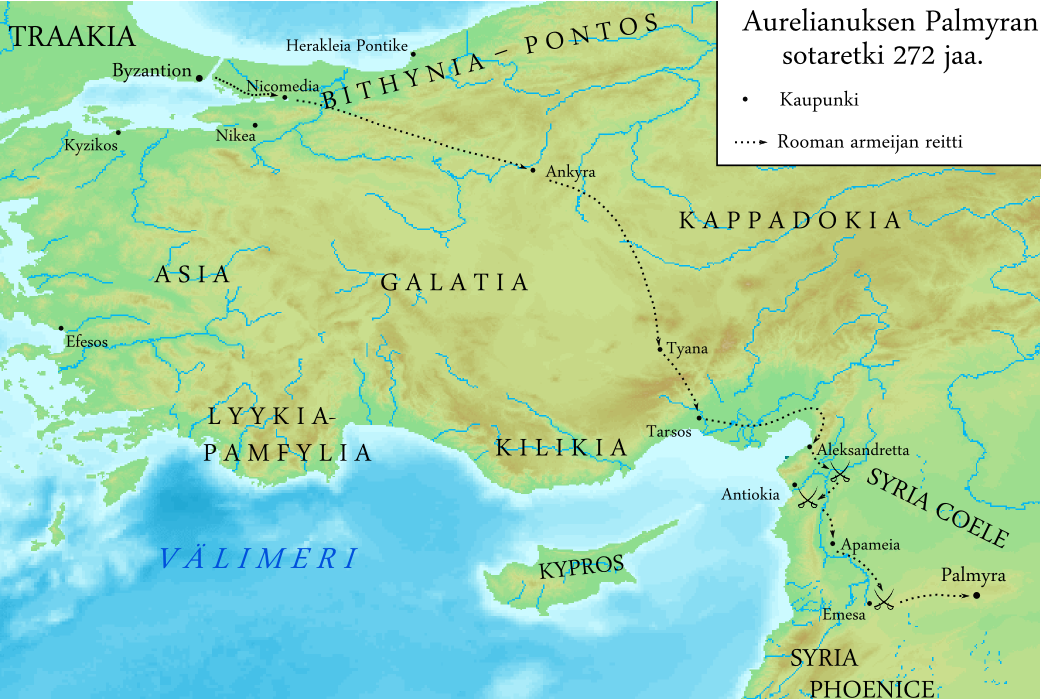
|
Rogiet Hoard
The Rogiet Hoard is a hoard of 3,778 Roman coins found at Rogiet, Monmouthshire, Wales in September 1998. The coins dated from 253 up until 295ŌĆō296. The hoard notably contained several faulty issues, and some rare denominations, including those depicting the usurper emperors Carausius and Allectus. Discovery and valuation The hoard was discovered by metal detectorist Colin Roberts on 10 September, 1998 and, after a coroner's inquest in December, 1998 was declared a treasure. It was valued at ┬Ż40,000 and is now owned by the National Museum and Galleries of Wales. Items discovered The hoard contained 3,778 silver radiates, including seven denarii, of which just over a third came from the reign of Probus (276ŌĆō282). The latest coin was struck around 295ŌĆō296. 766 of the coins were struck during the reigns of the usurper emperors, Carausius, and his eventual murderer and successor, Allectus. Coins from these reigns are infrequently found in hoards, and several of them d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romano-British
The Romano-British culture arose in Britain under the Roman Empire following the Roman conquest in AD 43 and the creation of the province of Britannia. It arose as a fusion of the imported Roman culture with that of the indigenous Britons, a people of Celtic language and custom. Scholars such as Christopher Snyder believe that during the 5th and 6th centuries ŌĆō approximately from 410 when the Roman legions withdrew, to 597 when St Augustine of Canterbury arrived ŌĆō southern Britain preserved an active sub-Roman culture that survived the attacks from the Anglo-Saxons and even used a vernacular Latin when writing. Arrival of the Romans Roman troops, mainly from nearby provinces, invaded in AD 43, in what is now part of England, during the reign of Emperor Claudius. Over the next few years the province of Britannia was formed, eventually including the whole of what later became England and Wales and parts of Scotland.Kinder, H. & Hilgemann W. ''The Penguin Atlas of World ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Denarius
The denarius (, d─ōn─üri─½ ) was the standard Roman silver coin from its introduction in the Second Punic War to the reign of Gordian III (AD 238ŌĆō244), when it was gradually replaced by the antoninianus. It continued to be minted in very small quantities, likely for ceremonial purposes, until and through the Tetrarchy (293ŌĆō313). The word ''d─ōn─ürius'' is derived from the Latin ''d─ōn─½'' "containing ten", as its value was originally of 10 ass─ōs.Its value was increased to 16 ass─ōs in the middle of the 2nd century BC. The word for "money" descends from it in Italian (''denaro''), Slovene (''denar''), Portuguese (''dinheiro''), and Spanish (''dinero''). Its name also survives in the dinar currency. Its symbol is represented in Unicode as Éå¢ (U+10196), a numeral monogram that appeared on the obverse in the Republican period, denoting the 10 asses ("X") to 1 denarius ("I") conversion rate. However it can also be represented as X╠Č (capital letter X with combining long ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Claudius II
Marcus Aurelius Claudius "Gothicus" (10 May 214 ŌĆō January/April 270), also known as Claudius II, was Roman emperor from 268 to 270. During his reign he fought successfully against the Alemanni and decisively defeated the Goths at the Battle of Naissus. He died after succumbing to a "pestilence", possibly the Plague of Cyprian that had ravaged the provinces of the Empire. Early life and origin The most significant source for Claudius II is the collection of imperial biographies called the ''Historia Augusta''. However, his story, like the rest of the ''Historia Augusta'', is riddled with fabrications and obsequious praises. In 4th century, Claudius was declared a relative of Constantine the Great's father, Constantius Chlorus, and, consequently, of the ruling dynasty. The ''Historia Augusta'' should be used with extreme caution and supplemented with information from other sources: the works of Aurelius Victor, Pseudo-Aurelius Victor, Eutropius, Orosius, Joannes Zonaras, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetricus II
Gaius Pius Esuvius Tetricus (also known as Tetricus II) was the son of Tetricus I, Emperor of the Gallic Empire (270/271-273/274). In 273, he was raised to the rank of ''Caesar'', with the title of ''princeps iuventutis'', and in January 274 he started his first consulship, together with his father. After the defeat and deposition of his father in the autumn of 274 by the Emperor Aurelian, he and his father appeared as prisoners in Aurelian's triumph, but the emperor spared their lives. According to some sources, Tetricus II also kept his senatorial rank.Aurelius Victor Sextus Aurelius Victor (c. 320 ŌĆō c. 390) was a historian and politician of the Roman Empire. Victor was the author of a short history of imperial Rome, entitled ''De Caesaribus'' and covering the period from Augustus to Constantius II. The work w ..., ''Liber de Caesaribus'', 35.5. References External links * Polfer, Michael, "Tetricus II (Caesar 273-274 AD)", ''De Imperatoribus Romanis'' {{DEFAULTSOR ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetricus I
Gaius Pius Esuvius Tetricus was the emperor of the Gallic Empire from 271 to 274 AD. He was originally the (governor) of Gallia Aquitania and became emperor after the murder of Emperor Victorinus in 271, with the support of Victorinus's mother, Victoria. During his reign, he faced external pressure from Germanic raiders, who pillaged the eastern and northern parts of his empire, and the Roman Empire, from which the Gallic Empire had seceded. He also faced increasing internal pressure, which led him to declare his son, Tetricus II, in 273 and possibly co-emperor in 274, although this is debated. The Roman emperor Aurelian invaded in 273 or 274, leading to the Battle of Châlons, at which Tetricus surrendered. Whether this capitulation was the result of a secret agreement between Tetricus and Aurelian or necessary after his defeat is debated. Aurelian spared Tetricus, and even made him a senator and (governor) of Lucania et Bruttium. Tetricus died of natural causes a few years a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victorinus
Marcus Piavonius VictorinusSome of the inscriptions record his name as M. Piavvonius Victorinus, as does the first release of coins from the Colonia mint. A mosaic from Augusta Treverorum (Trier) lists him as Piaonius. was emperor in the Gallic provinces from 268 to 270Martindale, p. 965 or 269 to 271,Polfer, ''Victorinus'' following the brief reign of Marius. He was murdered by a jealous husband whose wife he had tried to seduce. Reign Hailing from Gaul, Victorinus was born to a family of great wealth, and was a soldier under Postumus, the first of the so-called Gallic emperors. He showed considerable ability, as he held the title of tribunus praetorianorum (tribune of the praetorians) in 266/267, and rose swiftly to become co-consul with Postumus in 268.Southern, p. 118 It is also possible that Postumus then elevated him to the post of praetorian prefect.Potter, p. 266 Shortly after putting down a rebellion by Laelianus in 269, Postumus was murdered by his own troops, who a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Postumus
Marcus Cassianius Latinius Postumus was a Roman commander of Batavian origin, who ruled as Emperor of the splinter state of the Roman Empire known to modern historians as the Gallic Empire. The Roman army in Gaul threw off its allegiance to Gallienus around the year 260,The year of Postumus' accession was either 259 or 260. In the past, the year 259 was favoured; today, however, most scholars consider that the summer or fall of 260 is the more likely date that he was hailed emperor, according to and The ''terminus ante quem'' is an inscription from September 260 naming Postumus as emperor: Bakker (1993), pp. 369ŌĆō386. Other dates cited in this article must be pushed back one year for those who take 259 as the year of Postumus' accession. See . and Postumus assumed the title and powers of Emperor in the provinces of Gaul, Germania, Britannia and Hispania. He ruled for the better part of ten yearsBased on numismatic evidence, Postumus' rule extended over ten periods of tribun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallienus
Publius Licinius Egnatius Gallienus (; c. 218 ŌĆō September 268) was Roman emperor with his father Valerian from 253 to 260 and alone from 260 to 268. He ruled during the Crisis of the Third Century that nearly caused the collapse of the empire. He won numerous military victories against usurpers and Germanic tribes, but was unable to prevent the secession of important provinces. His 15-year reign was the longest in half a century. Born into a wealthy and traditional senatorial family, Gallienus was the son of Valerian and Mariniana. Valerian became Emperor in September 253 and had the Roman Senate elevate Gallienus to the ranks of ''Caesar'' and ''Augustus''. Valerian divided the empire between him and his son, with Valerian ruling the east and his son the west. Gallienus defeated the usurper Ingenuus in 258 and destroyed an Alemanni army at Mediolanum in 259. The defeat and capture of Valerian at Edessa in 260 by the Sasanian Empire threw the Roman Empire into the cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valerian (emperor)
Valerian (; la, Publius Licinius Valerianus; c. 199 ŌĆō 260 or 264) was Roman emperor from 253 to spring 260 AD. He persecuted Christians and was later taken captive by the Persian emperor Shapur I after the Battle of Edessa, becoming the first Roman emperor to be captured as a prisoner of war, causing shock and instability throughout the Roman Empire. The unprecedented event and the unknown fate of the captured emperor generated a variety of different reactions and "new narratives about the Roman Empire in diverse contexts". Biography Origins and rise to power Unlike many of the would-be emperors and rebels who vied for imperial power during the Crisis of the Third Century of the Roman Empire, Valerian was of a noble and traditional senatorial family. Details of his early life are sparse, except for his marriage to Egnatia Mariniana, with whom he had two sons: later emperor Publius Licinius Egnatius Gallienus and Licinius Valerianus. He was Consul for the first time either ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aurelian
Aurelian ( la, Lucius Domitius Aurelianus; 9 September 214 October 275) was a Roman emperor, who reigned during the Crisis of the Third Century, from 270 to 275. As emperor, he won an unprecedented series of military victories which reunited the Roman Empire after it had nearly disintegrated under the pressure of barbarian invasions and internal revolts. Born in humble circumstances, near the Danube River, he entered the Roman military in 235, and climbed up the ranks. He went on to lead the cavalry of the emperor Gallienus, until Gallienus' assassination in 268. Following that, Claudius Gothicus became emperor until his own death in 270. Claudius' brother Quintillus ruled the empire for three months, before Aurelian became emperor. During his reign, he defeated the Alamanni after a devastating war. He also defeated the Goths, Vandals, Juthungi, Sarmatians, and Carpi. Aurelian restored the Empire's eastern provinces after his conquest of the Palmyrene Empire in 273. The follow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quinarius
300px, A quinarius of 90 BC of L. Calpurnius Piso Frugi: Obv.: head of Roma right in a winged helmetq; V (asses) for quinarius. Rev.: Dioscuri riding right, stars above heads; ROMA below. The ''quinarius'' (plural: ''quinarii''Oxford English Dictionary, Webster's Third New International Dictionary of the English Language, Unabridged.) was a small silver Roman coin valued at half a denarius. The quinarius was struck for a few years, along with the silver sestertius, following the introduction of the denarius in 211 BC. At this time the quinarius was valued at 5 asses. The coin was reintroduced in 101 BC as a replacement for the victoriatus, this time valued at 8 asses due to retariffing of the denarius to 16 asses in 118 BC. For a few years following its reintroduction, large quantities of quinarii were produced, mostly for circulation in Gaul. The coin was produced sporadically until the 3rd century. Its symbol is ÉåŚ. The term ''gold quinarius'' or ''quinarius aureus'' is us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maximian
Maximian ( la, Marcus Aurelius Valerius Maximianus; c. 250 ŌĆō c. July 310), nicknamed ''Herculius'', was Roman emperor from 286 to 305. He was ''Caesar'' from 285 to 286, then ''Augustus'' from 286 to 305. He shared the latter title with his co-emperor and superior, Diocletian, whose political brain complemented Maximian's military brawn. Maximian established his residence at Trier but spent most of his time on campaign. In late 285, he suppressed rebels in Gaul known as the Bagaudae. From 285 to 288, he fought against Germanic tribes along the Rhine frontier. Together with Diocletian, he launched a scorched earth campaign deep into Alamannic territory in 288, refortifying the frontier. The man he appointed to police the Channel shores, Carausius, rebelled in 286, causing the secession of Britain and northwestern Gaul. Maximian failed to oust Carausius, and his invasion fleet was destroyed by storms in 289 or 290. Maximian's subordinate, Constantius, campaigned against Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






_obverse.jpg)