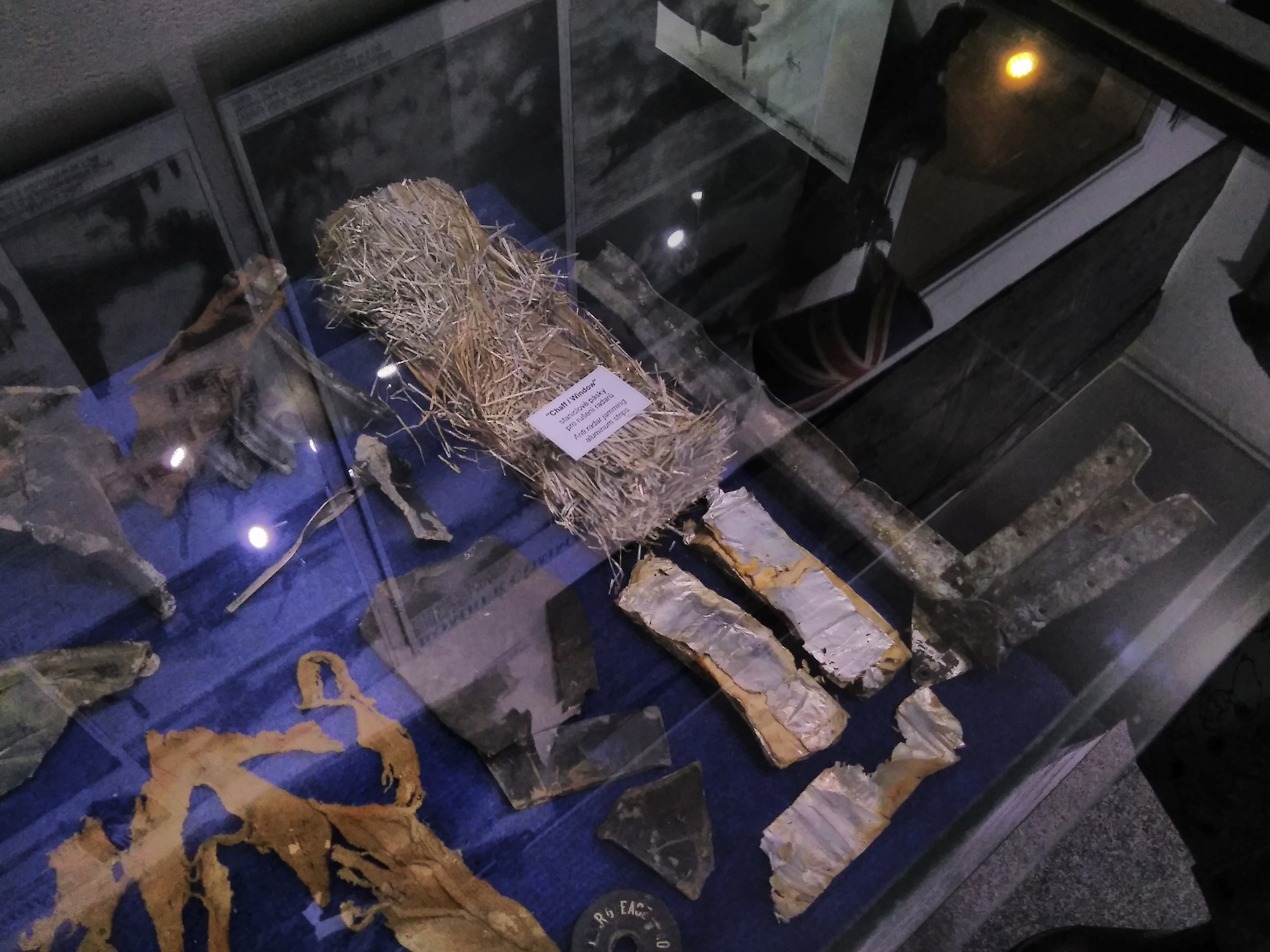
Chaff (radar Countermeasure)
Chaff, originally called Window by the British and ''Düppel'' by the Second World War era German Luftwaffe (from the Berlin suburb where it was first developed), is a radar countermeasure in which aircraft or other targets spread a cloud of small, thin pieces of aluminium, metallized glass fibre or plastic, which either appears as a cluster of primary targets on radar screens or swamps the screen with multiple returns, in order to confuse and distract. Modern armed forces use chaff (in naval applications, for instance, using short-range SRBOC rockets) to distract radar-guided missiles from their targets. Most military aircraft and warships have chaff dispensing systems for self-defense. An intercontinental ballistic missile may release in its midcourse phase several independent warheads as well as penetration aids such as decoy balloons and chaff. Modern radar systems can distinguish chaff from target objects by measuring the Doppler shift; chaff quickly loses speed compar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megacandela
The candela ( or ; symbol: cd) is the unit of luminous intensity in the International System of Units (SI). It measures luminous power per unit solid angle emitted by a light source in a particular direction. Luminous intensity is analogous to radiant intensity, but instead of simply adding up the contributions of every wavelength of light in the source's spectrum, the contribution of each wavelength is weighted by the standard luminosity function (a model of the sensitivity of the human eye to different wavelengths). A common wax candle emits light with a luminous intensity of roughly one candela. If emission in some directions is blocked by an opaque barrier, the emission would still be approximately one candela in the directions that are not obscured. The word ''candela'' is Latin for ''candle''. The old name "candle" is still sometimes used, as in ''foot-candle'' and the modern definition of ''candlepower''. Definition The 26th General Conference on Weights and Measures (CG ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mil Mi-8
The Mil Mi-8 (russian: Ми-8, NATO reporting name: Hip) is a medium twin-turbine helicopter, originally designed by the Soviet Union in the 1960s and introduced into the Soviet Air Force in 1968. It is now produced by Russia. In addition to its most common role as a transport helicopter, the Mi-8 is also used as an airborne command post, armed gunship, and reconnaissance platform. Along with the related, more powerful Mil Mi-17, the Mi-8 is among the world's most-produced helicopters, used by over 50 countries. As of 2015, when combined the two helicopters are the third most common operational military aircraft in the world. Design and development Mikhail Mil originally approached the Soviet government with a proposal to design an all-new two-engined turbine helicopter in 1959 after the success of the Mil Mi-4 and the emergence and effectiveness of turbines used in the Mil Mi-6. After design and development, the Mi-8 was subsequently introduced into the Soviet Air ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Aerospace Forces
The Russian Aerospace Forces or Russian Air and Space Forces ( rus, Воздушно-космические силы, r=Vozdushno-kosmicheskiye sily) or VKS ( rus, ВКС}) comprise the air and space Space is the boundless three-dimensional extent in which objects and events have relative position and direction. In classical physics, physical space is often conceived in three linear dimensions, although modern physicists usually con ... Military branch, branch of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation. Russia established the VKS as a new branch of its military on 1 August 2015 with the merging of the Russian Air Force (VVS) and the Russian Aerospace Defence Forces (VVKO) - as recommended by the Ministry of Defence (Russia), Ministry of Defence. The VKS has its headquarters in Moscow. Russia's Ministry of Defence (Russia), Defense Minister Sergei Shoigu explained the merger as improving efficiency and logistical support. Organisation Sub-branches According to Ja ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |