|
Cerium
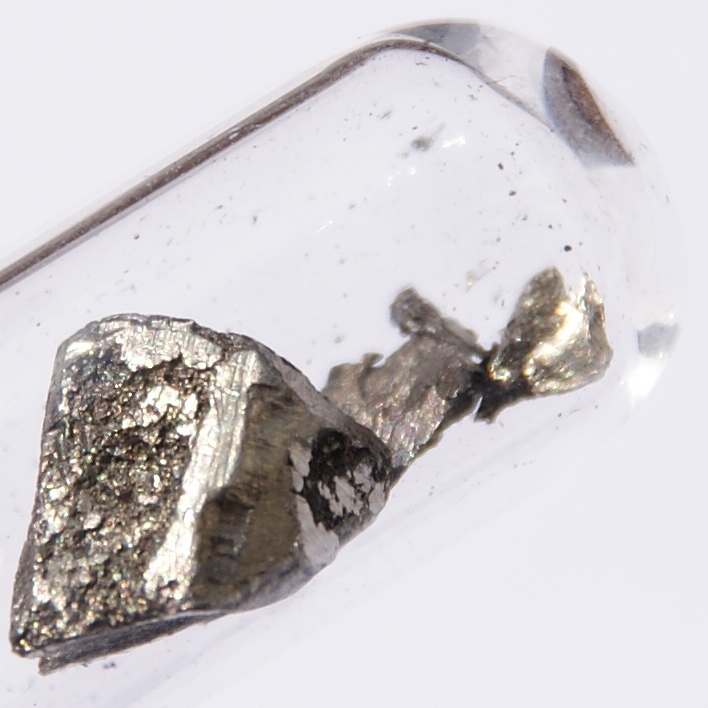
Cerium is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol Ce and atomic number 58. It is a hardness, soft, ductile, and silvery-white metal that tarnishes when exposed to air. Cerium is the second element in the lanthanide series, and while it often shows the oxidation state of +3 characteristic of the series, it also has a stable +4 state that does not oxidize water. It is considered one of the rare-earth elements. Cerium has no known biological role in humans but is not particularly toxic, except with intense or continued exposure. Despite always occurring in combination with the other rare-earth elements in minerals such as those of the monazite and bastnäsite groups, cerium is easy to extract from its ores, as it can be distinguished among the lanthanides by its unique ability to be oxidized to the +4 state in aqueous solution. It is the most common of the lanthanides, followed by neodymium, lanthanum, and praseodymium. Its estimated abundance of elements in Earth's crust, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lanthanide
The lanthanide () or lanthanoid () series of chemical elements comprises at least the 14 metallic chemical elements with atomic numbers 57–70, from lanthanum through ytterbium. In the periodic table, they fill the 4f orbitals. Lutetium (element 71) is also sometimes considered a lanthanide, despite being a d-block element and a transition metal. The informal chemical symbol Ln is used in general discussions of lanthanide chemistry to refer to any lanthanide. All but one of the lanthanides are f-block elements, corresponding to the filling of the 4f electron shell. Lutetium is a d-block element (thus also a transition metal), and on this basis its inclusion has been questioned; however, like its congeners scandium and yttrium in group 3, it behaves similarly to the other 14. The term rare-earth element or rare-earth metal is often used to include the stable group 3 elements Sc, Y, and Lu in addition to the 4f elements. All lanthanide elements form trivalent cations, Ln3+, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rare-earth Element
The rare-earth elements (REE), also called the rare-earth metals or rare earths, and sometimes the lanthanides or lanthanoids (although scandium and yttrium, which do not belong to this series, are usually included as rare earths), are a set of 17 nearly indistinguishable lustrous silvery-white soft heavy metals. Compounds containing rare earths have diverse applications in electrical and electronic components, lasers, glass, magnetic materials, and industrial processes. The term "rare-earth" is a misnomer because they are not actually scarce, but historically it took a long time to isolate these elements. They are relatively plentiful in the entire Earth's crust (cerium being the 25th-most-abundant element at 68 parts per million, more abundant than copper), but in practice they are spread thinly as trace impurities, so to obtain rare earths at usable purity requires processing enormous amounts of raw ore at great expense; thus the name "rare" earths. Scandium and yttrium are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferrocerium
Ferrocerium (also known in Europe as Auermetall) is a synthetic pyrophoric alloy of mischmetal (cerium, lanthanum, neodymium, other trace lanthanides and some iron – about 95% lanthanides and 5% iron) hardened by blending in oxides of iron and/or magnesium. When struck with a harder material, friction produces hot fragments that oxidize rapidly when exposed to the oxygen in the air, producing sparks that can reach temperatures of . The effect is due to the low ignition temperature of cerium, between . Ferrocerium has many commercial applications, such as the ignition source for lighters, strikers for gas welding and cutting torches, deoxidization in metallurgy, and ferrocerium rods. Because of ferrocerium's ability to ignite in adverse conditions, rods of ferrocerium (also called ferro rods, spark rods, and flint-spark-lighters) are commonly used as an emergency firelighting device in survival kits. The ferrocerium is referred to as a "flint" in this case, as bot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerium(IV) Oxide
Cerium(IV) oxide, also known as ceric oxide, ceric dioxide, ceria, cerium oxide or cerium dioxide, is an oxide of the rare-earth metal cerium. It is a pale yellow-white powder with the chemical formula CeO2. It is an important commercial product and an intermediate in the purification of the element from the ores. The distinctive property of this material is its reversible conversion to a Non-stoichiometric compound, non-stoichiometric oxide. Production Cerium occurs naturally as oxides, always as a mixture with other rare-earth elements. Its principal ores are bastnaesite and monazite. After extraction of the metal ions into aqueous base, Ce is separated from that mixture by addition of an oxidant followed by adjustment of the pH. This step exploits the low solubility of CeO2 and the fact that other rare-earth elements resist oxidation.. Cerium(IV) oxide is formed by the calcination of cerium oxalate or cerium hydroxide. Cerium also forms cerium(III) oxide, , which is unst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thorium
Thorium is a chemical element; it has symbol Th and atomic number 90. Thorium is a weakly radioactive light silver metal which tarnishes olive grey when it is exposed to air, forming thorium dioxide; it is moderately soft, malleable, and has a high melting point. Thorium is an electropositive actinide whose chemistry is dominated by the +4 oxidation state; it is quite reactive and can ignite in air when finely divided. All known thorium isotopes are unstable. The most stable isotope, 232Th, has a half-life of 14.05 billion years, or about the age of the universe; it decays very slowly via alpha decay, starting a decay chain named the thorium series that ends at stable 208 Pb. On Earth, thorium and uranium are the only elements with no stable or nearly-stable isotopes that still occur naturally in large quantities as primordial elements. Thorium is estimated to be over three times as abundant as uranium in the Earth's crust, and is chiefly refined from monazite sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Praseodymium
Praseodymium is a chemical element; it has symbol Pr and atomic number 59. It is the third member of the lanthanide series and is considered one of the rare-earth metals. It is a soft, silvery, malleable and ductile metal, valued for its magnetic, electrical, chemical, and optical properties. It is too reactive to be found in native form, and pure praseodymium metal slowly develops a green oxide coating when exposed to air. Praseodymium always occurs naturally together with the other rare-earth metals. It is the sixth-most abundant rare-earth element and fourth-most abundant lanthanide, making up 9.1 parts per million of the Earth's crust, an abundance similar to that of boron. In 1841, Swedish chemist Carl Gustav Mosander extracted a rare-earth oxide residue he called didymium from a residue he called "lanthana", in turn separated from cerium salts. In 1885, the Austrian chemist Carl Auer von Welsbach separated didymium into two elements that gave salts of different colours, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lanthanum
Lanthanum is a chemical element; it has symbol La and atomic number 57. It is a soft, ductile, silvery-white metal that tarnishes slowly when exposed to air. It is the eponym of the lanthanide series, a group of 15 similar elements between lanthanum and lutetium in the periodic table, of which lanthanum is the first and the prototype. Lanthanum is traditionally counted among the rare earth elements. Like most other rare earth elements, its usual oxidation state is +3, although some compounds are known with an oxidation state of +2. Lanthanum has no biological role in humans but is used by some bacteria. It is not particularly toxic to humans but does show some antimicrobial activity. Lanthanum usually occurs together with cerium and the other rare earth elements. Lanthanum was first found by the Swedish chemist Carl Gustaf Mosander in 1839 as an impurity in cerium nitrate – hence the name ''lanthanum'', from the ancient Greek (), meaning 'to lie hidden'. Although ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bastnäsite
The mineral bastnäsite (or bastnaesite) is one of a family of three fluorocarbonate minerals, which includes bastnäsite-(cerium, Ce) with a formula of (Ce, La)CO3F, bastnäsite-(lanthanum, La) with a formula of (La, Ce)CO3F, and bastnäsite-(yttrium, Y) with a formula of (Y, Ce)CO3F. Some of the bastnäsites contain OH− instead of F− and receive the name of hydroxylbastnasite. Most bastnäsite is bastnäsite-(Ce), and cerium is by far the most common of the rare earths in this class of minerals. Bastnäsite and the phosphate mineral monazite are the two largest sources of cerium and other rare-earth elements. Bastnäsite was first described by the Swedish chemist Wilhelm Hisinger in 1838. It is named for the Bastnäs mine near Riddarhyttan, Västmanland, Sweden. Bastnäsite also occurs as very high-quality specimens at the Zagi Mountains, Pakistan. Bastnäsite occurs in alkali granite and syenite and in associated pegmatites. It also occurs in carbonatites and in ass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
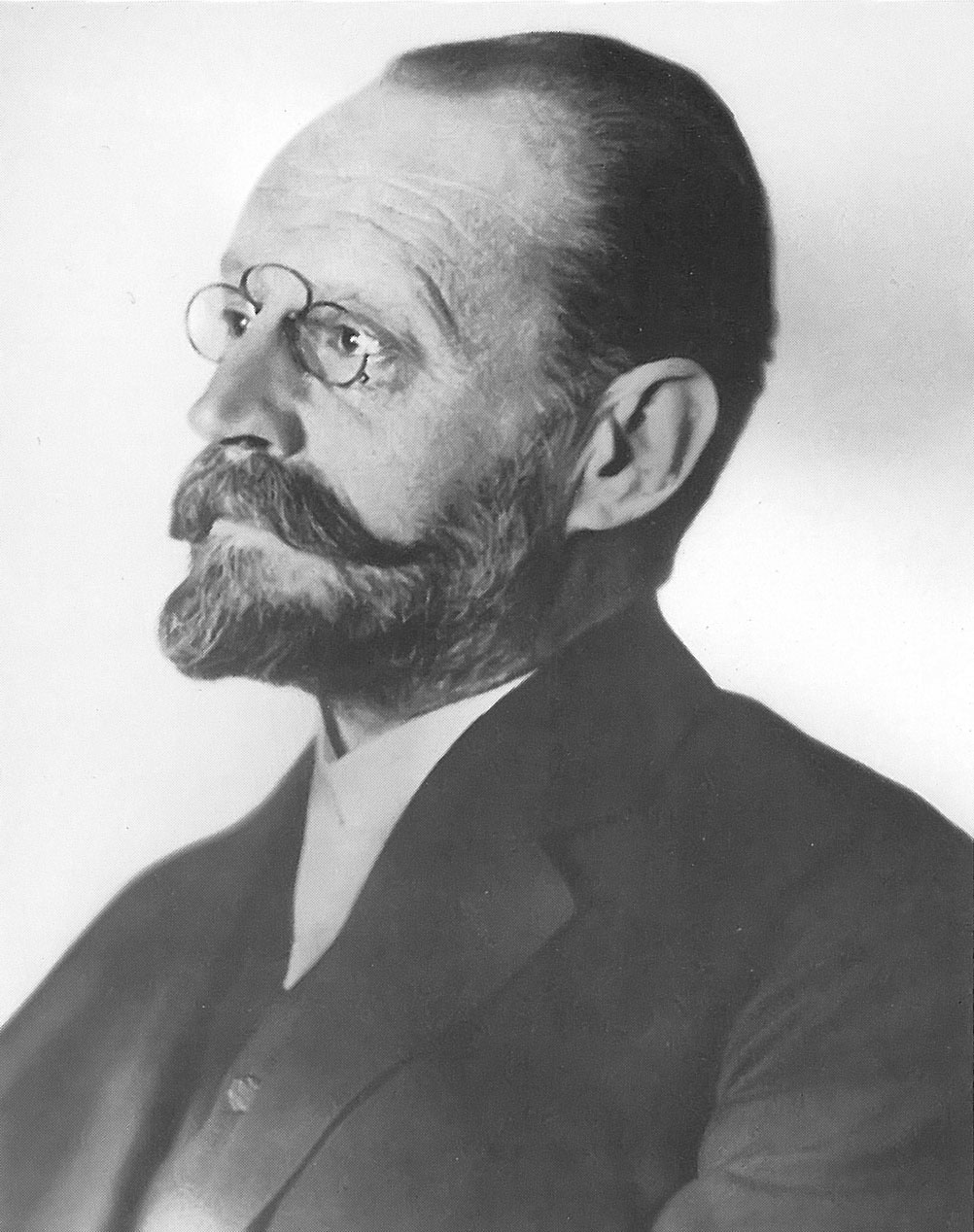
Wilhelm Hisinger
Wilhelm Hisinger (23 December 1766 – 28 June 1852) was a Swedish physicist and chemist who in 1807, working in coordination with Jöns Jakob Berzelius, noted that in electrolysis any given substance always went to the same pole, and that substances attracted to the same pole had other properties in common. This showed that there was at least a qualitative correlation between the chemical and electrical natures of bodies. Career In 1803, in separate laboratories, Martin Heinrich Klaproth in one, and Berzelius and Hisinger in another, the element Cerium was discovered, which was named after the newly discovered asteroid, Ceres. It was discovered nearly simultaneously by both laboratories, though it was later shown that Berzelius and Hisinger's cerium was actually a mixture of cerium, lanthanum and so-called didymium. The element was first isolated by Carl Gustaf Mosander in 1838. Hisinger was elected a member of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences in 1804. Death and leg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neodymium
Neodymium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Nd and atomic number 60. It is the fourth member of the lanthanide series and is considered to be one of the rare-earth element, rare-earth metals. It is a hard (physics), hard, slightly malleable, silvery metal that quickly tarnishes in air and moisture. When oxidized, neodymium reacts quickly producing pink, purple/blue and yellow compounds in the +2, +3 and +4 oxidation states. It is generally regarded as having one of the most complex emission spectrum, spectra of the elements. Neodymium was discovered in 1885 by the Austrian chemist Carl Auer von Welsbach, who also discovered praseodymium. Neodymium is present in significant quantities in the minerals monazite and bastnäsite. Neodymium is not found naturally in metallic form or unmixed with other lanthanides, and it is usually refined for general use. Neodymium is fairly common—about as common as cobalt, nickel, or copper—and is Abundance of elements in Eart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monazite
Monazite is a primarily reddish-brown phosphate mineral that contains rare-earth elements. Due to variability in composition, monazite is considered a group of minerals. The most common species of the group is monazite-(Ce), that is, the cerium-dominant member of the group. It occurs usually in small isolated crystals. It has a hardness of 5.0 to 5.5 on the Mohs scale of mineral hardness and is relatively dense, about 4.6 to 5.7 g/cm3. There are five different most common species of monazite, depending on the relative amounts of the rare earth elements in the mineral: * monazite-(Ce), (the most common member), * monazite-(La), , * monazite-(Nd), , * monazite-(Sm), , * monazite-(Pr), . The elements in parentheses are listed in the order of their relative proportion within the mineral: lanthanum is the most common rare-earth element in monazite-(La), and so forth. Silica () is present in trace amounts, as well as small amounts of uranium and thorium. Due to the alpha decay o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bastnäs
Bastnäs ( or ) is an ore field near Riddarhyttan, Västmanland, Sweden. The mines in Bastnäs were earliest mentioned in 1692. Iron, copper and rare-earth elements were extracted from the mines and 4,500 tons of cerium was produced between 1875 and 1888. The chemical element cerium was first discovered in Bastnäs in 1803 by Jöns Jakob Berzelius and Wilhelm Hisinger in the form of its oxide, ceria, and independently in Germany by Martin Heinrich Klaproth. Lanthanum was also first discovered in minerals from Bastnäs in 1839 by Carl Gustav Mosander. The mineral bastnäsite The mineral bastnäsite (or bastnaesite) is one of a family of three fluorocarbonate minerals, which includes bastnäsite-(cerium, Ce) with a formula of (Ce, La)CO3F, bastnäsite-(lanthanum, La) with a formula of (La, Ce)CO3F, and bastnäsite-(yt ... is named after Bastnäs. Gallery File:Bastnas maskinhus.jpg, Transmission house at Bastnäs mines File:Bastnas hakspel.jpg, Mechanism for hauling ore at Bastn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |