|
Rhamnoside
Rhamnose (Rha, Rham) is a naturally occurring deoxy sugar. It can be classified as either a methyl-pentose or a 6-deoxy-hexose. Rhamnose predominantly occurs in nature in its L-form as L-rhamnose (6-deoxy-L-mannose). This is unusual, since most of the naturally occurring sugars are in D-form. Exceptions are the methyl pentoses L-fucose and L-rhamnose and the pentose L-arabinose. However, examples of naturally-occurring D-rhamnose include some species of bacteria, such as ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' and ''Helicobacter pylori''. Rhamnose can be isolated from Buckthorn (''Rhamnus''), poison sumac, and plants in the genus ''Uncaria''. Rhamnose is also produced by microalgae belonging to class Bacillariophyceae (diatoms). Rhamnose is commonly bound to other sugars in nature. It is a common glycone component of glycosides from many plants. Rhamnose is also a component of the outer cell membrane of acid-fast bacteria in the ''Mycobacterium'' genus, which includes the organism that cau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deoxy Sugar
Deoxy sugars are sugars that have had a hydroxyl group replaced with a hydrogen atom. Examples include: * Deoxyribose, or 2-deoxy-D- ribose, a constituent of DNA * Fucose, or 6-deoxy-L- galactose, main component of fucoidan of brown algae, and present in N-linked glycans * Fuculose, or 6-deoxy-L- tagatose, one of the important components of avian influenza virus particles * Rhamnose, or 6-deoxy-L- mannose, present in plant glycosides In '' Escherichia coli'' bacteria, deoxyribose sugars are synthesized via two different pathways - one pathway involves aldol condensation, whereas the other pathway is conversion of a ribose sugar into a deoxyribose sugar by means of changes on the nucleotide or nucleoside level. Deoxyribose is synthesized through the reduction of ribose. Deoxyribose is derived from the same precursor as ribose being that the reduction of the sugar with the extra hydroxyl group results in the deoxy-sugar, which has its hydroxyl group replaced with a hydr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mycobacterium
''Mycobacterium'' is a genus of over 190 species in the phylum Actinomycetota, assigned its own family, Mycobacteriaceae. This genus includes pathogens known to cause serious diseases in mammals, including tuberculosis (''M. tuberculosis'') and leprosy ('' M. leprae'') in humans. The Greek prefix ''myco-'' means 'fungus', alluding to this genus' mold-like colony surfaces. Since this genus has cell walls with Gram-positive and Gram-negative features, acid-fast staining is used to emphasize their resistance to acids, compared to other cell types. Metabolism and Morphology Mycobacteria are aerobic with 0.2-0.6 µm wide and 1.0-10 µm long rod shapes. They are generally non-motile, except for the species ''Mycobacterium marinum'', which has been shown to be motile within macrophages. Mycobacteria possess capsules and most do not form endospores. ''M. marinum'' and perhaps ''M. bovis'' have been shown to sporulate; however, this has been contested by further research. The disting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neohesperidose
Neohesperidose is the disaccharide which is present in some flavonoids. It can be found in species of ''Typha.'' ''Delphinidin-3-neohesperidoside and cyanidin-3- neohesperidoside from receptacles of Podocarpus species, Oyvind M. Andersen, Phytochemistry, 1989, Volume 28, Issue 2, Pages 495–497, Neohesperidosides * Cyanidin-3-neohesperidoside * Delphinidin-3-neohesperidoside * Rhoifolin or apigenin Apigenin (4′,5,7-trihydroxyflavone), found in many plants, is a natural product belonging to the flavone class that is the aglycone of several naturally occurring glycosides. It is a yellow crystalline solid that has been used to dye wool. ... 7-''O''-neohesperidoside * Myricetin-3-''O''-neohesperidoside found in '' Physalis angulata''A novel cytotoxic flavonoid glycoside from Physalis angulata. N. Ismail and M. Alam, Fitoterapia, Volume 72, Issue 6, August 2001, Pages 676-679, * Neohesperidin ( hesperetin 7-''O''-neohesperidoside) * Neoeriocitrin ( eriodictyol 7-''O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rutinose
Rutinose is the disaccharide also known as 6-''O''-α-L- rhamnosyl-D-glucose (C12H22O10) that is present in some flavonoid glycosides. It is prepared from rutin by hydrolysis Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution reaction, substitution, elimination reaction, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water ... with the enzyme rhamnodiastase. References * Disaccharides Deoxy sugars {{organic-compound-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha-L-rhamnosidase
Alpha-L-rhamnosidase (, ''alpha-L-rhamnosidase T'', ''alpha-L-rhamnosidase N'') is an enzyme with systematic name ''alpha-L-rhamnoside rhamnohydrolase''. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction : Hydrolysis of terminal non-reducing alpha-L-rhamnose Rhamnose (Rha, Rham) is a naturally occurring deoxy sugar. It can be classified as either a methyl- pentose or a 6-deoxy- hexose. Rhamnose predominantly occurs in nature in its L-form as L-rhamnose (6-deoxy-L- mannose). This is unusual, since mo ... residues in alpha-L-rhamnosides References External links * {{Portal bar, Biology, border=no EC 3.2.1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galactose Binding Lectin Domain
In molecular biology, the galactose binding lectin domain is a protein domain. It is found in many proteins including the lectin purified from sea urchin (''Anthocidaris crassispina'') eggs, SUEL. This lectin exists as a disulfide-linked homodimer of two subunits; the dimeric form is essential for hemagglutination activity. The sea urchin egg lectin (SUEL) forms a new class of lectins. Although SUEL was first isolated as a D-galactoside binding lectin, it was later shown that it binds to L-rhamnose preferentially. L-rhamnose and D-galactose share the same hydroxyl group orientation at C2 and C4 of the pyranose ring structure. A cysteine-rich domain (the galactose binding lectin domain) homologous to the SUEL protein has been identified in the following proteins: *Plant beta-galactosidases (lactases). *Mammalian latrophilin, the calcium independent receptor of alpha- latrotoxin (CIRL). The galactose-binding lectin domain is not required for alpha-latratoxin binding. **Human la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diol
A diol is a chemical compound containing two hydroxyl groups ( groups). An aliphatic diol is also called a glycol. This pairing of functional groups is pervasive, and many subcategories have been identified. The most common industrial diol is ethylene glycol. Examples of diols in which the hydroxyl functional groups are more widely separated include 1,4-butanediol and propylene-1,3-diol, or beta propylene glycol, . Synthesis of classes of diols Geminal diols A geminal diol has two hydroxyl groups bonded to the same atom. These species arise by hydration of the carbonyl compounds. The hydration is usually unfavorable, but a notable exception is formaldehyde which, in water, exists in equilibrium with methanediol H2C(OH)2. Another example is (F3C)2C(OH)2, the hydrated form of hexafluoroacetone. Many gem-diols undergo further condensation to give dimeric and oligomeric derivatives. This reaction applies to glyoxal and related aldehydes. Vicinal diols In a vicinal dio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycerol
Glycerol (), also called glycerine in British English and glycerin in American English, is a simple triol compound. It is a colorless, odorless, viscous liquid that is sweet-tasting and non-toxic. The glycerol backbone is found in lipids known as glycerides. Because it has antimicrobial and antiviral properties, it is widely used in wound and burn treatments approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Conversely, it is also used as a bacterial culture medium. It can be used as an effective marker to measure liver disease. It is also widely used as a sweetener in the food industry and as a humectant in pharmaceutical formulations. Because of its three hydroxyl groups, glycerol is miscible with water and is hygroscopic in nature. Structure Although achiral, glycerol is prochiral with respect to reactions of one of the two primary alcohols. Thus, in substituted derivatives, the stereospecific numbering labels the molecule with a "sn-" prefix before the stem name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
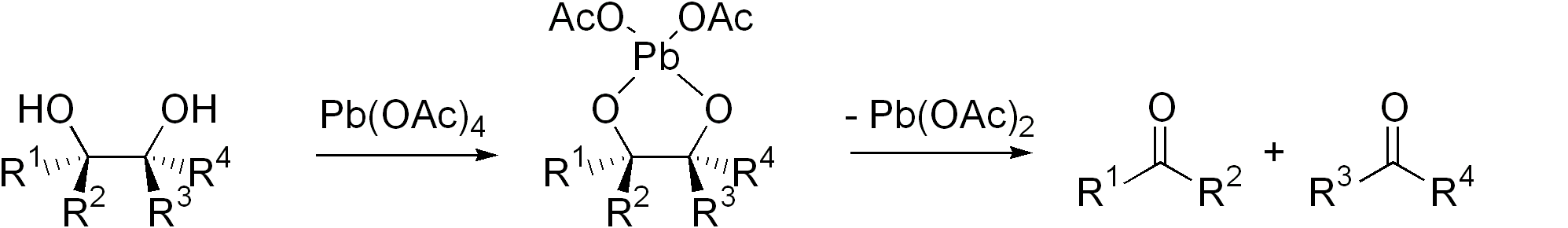
Diol Cleavage
Glycol cleavage is a specific type of organic chemistry oxidation. The carbon–carbon bond in a vicinal diol (glycol) is cleaved and instead the two oxygen atoms become double-bonded to their respective carbon atoms. Depending on the substitution pattern in the diol, these carbonyls can be either ketones or aldehydes. Glycol cleavage is an important reaction in the laboratory because it is useful for determining the structures of sugars. After cleavage takes place the ketone and aldehyde fragments can be inspected and the location of the former hydroxyl groups ascertained. Reagents Periodic acid (HIO4), (diacetoxyiodo)benzene (PhI(OAc)2) and lead tetraacetate (Pb(OAc)4) are the most common reagents used for glycol cleavage, processes called the Malaprade reaction and Criegee oxidation, respectively. These reactions are most efficient when a cyclic intermediate can form, with the iodine or lead atom linking both oxygen atoms. The ring then fragments, with breakage of the car ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vicinal (chemistry)
In chemistry the descriptor vicinal (from Latin ''vicinus'' = neighbor), abbreviated ''vic'', describes any two functional groups bonded to two adjacent carbon atoms (i.e., in a 1,2-relationship). Relation of atoms in a molecule For example, the molecule 2,3-dibromobutane carries two vicinal bromine atoms and 1,3-dibromobutane does not. Mostly, the use of the term vicinal is restricted to two ''identical'' functional groups. Likewise in a ''gem-''dibromide the prefix ''gem'', an abbreviation of geminal, signals that both bromine atoms are bonded to the ''same'' atom (i.e., in a 1,1-relationship). For example, 1,1-dibromobutane is geminal. While comparatively less common, the term hominal has been suggested as a descriptor for groups in a 1,3-relationship. Like other such descriptors as syn, anti, exo or endo, the description ''vicinal'' helps explain how different parts of a molecule are related to each other either structurally or spatially. The vicinal adjective is some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Periodate
Periodate is an anion composed of iodine and oxygen. It is one of a number of oxyanions of iodine and is the highest in the series, with iodine existing in oxidation state +7. Unlike other perhalogenates, such as perchlorate, it can exist in two forms: metaperiodate and orthoperiodate . In this regard it is comparable to the tellurate ion from the adjacent group. It can combine with a number of counter ions to form periodates, which may also be regarded as the salts of periodic acid. Periodates were discovered by Heinrich Gustav Magnus and C. F. Ammermüller; who first synthesised periodic acid in 1833. Synthesis Classically, periodate was most commonly produced in the form of sodium hydrogen periodate (). This is commercially available, but can also be produced by the oxidation of iodates with chlorine and sodium hydroxide. Or, similarly, from iodides by oxidation with bromine and sodium hydroxide: :\overset + Cl2 + 4 NaOH -> Na3H2IO6 + 2NaCl + H2O :NaI + 4 Br2 + 10 NaOH ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formaldehyde
Formaldehyde ( , ) ( systematic name methanal) is a naturally occurring organic compound with the formula and structure . The pure compound is a pungent, colourless gas that polymerises spontaneously into paraformaldehyde (refer to section Forms below), hence it is stored as an aqueous solution (formalin), which is also used to store animal specimens. It is the simplest of the aldehydes (). The common name of this substance comes from its similarity and relation to formic acid. Formaldehyde is an important precursor to many other materials and chemical compounds. In 1996, the installed capacity for the production of formaldehyde was estimated at 8.7 million tons per year. It is mainly used in the production of industrial resins, e.g., for particle board and coatings. Forms Formaldehyde is more complicated than many simple carbon compounds in that it adopts several diverse forms. These compounds can often be used interchangeably and can be interconverted. *Molecular for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |