|
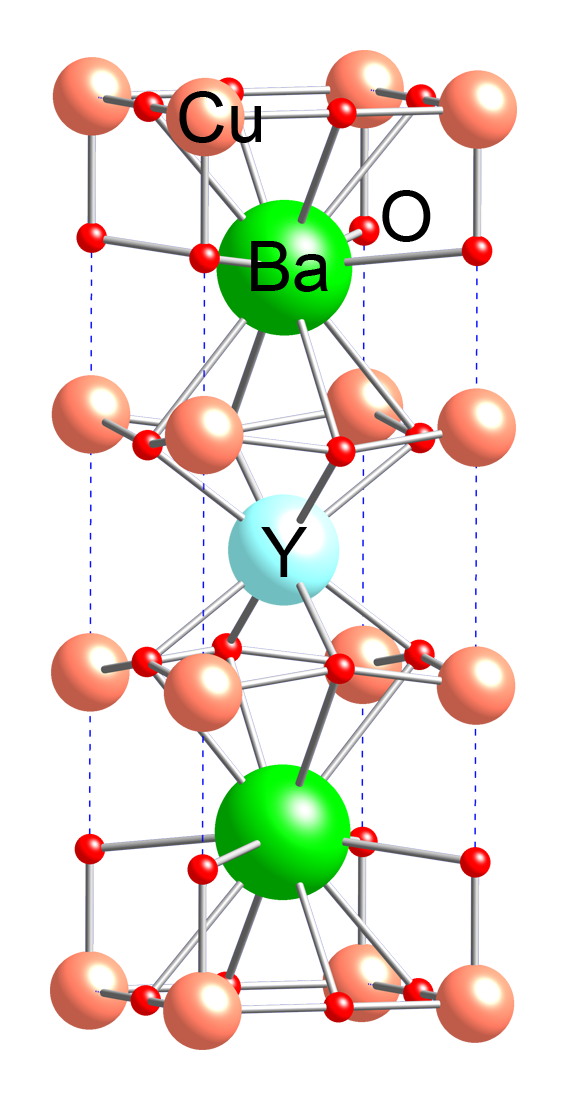
Rare-earth Barium Copper Oxide
Rare-earth barium copper oxide (also referred to as ReBCO) is a family of chemical compounds known for exhibiting high temperature superconductivity (HTS). ReBCO superconductors have the potential to sustain stronger magnetic fields than other superconductor materials. Due to their stronger magnetic field and relatively high superconducting critical temperature, this materials are proposed for future use in technical applications. This includes magnetic confinement fusion reactors such as the ARC reactor, allowing a more compact and potentially more economical construction, and superconducting magnets to use in future particle accelerators to come after the LHC at CERN which utilizes low-temperature superconductors. The most famous of these is yttrium barium copper oxide, YBa2Cu3O7−x (or Y123), the first superconductor found with a critical temperature above the boiling point of liquid nitrogen. Its molar ratio is 1 to 2 to 3 for yttrium, barium, and copper and it has a unit c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthorhombic Crystal System
In crystallography, the orthorhombic crystal system is one of the 7 crystal systems. Orthorhombic lattices result from stretching a cubic lattice along two of its orthogonal pairs by two different factors, resulting in a rectangular prism with a rectangular base (''a'' by ''b'') and height (''c''), such that ''a'', ''b'', and ''c'' are distinct. All three bases intersect at 90° angles, so the three lattice vectors remain mutually orthogonal. Bravais lattices There are four orthorhombic Bravais lattices: primitive orthorhombic, base-centered orthorhombic, body-centered orthorhombic, and face-centered orthorhombic. For the base-centered orthorhombic lattice, the primitive cell has the shape of a right rhombic prism;See , row oC, column Primitive, where the cell parameters are given as a1 = a2, α = β = 90° it can be constructed because the two-dimensional centered rectangular base layer can also be described with primitive rhombic axes. Note that the length a of the primiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ampere
The ampere (, ; symbol: A), often shortened to amp,SI supports only the use of symbols and deprecates the use of abbreviations for units. is the unit of electric current in the International System of Units (SI). One ampere is equal to electrons worth of charge moving past a point in a second. It is named after French mathematician and physicist André-Marie Ampère (1775–1836), considered the father of electromagnetism along with Danish physicist Hans Christian Ørsted. As of the 2019 redefinition of the SI base units, the ampere is defined by fixing the elementary charge to be exactly C ( coulomb), which means an ampere is an electrical current equivalent to elementary charges moving every seconds or elementary charges moving in a second. Prior to the redefinition the ampere was defined as the current that would need to be passed through 2 parallel wires 1 metre apart to produce a magnetic force of newtons per metre. The earlier CGS system had two definitio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commonwealth Fusion Systems
Commonwealth Fusion Systems (CFS) is an American company founded in 2018 aiming to build a compact fusion power plant based on the ARC tokamak power plant concept. The company is based in Cambridge, Massachusetts, and is a spin-off of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). CFS has participated in the United States Department of Energy’s INFUSE public-private knowledge innovation scheme, with several national labs and universities. History CFS was founded in 2018 as a spin-off from the MIT Plasma Science and Fusion Center. After initial funding of $50 million in 2018 from the Italian multinational Eni, CFS closed its series A round of venture capital funding in 2019 with a total of US$ 115 million in funding from Eni, Bill Gates's Breakthrough Energy Ventures, Vinod Khosla's Khosla Ventures, and others. CFS raised an additional US$ 84 million in series A2 funding from Singapore's Temasek, Norway's Equinor, and Devonshire Investors, as well as from previous investor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Europium
Europium is a chemical element with the symbol Eu and atomic number 63. Europium is the most reactive lanthanide by far, having to be stored under an inert fluid to protect it from atmospheric oxygen or moisture. Europium is also the softest lanthanide, as it can be dented with a fingernail and easily cut with a knife. When oxidation is removed a shiny-white metal is visible. Europium was isolated in 1901 and is named after the continent of Europe. Being a typical member of the lanthanide series, europium usually assumes the oxidation state +3, but the oxidation state +2 is also common. All europium compounds with oxidation state +2 are slightly reducing. Europium has no significant biological role and is relatively non-toxic as compared to other heavy metals. Most applications of europium exploit the phosphorescence of europium compounds. Europium is one of the rarest of the rare-earth elements on Earth.Stwertka, Albert. ''A Guide to the Elements'', Oxford University Press, 1996, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gadolinium
Gadolinium is a chemical element with the symbol Gd and atomic number 64. Gadolinium is a silvery-white metal when oxidation is removed. It is only slightly malleable and is a ductile rare-earth element. Gadolinium reacts with atmospheric oxygen or moisture slowly to form a black coating. Gadolinium below its Curie point of is ferromagnetic, with an attraction to a magnetic field higher than that of nickel. Above this temperature it is the most paramagnetic element. It is found in nature only in an oxidized form. When separated, it usually has impurities of the other rare-earths because of their similar chemical properties. Gadolinium was discovered in 1880 by Jean Charles de Marignac, who detected its oxide by using spectroscopy. It is named after the mineral gadolinite, one of the minerals in which gadolinium is found, itself named for the Finnish chemist Johan Gadolin. Pure gadolinium was first isolated by the chemist Paul-Émile Lecoq de Boisbaudran around 1886. Gadoliniu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neodymium
Neodymium is a chemical element with the symbol Nd and atomic number 60. It is the fourth member of the lanthanide series and is considered to be one of the rare-earth metals. It is a hard, slightly malleable, silvery metal that quickly tarnishes in air and moisture. When oxidized, neodymium reacts quickly producing pink, purple/blue and yellow compounds in the +2, +3 and +4 oxidation states. It is generally regarded as having one of the most complex spectra of the elements. Neodymium was discovered in 1885 by the Austrian chemist Carl Auer von Welsbach, who also discovered praseodymium. It is present in significant quantities in the minerals monazite and bastnäsite. Neodymium is not found naturally in metallic form or unmixed with other lanthanides, and it is usually refined for general use. Neodymium is fairly common—about as common as cobalt, nickel, or copper—and is widely distributed in the Earth's crust. Most of the world's commercial neodymium is mined in China, as is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samarium
Samarium is a chemical element with symbol Sm and atomic number 62. It is a moderately hard silvery metal that slowly oxidizes in air. Being a typical member of the lanthanide series, samarium usually has the oxidation state +3. Compounds of samarium(II) are also known, most notably the monoxide SmO, monochalcogenides SmS, SmSe and SmTe, as well as samarium(II) iodide. The last compound is a common reducing agent in chemical synthesis. Samarium has no significant biological role, and some samarium salts are slightly toxic. Samarium was discovered in 1879 by French chemist Paul-Émile Lecoq de Boisbaudran and named after the mineral samarskite from which it was isolated. The mineral itself was named after a Russian mine official, Colonel Vassili Samarsky-Bykhovets, who thus became the first person to have a chemical element named after him, albeit indirectly. Though classified as a rare-earth element, samarium is the 40th most abundant element in Earth's crust and more common than ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lanthanum Barium Copper Oxide
Lanthanum barium copper oxide, or LBCO, is an inorganic compound with the formula CuBa0.15La1.85O4. It is a black solid produced by heating an intimate mixture of barium oxide, copper(II) oxide, and lanthanum oxide in the presence of oxygen. The material was discovered in 1986 and was the first high temperature superconductor. Johannes Georg Bednorz and K. Alex Müller shared the 1987 Nobel Prize in physics for the discovery that this material exhibits superconductivity at the then unusually high temperature. This finding led to intense and fruitful efforts to generate other cuprate superconductor Cuprate superconductors are a family of high-temperature superconducting materials made of layers of copper oxides (CuO2) alternating with layers of other metal oxides, which act as charge reservoirs. At ambient pressure, cuprate superconductor ...s. Lanthanum barium copper oxide is related to the far simpler compound lanthanum cuprate, which has a similar structure. In lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lanthanum
Lanthanum is a chemical element with the symbol La and atomic number 57. It is a soft, ductile, silvery-white metal that tarnishes slowly when exposed to air. It is the eponym of the lanthanide series, a group of 15 similar elements between lanthanum and lutetium in the periodic table, of which lanthanum is the first and the prototype. Lanthanum is traditionally counted among the rare earth elements. Like most other rare earth elements, the usual oxidation state is +3. Lanthanum has no biological role in humans but is essential to some bacteria. It is not particularly toxic to humans but does show some antimicrobial activity. Lanthanum usually occurs together with cerium and the other rare earth elements. Lanthanum was first found by the Swedish chemist Carl Gustaf Mosander in 1839 as an impurity in cerium nitrate – hence the name ''lanthanum'', from the Ancient Greek (), meaning 'to lie hidden'. Although it is classified as a rare earth element, lanthanum is the 28th most abund ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yttrium Barium Copper Oxide
Yttrium barium copper oxide (YBCO) is a family of crystalline chemical compounds that display high-temperature superconductivity; it includes the first material ever discovered to become superconducting above the boiling point of liquid nitrogen (77 K) at about 93 K. Many YBCO compounds have the general formula Y Ba2 Cu3 O7−''x'' (also known as Y123), although materials with other Y:Ba:Cu ratios exist, such as Y Ba2 Cu4 Oy (Y124) or Y2 Ba4 Cu7 Oy (Y247). At present, there is no singularly recognised theory for high-temperature superconductivity. It is part of the more general group of rare-earth barium copper oxides (ReBCO) in which, instead of yttrium, other rare earths are present. History In April 1986, Georg Bednorz and Karl Müller, working at IBM in Zurich, discovered that certain semiconducting oxides became superconducting at relatively high temperature, in particular, a lanthanum barium copper oxide becomes superconducting at 35 K. This oxide was an oxyge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yttrium
Yttrium is a chemical element with the symbol Y and atomic number 39. It is a silvery-metallic transition metal chemically similar to the lanthanides and has often been classified as a "rare-earth element". Yttrium is almost always found in combination with lanthanide elements in rare-earth minerals, and is never found in nature as a free element. 89Y is the only stable isotope, and the only isotope found in the Earth's crust. The most important uses of yttrium are LEDs and phosphors, particularly the red phosphors in television set cathode ray tube displays. Yttrium is also used in the production of electrodes, electrolytes, electronic filters, lasers, superconductors, various medical applications, and tracing various materials to enhance their properties. Yttrium has no known biological role. Exposure to yttrium compounds can cause lung disease in humans. The element is named after '' ytterbite'', a mineral first identified in 1787 by the chemist Carl Axel Arrhenius. He n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |