|
Richard Dacres (Royal Navy Officer)
Sir Richard Dacres (September 1761 – 22 January 1837) was an officer of the British Royal Navy who saw service during the American War of Independence, and the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars. A member of a substantial naval dynasty, he eventually rose to the rank of vice admiral. Family and early life Richard Dacres was born in September 1761, the fifth son of Richard and Mary Dacres, and younger brother to James Richard Dacres.Tracy (2006), p. 109 The Dacres would eventually become a substantial naval dynasty; James Richard rose to be a vice-admiral, his son Barrington became a post-captain, and James became a vice-admiral. Richard's own son Sydney would eventually be an admiral, and First Sea Lord. American war Dacres himself entered the navy in 1775 to serve aboard the 50-gun fourth rate under Captain Francis Banks. He was present at the evacuation of Boston, the capture of New York —serving under Sir Peter Parker— the occupation of Aquidneck Island, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
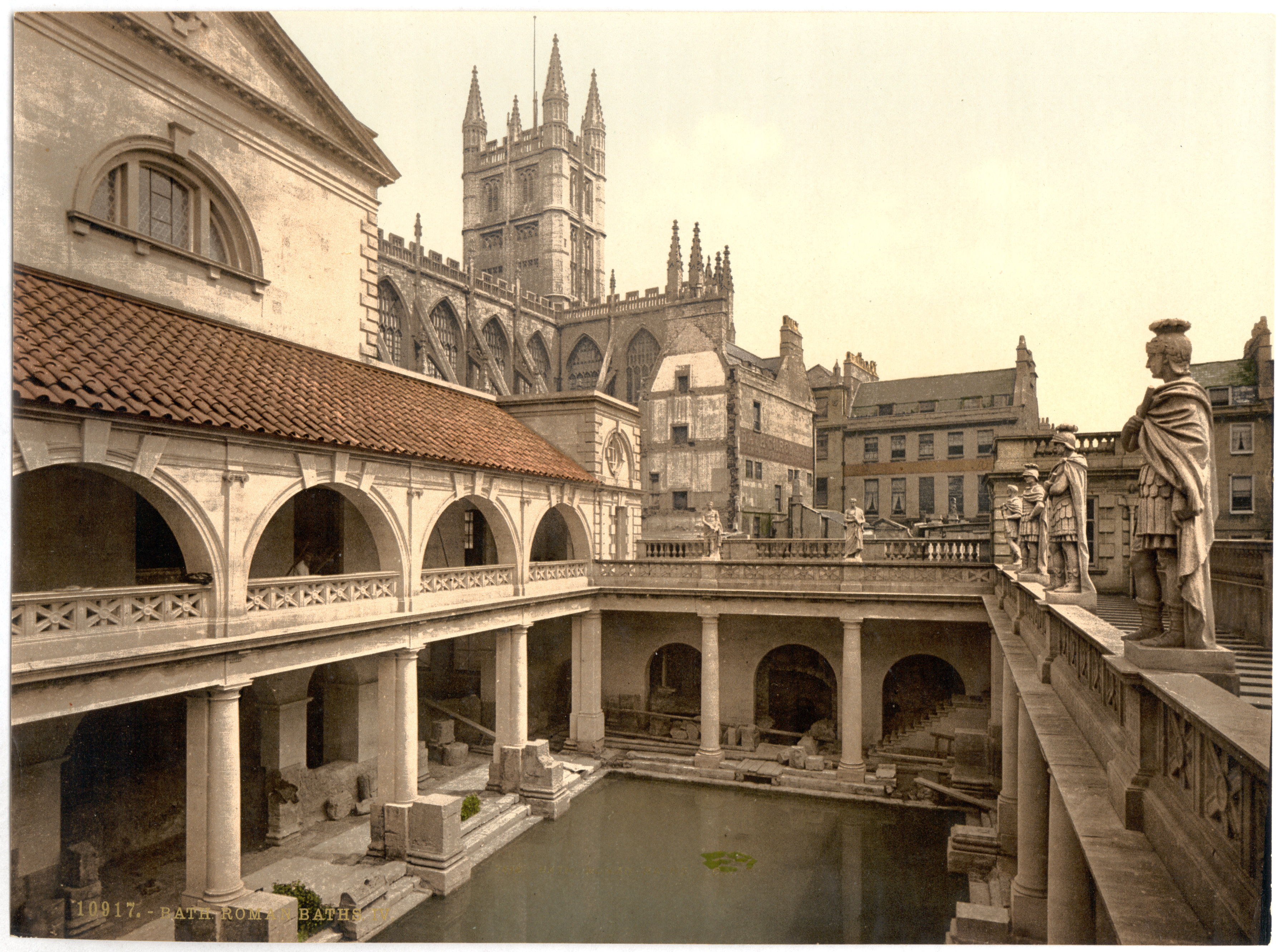
Bath, Somerset
Bath () is a city in the Bath and North East Somerset unitary area in the county of Somerset, England, known for and named after its Roman-built baths. At the 2021 Census, the population was 101,557. Bath is in the valley of the River Avon, west of London and southeast of Bristol. The city became a World Heritage Site in 1987, and was later added to the transnational World Heritage Site known as the "Great Spa Towns of Europe" in 2021. Bath is also the largest city and settlement in Somerset. The city became a spa with the Latin name ' ("the waters of Sulis") 60 AD when the Romans built baths and a temple in the valley of the River Avon, although hot springs were known even before then. Bath Abbey was founded in the 7th century and became a religious centre; the building was rebuilt in the 12th and 16th centuries. In the 17th century, claims were made for the curative properties of water from the springs, and Bath became popular as a spa town in the Georgian era. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Richard Dacres (1749–1810)
James Richard Dacres (February 1749 – 6 January 1810) was an officer of the Royal Navy who saw service during the Seven Years' War, the American War of Independence and the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars. He eventually rose to the rank of Vice-Admiral. Family and early life Dacres was born in Gibraltar in February 1749, the eldest son of the secretary of the garrison Richard Dacres, and his wife Mary Dacres, née Bateman. He had a younger brother, Richard Dacres, who also embarked on a naval career. James Richard entered the navy in February 1762, joining the 28-gun frigate , which was then under the command of Captain Herbert Sawyer. Shortly afterwards, on 21 May that year, the ''Active'' in company with captured the Spanish register ship ''Hermione''. The ''Hermione'' had been bound from Lima carrying a cargo of gold coin, gold, silver and tin ingots, and cocoa and when captured became the richest prize taken during the war. The ''Active''s share of the prize ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
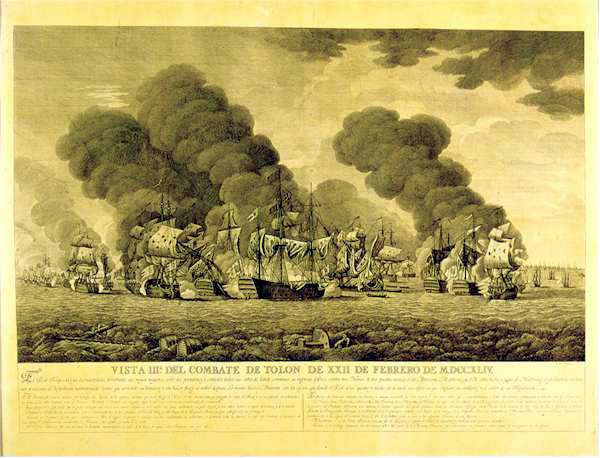
Sir Peter Parker, 1st Baronet
Admiral of the Fleet Sir Peter Parker, 1st Baronet (1721 – 21 December 1811) was a Royal Navy officer. As a junior officer, he was deployed with a squadron under Admiral Edward Vernon to the West Indies at the start of the War of Jenkins' Ear. He saw action again at the Battle of Toulon during the War of the Austrian Succession. As captain of the fourth-rate HMS ''Bristol'' he took part in the Invasion of Guadeloupe during the Seven Years' War. As a commodore, he was deployed to the North American Station, to provide naval support for an expedition led by General Sir Henry Clinton reinforcing loyalists in the Southern Colonies at an early stage of the American Revolutionary War. He led a naval attack against the fortifications on Sullivan's Island (later called Fort Moultrie after their commander), protecting Charleston, South Carolina. However, after a long and hard-fought battle, Parker was forced to call off the attack, having sustained heavy casualties, including ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New York And New Jersey Campaign
The New York and New Jersey campaign in 1776 and the winter months of 1777 was a series of American Revolutionary War battles for control of the Port of New York and New Jersey, Port of New York and the state of New Jersey, fought between Kingdom of Great Britain, British forces under William Howe, 5th Viscount Howe, General Sir William Howe and the Continental Army under General George Washington. Howe was successful in driving Washington out of New York, but overextended his reach into New Jersey, and ended the active campaign season in January 1777 with only a few outposts near the city. The British held New York Harbor for the rest of the war, using it as a base for expeditions against other targets. Landing unopposed on Staten Island on July 3, 1776, Howe had assembled an army composed of elements that had been withdrawn from Boston in March following their Boston campaign, failure to hold that city, combined with additional British troops, as well as Hessian (soldier), Hes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Boston
The siege of Boston (April 19, 1775 – March 17, 1776) was the opening phase of the American Revolutionary War. New England militiamen prevented the movement by land of the British Army, which was garrisoned in what was then the peninsular town of Boston, Massachusetts Bay. Both sides had to deal with resource, supply, and personnel issues over the course of the siege. British resupply and reinforcement was limited to sea access, which was impeded by American vessels. The British abandoned Boston after eleven months and transferred their troops and equipment to Nova Scotia. The siege began on April 19 after the Battles of Lexington and Concord, when Massachusetts militias blocked land access to Boston. The Continental Congress formed the Continental Army from the militias involved in the fighting and appointed George Washington as Commander in Chief. In June 1775, the British seized Bunker and Breed's Hills, from which the Continentals were preparing to bombard the city, but t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fourth Rate
In 1603 all English warships with a compliment of fewer than 160 men were known as 'small ships'. In 1625/26 to establish pay rates for officers a six tier naval ship rating system was introduced.Winfield 2009 These small ships were divided into three tiers, Fourth, Fifth and Sixth rates. Up to the end of the 17th century the number of guns and the compliment size was adjusted until the rating system was actually clarified. A 'Fourth Rate' was nominally a ship of over thirty guns with a complement of 140 men. In the rating system of the Royal Navy used to categorize sailing warships in the 18th century, a fourth-rate was a ship of the line with 46 to 60 guns mounted. They were phased out of ship of the line service during the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars, as their usefulness was declining; though they were still in service, especially on distant stations such as the East Indies. ''Fourth-rates'' took many forms, initially as small two decked warships, later as larg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Sea Lord
The First Sea Lord and Chief of the Naval Staff (1SL/CNS) is the military head of the Royal Navy and Naval Service of the United Kingdom. The First Sea Lord is usually the highest ranking and most senior admiral to serve in the British Armed Forces unless either the Chief or Vice-Chief of the Defence Staff are naval officers. Admiral Ben Key was appointed First Sea Lord in November 2021. Originally titled the "Senior Naval Lord to the Board of Admiralty" when the post was created in 1689, the office was re-styled "First Naval Lord" in 1771. The concept of a professional "First Naval Lord" was introduced in 1805, and the title of the office was changed to "First Sea Lord" on the appointment of Sir John Fisher in 1904. Since 1923, the First Sea Lord has been a member of the Chiefs of Staff Committee; he now sits on the Defence Council and the Admiralty Board. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Post-captain
Post-captain is an obsolete alternative form of the rank of Captain (Royal Navy), captain in the Royal Navy. The term served to distinguish those who were captains by rank from: * Officers in command of a naval vessel, who were (and still are) addressed as captain regardless of rank; * Commander (Royal Navy), Commanders, who received the title of captain as a courtesy, whether they currently had a command or not (e.g. the fictional Captain Jack Aubrey in ''Aubrey-Maturin series#Master and Commander, Master and Commander'' or the fictional Captain Horatio Hornblower in ''Hornblower and the Hotspur''); this custom is now defunct. In the Royal Navy of the 18th and 19th centuries, an officer might be promoted from commander to captain, but not have a command. Until the officer obtained a command, he was "on the beach" and on half-pay. An officer "took post" or was "made post" when he was first commissioned to command a vessel. Usually this was a rating system of the Royal Navy, ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Revolutionary War
The French Revolutionary Wars (french: Guerres de la Révolution française) were a series of sweeping military conflicts lasting from 1792 until 1802 and resulting from the French Revolution. They pitted French First Republic, France against Kingdom of Great Britain, Britain, Habsburg monarchy, Austria, Kingdom of Prussia, Prussia, Russian Empire, Russia, and several other monarchies. They are divided in two periods: the War of the First Coalition (1792–97) and the War of the Second Coalition (1798–1802). Initially confined to Europe, the fighting gradually assumed a global dimension. After a decade of constant warfare and aggressive diplomacy, France had conquered territories in the Italian Peninsula, the Low Countries and the Rhineland in Europe and abandoned Louisiana (New France), Louisiana in North America. French success in these conflicts ensured the spread of revolutionary principles over much of Europe. As early as 1791, the other monarchies of Europe looked with ou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American War Of Independence
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of the United States, fighting began on April 19, 1775, followed by the Lee Resolution on July 2, 1776, and the Declaration of Independence on July 4, 1776. The American Patriots were supported by the Kingdom of France and, to a lesser extent, the Dutch Republic and the Spanish Empire, in a conflict taking place in North America, the Caribbean, and the Atlantic Ocean. Established by royal charter in the 17th and 18th centuries, the American colonies were largely autonomous in domestic affairs and commercially prosperous, trading with Britain and its Caribbean colonies, as well as other European powers via their Caribbean entrepôts. After British victory over the French in the Seven Years' War in 1763, tensions between the motherland and her ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Richard Dacres (1788–1853)
James Richard Dacres (22 August 1788 – 4 December 1853) was an officer of the Royal Navy who saw service during the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars, and the War of 1812. A member of a substantial naval dynasty, he eventually rose to the rank of vice admiral, but is chiefly remembered for his engagement with the American frigate which saw the loss of his ship, . Family and early life Dacres was born in Lowestoft on 22 August 1788, the son of Captain, later Vice-Admiral, James Richard Dacres and his wife Eleanor Blandford Pearce. The Dacres would eventually become a substantial naval dynasty, James's elder brother Barrington Dacres embarked on a naval career and rose to be post-captain, while their uncle, Richard Dacres became a vice-admiral. His cousin, Richard's son Sydney Dacres would eventually be an admiral, and First Sea Lord. James Richard Dacres entered the navy in 1796 at the age of eight, serving aboard his father's old ship, the 64-gun , as a first cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_-_02.jpg)


