|
Ugroza
Ugroza (russian: Угроза, meaning "menace") is a precision-guided weapons system developed by the Russian Federation. It is an upgrade for standard Russian "dumb" rockets, including the S-5, S-8, and S-13 rockets. The system upgrades the "dumb" rockets with laser guidance, very significantly increasing their accuracy. It requires a laser target designator, from either an airborne or land based source, to "paint" a target. Circular error probable (CEP) is about 0.8 to 1.8 m, while maximum ranges of rockets varies from the rockets used 1.5–8 km. Ugroza allows rockets to be ripple-fired up to 7 at a time. The notable novelty is that the system does not use aerodynamic flight control (e.g. tail fins), but impulse steering with mini-thrusters. It has been dubbed as the Russian concept of impulse corrections (RCIC). The concept has been demonstrated by Ametech (russian: Аметех - Автоматизация и механизация технологий) on 1999 MAKS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Precision-guided Munition
A precision-guided munition (PGM, smart weapon, smart munition, smart bomb) is a guided munition intended to precisely hit a specific target, to minimize collateral damage and increase lethality against intended targets. During the First Gulf War guided munitions accounted for only 9% of weapons fired, but accounted for 75% of all successful hits. Despite guided weapons generally being used on more difficult targets, they were still 35 times more likely to destroy their targets per weapon dropped. Because the damage effects of explosive weapons decrease with distance due to an inverse cube law, even modest improvements in accuracy (hence reduction in miss distance) enable a target to be attacked with fewer or smaller bombs. Thus, even if some guided bombs miss, fewer air crews are put at risk and the harm to civilians and the amount of collateral damage may be reduced. The advent of precision-guided munitions resulted in the renaming of older, low-technology, bombs as " un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
S-5 Rocket
The S-5 (first designated ARS-57) is a rocket weapon developed by the Soviet Air Force and used by military aircraft against ground area targets. It is in service with the Russian Air Force and various export customers. It is based on a German design from World War 2.Comeback for Russia’s Unguided Rockets ''Aviation International News''. 24 October 2019. It is produced in a variety of sub-types with different s, including anti-armour (S-5K), high-explosive [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
S-13 Rocket
The S-13 is a 122 mm calibre unguided rocket weapon developed by the Soviet Air Force for use by military aircraft. It remains in service with the Russian Air Force and some other countries. Development The S-13 rocket was developed in the 1970s to meet requirements for a penetrating weapon capable of cratering runways and penetrating hardened aircraft shelters, bunkers and pillboxes, to fill a gap between 80 mm and 240 mm rockets and fulfill a role similar to the 127 mm Zuni rocket. The S-13 is conventional in layout, with a solid rocket motor and folding tail fins that provide stability after launch. The first trials were in 1973, but it was introduced only in 1983. S-13 rockets are shot from 5-tube launchers B-13L, that can be carried by most of Soviet and Russian attack and new fighter aircraft, like Sukhoi Su-17/20/22, Sukhoi Su-24, Sukhoi Su-25, Sukhoi Su-27, MiG-23BN, MiG-27, MiG-29. B-13L1 launcher is used by helicopters such as Mil Mi-24, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Federation
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eighth of Earth's inhabitable landmass. Russia extends across eleven time zones and shares land boundaries with fourteen countries, more than any other country but China. It is the world's ninth-most populous country and Europe's most populous country, with a population of 146 million people. The country's capital and largest city is Moscow, the largest city entirely within Europe. Saint Petersburg is Russia's cultural centre and second-largest city. Other major urban areas include Novosibirsk, Yekaterinburg, Nizhny Novgorod, and Kazan. The East Slavs emerged as a recognisable group in Europe between the 3rd and 8th centuries CE. Kievan Rus' arose as a state in the 9th century, and in 988, it adopted Orthodox Christianity from the Byz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
S-8 Rocket
S8, S-8, or S 8 may refer to: Routes * S8 (Berlin), a S-Bahn line in Berlin, Germany * S8 (Milan suburban railway network) * S8 (Munich) * Expressway S8 (Poland) * S8 (RER Vaud) * S8 (Rhine-Main S-Bahn) * S8 (Rhine-Ruhr S-Bahn) in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany * S8 (ZVV), a S-Bahn line in the cantons of Zürich and Zug in Switzerland * Short S.8 Calcutta, British transport flying boat * Stagecoach Gold bus route S8, a bus route in Oxfordshire, England * S8, a line in the Brussels Regional Express Network * Line S8 (Nanjing Metro) Other uses * S8 (classification), for disabled swimmers * S-8 (rocket), a Russian air-to-surface missile * S8: Keep container dry, a safety phrase in chemistry * Samsung Galaxy S8, a smartphone by Samsung * Samsung Galaxy Tab S8, a tablet computer by Samsung * Octasulfur Octasulfur is an inorganic substance with the chemical formula . It is an odourless and tasteless yellow solid, and is a major industrial chemical. It is the most common allotrope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nezavisimaya Gazeta
''Nezavisimaya Gazeta'' ( rus, Независимая газета, p=nʲɪzɐˈvʲisʲɪməjə ɡɐˈzʲetə, t=Independent Newspaper) is a Russian daily newspaper. History and profile ''Nezavisimaya Gazeta'' was first published on 21 December 1990. It was one of the most important daily newspapers in the early post-Soviet period, when it was seen as close to the opinion of the Moscow intelligentsia. The paper was temporarily closed for four months in 1995. Then it became part of the " Berezovsky Media Group". In 2007, following Berezovsky's political and economical disgrace, ''Nezavisimaya Gazeta'' was bought by Konstantin Remchukov, who became the new editor-in-chief, and his wife Yelena. Following the acquisition, the paper became mildly critical of the Putin administration. For example, it criticized the Kremlin's tightening control over the Central Election Commission and the Russian Academy of Science and in 2014 it was openly critical towards the annexation of Crimea by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laser Guidance
Laser guidance directs a robotics system to a target position by means of a laser beam. The laser guidance of a robot is accomplished by projecting a laser light, image processing and communication to improve the accuracy of guidance. The key idea is to show goal positions to the robot by laser light projection instead of communicating them numerically. This intuitive interface simplifies directing the robot while the visual feedback improves the positioning accuracy and allows for implicit localization. The guidance system may serve also as a mediator for cooperative multiple robots. Examples of proof-of-concept experiments of directing a robot by a laser pointer are shown on video. Laser guidance spans areas of robotics, computer vision, user interface, video games, communication and smart home technologies. Commercial systems Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. may have been using this technology in robotic vacuum cleaners since 2014. Google Inc. applied for a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laser Target Designator
A laser designator is a laser light source which is used to designate a target. Laser designators provide targeting for laser-guided bombs, missiles, or precision artillery munitions, such as the Paveway series of bombs, AGM-114 Hellfire, or the M712 Copperhead round, respectively. When a target is marked by a designator, the beam is invisible and does not shine continuously. Instead, a series of coded laser pulses, also called PRF codes (pulse repetition frequency), are fired at the target. These signals bounce off the target into the sky, where they are detected by the seeker on the laser-guided munition, which steers itself towards the centre of the reflected signal. Unless the people being targeted possess laser detection equipment or can hear aircraft overhead, it is extremely difficult for them to determine whether they are being marked. Laser designators work best in clear atmospheric conditions. Cloud cover, rain or smoke can make reliable designation of targets diff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
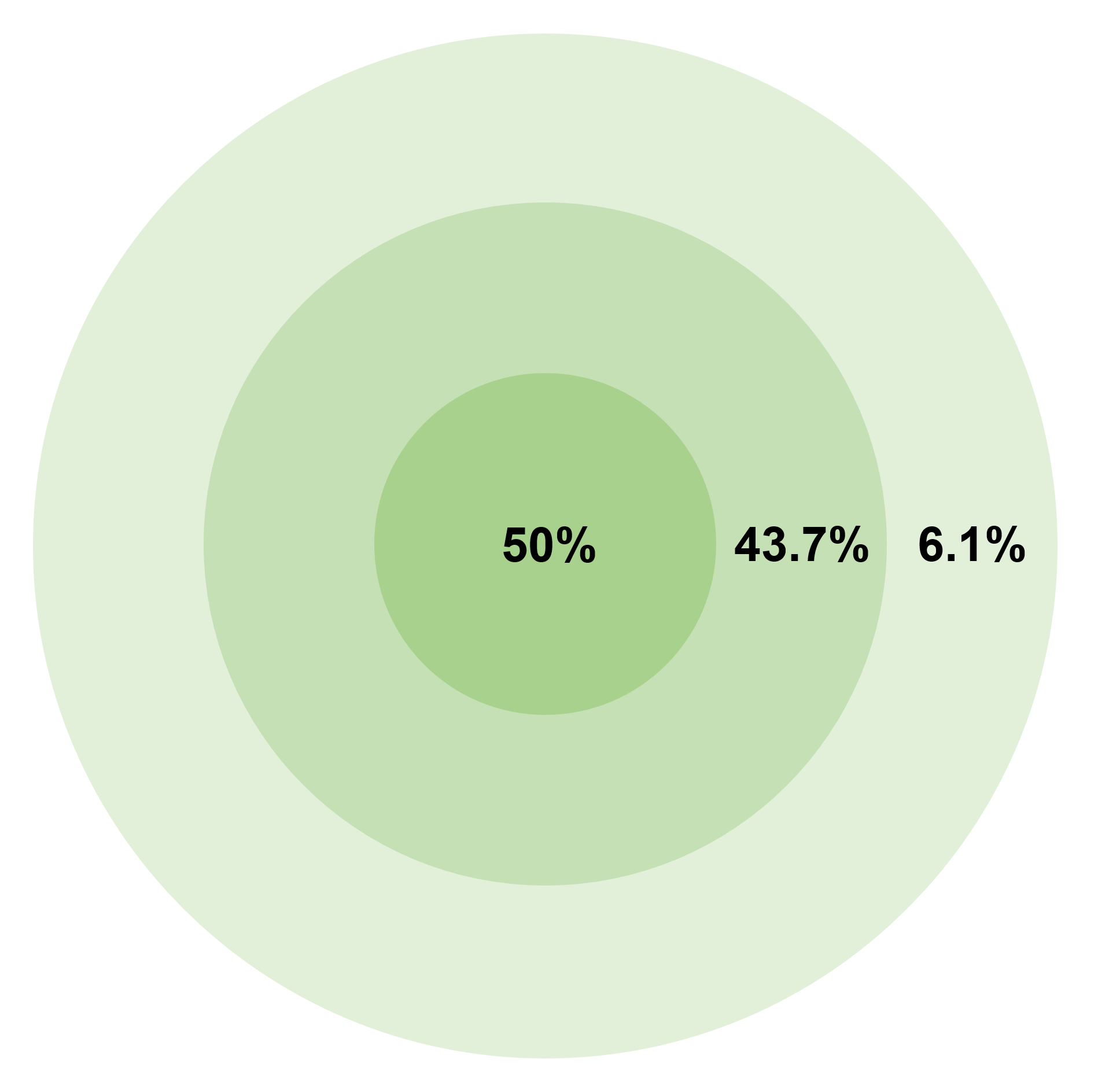
Circular Error Probable
In the military science of ballistics, circular error probable (CEP) (also circular error probability or circle of equal probability) is a measure of a weapon system's precision. It is defined as the radius of a circle, centered on the mean, whose perimeter is expected to include the landing points of 50% of the rounds; said otherwise, it is the median error radius. That is, if a given munitions design has a CEP of 100 m, when 100 munitions are targeted at the same point, 50 will fall within a circle with a radius of 100 m around their average impact point. (The distance between the target point and the average impact point is referred to as bias.) There are associated concepts, such as the DRMS (distance root mean square), which is the square root of the average squared distance error, and R95, which is the radius of the circle where 95% of the values would fall in. The concept of CEP also plays a role when measuring the accuracy of a position obtained by a navig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reaction Control System
A reaction control system (RCS) is a spacecraft system that uses thrusters to provide attitude control and translation. Alternatively, reaction wheels are used for attitude control. Use of diverted engine thrust to provide stable attitude control of a short-or-vertical takeoff and landing aircraft below conventional winged flight speeds, such as with the Harrier "jump jet", may also be referred to as a reaction control system. Reaction control systems are capable of providing small amounts of thrust in any desired direction or combination of directions. An RCS is also capable of providing torque to allow control of rotation ( roll, pitch, and yaw). Reaction control systems often use combinations of large and small ( vernier) thrusters, to allow different levels of response. Uses Spacecraft reaction control systems are used for: * attitude control during different stages of a mission; * station keeping in orbit; * close maneuvering during docking procedures; * con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MAKS Airshow
MAKS (russian: МАКС, russian: label=short for, Международный авиационно-космический салон, Mezhdunarodnyj aviatsionno-kosmicheskij salon, "International Aviation and Space Show") is an international air show held at Zhukovsky International Airport, the home of the Gromov Flight Research Institute in Zhukovsky, southeast of Moscow, Russia. The event was organized by the Russian Ministry of Industry and Trade until 2009, more recently by the Government of Moscow and Aviasalon. The first show, Mosaeroshow-92, was held in 1992. Since 1993, the air show was renamed as MAKS and is held biennially on odd years. MAKS is an important event for the Russian aviation industry and the Commonwealth of Independent States. Although it started mainly as an entertainment event, the show soon became a marketplace where Russian aerospace companies could negotiate export contracts and Russian air carriers could make foreign contacts. Background and histo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BM-21 Grad
The BM-21 "Grad" (russian: БМ-21 "Град", lit= hail) is a self-propelled 122 mm multiple rocket launcher designed in the Soviet Union. The system and the M-21OF rocket were first developed in the early 1960s, and saw their first combat use in March 1969 during the Sino-Soviet border conflict. ''BM'' stands for ''boyevaya mashina'' ( ru , боевая машина – combat vehicle), and the nickname means "hail". The complete system with the BM-21 launch vehicle and the M-21OF rocket is designated as the M-21 field-rocket system. The complete system is more commonly known as a Grad multiple rocket launcher system. In NATO countries the system, either the complete system or the launch vehicle only, was initially known as the M1964. Several other countries have copied the Grad or have developed similar systems. In Russian service its intended replacement is the 9A52-4 Tornado. Many similar 122 mm MLRS systems are made by different countries based on the BM-21 Grad. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_(526-04).jpg)