|
Ribes Oxyacanthoides
''Ribes oxyacanthoides'' is a species of flowering plant in the gooseberry family known by the common name Canadian gooseberry. Its various subspecies have common names of their own. It is native to North America, where it occurs in Alaska through much of Canada and the western and north-central United States.Carey, Jennifer H. 1995''Ribes oxyacanthoides''.In: Fire Effects Information System, nline U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station, Fire Sciences Laboratory. Subspecies:''Ribes oxyacanthoides''. USDA Plants Profile.''Ribes oxyacanthoides''. Flora of North America. *''R. o.'' ssp. ''cognatum'' (Umatilla go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (; 23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after his ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné Blunt (2004), p. 171. (), was a Swedish botanist, zoologist, taxonomist, and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the modern system of naming organisms. He is known as the "father of modern taxonomy". Many of his writings were in Latin; his name is rendered in Latin as and, after his 1761 ennoblement, as . Linnaeus was born in Råshult, the countryside of Småland, in southern Sweden. He received most of his higher education at Uppsala University and began giving lectures in botany there in 1730. He lived abroad between 1735 and 1738, where he studied and also published the first edition of his ' in the Netherlands. He then returned to Sweden where he became professor of medicine and botany at Uppsala. In the 1740s, he was sent on several journeys through Sweden to find and classify plants and animals. In the 1750s and 1760s, he continued to collect an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elevation
The elevation of a geographic location is its height above or below a fixed reference point, most commonly a reference geoid, a mathematical model of the Earth's sea level as an equipotential gravitational surface (see Geodetic datum § Vertical datum). The term ''elevation'' is mainly used when referring to points on the Earth's surface, while ''altitude'' or ''geopotential height'' is used for points above the surface, such as an aircraft in flight or a spacecraft in orbit, and '' depth'' is used for points below the surface. Elevation is not to be confused with the distance from the center of the Earth. Due to the equatorial bulge, the summits of Mount Everest and Chimborazo have, respectively, the largest elevation and the largest geocentric distance. Aviation In aviation the term elevation or aerodrome elevation is defined by the ICAO as the highest point of the landing area. It is often measured in feet and can be found in approach charts of the aerodrome. It is n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flora Of North America
The ''Flora of North America North of Mexico'' (usually referred to as ''FNA'') is a multivolume work describing the native plants and naturalized plants of North America, including the United States, Canada, St. Pierre and Miquelon, and Greenland. It includes bryophytes and vascular plants. All taxa are described and included in dichotomous keys, distributions of all species and infraspecific taxa are mapped, and about 20% of species are illustrated with line drawings prepared specifically for FNA. It is expected to fill 30 volumes when completed and will be the first work to treat all of the known flora north of Mexico; in 2015 it was expected tha the series would conclude in 2017. Twenty-nine of the volumes have been published as of 2022. Soon after publication, the contents are made available online. FNA is a collaboration of about 1,000 authors, artists, reviewers, and editors from throughout the world. Reception The series has been praised for "the comprehensive treatme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plants Used In Traditional Native American Medicine
Plants are predominantly photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all current definitions of Plantae exclude the fungi and some algae, as well as the prokaryotes (the archaea and bacteria). By one definition, plants form the clade Viridiplantae (Latin name for "green plants") which is sister of the Glaucophyta, and consists of the green algae and Embryophyta (land plants). The latter includes the flowering plants, conifers and other gymnosperms, ferns and their allies, hornworts, liverworts, and mosses. Most plants are multicellular organisms. Green plants obtain most of their energy from sunlight via photosynthesis by primary chloroplasts that are derived from endosymbiosis with cyanobacteria. Their chloroplasts contain chlorophylls a and b, which gives them their green color. Some plants are parasitic or mycotrophic and have lost the abilit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plants Used In Native American Cuisine
Plants are predominantly photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all current definitions of Plantae exclude the fungi and some algae, as well as the prokaryotes (the archaea and bacteria). By one definition, plants form the clade Viridiplantae (Latin name for "green plants") which is sister of the Glaucophyta, and consists of the green algae and Embryophyta (land plants). The latter includes the flowering plants, conifers and other gymnosperms, ferns and their allies, hornworts, liverworts, and mosses. Most plants are multicellular organisms. Green plants obtain most of their energy from sunlight via photosynthesis by primary chloroplasts that are derived from endosymbiosis with cyanobacteria. Their chloroplasts contain chlorophylls a and b, which gives them their green color. Some plants are parasitic or mycotrophic and have lost the ability ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ribes
''Ribes'' is a genus of about 200 known species of flowering plants, most of them native to the temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere. The various species are known as currants or gooseberries, and some are cultivated for their edible fruit or as ornamental plants. ''Ribes'' is the only genus in the family Grossulariaceae. Description ''Ribes'' species are medium shrublike plants with marked diversity in strikingly diverse flowers and fruit. They have either palmately lobed or compound leaves, and some have thorns. The sepals of the flowers are larger than the petals, and fuse into a tube or saucer shape. The ovary is inferior, maturing into a berry with many seeds. Taxonomy ''Ribes'' is the single genus in the Saxifragales family Grossulariaceae. Although once included in the broader circumscription of Saxifragaceae ''sensu lato'', it is now positioned as a sister group to Saxifragaceae ''sensu stricto''. Subdivision First treated on a worldwide basis in 1907, the in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
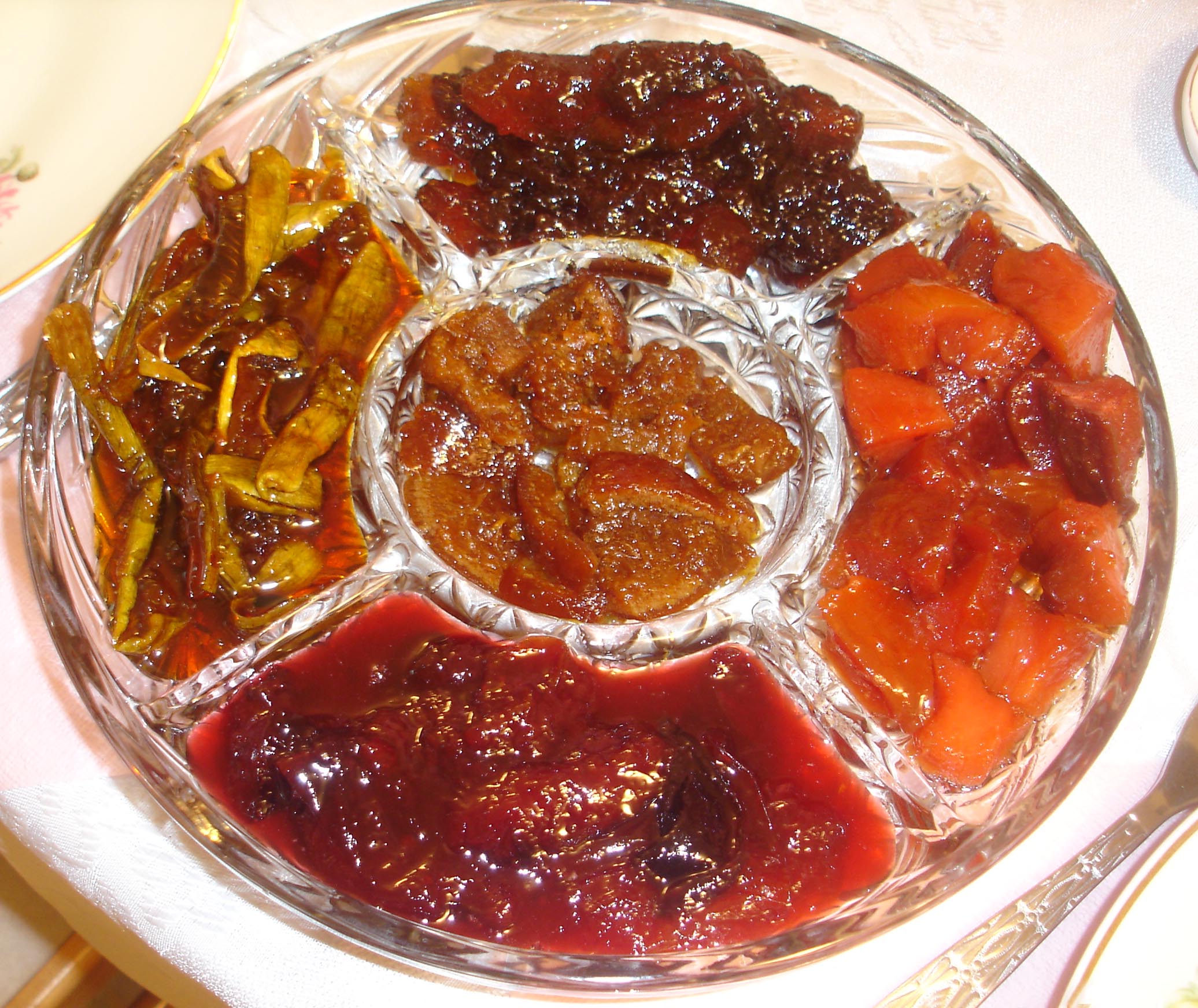
Fruit Preserves
Fruit preserves are preparations of fruits whose main preserving agent is sugar and sometimes acid, often stored in glass jars and used as a condiment or spread. There are many varieties of fruit preserves globally, distinguished by the method of preparation, type of fruit used, and place in a meal. Sweet fruit preserves such as jams, jellies, and marmalades are often eaten at breakfast with bread or as an ingredient of a pastry or dessert, whereas more savory and acidic preserves made from " vegetable fruits" such as tomato, squash or zucchini, are eaten alongside savory foods such as cheese, cold meats, and curries. Techniques There are several techniques of making jam, with or without added water. One factor depends on the natural pectin content of the ingredients. When making jam with low pectin fruits like strawberries either high pectin fruit like orange can be added, or additional pectin in the form of pectin powder, citric acid or citrus peels. Often the fruit will be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maize
Maize ( ; ''Zea mays'' subsp. ''mays'', from es, maíz after tnq, mahiz), also known as corn (North American and Australian English), is a cereal grain first domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 10,000 years ago. The leafy stalk of the plant produces pollen inflorescences (or "tassels") and separate ovuliferous inflorescences called ears that when fertilized yield kernels or seeds, which are fruits. The term ''maize'' is preferred in formal, scientific, and international usage as a common name because it refers specifically to this one grain, unlike ''corn'', which has a complex variety of meanings that vary by context and geographic region. Maize has become a staple food in many parts of the world, with the total production of maize surpassing that of wheat or rice. In addition to being consumed directly by humans (often in the form of masa), maize is also used for corn ethanol, animal feed and other maize products, such as corn starch and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ojibwe People
The Ojibwe, Ojibwa, Chippewa, or Saulteaux are an Anishinaabe people in what is currently southern Canada, the northern Midwestern United States, and Northern Plains. According to the U.S. census, in the United States Ojibwe people are one of the largest tribal populations among Native American peoples. In Canada, they are the second-largest First Nations population, surpassed only by the Cree. They are one of the most numerous Indigenous Peoples north of the Rio Grande. The Ojibwe population is approximately 320,000 people, with 170,742 living in the United States , and approximately 160,000 living in Canada. In the United States, there are 77,940 mainline Ojibwe; 76,760 Saulteaux; and 8,770 Mississauga, organized in 125 bands. In Canada, they live from western Quebec to eastern British Columbia. The Ojibwe language is Anishinaabemowin, a branch of the Algonquian language family. They are part of the Council of Three Fires (which also include the Odawa and Potawatomi) and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mule Deer
The mule deer (''Odocoileus hemionus'') is a deer indigenous to western North America; it is named for its ears, which are large like those of the mule. Two subspecies of mule deer are grouped into the black-tailed deer. Unlike the related white-tailed deer (''Odocoileus virginianus''), which is found throughout most of North America east of the Rocky Mountains and in the valleys of the Rocky Mountains from Idaho and Wyoming northward, mule deer are only found on the western Great Plains, in the Rocky Mountains, in the southwest United States, and on the west coast of North America. Mule deer have also been introduced to Argentina and Kauai, Kauai, Hawaii. Taxonomy Mule deer can be divided into two main groups: the mule deer (''sensu stricto'') and the black-tailed deer. The first group includes all subspecies, except ''O. h. columbianus'' and ''Sitka deer, O. h. sitkensis'', which are in the black-tailed deer group. The two main groups have been treated as separate species, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grizzly Bear
The grizzly bear (''Ursus arctos horribilis''), also known as the North American brown bear or simply grizzly, is a population or subspecies of the brown bear inhabiting North America. In addition to the mainland grizzly (''Ursus arctos horribilis''), other morphological forms of brown bear in North America are sometimes identified as grizzly bears. These include three living populations—the Kodiak bear (''U. a. middendorffi''), the Kamchatka bear (''U. a. beringianus''), and the peninsular grizzly (''U. a. gyas'')—as well as the extinct California grizzly (''U. a. californicus''†), Mexican grizzly (formerly ''U. a. nelsoni''†), and Ungava-Labrador grizzly (formerly ''U. a. ungavaesis''†). On average, grizzly bears near the coast tend to be larger while inland grizzlies tend to be smaller. The Ussuri brown bear (''U. a. lasiotus''), inhabiting Russia, Northern China, Japan, and Korea, is sometimes referred to as the "black grizzly", although it is no more closely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
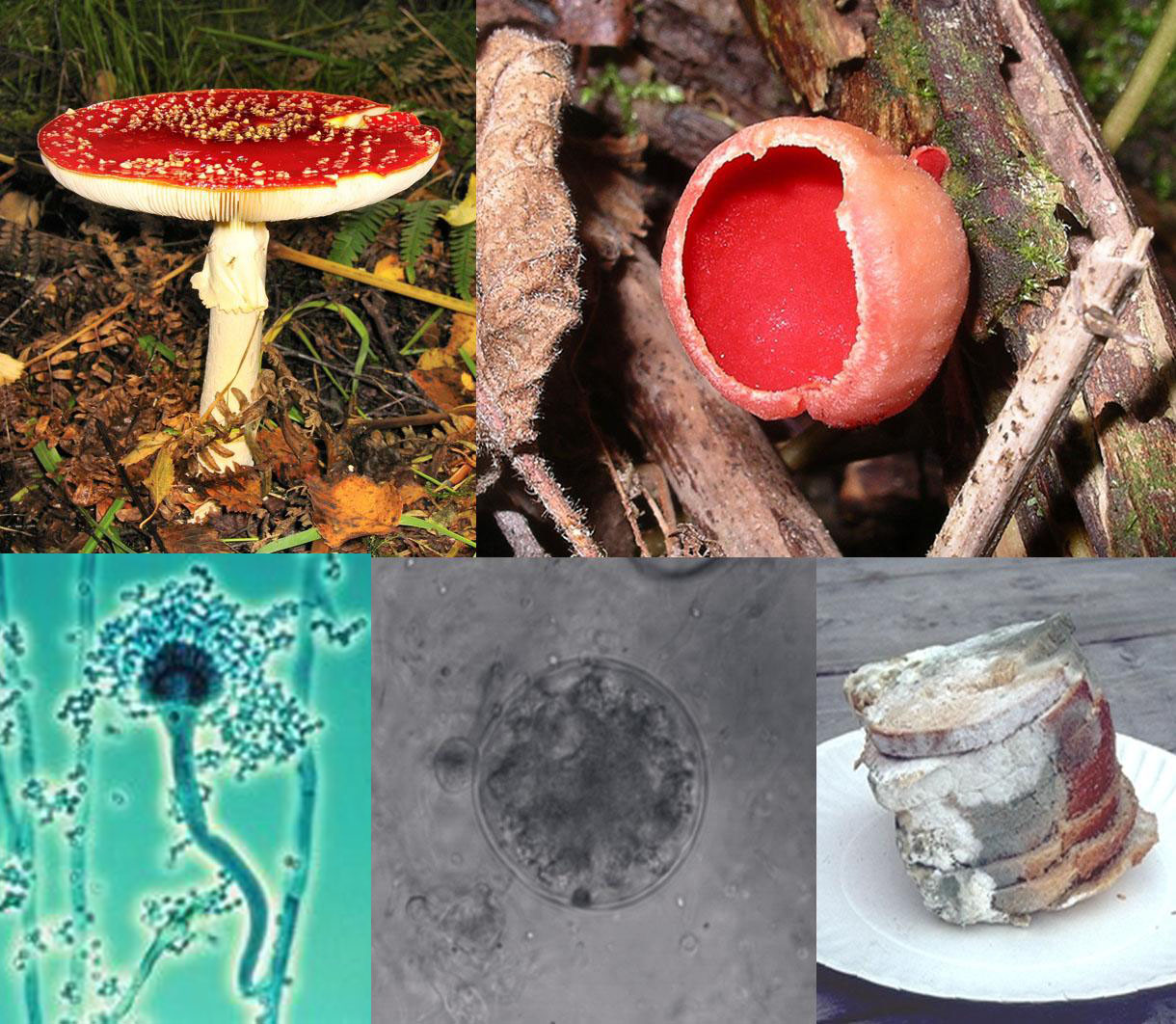
Cronartium Ribicola
''Cronartium ribicola'' is a species of rust fungus in the family Cronartiaceae that causes the disease white pine blister rust. Other names include: (French), (German), (Spanish). ''Cronartium ribicola'' is native to China, and was subsequently introduced to North America. Some European and Asian white pines (e.g. Macedonian pine, Swiss pine and blue pine) are mostly resistant to the disease, having co-evolved with the pathogen. It was accidentally introduced into North America in approximately 1900, where it is an invasive species causing serious damage to the American white pines, which have little genetic resistance. Mortality is particularly heavy in western white pine, sugar pine, limber pine and whitebark pine. Efforts are under way to select and breed the rare resistant individuals of these species; resistance breeding is concentrated at the United States Forest Service Dorena Genetic Resource Center in Oregon and the Moscow Forestry Services Laboratory in Idaho. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |