|
Reichsgaue
A (plural ) was an administrative subdivision created in a number of areas annexed by Nazi Germany between 1938 and 1945. Overview The term was formed from the words (realm, empire) and , the latter a deliberately medieval-sounding word with a meaning approximately equivalent to '' shire''. The were an attempt to resolve the administrative chaos resulting from the mutually overlapping jurisdictions and different boundaries of the NSDAP Party , placed under a Party , and the federal states, under a responsible to the Ministry of the Interior (in the Prussian provinces, the equivalent post was that of ). Interior Minister Wilhelm Frick had long desired to streamline the German administration, and the were the result: the borders of party and those of the federal states were to be identical, and the party also occupied the post of . Rival interests and the influence the wielded with Hitler prevented any reform from being undertaken in the " Old Reich" (german: Altreich), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gau (German)
''Gau'' (German , nl, gouw , fy, gea or ''goa'' ) is a Germanic term for a region within a country, often a former or current province. It was used in the Middle Ages, when it can be seen as roughly corresponding to an English shire. The administrative use of the term was revived as a subdivision during the period of Nazi Germany in 1933–1945. It still appears today in regional names, such as the Rheingau or Allgäu. Middle Ages Etymology The Germanic word is reflected in Gothic ''gawi'' (neuter; genitive ''gaujis'') and early Old High German ''gewi, gowi'' (neuter) and in some compound names ''-gawi'' as in Gothic (e.g. ''Durgawi'' " Canton of Thurgau", ''Alpagawi'' "Allgäu"), later ''gâi, gôi'', and after loss of the stem suffix ''gaw, gao'', and with motion to the feminine as ''gawa'' besides ''gowo'' (from ''gowio''). Old Saxon shows further truncation to ''gâ, gô''. As an equivalent of Latin ''pagus'', a ''gau'' is analogous with a ''pays'' of the Kingdom of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gau (country Subdivision)
''Gau'' (German , nl, gouw , fy, gea or ''goa'' ) is a Germanic term for a region within a country, often a former or current province. It was used in the Middle Ages, when it can be seen as roughly corresponding to an English shire. The administrative use of the term was revived as a subdivision during the period of Nazi Germany in 1933–1945. It still appears today in regional names, such as the Rheingau or Allgäu. Middle Ages Etymology The Germanic word is reflected in Gothic ''gawi'' (neuter; genitive ''gaujis'') and early Old High German ''gewi, gowi'' (neuter) and in some compound names ''-gawi'' as in Gothic (e.g. ''Durgawi'' " Canton of Thurgau", ''Alpagawi'' "Allgäu"), later ''gâi, gôi'', and after loss of the stem suffix ''gaw, gao'', and with motion to the feminine as ''gawa'' besides ''gowo'' (from ''gowio''). Old Saxon shows further truncation to ''gâ, gô''. As an equivalent of Latin ''pagus'', a ''gau'' is analogous with a ''pays'' of the Kingdom of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NSDAP
The Nazi Party, officially the National Socialist German Workers' Party (german: Nationalsozialistische Deutsche Arbeiterpartei or NSDAP), was a far-right politics, far-right political party in Germany active between 1920 and 1945 that created and supported the ideology of Nazism. Its precursor, the German Workers' Party (; DAP), existed from 1919 to 1920. The Nazi Party emerged from the Extremism, extremist German nationalism, German nationalist, racism, racist and populism, populist paramilitary culture, which fought against the communism, communist uprisings in post–World War I Germany. The party was created to draw workers away from communism and into nationalism. Initially, Nazi political strategy focused on anti–big business, anti-bourgeoisie, bourgeois, and anti-capitalism, anti-capitalist rhetoric. This was later downplayed to gain the support of business leaders, and in the 1930s, the party's main focus shifted to Antisemitism, antisemitic and Criticism of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
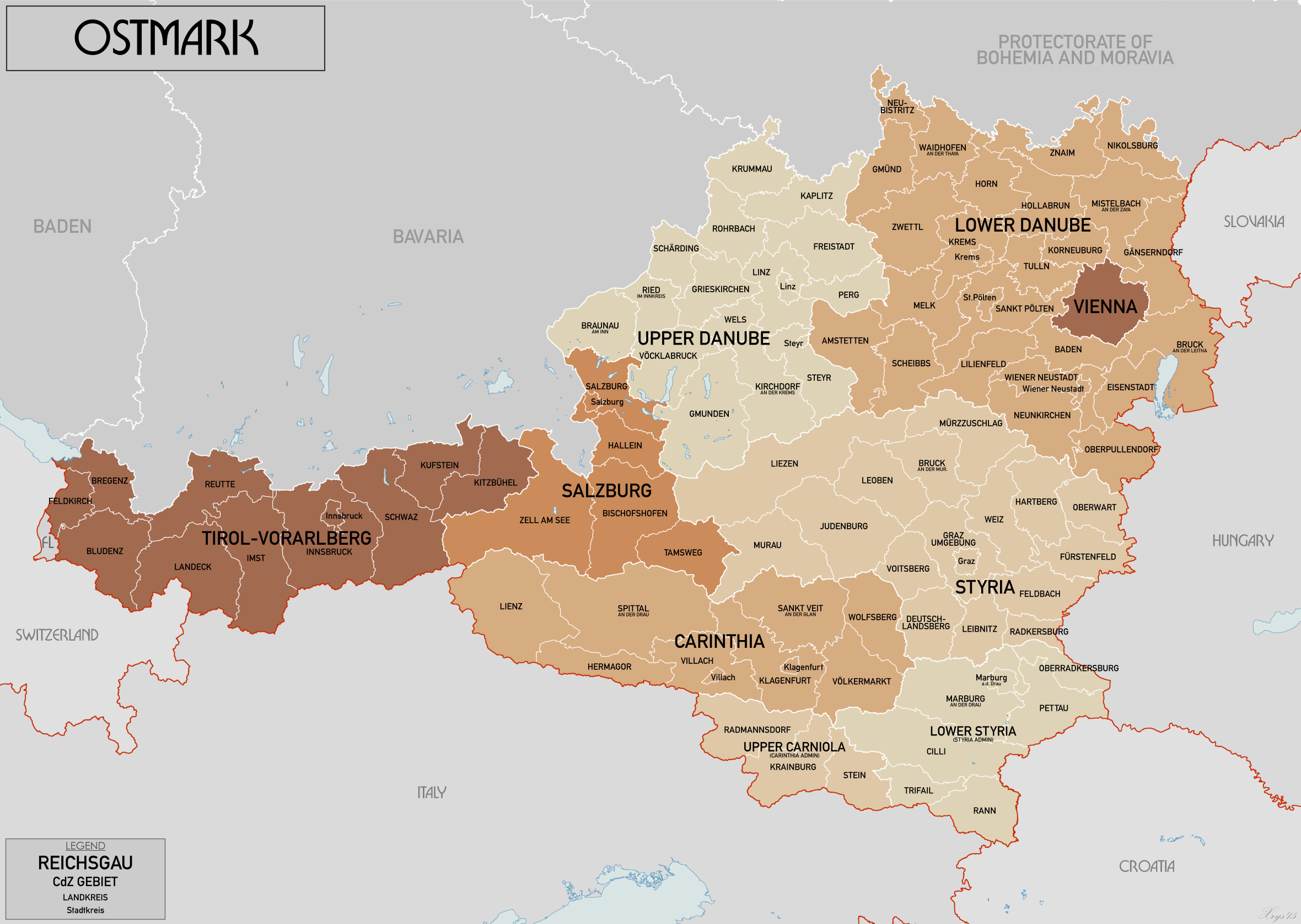
Ostmark (Austria)
Ostmark (, "Eastern March") was the name used by Nazi propaganda from 1938 to 1942 to replace that of the formerly independent Federal State of Austria after the ''Anschluss'' with Nazi Germany. From the ''Anschluss'' until 1939, the official name used was Land Österreich ("State of Austria"). History Once Austrian-born Adolf Hitler completed the union between his birth country and Germany ''(Anschluss)'', the Nazi government had the incorporated territory renamed. The name ''Austria'' (''Österreich'' in German, meaning "Eastern Realm") was at first replaced by "Ostmark", referring to the 10th century '' Marcha orientalis''. The change was meant to refer to Austria as the new "eastern march" of the Reich. In August 1938, the ''Donau-Zeitung'' proudly referred to Passau as "the cradle of the new ''Ostmark''". Subdivision According to the ''Ostmarkgesetz'' with effect from 1 May 1939 the former States of Austria were reorganized into seven ''Reichsgaue'', each under the rule of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gauleiter
A ''Gauleiter'' () was a regional leader of the Nazi Party (NSDAP) who served as the head of a ''Administrative divisions of Nazi Germany, Gau'' or ''Reichsgau''. ''Gauleiter'' was the third-highest Ranks and insignia of the Nazi Party, rank in the Nazi political leadership, subordinate only to ''Reichsleiter'' and to the ''Führer'' himself. The position was effectively abolished with the fall of the Nazi regime on 8 May 1945. History and development Origin and early years The first use of the term ''Gauleiter'' by the Nazi Party was in 1925 around the time Adolf Hitler re-founded the Party on 27 February, after the lifting of the ban that had been imposed on it in the aftermath of the Beer Hall Putsch of 9 November 1923. The word can be singular or plural in German usage, depending on its context, and derives from the German language, German words ''Gau (territory), Gau'' and ''leiter'' (''leader''). The word ''Gau'' is an old term for a region of the German ''Reich'' (Emp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sudetenland
The Sudetenland ( , ; Czech and sk, Sudety) is the historical German name for the northern, southern, and western areas of former Czechoslovakia which were inhabited primarily by Sudeten Germans. These German speakers had predominated in the border districts of Bohemia, Moravia, and Czech Silesia since the Middle Ages. Sudetenland had been since the 9th century an integral part of the Czech state (first within the Duchy of Bohemia and later the Kingdom of Bohemia) both geographically and politically. The word "Sudetenland" did not come into being until the early part of the 20th century and did not come to prominence until almost two decades into the century, after World War I, when Austria-Hungary was dismembered and the Sudeten Germans found themselves living in the new country of Czechoslovakia. The ''Sudeten crisis'' of 1938 was provoked by the Pan-Germanist demands of Nazi Germany that the Sudetenland be annexed to Germany, which happened after the later Munich Agreeme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carinthia (state)
Carinthia (german: Kärnten ; sl, Koroška ) is the southernmost Austrian state, in the Eastern Alps, and is noted for its mountains and lakes. The main language is German. Its regional dialects belong to the Southern Bavarian group. Carinthian Slovene dialects, forms of a South Slavic language that predominated in the southeastern part of the region up to the first half of the 20th century, are now spoken by a small minority in the area. Carinthia's main industries are tourism, electronics, engineering, forestry, and agriculture. Name The etymology of the name "Carinthia", similar to Carnia or Carniola, has not been conclusively established. The ''Ravenna Cosmography'' (about AD 700) referred to a Slavic "Carantani" tribe as the eastern neighbours of the Bavarians. In his ''History of the Lombards'', the 8th-century chronicler Paul the Deacon mentions "Slavs in Carnuntum, which is erroneously called Carantanum" (''Carnuntum, quod corrupte vocitant Carantanum'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Klagenfurt
Klagenfurt am WörtherseeLandesgesetzblatt 2008 vom 16. Jänner 2008, Stück 1, Nr. 1: ''Gesetz vom 25. Oktober 2007, mit dem die Kärntner Landesverfassung und das Klagenfurter Stadtrecht 1998 geändert werden.'/ref> (; ; sl, Celovec), usually known as just Klagenfurt ( ), is the capital of the state of Carinthia in Austria. With a population of 103,009 (1 January 2022), it is the sixth-largest city in the country. The city is the bishop's seat of the Roman Catholic Diocese of Gurk-Klagenfurt and home to the University of Klagenfurt, the Carinthian University of Applied Sciences and the Gustav Mahler University of Music. Geography Location The city of Klagenfurt is in southern Austria, near the border with Slovenia. It is in the lower middle of Austria, almost the same distance from Innsbruck in the west as it is from Vienna in the northeast. Klagenfurt is elevated above sea level and covers an area of . It is on the lake Wörthersee and on the Glan river. The city is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Tyrol
East Tyrol, occasionally East Tirol (german: Osttirol), is an exclave of the Austrian state of Tyrol, separated from the main North Tyrol part by the short common border of Salzburg and Italian South Tyrol (''Südtirol'', it, Alto Adige). It is congruent with the administrative district (''Bezirk'') of Lienz. History The area around the former Roman ''municipium'' of Aguntum was, from the 12th century, held by the Counts of Gorizia, who took their residence at Lienz and inherited the County of Tyrol in 1253. While Tyrol was lost to the Austrian House of Habsburg in 1363, the Gorizian counts retained Lienz until the extinction of the line in 1500. Emperor Maximilian I of Habsburg finally incorporated it into Austrian Tyrol. East Tyrol's present-day situation arose from the defeat of the Austro-Hungarian Empire in World War I and its subsequent dissolution. By the 1915 Treaty of London, the Kingdom of Italy, which had joined the victorious Triple Entente, was to obtain the Tyrol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reichsgau Kärnten
The Reichsgau Carinthia (German: ''Reichsgau Kärnten'') was an administrative division of Nazi Germany in Carinthia and East Tyrol (both in Austria) and Upper Carniola in Slovenia. It existed from 1938 to 1945. It was responsible for the administration of the ''de facto'' annexed Operational Zone of the Adriatic Littoral (''Operationszone Adriatisches Küstenland'', OZAK). History The Nazi Gau (plural Gaue) system was originally established in a party conference on 22 May 1926, in order to improve administration of the party structure. From 1933 onwards, after the Nazi seizure of power, the ''Gaue'' increasingly replaced the German states as administrative subdivisions in Germany. On 12 March 1938 Nazi Germany annexed Austria and on 24 May the Austrian provinces were reorganized and replaced by seven Nazi party ''Gaue.''"Administration of Austria," ''The Times'' (London) 25 May 1938, page 15. Under the Ostmarkgesetz law of 14 April 1939 with effect of 1 May, the Austrian ''Gaue'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slovenia
Slovenia ( ; sl, Slovenija ), officially the Republic of Slovenia (Slovene: , abbr.: ''RS''), is a country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the west, Austria to the north, Hungary to the northeast, Croatia to the southeast, and the Adriatic Sea to the southwest. Slovenia is mostly mountainous and forested, covers , and has a population of 2.1 million (2,108,708 people). Slovenes constitute over 80% of the country's population. Slovene, a South Slavic language, is the official language. Slovenia has a predominantly temperate continental climate, with the exception of the Slovene Littoral and the Julian Alps. A sub-mediterranean climate reaches to the northern extensions of the Dinaric Alps that traverse the country in a northwest–southeast direction. The Julian Alps in the northwest have an alpine climate. Toward the northeastern Pannonian Basin, a continental climate is more pronounced. Ljubljana, the capital and largest city of Slovenia, is geogr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Polish Republic
The Second Polish Republic, at the time officially known as the Republic of Poland, was a country in Central Europe, Central and Eastern Europe that existed between 1918 and 1939. The state was established on 6 November 1918, before the end of the First World War. The Second Republic ceased to exist in 1939, when Invasion of Poland, Poland was invaded by Nazi Germany, the Soviet Union and the Slovak Republic (1939–1945), Slovak Republic, marking the beginning of the European theatre of World War II, European theatre of the Second World War. In 1938, the Second Republic was the sixth largest country in Europe. According to the Polish census of 1921, 1921 census, the number of inhabitants was 27.2 million. By 1939, just before the outbreak of World War II, this had grown to an estimated 35.1 million. Almost a third of the population came from minority groups: 13.9% Ruthenians; 10% Ashkenazi Jews; 3.1% Belarusians; 2.3% Germans and 3.4% Czechs and Lithuanians. At the same time, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |