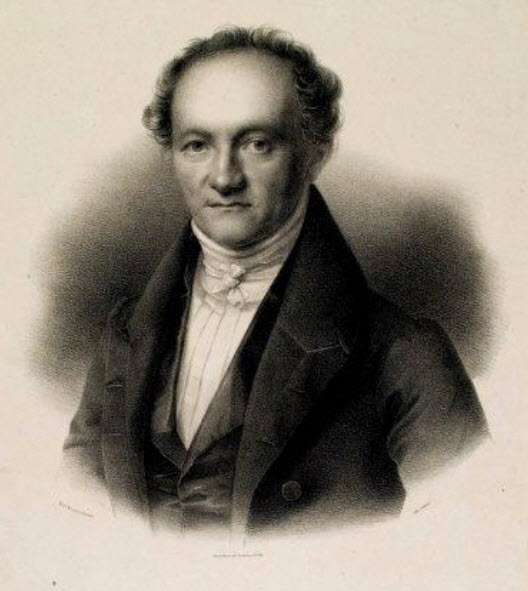|
Rivia
The Rivia (, []) is a Hebrew cantillation, cantillation mark commonly found in the Torah, Haftarah, and other biblical texts. The Aram word ) has its Hebrew counter part Rivi'i, with other variant English spellings. Its meaning is 'the fourth'. Rivia is considered to have medium strength. It is stronger than a Pashta or Tevir, but weaker than a Zakef or Tipcha. The Rivia can occur either by itself, or following one or two Munach The Munach (Hebrew: , also spelled ''Munah'' or ''Munakh''), translating to English as ''"to rest,"'' is a common cantillation sound. In Sephardi and Oriental traditions it is often called Shofar holekh. It is marked with a right angle below the co ...s. When there are two Munachs prior to a Rivia, the first Munach has a long melody, and the second one is short. When there is one Munach, it is short. Based on its translation with ''fourth'' in printouts it is represented by a diamond-shaped mark. However in manuscripts it's just a dot.The Art of Cantil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Munach
The Munach (Hebrew: , also spelled ''Munah'' or ''Munakh''), translating to English as ''"to rest,"'' is a common cantillation sound. In Sephardi and Oriental traditions it is often called Shofar holekh. It is marked with a right angle below the corresponding word. The munach is found in various groups, including the Katon, Etnachta, and Segol groups. One or more munachs can be followed by many different trope sounds, including Zakef katon, Etnachta, Rivia, Zarka, Segol, and Pazer. It is normally used when the number of syllables in a phrase are so long that an extra note is required to accommodate all the syllables. The munach is normally a short note. But when it is the first of two munachs followed by a Rivia, it has a longer melody. In this case it may also be called ''legarmeh'' (מֻנַּח לְגַרְמֵ֣הּ׀). Appearances The munach has the following appearances in the following sequences: *Katan group: Mahpach-Pashta-Munach-Zakef katan *Etnachta group: Mercha-Tipc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rivia
The Rivia (, []) is a Hebrew cantillation, cantillation mark commonly found in the Torah, Haftarah, and other biblical texts. The Aram word ) has its Hebrew counter part Rivi'i, with other variant English spellings. Its meaning is 'the fourth'. Rivia is considered to have medium strength. It is stronger than a Pashta or Tevir, but weaker than a Zakef or Tipcha. The Rivia can occur either by itself, or following one or two Munach The Munach (Hebrew: , also spelled ''Munah'' or ''Munakh''), translating to English as ''"to rest,"'' is a common cantillation sound. In Sephardi and Oriental traditions it is often called Shofar holekh. It is marked with a right angle below the co ...s. When there are two Munachs prior to a Rivia, the first Munach has a long melody, and the second one is short. When there is one Munach, it is short. Based on its translation with ''fourth'' in printouts it is represented by a diamond-shaped mark. However in manuscripts it's just a dot.The Art of Cantil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hebrew Cantillation
Hebrew cantillation is the manner of chanting ritual readings from the Hebrew Bible in synagogue services. The chants are written and notated in accordance with the special signs or marks printed in the Masoretic Text of the Bible, to complement the letters and vowel points. These marks are known in English as 'accents' (diacritics), 'notes' or trope symbols, and in Hebrew as () or just (). Some of these signs were also sometimes used in medieval manuscripts of the Mishnah. The musical motifs associated with the signs are known in Hebrew as or (not to be confused with Hasidic nigun) and in Yiddish as (): the word ''trope'' is sometimes used in Jewish English with the same meaning. There are multiple traditions of cantillation. Within each tradition, there are multiple tropes, typically for different books of the Bible and often for different occasions. For example, different chants may be used for Torah readings on Rosh Hashana and Yom Kippur than for the same tex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haftarah
The ''haftara'' or (in Ashkenazic pronunciation) ''haftorah'' (alt. ''haftarah, haphtara'', he, הפטרה) "parting," "taking leave", (plural form: ''haftarot'' or ''haftoros'') is a series of selections from the books of ''Nevi'im'' ("Prophets") of the Hebrew Bible (''Tanakh'') that is publicly read in synagogue as part of Jewish religious practice. The ''haftara'' reading follows the Torah reading on each Sabbath and on Jewish festivals and ta'anit, fast days. Typically, the ''haftara'' is thematically linked to the ''parashah'' (weekly Torah portion) that precedes it. The ''haftara'' is sung in a chant. (Chanting of Biblical texts is known as "''trope''" in Yiddish or "Cantillation" in English.) Related blessings precede and follow the haftara reading. The origin of haftara reading is lost to history, and several theories have been proposed to explain its role in Jewish practice, suggesting it arose in response to the persecution of the Jews under Antiochus IV Epiphane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilhelm Gesenius
Heinrich Friedrich Wilhelm Gesenius (3 February 178623 October 1842) was a German orientalist, lexicographer, Christian Hebraist, Lutheran theologian, Biblical scholar and critic. Biography Gesenius was born at Nordhausen. In 1803 he became a student of philosophy and theology at the University of Helmstedt, where Heinrich Henke was his most influential teacher; but the latter part of his university course was taken at Göttingen, where Johann Gottfried Eichhorn and Thomas Christian Tychsen were then at the height of their popularity. In 1806, shortly after graduation, he became ''Repetent'' and ''Privatdozent'' (or ''Magister legens'') at Göttingen; and, as he was later proud to say, had August Neander for his first pupil in Hebrew language. On 8 February 1810 he became ''professor extraordinarius'' in theology, and on 16 June 1811 was promoted to ''ordinarius'', at the University of Halle, where, in spite of many offers of high preferment elsewhere, he spent the rest of his l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pashta
Pashta (Hebrew: ) is a common Hebrew cantillation, cantillation mark found in the Torah, Haftarah, and other books of the Hebrew Bible. It is part of the Zakef katan, Katan group. Its mark symbol is identical to that of the Kadma (trope), Kadma. While Kadma and Pashta use the same symbol, Pashta is distinct from Kadma in the placement of the symbol. Kadma is always placed on the accented syllable, while Pashta is placed on the last letter as well as on the accented syllable, if it's not the last.Joshua R. Jacobson, ''Chanting the Hebrew Bible'', page 221 The Hebrew word translates into English as ''stretching out''. Occurrences In the Katan group, the Pashta can be found either following a Mahpach, or with the Mahpach absent. Following the Pashta will either be a Munach-Zakef katan or just a Zakef katan. The Pashta can also occur before the Segol (trope), Segol group. Numbers of occurrences Melody References {{Torah reading Cantillation marks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tevir
Tevir (Hebrew: , with variant English spellings including ''T'vir'' and ''Tebir'') is a cantillation mark commonly found in the Torah, Haftarah, and other Hebrew biblical books. It can be found independently or it can follow any number of other cantillation marks, very commonly a Mercha or Darga Darga (Hebrew: ) is a cantillation mark commonly found in the Torah, Haftarah, and other books. The symbol for the darga resembles a backwards Z. The darga is usually followed by a Tevir. It is most often found in places where a Tevir clause has ....Chanting the Hebrew Bible By Joshua R. Jacobson, page 113 The Hebrew word תְּבִ֛יר translates into English as ''broken''. Total occurrences Melody The Tevir is sung on a low tone, going downward at the beginning and upward at the end. References Cantillation marks {{Hebrew-Bible-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zakef (other) , a common independent trope
{{disambiguation ...
Zakef may refer to: *Zakef katon, a trope sound from the Katon group *Zakef gadol Zakef may refer to: * Zakef katon, a trope sound from the Katon group * Zakef gadol, a common independent trope {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tipcha
Tifcha ( he, טִפְחָ֖א, also spelled ''Tifkha'', ''Tipcha'' and other variant English spellings) is a cantillation mark commonly found in the Torah, Haftarah, and other books that are chanted. In Sephardic and Oriental traditions, it is called Tarcha, meaning "dragging" or "effort". The Tifcha is found in both the Etnachta group as the second member of that group, and in the Sof passuk group, though the melody varies slightly in each. While it is a weak sound, it is considered to be stronger than a Tevir The Hebrew word טִפְחָ֖א translates into English as ''diagonal''. It is related to the word tefach (''טפח'', measurement of the palm). The tifcha does not have a separating value of its own, as it is in the middle of a set of words. Tifcha occurs in the Torah 11,285 times, more than any other trope sound. Tifcha is the only trope sound to appear more than 10,000 times in the Torah. The first word of the Torah בראשית (''Bereshit'') is on a Tifcha. Total ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torah
The Torah (; hbo, ''Tōrā'', "Instruction", "Teaching" or "Law") is the compilation of the first five books of the Hebrew Bible, namely the books of Genesis, Exodus, Leviticus, Numbers and Deuteronomy. In that sense, Torah means the same as Pentateuch or the Five Books of Moses. It is also known in the Jewish tradition as the Written Torah (, ). If meant for liturgic purposes, it takes the form of a Torah scroll ('' Sefer Torah''). If in bound book form, it is called ''Chumash'', and is usually printed with the rabbinic commentaries (). At times, however, the word ''Torah'' can also be used as a synonym for the whole of the Hebrew Bible or Tanakh, in which sense it includes not only the first five, but all 24 books of the Hebrew Bible. Finally, Torah can even mean the totality of Jewish teaching, culture, and practice, whether derived from biblical texts or later rabbinic writings. The latter is often known as the Oral Torah. Representing the core of the Jewish spiri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Book Of Genesis
The Book of Genesis (from Greek ; Hebrew: בְּרֵאשִׁית ''Bəreʾšīt'', "In hebeginning") is the first book of the Hebrew Bible and the Christian Old Testament. Its Hebrew name is the same as its first word, ( "In the beginning"). Genesis is an account of the creation of the world, the early history of humanity, and of Israel's ancestors and the origins of the Jewish people. Tradition credits Moses as the author of Genesis, as well as the books of Exodus, Leviticus, Numbers and most of Deuteronomy; however, modern scholars, especially from the 19th century onward, place the books' authorship in the 6th and 5th centuries BC, hundreds of years after Moses is supposed to have lived.Davies (1998), p. 37 Based on scientific interpretation of archaeological, genetic, and linguistic evidence, most scholars consider Genesis to be primarily mythological rather than historical. It is divisible into two parts, the primeval history (chapters 1–11) and the ancestr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Book Of Exodus
The Book of Exodus (from grc, Ἔξοδος, translit=Éxodos; he, שְׁמוֹת ''Šəmōṯ'', "Names") is the second book of the Bible. It narrates the story of the Exodus, in which the Israelites leave slavery in Biblical Egypt through the strength of Yahweh, who has chosen them as his people. The Israelites then journey with the prophet Moses to Mount Sinai, where Yahweh gives the 10 commandments and they enter into a covenant with Yahweh, who promises to make them a "holy nation, and a kingdom of priests" on condition of their faithfulness. He gives them their laws and instructions to build the Tabernacle, the means by which he will come from heaven and dwell with them and lead them in a holy war to possess the land of Canaan (the "Promised Land"), which had earlier, according to the story of Genesis, been promised to the seed of Abraham. Traditionally ascribed to Moses himself, modern scholars see its initial composition as a product of the Babylonian exile (6th ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |