|
Roman Africa
Roman Africa may refer to the following areas of Northern Africa which were part of the Imperium Romanum and/or the Western/Byzantine successor empires : ; in the unified Roman empire : * Africa (Roman province), with the great metropolis Carthage ** later restricted to Africa Proconsularis (which would be split into Tripolitania, Africa Byzacena and Africa Zeugitana) after the detachment of Numidia * the whole of Roman North Africa, stretching from Egypt, with the greatest metropolis Alexandria, and Cyrenaica to the east of above Africa proper to the westernmost provinces in Mauretania ; later : * Diocese of Africa, from Diocletian's tetrarchy reform till the Vandal conquest, under the (Western) Praetorian prefecture of Italy * the early-Byzantine Praetorian prefecture of Africa * the later Byzantine Exarchate of Africa See also * Africa (other) Africa is the world's second largest continent. Africa may also refer to: Arts and entertainment Film and television * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in the west, to Egypt's Suez Canal. Varying sources limit it to the countries of Algeria, Libya, Morocco, and Tunisia, a region that was known by the French during colonial times as "''Afrique du Nord''" and is known by Arabs as the Maghreb ("West", ''The western part of Arab World''). The United Nations definition includes Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia, Libya, Egypt, Sudan, and the Western Sahara, the territory disputed between Morocco and the Sahrawi Republic. The African Union definition includes the Western Sahara and Mauritania but not Sudan. When used in the term Middle East and North Africa (MENA), it often refers only to the countries of the Maghreb. North Africa includes the Spanish cities of Ceuta and Melilla, and plazas de soberanía ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egypt (Roman Province)
, conventional_long_name = Roman Egypt , common_name = Egypt , subdivision = Roman province, Province , nation = the Roman Empire , era = Late antiquity , capital = Alexandria , title_leader = Praefectus Augustalis , image_map = Roman Empire - Aegyptus (125 AD).svg , image_map_caption = Province of Aegyptus in AD 125 , year_start = 30 BC , event_start = Conquest of Ptolemaic Kingdom , event1 = Formation of the Diocese of Egypt, Diocese , date_event1 = 390 , year_end = 641 , event_end = Muslim conquest of Egypt, Muslim conquest , life_span = 30 BC – 641 AD , stat_year1 = 1st century AD , stat_pop1 = . , today = Egypt , p1 = Ptolemaic Kingdom , flag_p1 = Ptolemaic-Empire 200bc.jpg , s1 = Sasanian Egypt , flag_s1 = Derafsh Kaviani flag of the late Sassanid Empire.svg , s2 = Rashidun Caliphate , flag_s2 = Mohammad adil-Rashidun-empire-at-its-peak-close.PNG , demon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Africa (other)
Africa is the world's second largest continent. Africa may also refer to: Arts and entertainment Film and television * ''Africa'' (1930 film), an American animated short featuring Oswald the Lucky Rabbit * ''África'' (film), 1996 Spanish film * ''Africa'' (2011 film), an Iranian crime drama * ''Africa'' (2019 film), an Israeli drama * ''Africa'' (1984 TV series), a Channel 4 documentary series * ''Africa'' (2013 TV series), a BBC documentary series Music Classical music * "Africa" (William Billings), an 18th-century hymn tune * "Africa", an 1891 fantasia by Camille Saint-Saëns * ''Africa'' (Still), a 1930 symphonic poem Albums * ''Africa'' (Miriam Makeba album), a 1991 compilation album * ''Africa'' (Perpetuum Jazzile album), 2009 * ''Africa'' (Pharoah Sanders album), 1987 Songs * "Africa" (Toto song), 1982, also covered by Weezer ** "Africa" (Karl Wolf song), 2007, based on the Toto song * "Africa" (Rose Laurens song), 1982, also released as "Africa (Voodoo Mas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
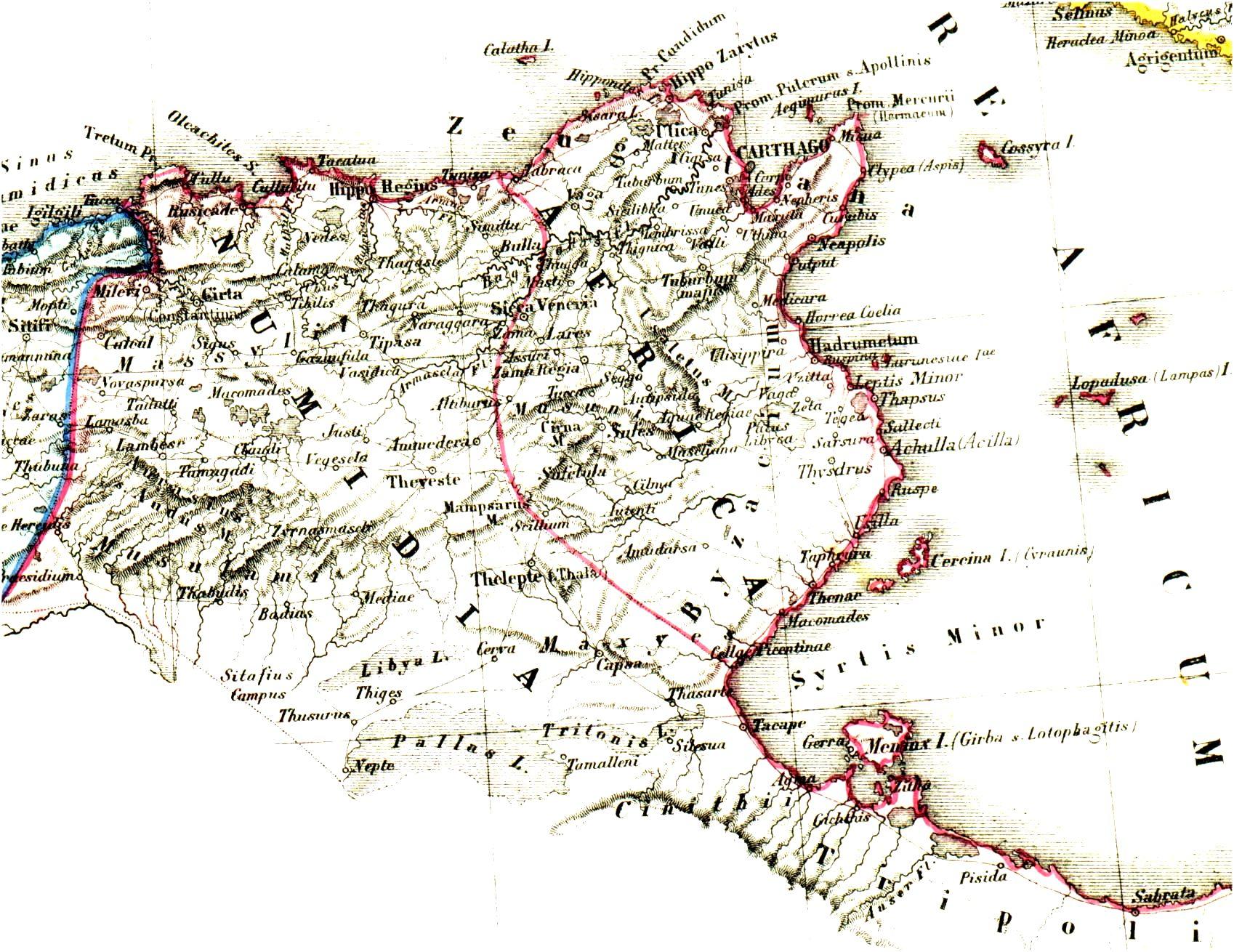
Exarchate Of Africa
The Exarchate of Africa was a division of the Byzantine Empire around Carthage that encompassed its possessions on the Western Mediterranean. Ruled by an exarch (viceroy), it was established by the Emperor Maurice in the late 580s and survived until the Muslim conquest of the Maghreb in the late 7th century. It was, along with the Exarchate of Ravenna, one of two exarchates established following the western reconquests under Emperor Justinian I to administer the territories more effectively. History Background In the Vandalic War of 533, Byzantine forces under Belisarius reconquered the Maghreb along with Corsica and Sardinia and the Balearic Islands. Emperor Justinian I () organized the recovered territories as the Praetorian prefecture of Africa, which included the provinces of Africa Proconsularis, Byzacena, Tripolitania, Numidia, Mauretania Caesariensis and Mauretania Sitifensis, and was centered at Carthage. In the 550s, a Roman expedition succeeded in regaining pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Praetorian Prefecture Of Africa
The praetorian prefecture of Africa ( la, praefectura praetorio Africae) was an administrative division of the Eastern Roman Empire in the Maghreb. With its seat at Carthage, it was established after the reconquest of northwestern Africa from the Vandals in 533–534 by the Byzantine Emperor Justinian I. It continued to exist until 591, when it was replaced by the Exarchate of Africa. History Establishment In 533, the Roman army under Belisarius defeated and destroyed the Vandal Kingdom that had existed in the former Roman territories of Northern Africa. Immediately after the victory, in April 534, the emperor Justinian published a law concerning the administrative organization of the recovered territories. The old provinces of the Roman Diocese of Africa had been mostly preserved by the Vandals, but large parts, including almost all of Mauretania Tingitana, much of Mauretania Caesariensis and Mauretania Sitifensis and large parts of the interior of Numidia and Byzacena, had be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diocese Of Africa
The Diocese of Africa ( la, Dioecesis Africae) was a diocese of the later Roman Empire, incorporating the provinces of North Africa, except Mauretania Tingitana. Its seat was at Carthage, and it was subordinate to the Praetorian prefecture of Italy. The diocese included the provinces of Africa proconsularis (also known as Zeugitana), Byzacena, Mauretania Sitifensis, Mauretania Caesariensis, Numidia Cirtensis, Numidia Militiana and Tripolitania. In current geo-political terms, the Diocese of Africa included the entire coastline of Tunisia, Algeria with some mountainous hinterlands, plus the western half of Libya's coastline. The diocese existed from the time of the Diocletianian and Constantinian reforms in the last years of the 3rd century until it was overrun by the Vandals in the 430s. The provincial organization were retained under the Vandals, and after their defeat and the reconquest of Africa by the Eastern Roman Empire in the Vandalic War, they were grouped anew, but th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mauretania
Mauretania (; ) is the Latin name for a region in the ancient Maghreb. It stretched from central present-day Algeria westwards to the Atlantic, covering northern present-day Morocco, and southward to the Atlas Mountains. Its native inhabitants, seminomadic pastoralists of Berber ancestry, were known to the Romans as the Mauri and the Masaesyli. In 25 BC, the kings of Mauretania became Roman vassals until about 44 AD, when the area was annexed to Rome and divided into two provinces: Mauretania Tingitana and Mauretania Caesariensis. Christianity spread there from the 3rd century onwards. After the Muslim Arabs subdued the region in the 7th century, Islam became the dominant religion. Moorish kingdom Mauretania existed as a tribal kingdom of the Berber Mauri people. In the early 1st century Strabo recorded ''Maûroi'' (Μαῦροι in greek) as the native name of a people opposite the Iberian Peninsula. This appellation was adopted into Latin, whereas the Greek name for t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crete And Cyrenaica
Crete and Cyrenaica ( la, Provincia Creta et Cyrenaica, Ancient Greek ) was a senatorial province of the Roman Republic and later the Roman Empire, established in 67 BC. It comprised the island of Crete and the region of Cyrenaica in present-day Libya. Apion's will and Roman rule of Cyrenaica Ptolemy Apion, the last king of the Hellenistic Kingdom of Cyrenaica left his kingdom to the Roman Republic when he died childless in 96 BC. Rome readily accepted this inheritance from Ptolemy Apion but preferred to leave the administration to local rulers, rather than enforcing direct control. However, by the 70s BC, civil uprisings by Jewish settlers began to destabilise the province and the Senate was forced to take action. In 74 BC, they sent a low level official, the quaestor Cornelius Lentulus Marcellinus, to officially annex Cyrenaica as a Roman province and restore order. That the Senate sent such a low-ranking official indicates the political difficulty the Republic had in governin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Numidia
Numidia ( Berber: ''Inumiden''; 202–40 BC) was the ancient kingdom of the Numidians located in northwest Africa, initially comprising the territory that now makes up modern-day Algeria, but later expanding across what is today known as Tunisia, Libya, and some parts of Morocco. The polity was originally divided between the Massylii in the east and the Masaesyli in the west. During the Second Punic War (218–201 BC), Masinissa, king of the Massylii, defeated Syphax of the Masaesyli to unify Numidia into one kingdom. The kingdom began as a sovereign state and later alternated between being a Roman province and a Roman client state. Numidia, at its largest extent, was bordered by Mauretania to the west, at the Moulouya River, Africa Proconsularis to the east, the Mediterranean Sea to the north, and the Sahara to the south. It was one of the first major states in the history of Algeria and the Berbers. History Independence The Greek historians referred to these peoples as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterranean Sea in Europe, North Africa, and Western Asia, and was ruled by emperors. From the accession of Caesar Augustus as the first Roman emperor to the military anarchy of the 3rd century, it was a Principate with Italia as the metropole of its provinces and the city of Rome as its sole capital. The Empire was later ruled by multiple emperors who shared control over the Western Roman Empire and the Eastern Roman Empire. The city of Rome remained the nominal capital of both parts until AD 476 when the imperial insignia were sent to Constantinople following the capture of the Western capital of Ravenna by the Germanic barbarians. The adoption of Christianity as the state church of the Roman Empire in AD 380 and the fall of the Western ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Africa Zeugitana
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area and 20% of its land area.Sayre, April Pulley (1999), ''Africa'', Twenty-First Century Books. . With billion people as of , it accounts for about of the world's human population. Africa's population is the youngest amongst all the continents; the median age in 2012 was 19.7, when the worldwide median age was 30.4. Despite a wide range of natural resources, Africa is the least wealthy continent per capita and second-least wealthy by total wealth, behind Oceania. Scholars have attributed this to different factors including geography, climate, tribalism, colonialism, the Cold War, neocolonialism, lack of democracy, and corruption. Despite this low concentration of wealth, recent economic expansion and the large and young population make Afric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Africa Byzacena
Byzacena (or Byzacium) ( grc, Βυζάκιον, ''Byzakion'') was a Late Roman province in the central part of Roman North Africa, which is now roughly Tunisia, split off from Africa Proconsularis. History At the end of the 3rd century AD, the Roman emperor Diocletian divided the great Roman province of Africa Proconsularis into three smaller provinces: Zeugitana in the north, still governed by a proconsul and referred to as Proconsularis; Byzacena to its adjacent south, and Tripolitania to its adjacent south, roughly corresponding to southeast Tunisia and northwest Libya. Byzacena corresponded roughly to eastern Tunisia or the modern Tunisian region of Sahel. Hadrumetum (modern Sousse) became the capital of the newly made province, whose governor had the rank of ''consularis''. At this period the Metropolitan Archbishopric of Byzacena was, after the great metropolis Carthage, the most important city in Roman (North) Africa west of Egypt and its Patriarch of Alexandria. Episc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)