|
Ramesses VI
Ramesses VI Nebmaatre-Meryamun (sometimes written Ramses or Rameses, also known under his princely name of Amenherkhepshef C) was the fifth ruler of the Twentieth Dynasty of Egypt. He reigned for about eight years in the mid-to-late 12th century BC and was a son of Ramesses III and queen Iset Ta-Hemdjert. As a prince, he was known as Ramesses Amunherkhepeshef and held the titles of royal scribe and cavalry general. He was succeeded by his son, Ramesses VII Itamun, whom he had fathered with queen Nubkhesbed. After the death of the ruling pharaoh, Ramesses V, who was the son of Ramesses VI's older brother, Ramesses IV, Ramesses VI ascended the throne. In the first two years after his coronation, Ramesses VI stopped frequent raids by Libyan or Egyptian marauders in Upper Egypt and buried his predecessor in what is now an unknown tomb of the Theban necropolis. Ramesses VI usurped KV9, a tomb in the Valley of the Kings planned by and for Ramesses V, and had it enlarged and redecor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twentieth Dynasty Of Egypt
The Twentieth Dynasty of Egypt (notated Dynasty XX, alternatively 20th Dynasty or Dynasty 20) is the third and last dynasty of the Ancient Egyptian New Kingdom period, lasting from 1189 BC to 1077 BC. The 19th and 20th Dynasties furthermore together constitute an era known as the ''Ramesside period''. This dynasty is generally considered to be the start of the decline of Ancient Egypt. History Background Upon the death of the last pharaoh of the 19th Dynasty, Queen Twosret, Egypt descended into a period of civil war, as attested by the Elephantine stela built by Setnakhte. The circumstances of Twosret's demise are uncertain, as she may have died peacefully during her reign or been overthrown by Setnakhte, who was likely already middle aged at the time. 20th Dynasty A consistent theme of this dynasty was the loss of pharaonic power to the High Priests of Amun. Horemheb, a pharaoh of the 18th Dynasty, had restored the traditional Ancient Egyptian religion and the priesthood ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Museum
The British Museum is a public museum dedicated to human history, art and culture located in the Bloomsbury area of London. Its permanent collection of eight million works is among the largest and most comprehensive in existence. It documents the story of human culture from its beginnings to the present.Among the national museums in London, sculpture and decorative and applied art are in the Victoria and Albert Museum; the British Museum houses earlier art, non-Western art, prints and drawings. The National Gallery holds the national collection of Western European art to about 1900, while art of the 20th century on is at Tate Modern. Tate Britain holds British Art from 1500 onwards. Books, manuscripts and many works on paper are in the British Library. There are significant overlaps between the coverage of the various collections. The British Museum was the first public national museum to cover all fields of knowledge. The museum was established in 1753, largely b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
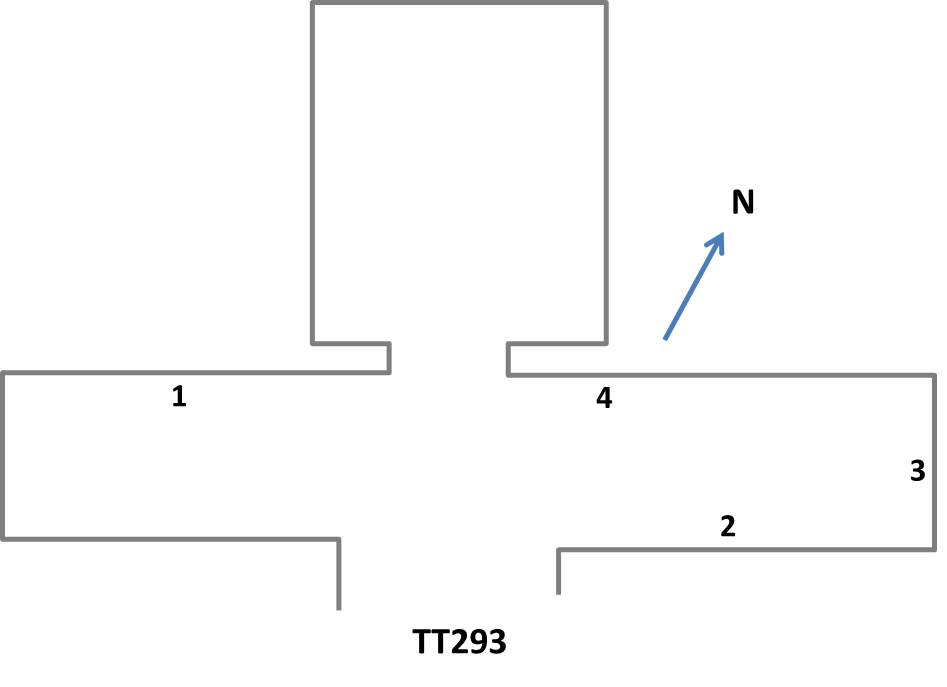
Amun-her-khepeshef (20th Dynasty)
Amun-her-khepeshef (also Amun-her-khepeshef B) was the eldest son and appointed heir of Pharaoh Ramesses III. Like at least another of his brothers, he was named after a son of Ramesses II, Amun-her-khepeshef. , p.192 He died when he was about fifteen years old.Alberto Siliotti: Guide to the Valley of the Kings. Barnes and Noble (1997). He is also mentioned as ''Ramesses Amun-her- khepeshef.'' He is not identical with his brother Ramesses VI, who was also called Amun-her-khepeshef before he became pharaoh. He is depicted in his father's temple at Medinet Habu. His well preserved tomb, QV55 (in the Valley of the Queens The Valley of the Queens ( ar, وادي الملكات ) is a site in Egypt, where the wives of pharaohs were buried in ancient times. It was known then as Ta-Set-Neferu, meaning "the place of beauty". It was most famous for being the burial site ...) was excavated by Italian archaeologists in 1903–1904. Sources Ancient Egyptian princes Ramesses III P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KV35
Tomb KV35 is the tomb of Pharaoh Amenhotep II located in the Valley of the Kings in Luxor, Egypt. Later, it was used as a cache for other royal mummies. It was discovered by Victor Loret in March 1898. Layout and history It has a dog's leg shape, typical of the layout of early Eighteenth Dynasty tombs, but several features make this tomb stand out. The burial chamber is rectangular and divided into upper and lower pillared sections, with the lower part holding the sarcophagus of the king. This style of burial chamber became standard for royal burials in the later New Kingdom. Later the tomb was used as a mummy cache. Mummies belonging to the following individuals were relocated here during the Third Intermediate Period and were identified by inscriptions on their burial wrappings: * Amenhotep II (the original tomb owner found in his original sarcophagus) Side Chamber: * Thutmose IV * Amenhotep III * Merneptah * Seti II * Siptah * Ramesses IV * Ramesses V * Ramesses VI * Queen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Egypt
Lower Egypt ( ar, مصر السفلى '; ) is the northernmost region of Egypt, which consists of the fertile Nile Delta between Upper Egypt and the Mediterranean Sea, from El Aiyat, south of modern-day Cairo, and Dahshur. Historically, the Nile River split into seven branches of the delta in Lower Egypt. Lower Egypt was divided into nomes and began to advance as a civilization after 3600 BC. Today, it contains two major channels that flow through the delta of the Nile River – Mahmoudiyah Canal (ancient Agathos Daimon) and Muways Canal (, "waterway of Moses"). Name In Ancient Egyptian, Lower Egypt was as ''mḥw'' and means ''"north"''. Later on, during Antiquity and the Middle Ages, Greeks and Romans called it ''Κάτω Αἴγυπτος'' or ''Aegyptus Inferior'' both meaning "Lower Egypt", but Copts carried on using the old name related to the north – ''Tsakhet'' () or ''Psanemhit'' () meaning the "Northern part". It was further divided into number of regio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pi-Ramesses
Pi-Ramesses (; Ancient Egyptian: , meaning "House of Ramesses") was the new capital built by the Nineteenth Dynasty Pharaoh Ramesses II (1279–1213 BC) at Qantir, near the old site of Avaris. The city had served as a summer palace under Seti I (c. 1290–1279 BC), and may have been founded by Ramesses I (c. 1292–1290 BC) while he served under Horemheb. Discovery In 1884, Flinders Petrie arrived in Egypt to begin his excavations there. His first dig was at Tanis, where he arrived with 170 workmen. Later in the 1930s, the ruins at Tanis were explored by Pierre Montet. The masses of broken Ramesside stonework at Tanis led archaeologists to identify it as Pi-Ramesses. Yet it eventually came to be recognised that none of these monuments and inscriptions originated at the site. In the 1960s, Manfred Bietak recognised that Pi-Ramesses was known to have been located on the then-easternmost branch of the Nile. He painstakingly mapped all the branches of the ancient Delta and establ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ramessesnakht
Ramessesnakht was High Priest of Amun during many years in the 20th Dynasty. He was appointed as the High Priest at Thebes under Ramesses IV. He served in office until the reign of Ramesses IX. It was during Ramessesnakht's tenure that the power and importance of the Amun priesthood grew over Egypt while the Pharaoh's power began to noticeably decline. Biography He was the son of Meribastet, steward to the pharaoh. Ramessesnakht was married to Adjedet-Aat, the daughter of Setau, High Priest of Nekhbet, and had at least two sons: Amenhotep and Nesamun and a daughter Tamerit. His son Amenhotep would succeed him in office and there is evidence that, at least for a while, his son, the Second Prophet of Amun Nesamun also acted as High Priest of Amun. His daughter Tamerit married Amenemopet, Third Prophet of Amun, making the family related through marriage to another important priestly family, that of Bakenkhonsu who served as High Priest of Amun under Ramesses II. (Amenemopet w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Priests Of Amun
The High Priest of Amun or First Prophet of Amun ('' ḥm nṯr tpj n jmn'') was the highest-ranking priest in the priesthood of the ancient Egyptian god Amun. The first high priests of Amun appear in the New Kingdom of Egypt, at the beginning of the Eighteenth Dynasty. History The priesthood of Amun rose in power during the early Eighteenth dynasty through significant tributes to the god Amun by ruler such as Hatshepsut and more importantly Thutmose III. The Amun priesthood in Thebes had four high-ranking priests: * The Chief Prophet of Amun at Karnak (''ḥm nṯr tpj n jmn''), also referred to as the Chief Priest of Amun. * The Second Prophet of Amun at Karnak (''ḥm nṯr snnw n jmn''), also referred to as the Second Priest of Amun. * The Third Prophet of Amun at Karnak (''ḥm nṯr ḫmtnw n jmn khemet-nu''), also referred to as the Third Priest of Amun. * The Fourth Prophet of Amun at Karnak (''ḥm nṯr jfdw n jmn''), also referred to as the Fourth Priest of Amun. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
God's Wife Of Amun
God's Wife of Amun (Egyptian: ''ḥm.t nṯr n ỉmn'') was the highest-ranking priestess of the Amun cult, an important religious institution in ancient Egypt. The cult was centered in Thebes in Upper Egypt during the Twenty-fifth and Twenty-sixth dynasties (circa 740–525 BC). The office had political importance as well as religious, since the two were closely related in ancient Egypt. Although the title is first attested in the Middle Kingdom, its full political potential was not realized until the advent of the Eighteenth Dynasty. History of the office nTr-N41:X1 The shorter version of the title, God's Wife, is in use by the time of the Twelfth Dynasty, when the title is attested for the non-royal women Iy-meret-nebes and Neferu.Mariam F. Ayad (2009), ''God’s Wife, God’s Servant''. As early as the First Intermediate Period, there is mention of A "Wife of the God" in reference to the god Min. The full title of God's Wife of Amun is only used during and after the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nubia
Nubia () (Nobiin: Nobīn, ) is a region along the Nile river encompassing the area between the first cataract of the Nile (just south of Aswan in southern Egypt) and the confluence of the Blue and White Niles (in Khartoum in central Sudan), or more strictly, Al Dabbah. It was the seat of one of the earliest civilizations of ancient Africa, the Kerma culture, which lasted from around 2500 BC until its conquest by the New Kingdom of Egypt under Pharaoh Thutmose I around 1500 BC, whose heirs ruled most of Nubia for the next 400 years. Nubia was home to several empires, most prominently the Kingdom of Kush, which conquered Egypt in the eighth century BC during the reign of Piye and ruled the country as its 25th Dynasty (to be replaced a century later by the native Egyptian 26th Dynasty). From the 3rd century BC to 3rd century AD, northern Nubia would be invaded and annexed to Egypt, ruled by the Greeks and Romans. This territory would be known in the Greco-Roman world as Dodekasc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canaan
Canaan (; Phoenician: 𐤊𐤍𐤏𐤍 – ; he, כְּנַעַן – , in pausa – ; grc-bib, Χανααν – ;The current scholarly edition of the Greek Old Testament spells the word without any accents, cf. Septuaginta : id est Vetus Testamentum graece iuxta LXX interpretes. 2. ed. / recogn. et emendavit Robert Hanhart. Stuttgart : Dt. Bibelges., 2006 . However, in modern Greek the accentuation is , while the current (28th) scholarly edition of the New Testament has . ar, كَنْعَانُ – ) was a Semitic-speaking civilization and region in the Ancient Near East during the late 2nd millennium BC. Canaan had significant geopolitical importance in the Late Bronze Age Amarna Period (14th century BC) as the area where the spheres of interest of the Egyptian, Hittite, Mitanni and Assyrian Empires converged or overlapped. Much of present-day knowledge about Canaan stems from archaeological excavation in this area at sites such as Tel Hazor, Tel Megiddo, En Esur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valley Of The Queens
The Valley of the Queens ( ar, وادي الملكات ) is a site in Egypt, where the wives of pharaohs were buried in ancient times. It was known then as Ta-Set-Neferu, meaning "the place of beauty". It was most famous for being the burial site of many wives of Pharaohs. Pharaohs themselves were buried in the Valley of the Kings. Using the limits described by Christian Leblanc, the Valley of the Queens consists of the main wadi, which contains most of the tombs, along with the Valley of Prince Ahmose, the Valley of the Rope, the Valley of the Three Pits, and the Valley of the Dolmen. The main wadi contains 91 tombs and the subsidiary valleys add another 19 tombs. The burials in the subsidiary valleys all date to the 18th Dynasty. The reason for choosing the Valley of the Queens as a burial site is not known. The close proximity to the workers' village of Deir el-Medina and the Valley of the Kings may have been a factor. Another consideration could have been the existence of a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |