|
Robot
A robot is a machine—especially one Computer program, programmable by a computer—capable of carrying out a complex series of actions Automation, automatically. A robot can be guided by an external control device, or the robot control, control may be embedded within. Robots may be constructed to evoke Humanoid robot, human form, but most robots are task-performing machines, designed with an emphasis on stark functionality, rather than expressive aesthetics. Robots can be autonomous robot, autonomous or semi-autonomous and range from humanoids such as Honda's ''Advanced Step in Innovative Mobility'' (ASIMO) and TOSY's ''TOSY Ping Pong Playing Robot'' (TOPIO) to industrial robots, robot-assisted surgery, medical operating robots, patient assist robots, dog therapy robots, collectively programmed Swarm robotics, ''swarm'' robots, UAV drones such as General Atomics MQ-1 Predator, and even microscopic Nanorobotics, nanorobots. By mimicking a lifelike appearance or automating mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robotics
Robotics is the interdisciplinary study and practice of the design, construction, operation, and use of robots. Within mechanical engineering, robotics is the design and construction of the physical structures of robots, while in computer science, robotics focuses on robotic automation algorithms. Other disciplines contributing to robotics include electrical engineering, electrical, control engineering, control, software engineering, software, Information engineering (field), information, electronics, electronic, telecommunications engineering, telecommunication, computer engineering, computer, mechatronic, and materials engineering, materials engineering. The goal of most robotics is to design machines that can help and assist humans. Many robots are built to do jobs that are hazardous to people, such as finding survivors in unstable ruins, and exploring space, mines and shipwrecks. Others replace people in jobs that are boring, repetitive, or unpleasant, such as cleaning, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Humanoid Robot
A humanoid robot is a robot resembling the human body in shape. The design may be for functional purposes, such as interacting with human tools and environments and working alongside humans, for experimental purposes, such as the study of bipedal locomotion, or for other purposes. In general, humanoid robots have a torso, a head, two arms, and two legs, though some humanoid robots may replicate only part of the body. Androids are humanoid robots built to aesthetically resemble humans. History The concept of a humanoid robot originated in many different cultures around the world. Some of the earliest accounts of the idea of humanoid automata date to the 4th century BCE in Greek mythologies and various religious and philosophical texts from China. Physical prototypes of humanoid automata were later created in the Middle East, Italy, Japan, France and South Korea. Greece The Greek god of blacksmiths, Hephaestus, created several different humanoid automata in various myths. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robot-assisted Surgery
Robot-assisted surgery or robotic surgery are any types of surgical procedures that are performed using robotic systems. Robotically assisted surgery was developed to try to overcome the limitations of pre-existing minimally-invasive surgical procedures and to enhance the capabilities of surgeons performing open surgery. In the case of robotically assisted minimally-invasive surgery, instead of the surgeon directly moving the instruments, the surgeon uses one of two methods to perform dissection, hemostasis and resection, using a direct telemanipulator, or through computer control. * A telemanipulator (e.g. the da Vinci Surgical System) is a system of remotely controlled manipulators that allows the surgeon to operate real-time under stereoscopic vision from a control console separate from the operating table. The robot is docked next to the patient, and robotic arms carry out endoscopy-like maneuvers via end-effectors inserted through specially designed trocars. A surgica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
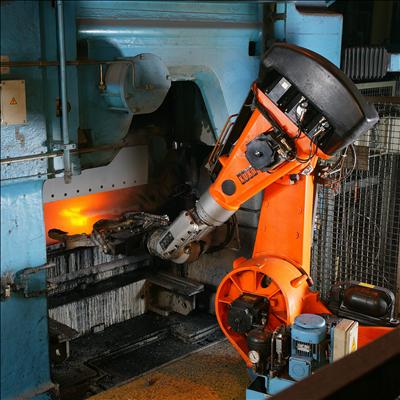
Industrial Robot
An industrial robot is a robot system used for manufacturing. Industrial robots are automated, programmable and capable of movement on three or more axes. Typical applications of robots include robot welding, welding, painting, assembly, Circular economy, disassembly, Automated storage and retrieval system, pick and place for printed circuit boards, packaging and labeling, Palletizer, palletizing, product inspection, and testing; all accomplished with high endurance, speed, and precision. They can assist in material handling. In the year 2023, an estimated 4,281,585 industrial robots were in operation worldwide according to International Federation of Robotics, International Federation of Robotics (IFR). Types and features There are six types of industrial robots. Articulated robots Articulated robots are the most common industrial robots. They look like a Arm, human arm, which is why they are also called robotic arm or Manipulator (device), manipulator arm. Their articu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
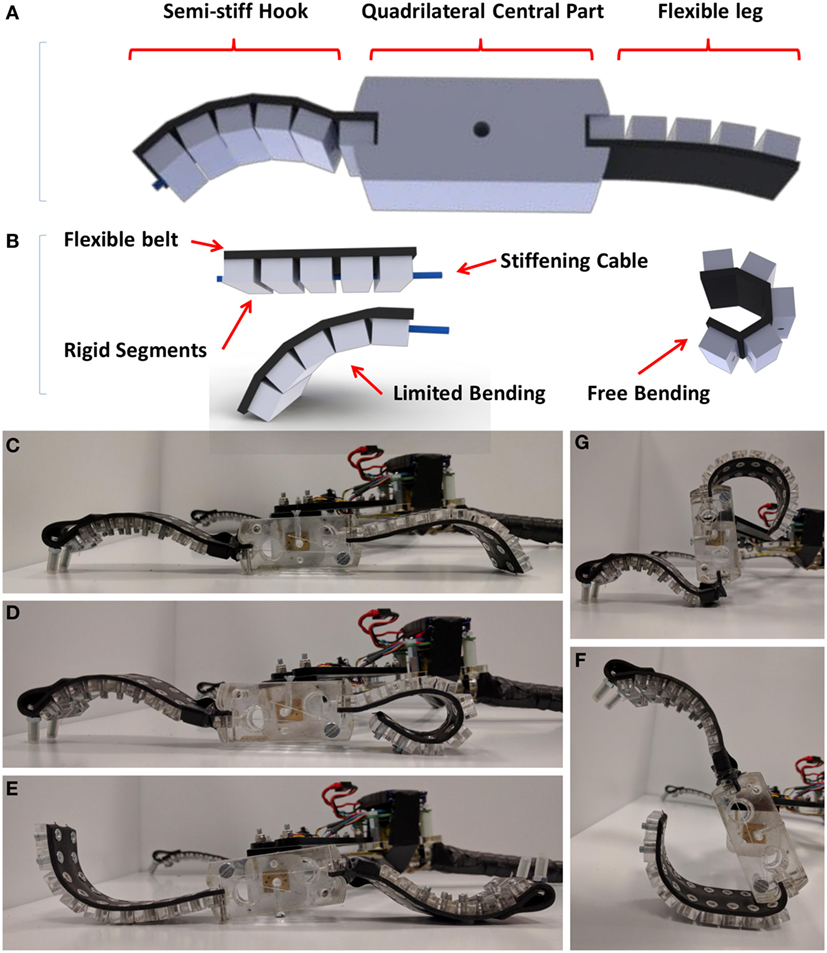
Soft Robotics
Soft robotics is a subfield of robotics that concerns the design, control, and fabrication of robots composed of Stiffness#Compliance, compliant materials, instead of kinematic chain, rigid links. In contrast to rigid-bodied robots built from metals, ceramics and hard plastics, the compliance of soft robots can improve their safety when working in close contact with humans. Types and designs The goal of soft robotics is the design and construction of robots with physically flexible bodies and electronics. In some applications, softness is restricted to a localized region of a machine. For example, rigid-bodied robotic arms can employ soft end effectors to gently grab and manipulate delicate or irregularly shaped objects. Most rigid-bodied mobile robots also strategically employ soft components, such as foot pads to absorb shock or springy joints to store/release elastic energy. However, the field of soft robotics generally focuses on the creation of machines that are predomina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bio-inspired Robotics
