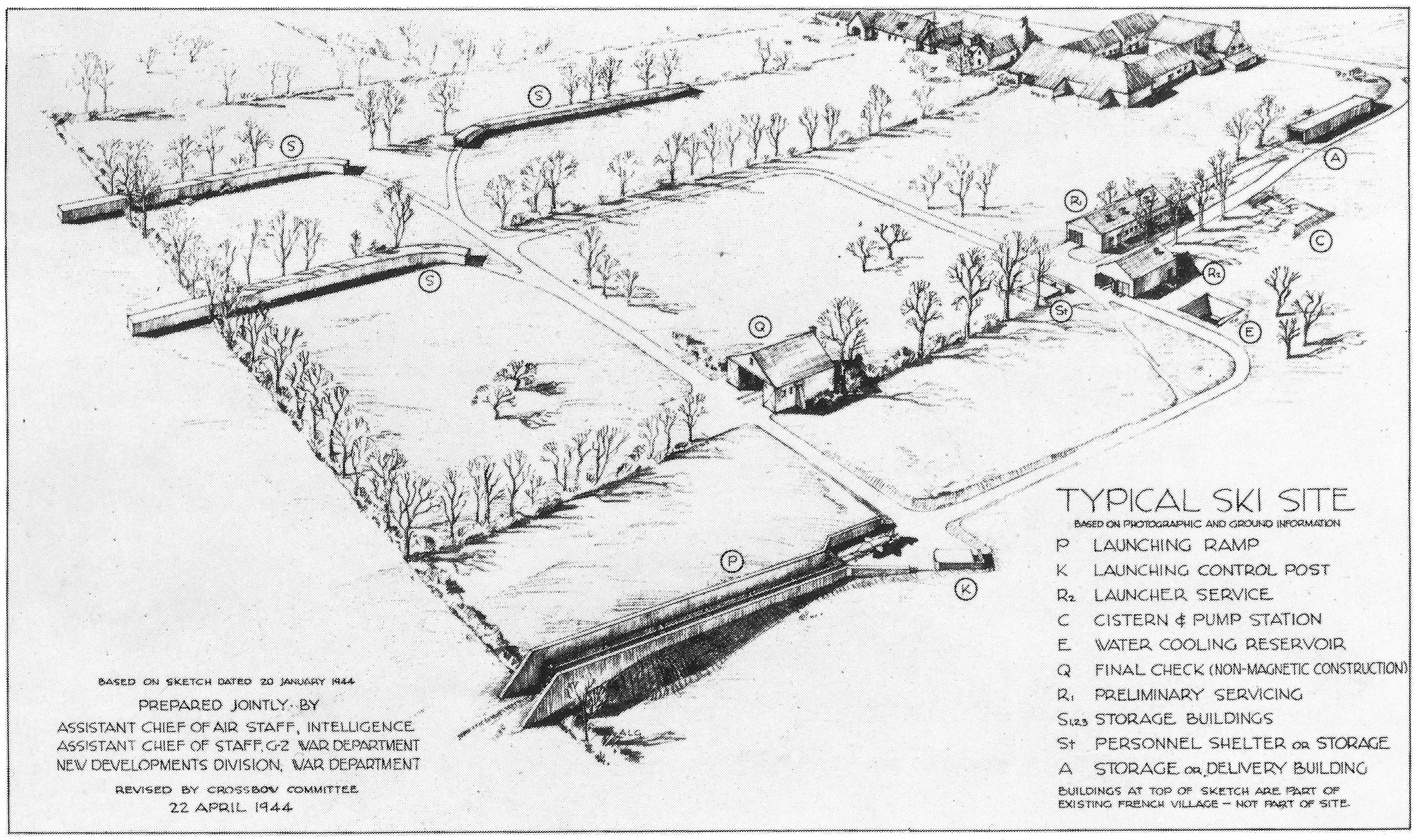
|
Réseau AGIR
The Réseau AGIR () was a World War II espionage group founded by French wartime resister Michel Hollard that provided decisive human intelligence on V-1 flying bomb facilities in the North of France. Thanks to Hollard's reports and information from his agents of the Réseau AGIR, the V1 launch sites located across North-Eastern Normandy to the Strait of Dover, were systematically bombed during Operation Crossbow. Creation and organisation The Réseau AGIR was created by Michel Hollard in 1941. The espionage network had no contact with other French resistance groups and reported directly to the British Secret Intelligence Service (S.I.S.). During the war, the network was codenamed "''Z 165''" after the codename given to Hollard himself by the ''Intelligence Service''. ''AGIR'' or ''Réseau AGIR'' only emerged after Hollard's return from the Liberation of France. Early 1941, Hollard became the concessionaire for the Seine department for the "Maison ''Gazogène Autobloc''" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Occupied France
The Military Administration in France (; ) was an interim occupation authority established by Nazi Germany during World War II to administer the occupied zone in areas of northern and western France. This so-called ' was established in June 1940, and renamed ' ("north zone") in November 1942, when the previously unoccupied zone in the south known as ' ("free zone") was also occupied and renamed ' ("south zone"). Its role in France was partly governed by the conditions set by the Armistice of 22 June 1940 after the success of the leading to the Fall of France; at the time both French and Germans thought the occupation would be temporary and last only until Britain came to terms, which was believed to be imminent. For instance, France agreed that its soldiers would remain prisoners of war until the cessation of all hostilities. The "French State" (') replaced the French Third Republic that had dissolved in defeat. Though nominally extending its sovereignty over the whole cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Military Administration In Occupied France During World War II
The Military Administration in France (; ) was an Military Administration (Nazi Germany), interim occupation authority established by Nazi Germany during World War II to administer the occupied zone in areas of northern and western French Third Republic, France. This so-called ' was established in June 1940, and renamed ' ("north zone") in November 1942, when the previously unoccupied zone in the south known as ' ("free zone") was also occupied and renamed ' ("south zone"). Its role in France was partly governed by the conditions set by the Armistice of 22 June 1940 after the success of the leading to the Battle of France, Fall of France; at the time both French and Germans thought the occupation would be temporary and last only until Britain came to terms, which was believed to be imminent. For instance, France agreed that its French prisoners of war in World War II, soldiers would remain prisoners of war until the cessation of all hostilities. The "French State" (') replace ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milice
The (French Militia), generally called (; ), was a political paramilitary organization created on 30 January 1943 by the Vichy France, Vichy régime (with Nazi Germany, German aid) to help fight against the French Resistance during World War II. The Milice's formal head was Vichy France's Prime Minister Pierre Laval (in office 1942 to 1944), although its chief of operations and ''de facto'' leader was Secretary General Joseph Darnand. The participated in summary executions and assassinations, helping to round up Jews and in France for deportation. It was the successor to Darnand's (SOL) militia (founded in 1941). The was the Vichy régime's most extreme manifestation of fascism. Ultimately, Darnand envisaged the as a fascist One-party state, single-party political movement for the État Français , French State. members frequently used torture to extract information or confessions from those whom they interrogated. The French Resistance considered the more dangerous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gestapo
The (, ), Syllabic abbreviation, abbreviated Gestapo (), was the official secret police of Nazi Germany and in German-occupied Europe. The force was created by Hermann Göring in 1933 by combining the various political police agencies of Free State of Prussia, Prussia into one organisation. On 20 April 1934, oversight of the Gestapo passed to the head of the ''Schutzstaffel'' (SS), Heinrich Himmler, who was also appointed Chief of German Police by Hitler in 1936. Instead of being exclusively a Prussian state agency, the Gestapo became a national one as a sub-office of the (SiPo; Security Police). From 27 September 1939, it was administered by the Reich Security Main Office (RSHA). It became known as (Dept) 4 of the RSHA and was considered a sister organisation to the (SD; Security Service). The Gestapo committed widespread atrocities during its existence. The power of the Gestapo was used to focus upon political opponents, ideological dissenters (clergy and religious org ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waterboarding
Waterboarding is a form of torture in which water is poured over a cloth covering the face and breathing passages of an immobilized captive, causing the person to experience the sensation of drowning. In the most common method of waterboarding, the captive's face is covered with cloth or some other thin material and immobilized on their back at an incline of 10 to 20 degrees. Torturers pour water onto the face over the breathing passages, causing an almost immediate gag reflex and creating a drowning sensation for the captive. Normally, water is poured intermittently to prevent death; however, if the water is poured uninterruptedly it will lead to death by asphyxia. Waterboarding can cause extreme pain, damage to lungs, brain damage from oxygen deprivation, other physical injuries including broken bones due to struggling against restraints, and lasting psychological damage. Adverse physical effects can last for months, and psychological effects for years. The term "water ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rue Du Faubourg-Saint-Denis
The Rue du Faubourg-Saint-Denis () is a street in the 10th arrondissement of Paris. It crosses the arrondissement from north to south, linking the Porte Saint-Denis to La Chapelle Métro station and passing the Gare du Nord. History The Rue du Faubourg-Saint-Denis owes its name to the fact that it is an extension of the Rue Saint-Denis to the faubourg or area outside Paris's walls (as marked today by the Porte Saint-Denis). It also marked the eastern boundary of the enclos (later prison) Saint-Lazare. Historically, this street was an extremely upper-class area, occupied by jewellers and textile merchants, since it was part of the King's processional route to the Basilica of Saint-Denis. After the French Revolution, the street briefly bore the name 'Rue du Faubourg Franciade' in 1793 (with the portion between the Rue Saint-Laurent and the Place de la Chapelle being renamed the Rue du Faubourg Saint-Lazare and the Rue du Faubourg de Gloire). Length * From the to the Boule ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lausanne
Lausanne ( , ; ; ) is the capital and largest List of towns in Switzerland, city of the Swiss French-speaking Cantons of Switzerland, canton of Vaud, in Switzerland. It is a hilly city situated on the shores of Lake Geneva, about halfway between the Jura Mountains and the Alps, and facing the French town of Évian-les-Bains across the lake. Lausanne is located (as the crow flies) northeast of Geneva, the nearest major city. The Federal Supreme Court of Switzerland convenes in Lausanne, although it is not the ''de jure'' capital of the nation. The municipality of Lausanne has a population of about 140,000, making it the List of cities in Switzerland, fourth largest city in Switzerland after Basel, Geneva, and Zurich, with the entire agglomeration area having about 420,000 inhabitants (as of January 2019). The metropolitan area of Lausanne-Geneva (including Vevey-Montreux, Yverdon-les-Bains, Valais and foreign parts), commonly designated as ''Lake Geneva region, Arc lémanique ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Attaché
A military attaché or defence attaché (DA),Defence Attachés ''Geneva Centre for the Democratic Control of Armed Forces (DCAF)'' sometimes known as a "military diplomat",Prout, John. THE ORIGINS OF THE MILITARY ATTACHÉ CORPS " ''American Intelligence Journal'' 21, no. 1/2 (2002): 47–55. is an responsible for matters within a [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
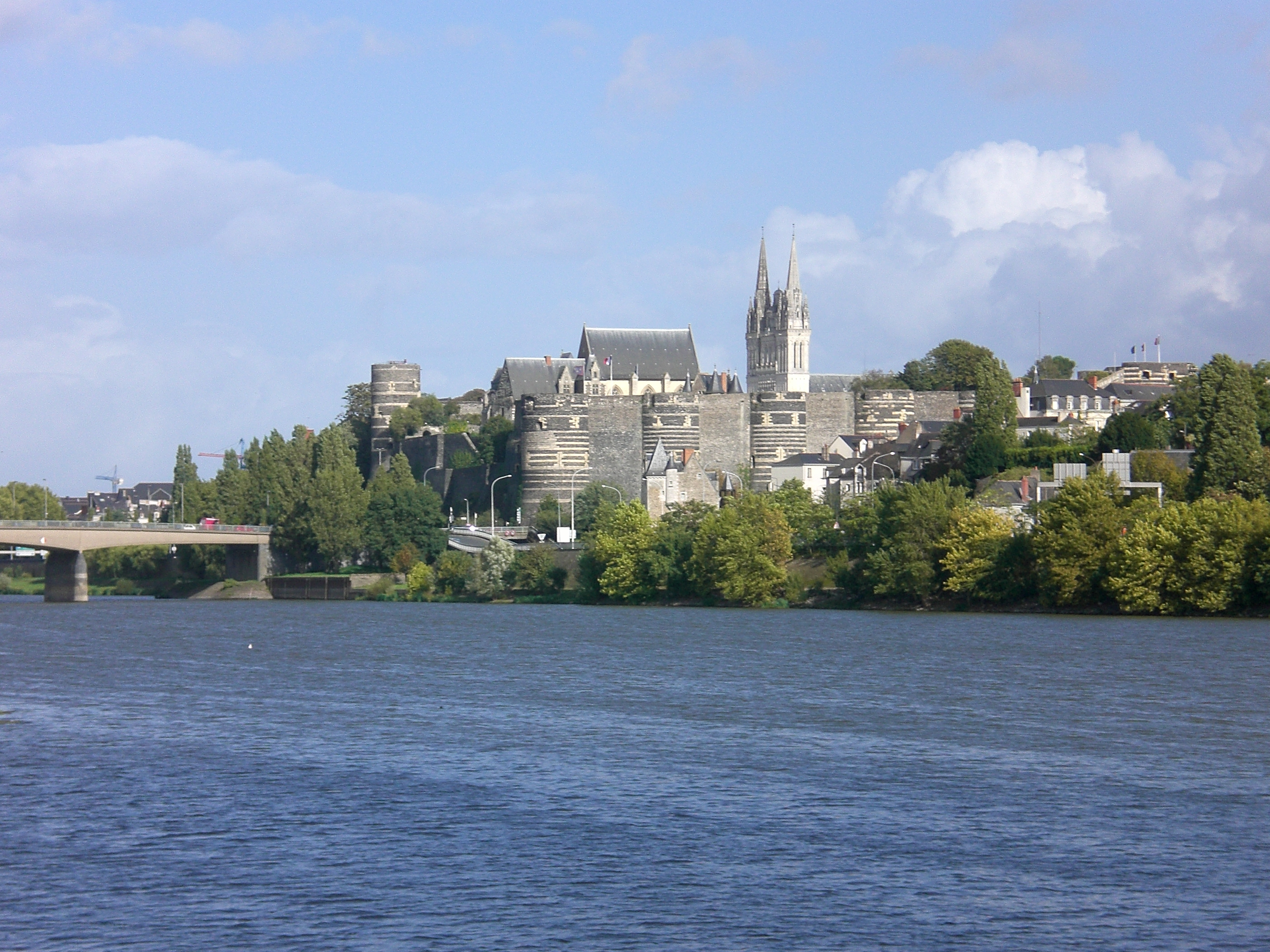
Angers
Angers (, , ;) is a city in western France, about southwest of Paris. It is the Prefectures of France, prefecture of the Maine-et-Loire department and was the capital of the province of Duchy of Anjou, Anjou until the French Revolution. The inhabitants of both the city and the province are called ''Angevins'' or, more rarely, ''Angeriens''. Angers proper covers and has a population of 154,508 inhabitants, while around 432,900 live in its metropolitan area (''aire d'attraction''). The Communauté urbaine Angers Loire Métropole, Angers Loire Métropole is made up of 29 communes covering with 299,500 inhabitants (2018).Comparateur de territoire INSEE Not including the broader metropolitan area, Angers is the third most populous Communes of France, commune in northwes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Domestic Worker
A domestic worker is a person who works within a residence and performs a variety of household services for an individual, from providing cleaning and household maintenance, or cooking, laundry and ironing, or care for children and elderly dependents, and other household errands. The term "domestic service" applies to the equivalent occupational category. In traditional English contexts, such a person was said to be "in service". Some domestic workers live within their employer's household. In some cases, the contribution and skill of servants whose work encompassed complex management tasks in large households have been highly valued. However, for the most part, domestic work tends to be demanding and is commonly considered to be undervalued, despite often being necessary. Although legislation protecting domestic workers is in place in many countries, it is often not extensively enforced. In many jurisdictions, domestic work is poorly regulated and domestic workers are subje ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zone Libre
The ''zone libre'' (, ''free zone'') was a partition of the French metropolitan territory during World War II, established at the Second Armistice at Compiègne on 22 June 1940. It lay to the south of the demarcation line and was administered by the French government of Philippe Pétain based in Vichy, in a relatively unrestricted fashion. To the north lay the ''zone occupée'' (" occupied zone"), in which the powers of Vichy France were severely limited. In November 1942, the ''zone libre'' was invaded by the German and Italian armies in Case Anton, as a response to Operation Torch, the Allied landings in North Africa. Thenceforth, the ''zone libre'' and ''zone occupée'' were renamed the ''zone sud'' (southern zone) and ''zone nord'' (northern zone) respectively. From then on both were under German military administration. Origins of the ''zone libre'' On 22 June 1940, after the Battle of France, Wilhelm Keitel, representing Nazi Germany, and Charles Huntziger, represen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |