|
Russian Sign Language
Russian Sign Language (RSL) is the sign language used by the Deaf community in Russia and possibly Ukraine, Belarus and Tajikistan. It belongs to the French Sign Language family. RSL is a natural language with a grammar that differs from spoken or written Russian language. Signed Russian is an artificial form of communication used in schools and differs from RSL in strictly following Russian grammar. Although RSL is legally recognized in Russia, it does not enjoy state support and there is a lack of skilled RSL interpreters in the country. History In 1806, the first Russian deaf school was founded near St. Petersburg. It is believed that RSL belongs to the French sign language family due to the fact that the first two sign language teachers were from France and Austria. Researchers do not know for sure if RSL is used outside of Russia; it may also be used in Ukraine, Belarus or Tajikistan. Much of the early research on RSL was done by Galina Lazarevna Zaitseva, who wrote h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eighth of Earth's inhabitable landmass. Russia extends across eleven time zones and shares land boundaries with fourteen countries, more than any other country but China. It is the world's ninth-most populous country and Europe's most populous country, with a population of 146 million people. The country's capital and largest city is Moscow, the largest city entirely within Europe. Saint Petersburg is Russia's cultural centre and second-largest city. Other major urban areas include Novosibirsk, Yekaterinburg, Nizhny Novgorod, and Kazan. The East Slavs emerged as a recognisable group in Europe between the 3rd and 8th centuries CE. Kievan Rus' arose as a state in the 9th century, and in 988, it adopted Orthodox Christianity from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
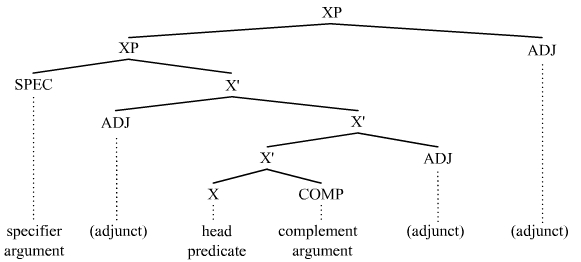
Object (grammar)
In linguistics, an object is any of several types of arguments. In subject-prominent, nominative-accusative languages such as English, a transitive verb typically distinguishes between its subject and any of its objects, which can include but are not limited to direct objects, indirect objects, and arguments of adpositions ( prepositions or postpositions); the latter are more accurately termed ''oblique arguments'', thus including other arguments not covered by core grammatical roles, such as those governed by case morphology (as in languages such as Latin) or relational nouns (as is typical for members of the Mesoamerican Linguistic Area). In ergative-absolutive languages, for example most Australian Aboriginal languages, the term "subject" is ambiguous, and thus the term " agent" is often used instead to contrast with "object", such that basic word order is often spoken of in terms such as Agent-Object-Verb (AOV) instead of Subject-Object-Verb (SOV). Topic-prominent l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classifier Constructions In Sign Languages
In sign languages, the term classifier construction (also known as classifier predicates) refers to a morphological system that can express events and states. They use handshape classifiers to represent movement, location, and shape. Classifiers differ from signs in their morphology, namely in that signs consist of a single morpheme. Signs are composed of three meaningless phonological features: handshape, location, and movement. Classifiers, on the other hand, consist of many morphemes. Specifically, the handshape, location, and movement are all meaningful on their own. The handshape represents an entity and the hand's movement iconically represents the movement of that entity. The relative location of multiple entities can be represented iconically in two-handed constructions. Classifiers share some limited similarities with the gestures of hearing non-signers. Those who do not know the sign language can often guess the meaning of these constructions. This is because they are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linguistic Typology
Linguistic typology (or language typology) is a field of linguistics that studies and classifies languages according to their structural features to allow their comparison. Its aim is to describe and explain the structural diversity and the common properties of the world's languages. Its subdisciplines include, but are not limited to phonological typology, which deals with sound features; syntactic typology, which deals with word order and form; lexical typology, which deals with language vocabulary; and theoretical typology, which aims to explain the universal tendencies. Linguistic typology is contrasted with genealogical linguistics on the grounds that typology groups languages or their grammatical features based on formal similarities rather than historic descendence. The issue of genealogical relation is however relevant to typology because modern data sets aim to be representative and unbiased. Samples are collected evenly from different language families, emphasizing t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Causative Alternation
In linguistics, causative alternation is a phenomenon in which certain verbs that express a change of state (or a change of degree) can be used transitively or intransitively.Levin, Beth. "Causative Alternation". ''English Verb Classes and Alternations''. Chicago: University Press of Chicago, 1993. 26–27. Print.Schäfer, Florian. 2009. "The Causative Alternation". Language and Linguistics Compass 3.2: 641. Print. A causatively alternating verb, called a labile or ergative verb, such as "open", has both a transitive meaning ("I opened the door") and an intransitive meaning ("The door opened"). When causatively alternating verbs are used transitively they are called causatives since, in the transitive use of the verb, the subject is ''causing'' the action denoted by the intransitive version. When causatively alternating verbs are used intransitively, they are referred to as anticausatives or inchoatives because the intransitive variant describes a situation in which the ''theme' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reciprocal Construction
A reciprocal construction (abbreviated ) is a grammatical pattern in which each of the participants occupies both the role of agent and patient with respect to the other. An example is the English sentence ''John and Mary criticized each other'': John criticized Mary, and Mary criticized John. Reciprocal constructions can be said to express mutual relationships. Many languages, such as Semitic languages, Altaic languages or Bantu languages, have special reciprocal affixes in verbs. Other languages, including English, use reciprocal pronouns such as ''"each other"'' to indicate a mutual relation. Latin uses the preposition ''inter'' and its reflexive pronoun ''inter se'' (between themselves) when the verb is third person. Most Indo-European languages do not have special reciprocal affixes on verbs, and mutual relations are expressed through reflexive constructions or other mechanisms. For example, Russian reciprocal constructions have the suffix -sja (-ся, 'self'), which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Impersonal Passive Voice
The impersonal passive voice is a verb voice that decreases the valency of an intransitive verb (which has valency one) to zero. Dixon, R. M. W. & Alexandra Aikhenvald (1997). "A Typology of Argument-Determined Constructions". In Bybee, Joan, John Haiman, & Sandra A. Thompson (eds.) ''Essays on Language Function and Language Type: Dedicated to T. Givón''. Amsterdam: John Benjamins, 71–112. The impersonal passive deletes the subject of an intransitive verb. In place of the verb's subject, the construction instead may include a syntactic placeholder, also called a '' dummy''. This placeholder has neither thematic nor referential content. (A similar example is the word "there" in the English phrase "There are three books.") In some languages, the deleted argument can be reintroduced as an '' oblique argument'' or ''complement''. Test of unergative verbs In most languages that allow impersonal passives, only unergative verbs may undergo impersonal passivization. Unaccusative ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valency (linguistics)
In linguistics, valency or valence is the number and type of arguments controlled by a predicate, content verbs being typical predicates. Valency is related, though not identical, to subcategorization and transitivity, which count only object arguments – valency counts all arguments, including the subject. The linguistic meaning of valency derives from the definition of valency in chemistry. The valency metaphor appeared first in linguistics in Charles Sanders Peirce's essay "The Logic of Relatives" in 1897, and it then surfaced in the works of a number of linguists decades later in the late 1940s and 1950s. Lucien Tesnière is credited most with having established the valency concept in linguistics. A major authority on the valency of the English verbs is Allerton (1982), who made the important distinction between semantic and syntactic valency. Types There are several types of valency: #impersonal (= avalent) ''it rains'' #intransitive (monovalent/monadic) '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argument (linguistics)
In linguistics, an argument is an expression that helps complete the meaning of a predicate, the latter referring in this context to a main verb and its auxiliaries. In this regard, the '' complement'' is a closely related concept. Most predicates take one, two, or three arguments. A predicate and its arguments form a ''predicate-argument structure''. The discussion of predicates and arguments is associated most with (content) verbs and noun phrases (NPs), although other syntactic categories can also be construed as predicates and as arguments. Arguments must be distinguished from adjuncts. While a predicate needs its arguments to complete its meaning, the adjuncts that appear with a predicate are optional; they are not necessary to complete the meaning of the predicate. Most theories of syntax and semantics acknowledge arguments and adjuncts, although the terminology varies, and the distinction is generally believed to exist in all languages. Dependency grammars sometimes call ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Definiteness
In linguistics, definiteness is a semantic feature of noun phrases, distinguishing between referents or senses that are identifiable in a given context (definite noun phrases) and those which are not (indefinite noun phrases). The prototypical definite noun phrase picks out a unique, familiar, specific referent such as ''the sun'' or ''Australia'', as opposed to indefinite examples like ''an idea'' or ''some fish''. There is considerable variation in the expression of definiteness across languages, and some languages such as Japanese do not generally mark it so that the same expression could be definite in some contexts and indefinite in others. In other languages, such as English, it is usually marked by the selection of determiner (e.g., ''the'' vs ''a''). In still other languages, such as Danish, definiteness is marked morphologically. Definiteness as a grammatical category There are times when a grammatically marked definite NP is not in fact identifiable. For examp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demonstrative
Demonstratives (abbreviated ) are words, such as ''this'' and ''that'', used to indicate which entities are being referred to and to distinguish those entities from others. They are typically deictic; their meaning depending on a particular frame of reference and cannot be understood without context. Demonstratives are often used in spatial deixis (where the speaker or sometimes the listener are to provide context), but also in intra-discourse reference (including abstract concepts) or anaphora, where the meaning is dependent on something other than the relative physical location of the speaker, for example whether something is currently being said or was said earlier. Demonstrative constructions include demonstrative adjectives or demonstrative determiners, which qualify nouns (as in ''Put that coat on''); and demonstrative pronouns, which stand independently (as in ''Put that on''). The demonstratives in English are ''this'', ''that'', ''these'', ''those'', and the archaic ''yon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Determiner
A determiner, also called determinative ( abbreviated ), is a word, phrase, or affix that occurs together with a noun or noun phrase and generally serves to express the reference of that noun or noun phrase in the context. That is, a determiner may indicate whether the noun is referring to a definite or indefinite element of a class, to a closer or more distant element, to an element belonging to a specified person or thing, to a particular number or quantity, etc. Common kinds of determiners include definite and indefinite articles (''the'', ''a''), demonstratives (''this'', ''that''), possessive determiners (''my,'' ''their''), cardinal numerals (''one'', ''two''), quantifiers (''many'', ''both''), distributive determiners (''each'', ''every''), and interrogative determiners (''which'', ''what''). Description Most determiners have been traditionally classed either as adjectives or pronouns, and this still occurs in traditional grammars: for example, demonstrative and p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)