Bio-inspired robotic locomotion is a subcategory of bio-inspired design. It is about learning concepts from nature and applying them to the design of real-world engineered systems. More specifically, this field is about making robots that are inspired by Biology, biological systems, including Biomimicry. Biomimicry is copying from nature while bio-inspired design is learning from nature and making a mechanism that is simpler and more effective than the system observed in nature. Biomimicry has led to the development of a different branch of robotics called soft robotics. The biological systems have been optimized for specific tasks according to their habitat. However, they are multifunctional and are not designed for only one specific functionality. Bio-inspired robotics is about studying biological systems, and looking for the mechanisms that may solve a problem in the engineering field. The designer should then try to simplify and enhance that mechanism for the specific task of in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autonomous Robot
An autonomous robot is a robot that acts without recourse to human control. Historic examples include space probes. Modern examples include self-driving Robotic vacuum cleaner, vacuums and Self-driving car, cars. Industrial robot, Industrial robot arms that work on assembly lines inside factories may also be considered autonomous robots, though their Agency (psychology), autonomy is restricted due to a highly structured environment and their inability to Robot locomotion, locomote. Components and criteria of robotic autonomy Self-maintenance The first requirement for complete physical autonomy is the ability for a robot to take care of itself. Many of the battery-powered robots on the market today can find and connect to a charging station, and some toys like Sony's ''Aibo'' are capable of self-docking to charge their batteries. Self-maintenance is based on "proprioception", or sensing one's own internal status. In the battery charging example, the robot can tell propriocep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TOSY
TOSY Robotics specializes in designing and manufacturing robots and smart toys. The most famous products from TOSY Robotics are TOPIO Robot, DiscoRobo, TOOP and AFO. Brand TOSY Robotics focuses on research and development and manufacturing of robots. TOSY's core value is: Technology – Originality – Satisfaction – Yearning. TOSY is a company that designs and manufactures unique robots since 2002. History TOSY Robotics was founded in 2004. In 2007, the company made its first international appearance in IREX (International Robot Exhibition) in Tokyo, Japan and introduced TOPIO 1.0. In 2009, the company introduced TOPIO 2.0 at the Spielwarenmesse Toy Trade Fair in Nuremberg, Germany, in addition to other smart toys like BallRobo, TyreRobo & AFO. In 2011, TOSY TOOP received the Guinness World Record for “the world’s longest-running mechanical spinning top.” In 2012, the company Introduced mRobo 1.0 at the CES (Consumer Electronics Show) held in Las ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FANUC 6-axis Welding Robots
FANUC ( or ; often styled Fanuc) is a Japanese group of companies that provide automation products and services such as robotics and computer numerical control wireless systems. These companies are principally of Japan, Fanuc America Corporation of Rochester Hills, Michigan, USA, and FANUC Europe Corporation S.A. of Luxembourg. FANUC is one of the largest makers of industrial robots in the world. FANUC had its beginnings as part of Fujitsu developing early numerical control (NC) and servo systems. FANUC is acronym for Fuji Automatic Numerical Control. FANUC is organized into 3 business units: FA (Factory Automation), ROBOT, and ROBOMACHINE. These three units are unified with SERVICE as "one FANUC". Service is an integral part of FANUC and the company supports products for as long as customers use them. History In 1955, Fujitsu Ltd. approached Seiuemon Inaba ( :ja:稲葉清右衛門), who was then a young engineer, to lead a new subsidiary purposed to make the field ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
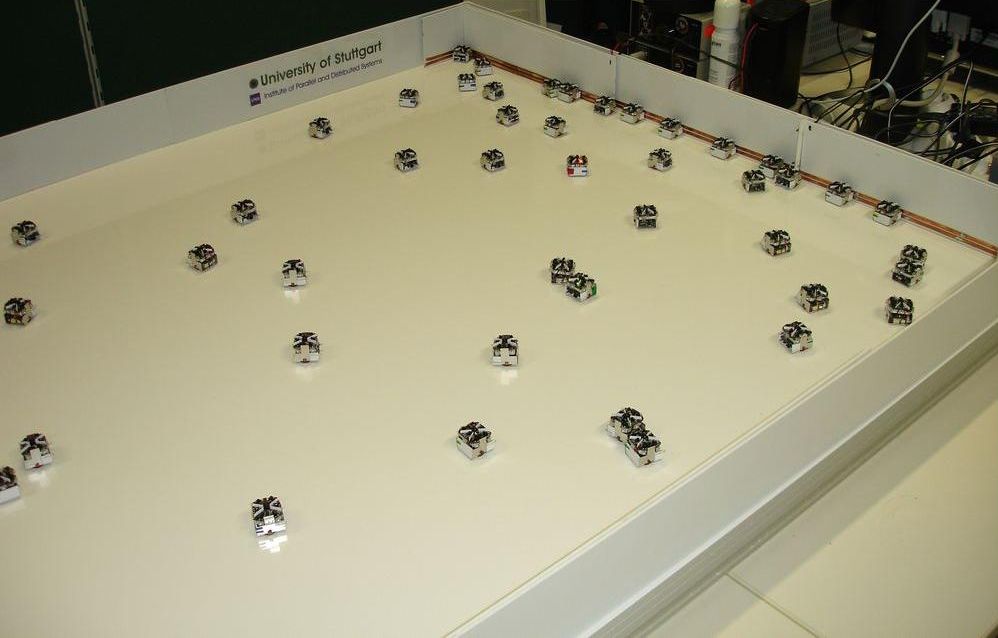
Swarm Robotics
Swarm robotics is the study of how to design independent systems of robots without centralized control. The emerging swarming behavior of robotic swarms is created through the interactions between individual robots and the environment.H. Pan; M. Zahmatkesh; F. Rekabi-Bana; F. Arvin; J. HuT-STAR: Time-Optimal Swarm Trajectory Planning for Quadrotor Unmanned Aerial Vehicles IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2025. This idea emerged on the field of artificial swarm intelligence, as well as the studies of insects, ants and other fields in nature, where swarm behavior occurs. Relatively simple individual rules can produce a large set of complex swarm behaviors. A key component is the communication between the members of the group that build a system of constant feedback. The swarm behavior involves constant change of individuals in cooperation with others, as well as the behavior of the whole group. Key Attributes of Robotic Swarms The design of swarm rob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Automation
Automation describes a wide range of technologies that reduce human intervention in processes, mainly by predetermining decision criteria, subprocess relationships, and related actions, as well as embodying those predeterminations in machines. Automation has been achieved by various means including Mechanical system, mechanical, hydraulic, pneumatic, electrical, electronic devices, and computers, usually in combination. Complicated systems, such as modern Factory, factories, airplanes, and ships typically use combinations of all of these techniques. The benefit of automation includes labor savings, reducing waste, savings in electricity costs, savings in material costs, and improvements to quality, accuracy, and precision. Automation includes the use of various equipment and control systems such as machinery, processes in factories, boilers, and heat-treating ovens, switching on telephone networks, steering, Stabilizer (ship), stabilization of ships, aircraft and other applic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ASIMO
ASIMO (Advanced Step in Innovative Mobility) is a humanoid robot created by Honda in 2000. In 2002, there were 20 units of the first ASIMO model produced; three different ASIMO models subsequently followed. As of February 2009, there were over 100 ASIMO units in existence. In July of 2018, Honda stated that it would be ceasing all development and production of ASIMO robots in order to focus on more practical applications using the technology developed through ASIMO's lifespan. It made its last active appearance in March 2022, as Honda announced the retirement of ASIMO to concentrate on Remote control, remote-controlled, Avatar (computing), avatar-style robotic technology. Development Honda began developing humanoid robots in the 1980s with the goal of making a walking robot, including several prototypes that preceded ASIMO. E0 was the first Bipedalism, bipedal model produced as part of the Honda E series, which was an early experimental line of self-regulating walking robots ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |