|
Religion In Hubei
Hubei (; ; alternately Hupeh) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China, and is part of the Central China region. The name of the province means "north of the lake", referring to its position north of Dongting Lake. The provincial capital, Wuhan, serves as a major transportation hub and the political, cultural, and economic hub of central China. Hubei's name is officially abbreviated to "" (), an ancient name associated with the eastern part of the province since the State of E of the Western Zhou dynasty of –771 BCE; a popular name for Hubei is "" () (suggested by that of the powerful State of Chu, which existed in the area during the Eastern Zhou dynasty of 770 – 256 BCE). Hubei borders the provinces of Henan to the north, Anhui to the east, Jiangxi to the southeast, Hunan to the south, Chongqing to the west, and Shaanxi to the northwest. The high-profile Three Gorges Dam is located at Yichang, in the west of the province. Hubei is the 7th-largest pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hebei
Hebei or , (; alternately Hopeh) is a northern province of China. Hebei is China's sixth most populous province, with over 75 million people. Shijiazhuang is the capital city. The province is 96% Han Chinese, 3% Manchu, 0.8% Hui, and 0.3% Mongol. Three Mandarin dialects are spoken: Jilu Mandarin, Beijing Mandarin and Jin. Hebei borders the provinces of Shanxi to the west, Henan to the south, Shandong to the southeast, Liaoning to the northeast, and the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region to the north. Its economy is based on agriculture and manufacturing. The province is China's premier steel producer, although the steel industry creates serious air pollution. Five UNESCO World Heritage Sites can be found in the province, the: Great Wall of China, Chengde Mountain Resort, Grand Canal, Eastern Qing tombs, and Western Qing tombs. It is also home to five National Famous Historical and Cultural Cities: Handan, Baoding, Chengde, Zhengding and Shanhaiguan. Historic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Governor (China)
In China, the governor () is the head of government of a province. There are currently 22 provincial governors under PRC control; in China's five autonomous regions, the analogous head of the provincial government is officially titled a chairman, not a governor. Legal basis In the Constitution of the Republic of China promulgated on December 25, 1947, Chapter XI, Article 113, Section 2 describes that in each province, there shall be a provincial government with a provincial governor who shall be elected by the people of the province. This was codified in Article 9, Section 1 in the Additional Articles of the Constitution of the Republic of China in 2005. Source of talent Most if not all governors are not local to the provinces they are appointed to govern. In many cases, they are from outside the province and are graduates of the Central Party School of the Chinese Communist Party or CCP affiliated education institutions. Most governors were deputy governors, bureaucrats in c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Yangtze Mandarin
Lower Yangtze Mandarin () is one of the most divergent and least mutually-intelligible of the Mandarin languages, as it neighbours the Wu, Hui, and Gan groups of Sinitic languages. It is also known as Jiang–Huai Mandarin (), named after the Yangtze (Jiang) and Huai Rivers. Lower Yangtze is distinguished from most other Mandarin varieties by the retention of a final glottal stop in words that ended in a stop consonant in Middle Chinese. During the Ming dynasty and early Qing dynasty, the lingua franca of administration was based on Lower Yangtze Mandarin. In the 19th century the base shifted to the Beijing dialect. Geographic distribution Lower Yangtze Mandarin is spoken in central Anhui, eastern Hubei, most of Jiangsu north of the Yangtze, as well as the area around Nanjing. The number of speakers was estimated in 1987 at 67 million. Subgrouping The ''Language Atlas of China'' divides Lower Yangtze Mandarin into three branches: ;Hongchao dialects :The largest and mos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
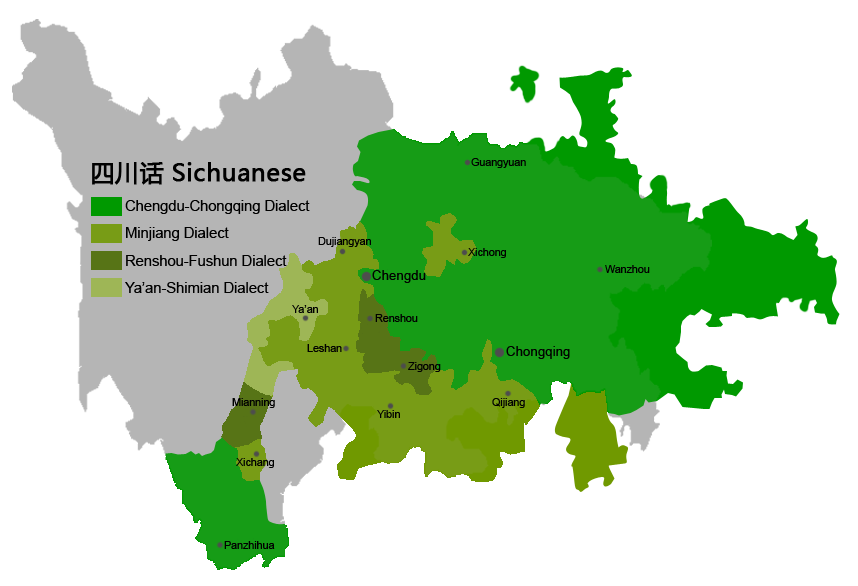
Southwestern Mandarin
Southwestern Mandarin (), also known as Upper Yangtze Mandarin (), is a Mandarin Chinese language spoken in much of Southwest China, including in Sichuan, Yunnan, Chongqing, Guizhou, most parts of Hubei, the northwestern part of Hunan, the northern part of Guangxi and some southern parts of Shaanxi and Gansu. Southwestern Mandarin is spoken by roughly 260 million people. If considered a language distinct from central Mandarin, it would be the eighth-most spoken language by native speakers in the world, behind Mandarin itself, Spanish, English, Hindi, Portuguese, Arabic and Bengali. Overview Modern Southwestern Mandarin was formed by the waves of immigrants brought to the regions during the Ming and Qing Dynasties. Because of the comparatively recent move, such dialects show more similarity to modern Standard Mandarin than to other varieties of Chinese like Cantonese or Hokkien. For example, like most Southern Chinese dialects, Southwestern Mandarin does not possess the retroflex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hmong People
The Hmong people ( RPA: ''Hmoob'', Nyiakeng Puachue: , Pahawh Hmong: , ) are a sub-ethnic group of the Miao people who originated from Central China. The modern Hmongs presently reside mainly in Southwest China (Guizhou, Yunnan, Sichuan, Chongqing, and Guangxi) and countries in Southeast Asia such as Vietnam, Laos, Thailand, and Myanmar. There is also a very large diasporic community in the United States, comprising more than 300,000 Hmong. The Hmong diaspora also has smaller communities in Australia and South America (specifically Argentina and French Guiana, the latter being an overseas region of France). During the First and Second Indo-China Wars, France and the United States intervened in the Lao Civil War by recruiting thousands of Hmong people to fight against forces from North and South Vietnam, which were stationed in Laos in accordance with their mission to support the communist Pathet Lao insurgents. The CIA operation is known as the Secret War. Etymol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tujia People
The Tujia ( Northern Tujia: ''Bifjixkhar'' / ''Bifzixkar'', IPA: , Southern Tujia: ''Mongrzzir'', ; ) are an ethnic group and, with a total population of over 8 million, the eighth-largest officially recognized ethnic minority in the People's Republic of China. They live in the Wuling Mountains, straddling the common borders of Hunan, Hubei and Guizhou Provinces and Chongqing Municipality. The endonym ''Bizika'' means "native dwellers". In Chinese, ''Tujia'' literally means "local families", in contrast to the Hakka (), whose name literally means "guest families" and implies migration. Origins Although there are different accounts of their origins, the Tujia may trace their history back over twelve centuries and possibly beyond, to the ancient Ba people who occupied the area around modern-day Chongqing some 2,500 years ago. The Ba Kingdom reached the zenith of its power between 600 BC and 400 BC but was destroyed by the Qin in 316 BC. After being referred to by a long suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Han Chinese
The Han Chinese () or Han people (), are an East Asian ethnic group native to China. They constitute the world's largest ethnic group, making up about 18% of the global population and consisting of various subgroups speaking distinctive varieties of the Chinese language. The estimated 1.4 billion Han Chinese people, worldwide, are primarily concentrated in the People's Republic of China (including Mainland China, Hong Kong and Macau) where they make up about 92% of the total population. In the Republic of China (Taiwan), they make up about 97% of the population. People of Han Chinese descent also make up around 75% of the total population of Singapore. Originating from Northern China, the Han Chinese trace their cultural ancestry to the Huaxia, the confederation of agricultural tribes living along the Yellow River. This collective Neolithic confederation included agricultural tribes Hua and Xia, hence the name. They settled along the Central Plains around the middle and lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Chinese Administrative Divisions By Population Density
The provincial level administrative divisions () are the highest-level administrative divisions of China. There are 34 such divisions claimed by the People's Republic of China, classified as 23 provinces (), five autonomous regions, four municipalities and two special administrative regions. The political status of Taiwan Province along with a small fraction of Fujian Province remain in dispute; those are under separate rule by the Republic of China, which is usually referred to as "Taiwan". Every province on Mainland China (including the island province of Hainan) has a Chinese Communist Party (CCP) provincial committee (), headed by a secretary (). The Committee Secretary is effectively in charge of the province, rather than the governor of the provincial government. The same arrangement exists for the autonomous regions and municipalities. Types of provincial level divisions Province The government of each standard province () is nominally led by a provincial committee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Chinese Administrative Divisions By Population
This is a list of Chinese administrative divisions in order of their total resident populations. It includes all provinces, autonomous regions, direct-controlled municipalities and special administrative regions controlled by the Republic of China (1912–1949) or the People's Republic of China (1949–present). For the Republic of China after 1949, see List of administrative divisions of Taiwan. Census data Current population References Footnotes Sources {{DEFAULTSORT:Chinese Administrative Divisions By Population Population Population Population typically refers to the number of people in a single area, whether it be a city or town, region, country, continent, or the world. Governments typically quantify the size of the resident population within their jurisdiction using a ... Demographic lists China, population ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Bureau Of Statistics Of China
The National Bureau of Statistics (), abbreviated as NBS, is an deputy-cabinet level agency directly under the State Council of the People's Republic of China. It is responsible for collection, investigation, research and publication of statistics concerning the nation's economy, population and other aspects of the society. Ning Jizhe is the commissioner of the bureau since 2016. Responsibilities The bureau's authority and responsibilities are defined in ''China's Statistics Law''. It is responsible for the research of the nation's overall statistics and oversee the operations of its local counterparts. Organizations The bureau is led by a commissioner, with several deputy commissioners (currently four), a chief methodologist, a chief economist, and a chief information officer. It is composed of 18 departments, oversees 12 affiliated institutions and manages 32 survey organizations stationed in respective provinces. It also operates China Statistics Press. The national b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
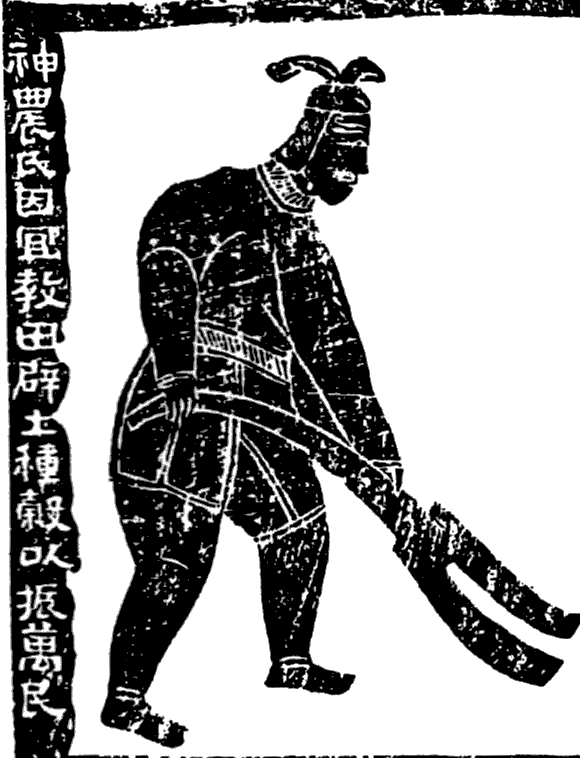
Shennong Peak
Shennong (), variously translated as "Divine Farmer" or "Divine Husbandman", born Jiang Shinian (), was a mythological Chinese ruler known as the first Yan Emperor who has become a deity in Chinese and Vietnamese folk religion. He is venerated as a culture hero in China and Vietnam. In Vietnamese he is referred to as Thần Nông. Shennong has at times been counted amongst the Three Sovereigns (also known as "Three Kings" or "Three Patrons"), a group of ancient deities or deified kings of prehistoric China. Shennong has been thought to have taught the ancient Chinese not only their practices of agriculture, but also the use of herbal drugs. Shennong was credited with various inventions: these include the hoe, plow (both ''leisi'' () style and the plowshare), axe, digging wells, agricultural irrigation, preserving stored seeds by using boiled horse urine, the weekly farmers market, the Chinese calendar (especially the division into the 24 ''jieqi'' or solar terms), and to ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Chinese Administrative Divisions By Area
This is a list of the first-level administrative divisions of the People's Republic of China (PRC), including all provinces (except the claimed Taiwan Province), autonomous regions, special administrative regions, and municipalities, in order of their total land area as reported by the national or provincial-level government. Notes References {{reflist, 30em Area Area is the quantity that expresses the extent of a region on the plane or on a curved surface. The area of a plane region or ''plane area'' refers to the area of a shape A shape or figure is a graphics, graphical representation of an obje ... China, area ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)