|
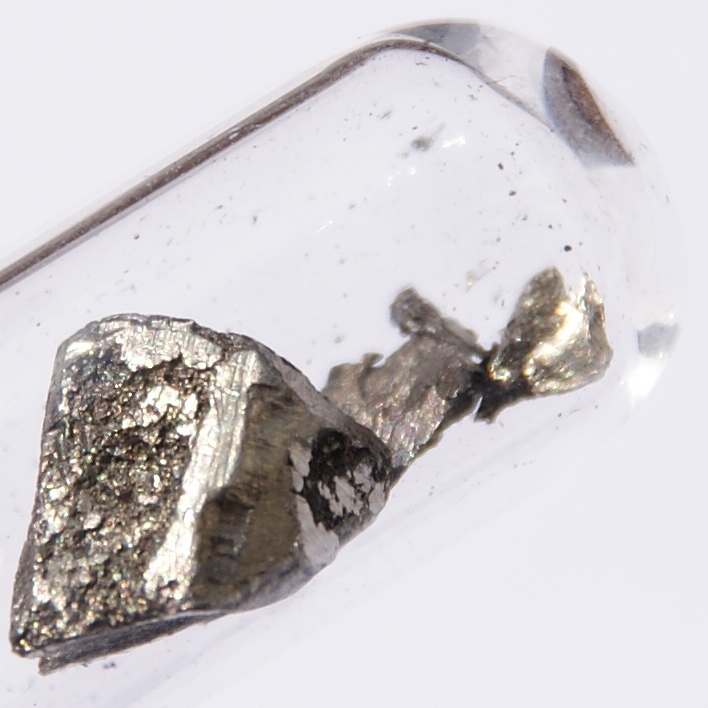
Lanthanum
Lanthanum is a chemical element with the symbol La and atomic number 57. It is a soft, ductile, silvery-white metal that tarnishes slowly when exposed to air. It is the eponym of the lanthanide series, a group of 15 similar elements between lanthanum and lutetium in the periodic table, of which lanthanum is the first and the prototype. Lanthanum is traditionally counted among the rare earth elements. Like most other rare earth elements, the usual oxidation state is +3. Lanthanum has no biological role in humans but is essential to some bacteria. It is not particularly toxic to humans but does show some antimicrobial activity. Lanthanum usually occurs together with cerium and the other rare earth elements. Lanthanum was first found by the Swedish chemist Carl Gustaf Mosander in 1839 as an impurity in cerium nitrate – hence the name ''lanthanum'', from the Ancient Greek (), meaning 'to lie hidden'. Although it is classified as a rare earth element, lanthanum is the 28th most abund ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
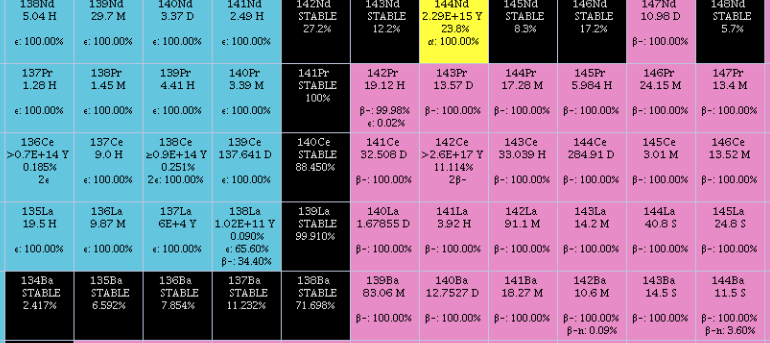
Lanthanide
The lanthanide () or lanthanoid () series of chemical elements comprises the 15 metallic chemical elements with atomic numbers 57–71, from lanthanum through lutetium. These elements, along with the chemically similar elements scandium and yttrium, are often collectively known as the rare-earth elements or rare-earth metals. The informal chemical symbol Ln is used in general discussions of lanthanide chemistry to refer to any lanthanide. All but one of the lanthanides are f-block elements, corresponding to the filling of the 4f electron shell. There is some dispute on whether lanthanum or lutetium is a d-block element, but lutetium is usually considered so by those who study the matter; it is included due to its chemical similarities with the other 14. All lanthanide elements form trivalent cations, Ln3+, whose chemistry is largely determined by the ionic radius, which decreases steadily from lanthanum to lutetium. These elements are called lanthanides because the elements i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Periodic Table
The periodic table, also known as the periodic table of the (chemical) elements, is a rows and columns arrangement of the chemical elements. It is widely used in chemistry, physics, and other sciences, and is generally seen as an icon of chemistry. It is a graphic formulation of the periodic law, which states that the properties of the chemical elements exhibit an approximate periodic dependence on their atomic numbers. The table is divided into four roughly rectangular areas called blocks. The rows of the table are called periods, and the columns are called groups. Elements from the same group of the periodic table show similar chemical characteristics. Trends run through the periodic table, with nonmetallic character (keeping their own electrons) increasing from left to right across a period, and from down to up across a group, and metallic character (surrendering electrons to other atoms) increasing in the opposite direction. The underlying reason for these trends is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lanthanum Carbonate
Lanthanum carbonate, La( C O3)3, is the salt formed by lanthanum(III) cations and carbonate anions. It is an ore of lanthanum metal (bastnäsite), along with monazite. Chemistry Lanthanum carbonate is used as a starting material in lanthanum chemistry, particularly in forming mixed oxides, for example * for production of lanthanum strontium manganite, primarily for solid oxide fuel cell applications; * for production of certain high-temperature superconductors, such as LaSrCuO. Medical uses Lanthanum carbonate is used in medicine as a phosphate binder. As a medication it is sold under the trade name Fosrenol by the pharmaceutical company Shire Pharmaceuticals. Due to its large size (1000 mg tablet is 2.2 cm in diameter), it may be possible to choke on the tablet if it is not chewed. It is prescribed for the treatment of hyperphosphatemia, primarily in patients with chronic kidney disease. It is taken with meals and binds to dietary phosphate, preventing phosphate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerium
Cerium is a chemical element with the symbol Ce and atomic number 58. Cerium is a soft, ductile, and silvery-white metal that tarnishes when exposed to air. Cerium is the second element in the lanthanide series, and while it often shows the +3 oxidation state characteristic of the series, it also has a stable +4 state that does not oxidize water. It is also considered one of the rare-earth elements. Cerium has no known biological role in humans but is not particularly toxic, except with intense or continued exposure. Despite always occurring in combination with the other rare-earth elements in minerals such as those of the monazite and bastnäsite groups, cerium is easy to extract from its ores, as it can be distinguished among the lanthanides by its unique ability to be oxidized to the +4 state in aqueous solution. It is the most common of the lanthanides, followed by neodymium, lanthanum, and praseodymium. It is the 25th-most abundant element, making up 66 ppm of the Ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Gustaf Mosander
Carl Gustaf Mosander (10 September 1797 – 15 October 1858) was a Swedish chemist. He discovered the rare earth elements lanthanum, erbium and terbium. Early life and education Born in Kalmar, Mosander attended school there until he moved to Stockholm with his mother in 1809. In Stockholm, he became an apprentice at the ''Ugglan'' pharmacy. He took his pharmacy examination in 1817, but had an interest in medicine and joined the Karolinska Institute in 1820. He passed his medical examination in 1825. He worked in the laboratory of Jöns Jakob Berzelius and became a close friend of fellow student Friedrich Wöhler. Career In 1832 Jöns Jakob Berzelius retired in favor of his student Carl Gustaf Mosander who succeeded him as professor of chemistry and pharmacy in the Karolinska Institute. From 1845 Mosander was also a professor at and inspector for the Pharmaceutical Institute. Mosander was an assistant curator of the mineralogical collections of the Swedish Museum of Natu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bastnäsite
The mineral bastnäsite (or bastnaesite) is one of a family of three carbonate-fluoride minerals, which includes bastnäsite-( Ce) with a formula of (Ce, La)CO3F, bastnäsite-( La) with a formula of (La, Ce)CO3F, and bastnäsite-( Y) with a formula of (Y, Ce)CO3F. Some of the bastnäsites contain OH− instead of F− and receive the name of hydroxylbastnasite. Most bastnäsite is bastnäsite-(Ce), and cerium is by far the most common of the rare earths in this class of minerals. Bastnäsite and the phosphate mineral monazite are the two largest sources of cerium and other rare-earth elements. Bastnäsite was first described by the Swedish chemist Wilhelm Hisinger in 1838. It is named for the Bastnäs mine near Riddarhyttan, Västmanland, Sweden. Bastnäsite also occurs as very high-quality specimens at the Zagi Mountains, Pakistan. Bastnäsite occurs in alkali granite and syenite and in associated pegmatites. It also occurs in carbonatites and in associated fenites and ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rare Earth Element
The rare-earth elements (REE), also called the rare-earth metals or (in context) rare-earth oxides or sometimes the lanthanides (yttrium and scandium are usually included as rare earths), are a set of 17 nearly-indistinguishable lustrous silvery-white soft heavy metals. Compounds containing rare earths have diverse applications in electrical and electronic components, lasers, glass, magnetic materials, and industrial processes. Scandium and yttrium are considered rare-earth elements because they tend to occur in the same ore deposits as the lanthanides and exhibit similar chemical properties, but have different electronic and magnetic properties. These metals tarnish slowly in air at room temperature and react slowly with cold water to form hydroxides, liberating hydrogen. They react with steam to form oxides, and at elevated temperature (400°C) ignite spontaneously. These elements and their compounds have no biological function other than in several specialized enzymes, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scintillator
A scintillator is a material that exhibits scintillation, the property of luminescence, when excited by ionizing radiation. Luminescent materials, when struck by an incoming particle, absorb its energy and scintillate (i.e. re-emit the absorbed energy in the form of light). Sometimes, the excited state is metastable, so the relaxation back down from the excited state to lower states is delayed (necessitating anywhere from a few nanoseconds to hours depending on the material). The process then corresponds to one of two phenomena: delayed fluorescence or phosphorescence. The correspondence depends on the type of transition and hence the wavelength of the emitted optical photon. Principle of operation A scintillation detector or scintillation counter is obtained when a scintillator is coupled to an electronic light sensor such as a photomultiplier tube (PMT), photodiode, or silicon photomultiplier. PMTs absorb the light emitted by the scintillator and re-emit it in the form of ele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monazite
Monazite is a primarily reddish-brown phosphate mineral that contains rare-earth elements. Due to variability in composition, monazite is considered a group of minerals. The most common species of the group is monazite-(Ce), that is, the cerium-dominant member of the group. It occurs usually in small isolated crystals. It has a hardness of 5.0 to 5.5 on the Mohs scale of mineral hardness and is relatively dense, about 4.6 to 5.7 g/cm3. There are five different most common species of monazite, depending on the relative amounts of the rare earth elements in the mineral: * monazite-(Ce), ( Ce, La, Nd, Th) PO4 (the most common member), * monazite-(La), (La,Ce,Nd)PO4, * monazite-(Nd), (Nd,La,Ce)PO4, * monazite-(Sm), ( Sm, Gd,Ce,Th)PO4, * monazite-(Pr), ( Pr,Ce,Nd,Th)PO4. The elements in parentheses are listed in the order of their relative proportion within the mineral: lanthanum is the most common rare-earth element in monazite-(La), and so forth. Silica (SiO2) is present in trace a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
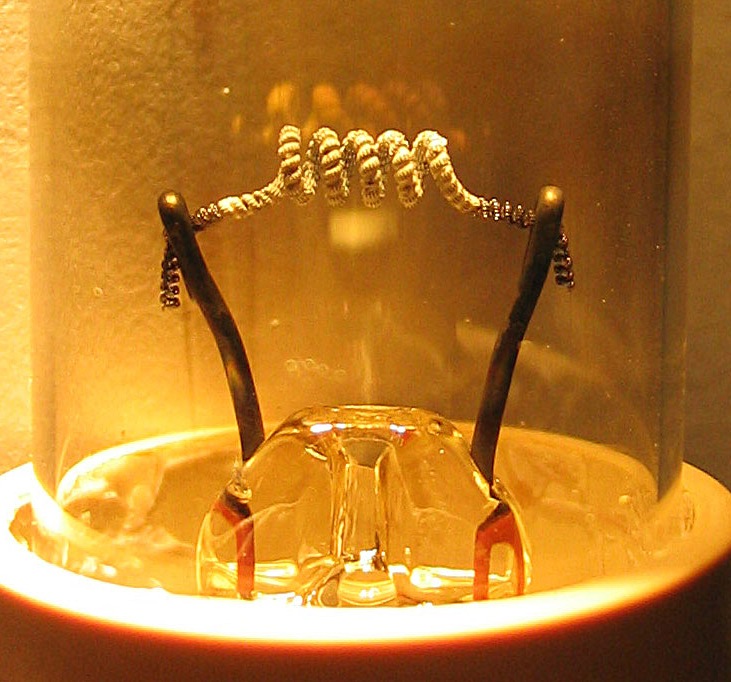
Hot Cathode
In vacuum tubes and gas-filled tubes, a hot cathode or thermionic cathode is a cathode electrode which is heated to make it emit electrons due to thermionic emission. This is in contrast to a cold cathode, which does not have a heating element. The heating element is usually an electrical filament heated by a separate electric current passing through it. Hot cathodes typically achieve much higher power density than cold cathodes, emitting significantly more electrons from the same surface area. Cold cathodes rely on field electron emission or secondary electron emission from positive ion bombardment, and do not require heating. There are two types of hot cathode. In a ''directly heated cathode'', the filament is the cathode and emits the electrons. In an ''indirectly heated cathode'', the filament or ''heater'' heats a separate metal cathode electrode which emits the electrons. From the 1920s to the 1960s, a wide variety of electronic devices used hot-cathode vacuum tubes. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphate Binder
Phosphate binders are medications used to reduce the absorption of dietary phosphate; they are taken along with meals and snacks. They are frequently used in people with chronic kidney failure (CKF), who are less able to excrete phosphate, resulting in an elevated serum phosphate. Mechanism of action These agents work by binding to phosphate in the GI tract, thereby making it unavailable to the body for absorption. Hence, these drugs are usually taken with meals to bind any phosphate that may be present in the ingested food. Phosphate binders may be simple molecular entities (such as magnesium, aluminium, calcium, or lanthanum salts) that react with phosphate and form an insoluble compound. Phosphate binders such as sevelamer may also be polymeric structures which bind to phosphate and are then excreted. Medical use For people with chronic kidney failure, controlling serum phosphate is important because it is associated with bone pathology and regulated together with serum calcium ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Element
A chemical element is a species of atoms that have a given number of protons in their nuclei, including the pure substance consisting only of that species. Unlike chemical compounds, chemical elements cannot be broken down into simpler substances by any chemical reaction. The number of protons in the nucleus is the defining property of an element, and is referred to as its atomic number (represented by the symbol ''Z'') – all atoms with the same atomic number are atoms of the same element. Almost all of the baryonic matter of the universe is composed of chemical elements (among rare exceptions are neutron stars). When different elements undergo chemical reactions, atoms are rearranged into new compounds held together by chemical bonds. Only a minority of elements, such as silver and gold, are found uncombined as relatively pure native element minerals. Nearly all other naturally occurring elements occur in the Earth as compounds or mixtures. Air is primarily a mixture o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






%2C_black_and_white.png)