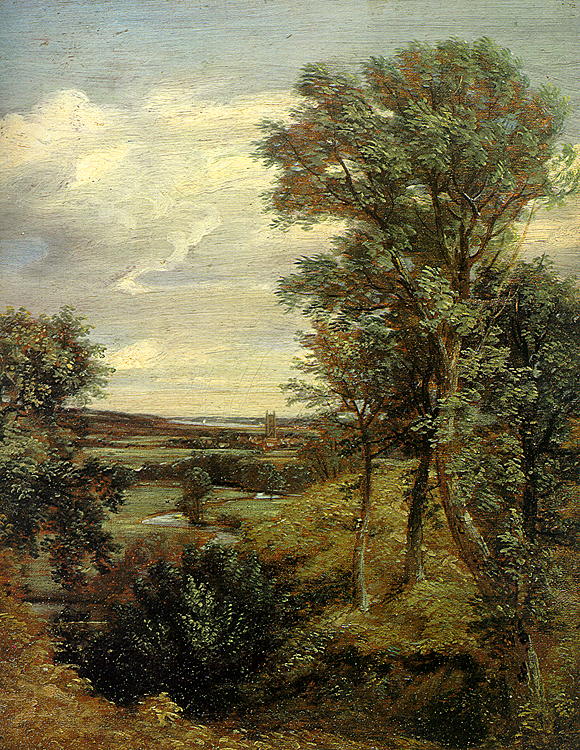|
River Stour, Suffolk
The River Stour () is a river in East Anglia, England. It is long and forms most of the county boundary between Suffolk to the north, and Essex to the south. It rises in eastern Cambridgeshire, passes to the east of Haverhill, through Cavendish, Bures, Sudbury, Nayland, Stratford St Mary, Dedham and flows through the Dedham Vale Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty. It becomes tidal just before Manningtree in Essex and joins the North Sea at Harwich. Etymology and usage The name is of ambiguous and disputed origin. On one theory, the name ''Stour'' derives from the Celtic ''sturr'' meaning "strong". However, the river-name ''Stour'', common in England, does not occur at all in Wales; Crawford noted two tributaries of the Po River near Turin, spelled ''Stura''. In Germany the ''Stoer'' is a tributary of the River Elbe. According to ''Brewer's Britain and Ireland'' the ''Stour'' is pronounced differently in different cases: the Kentish and East Anglian Stours rhyme with ''tou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manningtree
Manningtree is a town and civil parish in the Tendring district of Essex, England, which lies on the River Stour. It is part of the Suffolk Coast and Heaths Area of Natural Beauty. Smallest town claim Manningtree has traditionally claimed to be the smallest town in England, but its 2007 population of 700 people in 20 hectares and the 2011 census population for the civil parish of 900 are much higher than the 351 population of Fordwich, Kent. However, it is believed to be the smallest town by area. In April 2009 it was proposed that Manningtree should merge with Mistley and Lawford to form a single parish, losing its separate identity as a town. As of 2018 such a merger has not occurred. History The name Manningtree is thought to derive from 'many trees'. The town grew around the wool trade from the 15th century until its decline in the 18th century and also had a thriving shipping trade in corn, timber and coal until this declined with the coming of the railway. Manningtr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dedham, Essex
Dedham is a village within the borough of Colchester in northeast Essex, England, on the River Stour and the border of Essex and Suffolk. The nearest town to Dedham is the small market town of Manningtree. Governance Dedham is part of the electoral ward called Dedham and Langham. The population of this ward at the 2011 Census was 2,943. Geography Dedham is frequently rated as containing some of England's most beautiful Lowland landscape, most particularly the water meadows of the River Stour, which passes along the northern boundary of the village forming the boundary between Essex and Suffolk. Dedham has a central nuclear settlement around the Church and the junction of Mill Lane and the High Street (part of the B1029). Connected to Dedham are the hamlets of The Heath and Lamb Corner. The village forms a key part of the Dedham Vale. History Early documents record the name as Diddsham, presumably for a family known as Did or Didd. Dedham Classis In 1582–1587, a schis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Estuary
An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of brackish water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and maritime environments and are an example of an ecotone. Estuaries are subject both to marine influences such as tides, waves, and the influx of saline water, and to fluvial influences such as flows of freshwater and sediment. The mixing of seawater and freshwater provides high levels of nutrients both in the water column and in sediment, making estuaries among the most productive natural habitats in the world. Most existing estuaries formed during the Holocene epoch with the flooding of river-eroded or glacially scoured valleys when the sea level began to rise about 10,000–12,000 years ago. Estuaries are typically classified according to their geomorphological features or to water-circulation patterns. They can have many different names, such as bay ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weston Colville
Weston Colville is a village in South Cambridgeshire, 10 miles southeast of Cambridge and 6 miles south of Newmarket, close to the border with Suffolk. History The parish of Weston Colville forms a long thin area of 3235 acres stretching from just south of the A11 to the Suffolk border. It is wedged between the parishes of Carlton-cum-Willingham to the north and West Wratting to the south, and has a short border with both Great Wilbraham and Little Wilbraham to the northwest. The site has been occupied since at least the 10th century, and there were 40 residents registered at the time of the Domesday Book. By 1150 the manor was owned by the Stutville family. After the death of Anselm de Stutville in around 1198, the land passed to his sister Beatrice, who married William de Colville, lord of Castle Bytham __NOTOC__ Castle Bytham is a village and civil parish of around 300 houses in South Kesteven, Lincolnshire, England. It is located 9 miles (15 km) north of Sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isaac Taylor (canon)
Isaac Taylor (2 May 1829 – 18 October 1901), son of Isaac Taylor, was a philologist, toponymist, and Anglican canon of York (from 1885). Life Though he wrote several inflammatory theological pamphlets, such as ''The Liturgy and the Dissenters'' (1860) and ''Leaves from an Egyptian Notebook'' (1888), he is chiefly remembered today for his archaeological and philological studies, which include ''Words and Places'' (1864), ''Etruscan Researches'' (1874), ''The Alphabet'' (1883), and ''Greeks and Goths'' (1879), in which he argued that the runes were derived from a variety of the Hellenic alphabet used in the Greek colonies on the Black Sea about the 6th century B.C. "It would seem that the Goths, who then occupied the region between the southern coast of the Baltic and the upper waters of the Dnieper," Taylor argued in a subsequent paper, "must have obtained a knowledge of the art of writing from the merchants of Olbia and other Greek colonies on the Euxine, who, according to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire .... It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, Anglo-Saxon settlers in the mid-5th century, and the first Old English literature, Old English literary works date from the mid-7th century. After the Norman conquest of 1066, English was replaced, for a time, by Anglo-Norman language, Anglo-Norman (a langues d'oïl, relative of French) as the language of the upper classes. This is regarded as marking the end of the Old English era, since during this period the English language was heavily influenced by Anglo-Norman, developing into a phase know ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old European Hydronymy
Old European (german: Alteuropäisch) is the term used by Hans Krahe (1964) for the language of the oldest reconstructed stratum of European hydronymy (river names) in Central and Western Europe.Hans Krahe, ''Unsere ältesten Flussnamen'', Wiesbaden Edition Otto Harrassowiitz (1964)"Old European" in this sense is not to be confused with the term as used by Marija Gimbutas who applies it to non-Indo-European or pre-Indo-European Neolithic Europe. Geography Krahe writes in A1, chapter III, "Introducing preface" Number 2 that the old European hydronomy extended from Scandinavia to South Italy, from Western Europe including the British Isles to the Baltic countries. Of the three Mediterranean peninsulas, Italy was most completely included, whilst the Balkan Peninsula was only scarcely covered. He writes that what he presents for hydronomy also applies to mountains and ranges of mountains, and continues with "Karpaten" and "Karawanken", certainly within the Slavic settlement area, om ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle English
Middle English (abbreviated to ME) is a form of the English language that was spoken after the Norman conquest of 1066, until the late 15th century. The English language underwent distinct variations and developments following the Old English period. Scholarly opinion varies, but the '' Oxford English Dictionary'' specifies the period when Middle English was spoken as being from 1150 to 1500. This stage of the development of the English language roughly followed the High to the Late Middle Ages. Middle English saw significant changes to its vocabulary, grammar, pronunciation, and orthography. Writing conventions during the Middle English period varied widely. Examples of writing from this period that have survived show extensive regional variation. The more standardized Old English language became fragmented, localized, and was, for the most part, being improvised. By the end of the period (about 1470) and aided by the invention of the printing press by Johannes Gutenberg in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Elbe
The Elbe (; cs, Labe ; nds, Ilv or ''Elv''; Upper Sorbian, Upper and dsb, Łobjo) is one of the major rivers of Central Europe. It rises in the Giant Mountains of the northern Czech Republic before traversing much of Bohemia (western half of the Czech Republic), then Germany and flowing into the North Sea at Cuxhaven, northwest of Hamburg. Its total length is . The Elbe's major Tributary, tributaries include the rivers Vltava, Saale, Havel, Mulde, Schwarze Elster, and Ohře. The Elbe river basin, comprising the Elbe and its tributaries, has a catchment area of , the twelfth largest in Europe. The basin spans four countries, however it lies almost entirely just in two of them, Germany (65.5%) and the Czech Republic (33.7%, covering about two thirds of the state's territory). Marginally, the basin stretches also to Austria (0.6%) and Poland (0.2%). The Elbe catchment area is inhabited by 24.4 million people, the biggest cities within are Berlin, Hamburg, Prague, Dresden and Le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG),, is a country in Central Europe. It is the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany lies between the Baltic and North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its 16 constituent states have a total population of over 84 million in an area of . It borders Denmark to the north, Poland and Czechia to the east, Austria and Switzerland to the south, and France, Luxembourg, Belgium, and the Netherlands to the west. The nation's capital and most populous city is Berlin and its main financial centre is Frankfurt; the largest urban area is the Ruhr. Settlement in what is now Germany began in the Lower Paleolithic, with various tribes inhabiting it from the Neolithic onward, chiefly the Celts. Various Germanic tribes have inhabited the northern parts of modern Germany since classical antiquity. A region named Germania was documented before AD 100. In 962, the Kingdom of Germany formed the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turin
Turin ( , Piedmontese: ; it, Torino ) is a city and an important business and cultural centre in Northern Italy. It is the capital city of Piedmont and of the Metropolitan City of Turin, and was the first Italian capital from 1861 to 1865. The city is mainly on the western bank of the Po River, below its Susa Valley, and is surrounded by the western Alpine arch and Superga Hill. The population of the city proper is 847,287 (31 January 2022) while the population of the urban area is estimated by Eurostat to be 1.7 million inhabitants. The Turin metropolitan area is estimated by the OECD to have a population of 2.2 million. The city used to be a major European political centre. From 1563, it was the capital of the Duchy of Savoy, then of the Kingdom of Sardinia ruled by the House of Savoy, and the first capital of the Kingdom of Italy from 1861 to 1865. Turin is sometimes called "the cradle of Italian liberty" for having been the political and intellectual centre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |