|
Rhodophana
''Rhodophana'' is a genus of mushroom-forming fungi in the family Entolomataceae. It originally described as a genus in 1947 by Robert Kühner, but the description was invalid until it was re-published in 1971, though as a subgenus of ''Rhodocybe''. It did not find favour as a genus until ''Rhodocybe'' was found to be polyphyletic and Kluting et al. resurrected the name in 2014 as part of a DNA-based reclassification of the family. ''Rhodophana'' is distinguished from other genera of the Entolomataceae because there are clamp connections and based on the structure of the cap skin. This genus has a thin outer cutis in a single layer merging into the main trama whilst other family members have a two-layer cap skin. The type species is ''Rhodophana nitellina''. The name is derived from "rhodon" (ῥόδον) = "rose" (referring to the pink colour of the spores and gills) and "phanos" (φανός) = bright or conspicuous (referring to the cap colour). See also *List of Agarical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Entolomataceae Genera
The mushroom genera in the family Entolomataceae collectively contain over 1500 species, the large majority of which are in ''Entoloma''. There have been many different classifications of this group, and so the table below includes not only genera which are supposedly current, but also other proposed genera whose names have been important. For instance several taxa such as ''Leptonia'' and ''Nolanea'' were defined as independent genera, and are still sometimes used as such, but in recent classifications they have been demoted to being subgenera of ''Entoloma''. Previously there was a view that Entolomataceae with angular (polyhedral) spores should be classified in genus ''Entoloma'', those with bumpy spores should be in ''Rhodocybe'', and those with longitudinally ridged spores should be put in ''Clitopilus''. However DNA studies in 2009 and 2017 have changed this situation for the ''Rhodocybe''/''Clitopilus'' group. Firstly ''Clitopilus'' was found to be a clade embedded within ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entolomataceae
The Entolomataceae, also known as Rhodophyllaceae, are a large family of pink-spored terrestrial gilled mushrooms which includes the genera ''Entoloma'', '' Rhodocybe'', and ''Clitopilus''. The family collectively contains over 1500 species, the large majority of which are in ''Entoloma''. Genera formerly known as ''Leptonia'' and ''Nolanea'', amongst others, have been subsumed into ''Entoloma''. Mushrooms in the Entolomataceae typically grow in woodlands or grassy areas and have attached gills, differentiating them from the Pluteaceae, which have free gills. Description The very large family Entolomataceae has a cosmopolitan distribution, and species are common in both temperate and tropical climates. Although the shape of the fruiting body and many microscopic characteristics are very diverse, it forms a well-defined group due to the distinctive spores: the spore print is pink (or brownish or greyish pink) and the spores are ornamented with bumps or ridges, or have a sharp-p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhodocybe
''Rhodocybe'' is a small genus of small and medium-sized brownish-pink spored mushrooms, or (following recent mycological research) it is a subgroup of genus ''Clitopilus''. These mushrooms are saprotrophic and most grow on the ground, but some are found on wood. Most are drab in appearance, though a few have vivid colors. Description The cap shape can be convex, plane, or depressed. The gills usually have adnate to decurrent attachment, rarely notched and the stems of the mushrooms are highly variable, but always lack a veil or volva. The spores are flesh-colored to salmon to brownish pink. Microscopically the shape of the spores is important in defining the group. About 20 species of ''Rhodocybe'' have been documented in Europe, but ''R. gemina'' (sometimes wrongly named ''R. truncata'') is the commonest and best known, though rare in Britain. The type species is ''Rhodocybe caelata'' (Fr.) Maire. Little is known about the edibility of ''Rhodocybes'', but one prominen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungi
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the ''Eumycota'' (''t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basidiomycota
Basidiomycota () is one of two large divisions that, together with the Ascomycota, constitute the subkingdom Dikarya (often referred to as the "higher fungi") within the kingdom Fungi. Members are known as basidiomycetes. More specifically, Basidiomycota includes these groups: mushrooms, puffballs, stinkhorns, bracket fungi, other polypores, jelly fungi, boletes, chanterelles, earth stars, smuts, bunts, rusts, mirror yeasts, and ''Cryptococcus'', the human pathogenic yeast. Basidiomycota are filamentous fungi composed of hyphae (except for basidiomycota-yeast) and reproduce sexually via the formation of specialized club-shaped end cells called basidia that normally bear external meiospores (usually four). These specialized spores are called basidiospores. However, some Basidiomycota are obligate asexual reproducers. Basidiomycota that reproduce asexually (discussed below) can typically be recognized as members of this division by gross similarity to others, by the form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agaricomycetes
The Agaricomycetes are a class of fungi in the division Basidiomycota. The taxon is roughly identical to that defined for the Homobasidiomycetes (alternatively called holobasidiomycetes) by Hibbett & Thorn, with the inclusion of Auriculariales and Sebacinales. It includes not only mushroom-forming fungi, but also most species placed in the deprecated taxa Gasteromycetes and Homobasidiomycetes. Within the subdivision Agaricomycotina, which already excludes the smut and rust fungi, the Agaricomycetes can be further defined by the exclusion of the classes Tremellomycetes and Dacrymycetes, which are generally considered to be jelly fungi. However, a few former "jelly fungi", such as ''Auricularia'', are classified in the Agaricomycetes. According to a 2008 estimate, Agaricomycetes include 17 orders, 100 families, 1147 genera, and about 21000 species. Modern molecular phylogenetic analyses have been since used to help define several new orders in the Agaricomycetes: Amylocorticiales ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agaricales
The fungal order Agaricales, also known as gilled mushrooms (for their distinctive gills) or euagarics, contains some of the most familiar types of mushrooms. The order has 33 extant families, 413 genera, and over 13,000 described species, along with six extinct genera known only from the fossil record. They range from the ubiquitous common mushroom to the deadly destroying angel and the hallucinogenic fly agaric to the bioluminescent jack-o-lantern mushroom. History, classification and phylogeny In his three volumes of '' Systema Mycologicum'' published between 1821 and 1832, Elias Fries put almost all of the fleshy, gill-forming mushrooms in the genus ''Agaricus''. He organized the large genus into "tribes", the names of many of which still exist as common genera of today. Fries later elevated several of these tribes to generic level, but later authors—including Gillet, Karsten, Kummer, Quélet, and Staude—made most of the changes. Fries based his classification on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elias Magnus Fries
Elias Magnus Fries (15 August 1794 – 8 February 1878) was a Swedish mycologist and botanist. Career Fries was born at Femsjö (Hylte Municipality), Småland, the son of the pastor there. He attended school in Växjö. He acquired an extensive knowledge of flowering plants from his father. In 1811 Fries entered Lund University where he obtained a doctorate in 1814. In the same year he was appointed an associate professorship in botany. He was elected a member of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences, and in 1824, became a full professor. In 1834 he became Borgström professor (Swed. ''Borgströmianska professuren'', a chair endowed by Erik Eriksson Borgström, 1708–1770) in applied economics at Uppsala University. The position was changed to "professor of botany and applied economics" in 1851. He was elected a Foreign Honorary Member of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences in 1849. That year he was also appointed director of the Uppsala University Botanica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family (taxonomy), family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. ''Panthera leo'' (lion) and ''Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomy (biology), taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Kühner
Robert Kühner (15 March 1903 in Paris – 27 February 1996 in Lyon) was a French mycologist most notable for reviewing many forms of agaric (mushroom fungus) genera. He studied at the Sorbonne, afterwards from 1921 until 1932, he was working as a high school teacher in Lille. Then from 1938 till 1973, he was associated with the Faculty of Sciences at Lyon. He was honoured in 1946, with ''Kuehneromyces'', which is a genus of fungi in the family Strophariaceae. Selected works * ''Contribution à l'étude des hyménomycètes et spécialement des agaricacés'', 1926 - Contribution to the study of Hymenomycetes and especially of Agaricales. * ''Le genre Galera (Fries) Quélet'', 1935 - The genus Galera (Fries) Quélet. * ''Le genre Mycena (Fries) Étude cytologique et systématique des espèces d'Europe et d'Amérique du Nord'', 1938 - The genus Mycena (Fries), cytological and systematic studies of species native to Europe and North America. * ''Flore analytique des champigno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyphyly
A polyphyletic group is an assemblage of organisms or other evolving elements that is of mixed evolutionary origin. The term is often applied to groups that share similar features known as homoplasies, which are explained as a result of convergent evolution. The arrangement of the members of a polyphyletic group is called a polyphyly .. ource for pronunciation./ref> It is contrasted with monophyly and paraphyly. For example, the biological characteristic of warm-bloodedness evolved separately in the ancestors of mammals and the ancestors of birds; "warm-blooded animals" is therefore a polyphyletic grouping. Other examples of polyphyletic groups are algae, C4 photosynthetic plants, and edentates. Many taxonomists aim to avoid homoplasies in grouping taxa together, with a goal to identify and eliminate groups that are found to be polyphyletic. This is often the stimulus for major revisions of the classification schemes. Researchers concerned more with ecology than with system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
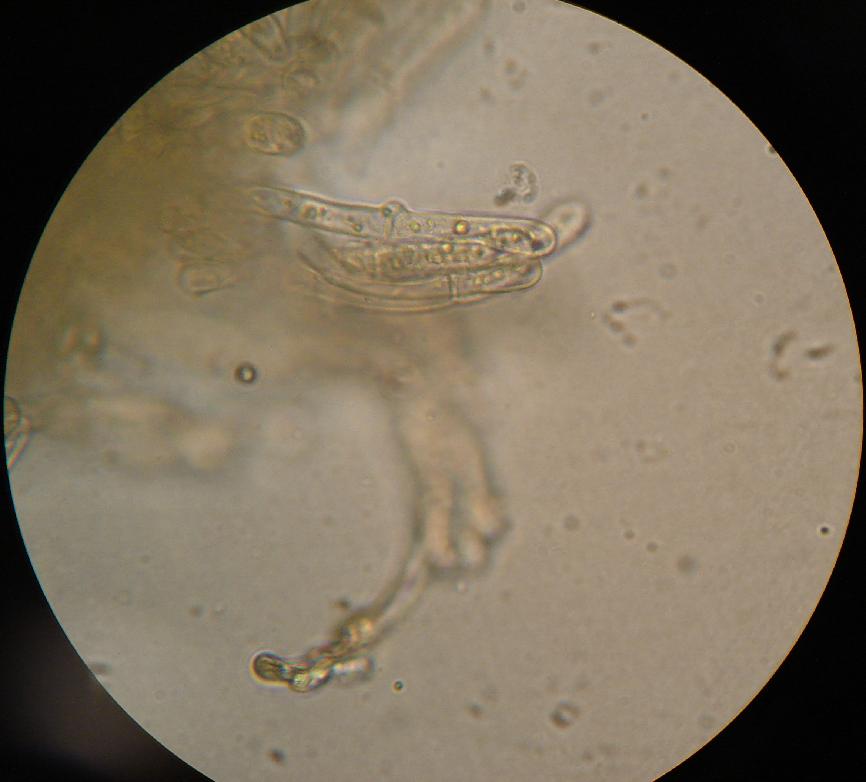
Clamp Connections
A clamp connection is a hook-like structure formed by growing hyphal cells of certain fungi. It is a characteristic feature of Basidiomycetes fungi. It is created to ensure that each cell, or segment of hypha separated by septa (cross walls), receives a set of differing nuclei, which are obtained through mating of hyphae of differing sexual types. It is used to maintain genetic variation within the hypha much like the mechanisms found in crozier (hook) during sexual reproduction. Formation Clamp connections are formed by the terminal hypha during elongation. Before the clamp connection is formed this terminal segment contains two nuclei. Once the terminal segment is long enough it begins to form the clamp connection. At the same time, each nucleus undergoes mitotic division to produce two daughter nuclei. As the clamp continues to develop it uptakes one of the daughter (green circle) nuclei and separates it from its sister nucleus. While this is occurring the remaining nuclei (o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |