|
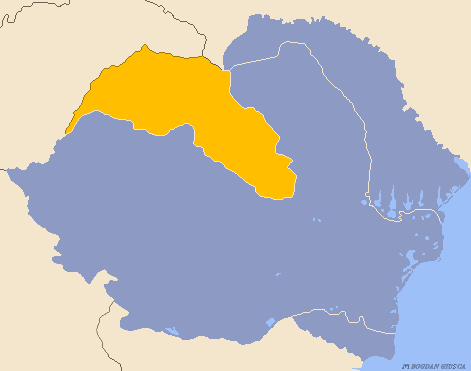
Reformed Diocese Of Transylvania
The Reformed Diocese of Transylvania ( hu, Erdélyi Református Egyházkerület; ro, Episcopia Reformată din Ardeal) is a moderately conservative Reformed, Calvinist church in Romania; its seat is in Cluj-Napoca. Alongside the Reformed Diocese of Királyhágómellék, which has its seat in Oradea, it forms the Reformed Church in Romania. History The Reformation took roots in Transylvania in the 1550s. Among the Hungarian-speaking population, the Calvinist branch was the dominant religion. In 1564, in the Synod of Nagyenyed (Aiud), the Calvinists and the Lutherans separated. This is the formation date of the Transylvanian Reformed Church, which formed part of the Reformed Church in Hungary and officially adopted the Heidelberg Catechism. At the end of the 16th century, the Reformed Church became the dominant church in the Duchy of Transylvania. The church has schools in Deva, Târgu Mureș, Aiud, Alba Iulia, Făgăraș and Târgu Secuiesc. The dukes of Transylvania belonged to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protestant
Protestantism is a Christian denomination, branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Reformation, Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century against what its followers perceived to be growing Criticism of the Catholic Church, errors, abuses, and discrepancies within it. Protestantism emphasizes the Christian believer's justification by God in faith alone (') rather than by a combination of faith with good works as in Catholicism; the teaching that Salvation in Christianity, salvation comes by Grace in Christianity, divine grace or "unmerited favor" only ('); the Universal priesthood, priesthood of all faithful believers in the Church; and the ''sola scriptura'' ("scripture alone") that posits the Bible as the sole infallible source of authority for Christian faith and practice. Most Protestants, with the exception of Anglo-Papalism, reject the Catholic doctrine of papal supremacy, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heidelberg Catechism
The Heidelberg Catechism (1563), one of the Three Forms of Unity, is a Protestant confessional document taking the form of a series of questions and answers, for use in teaching Calvinist Christian doctrine. It was published in 1563 in Heidelberg, Germany. Its original title translates to ''Catechism, or Christian Instruction, according to the Usages of the Churches and Schools of the Electoral Palatinate''. Commissioned by the prince-elector of the Electoral Palatinate, it is sometimes referred to as the "Palatinate Catechism." It has been translated into many languages and is regarded as one of the most influential of the Reformed catechisms. History Elector Frederick III, sovereign of the Electoral Palatinate from 1559 to 1576, commissioned the composition of a new Catechism for his territory. While the catechism's introduction credits the "entire theological faculty here" (at the University of Heidelberg) and "all the superintendents and prominent servants of the church"Emil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communist Romania
The Socialist Republic of Romania ( ro, Republica Socialistă România, RSR) was a Marxism–Leninism, Marxist–Leninist One-party state, one-party socialist state that existed officially in Romania from 1947 to 1989. From 1947 to 1965, the state was known as the Romanian People's Republic (, RPR). The country was an Eastern Bloc state and a member of the Warsaw Pact with a dominant role for the Romanian Communist Party enshrined in :Template:RomanianConstitutions, its constitutions. Geographically, RSR was bordered by the Black Sea to the east, the Soviet Union (via the Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic, Ukrainian and Moldavian Soviet Socialist Republic, Moldavian SSRs) to the north and east, Hungarian People's Republic, Hungary and Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, Yugoslavia (via Socialist Republic of Serbia, SR Serbia) to the west, and People's Republic of Bulgaria, Bulgaria to the south. As World War II ended, Kingdom of Romania, Romania, a former Axis powers, A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Transylvania
Northern Transylvania ( ro, Transilvania de Nord, hu, Észak-Erdély) was the region of the Kingdom of Romania that during World War II, as a consequence of the August 1940 territorial agreement known as the Second Vienna Award, became part of the Kingdom of Hungary. With an area of , the population was largely composed of both ethnic Romanians and Hungarians. In October 1944, Soviet and Romanian forces gained control of the territory, and by March 1945 Northern Transylvania returned to Romanian administration. After the war, this was confirmed by the Paris Peace Treaties of 1947. Background The region has a varied history. It was once the nucleus of the Kingdom of Dacia (82 BC–106 AD). In 106 AD the Roman Empire conquered the territory, systematically exploiting its resources. After the Roman legions withdrew in 271 AD, it was overrun by a succession of various tribes, bringing it under the control of the Carpi, Visigoths, Huns, Gepids, Avars, and Slavs. During the 9th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Union Of Transylvania With Romania
The union of Transylvania with Romania was declared on by the assembly of the delegates of ethnic Romanians held in Alba Iulia. The Great Union Day (also called ''Unification Day''), celebrated on 1 December, is a national holiday in Romania that celebrates this event. The holiday was established after the Romanian Revolution, and celebrates the unification not only of Transylvania, but also of Bessarabia and Bukovina and parts of Banat, Crișana and Maramureș with the Romanian Kingdom. Bessarabia and Bukovina had joined with the Kingdom of Romania earlier in 1918. Causes and leading events *August 17, 1916: Romania signed a secret treaty with the Entente Powers (United Kingdom, France, Italy and Russia), according to which Transylvania, Banat, and Partium would become part of Romania after World War I if the country entered the war. The planned border followed a line some 20-40 kilometres west of the present Hungarian-Romanian border, but joined river Tisza in the South, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated between the Baltic and North seas to the north, and the Alps to the south; it covers an area of , with a population of almost 84 million within its 16 constituent states. Germany borders Denmark to the north, Poland and the Czech Republic to the east, Austria and Switzerland to the south, and France, Luxembourg, Belgium, and the Netherlands to the west. The nation's capital and most populous city is Berlin and its financial centre is Frankfurt; the largest urban area is the Ruhr. Various Germanic tribes have inhabited the northern parts of modern Germany since classical antiquity. A region named Germania was documented before AD 100. In 962, the Kingdom of Germany formed the bulk of the Holy Roman Empire. During the 16th ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Netherlands
) , anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau") , image_map = , map_caption = , subdivision_type = Sovereign state , subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands , established_title = Before independence , established_date = Spanish Netherlands , established_title2 = Act of Abjuration , established_date2 = 26 July 1581 , established_title3 = Peace of Münster , established_date3 = 30 January 1648 , established_title4 = Kingdom established , established_date4 = 16 March 1815 , established_title5 = Liberation Day (Netherlands), Liberation Day , established_date5 = 5 May 1945 , established_title6 = Charter for the Kingdom of the Netherlands, Kingdom Charter , established_date6 = 15 December 1954 , established_title7 = Dissolution of the Netherlands Antilles, Caribbean reorganisation , established_date7 = 10 October 2010 , official_languages = Dutch language, Dutch , languages_type = Regional languages , languages_sub = yes , languages = , languages2_type = Reco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Switzerland
). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the federal parliament and government are installed in Bern, while other federal institutions, such as the federal courts, are in other cities (Bellinzona, Lausanne, Luzern, Neuchâtel, St. Gallen a.o.). , coordinates = , largest_city = Zürich , official_languages = , englishmotto = "One for all, all for one" , religion_year = 2020 , religion_ref = , religion = , demonym = , german: Schweizer/Schweizerin, french: Suisse/Suissesse, it, svizzero/svizzera or , rm, Svizzer/Svizra , government_type = Federalism, Federal assembly-independent Directorial system, directorial republic with elements of a direct democracy , leader_title1 = Federal Council (Switzerland), Federal Council , leader_name1 = , leader_title2 = , leader_name2 = Walter Thurnherr , legislature = Fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reformed City Fortress Church Of Targu Mures
Reform is beneficial change Reform may also refer to: Media * ''Reform'' (album), a 2011 album by Jane Zhang *Reform (band), a Swedish jazz fusion group * ''Reform'' (magazine), a Christian magazine *''Reforme'' ("Reforms"), initial name of the Aromanian newspaper ''Românul de la Pind'' Places *Reform, Alabama *Reform, Mississippi *Reform, Missouri Religion *Reform (religion), the process of reforming teachings within a religious community *Reform (Anglican), an evangelical organisation within Anglicanism *Reform Judaism, a denomination of Judaism *Reformed tradition or Calvinism, a Protestant branch of Christianity Other *Reform (horse) (1964–1983), a Thoroughbred racehorse *Reform (think tank), a British think tank *Reform Act, a series of 19th- and 20th-century UK voting reforms *Reform Club (other) *Reform Movement (other) *Reform Party (other) See also *Catalytic reforming, a chemical process in oil refining *''La Reforma'' or The Liberal Ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gabor Bethlen
Gabriel Bethlen ( hu, Bethlen Gábor; 15 November 1580 – 15 November 1629) was Prince of Transylvania from 1613 to 1629 and Duke of Opole from 1622 to 1625. He was also King-elect of Hungary from 1620 to 1621, but he never took control of the whole kingdom. Bethlen, supported by the Ottomans, led his Calvinist principality against the Habsburgs and their Catholic allies. Early life Gabriel was the elder of the two sons of Farkas Bethlen de Iktár and Druzsiána Lázár de Szárhegy. Gabriel was born in his father's estate, Marosillye (now Ilia in Romania), on 15 November 1580. Farkas Bethlen was a Hungarian nobleman who lost his ancestral estate, Iktár (now Ictar-Budinț in Romania), due to the Ottoman occupation of the central territories of the Kingdom of Hungary. Stephen Báthory, Prince of Transylvania, granted Marosillye to him and made him captain-general of the principality. Druzsiána Lázár was descended from a Székely noble family. Both Farkas Bethlen and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Târgu Secuiesc
Târgu Secuiesc (; hu, Kézdivásárhely, ; german: Szekler Neumarkt; la, Neoforum Siculorum) is a municipiu, city in Covasna County, Transylvania, Romania. It administers one village, Lunga (''Nyujtód''). History The town was first mentioned in 1407 as ''Torjawasara'', meaning in Hungarian “Torja Market”. (Turia (Cașin), Torja is the name of a stream nearby and is also the Hungarian name of the nearby village Turia, Covasna, Turia.) Originally, the Hungarian name Kézdivásárhely was also used in Romanian in the form Chezdi-Oșorheiu, but this was altered to Tîrgu Secuiesc (now spelled Târgu Secuiesc) after the accession to Romania in 1920 under the Treaty of Trianon. The Hungarian native name means “Kézdi Market”, Kézdi being the name of a Székely Land, Székely “seat”, a historical administrative unit. Its status as a market town dates back to the Middle Ages. The city was taken over by Hungary during World War II, following the Second Vienna Award of Aug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Făgăraș
Făgăraș (; german: Fogarasch, Fugreschmarkt, hu, Fogaras) is a municipiu, city in central Romania, located in Brașov County. It lies on the Olt (river), Olt River and has a population of 28,330 as of 2011. It is situated in the historical region of Transylvania, and is the main city of a subregion, Țara Făgărașului. Geography The city is located at the foothills of the Făgăraș Mountains, on their northern side. It is traversed by the DN1 road, west of Brașov and east of Sibiu. On the east side of the city, between an abandoned field and a gas station, lies the Geographical centre, geographical center of Romania, at . The Olt River flows east to west on the north side of the city; its left tributary, the Berivoi, Berivoi River, discharges into the Olt on the west side of the city, after receiving the waters of the Racovița (Făgăraș), Racovița River. The Berivoi and the Racovița were used to bring water to a since-closed major chemical plant located on the outsk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)
_in_Hungary%2C_census_1890.jpg)

