|
Red Byron
Robert Nold "Red" Byron (March 12, 1915 – November 11, 1960) was an American stock car racing driver, who was successful in NASCAR competition in the sanctioning body's first years. He was NASCAR's first Modified champion (and its first champion in any division) in 1948 and its first Strictly Stock (predecessor to NASCAR Cup Series) champion in 1949. Along with Bob Flock, he is considered one of the best drivers of the era. He won the first NASCAR race at Daytona Beach and Road Course and won the inaugural NASCAR Strictly Stock driver's championship. Background Born in Washington County, Virginia, he moved to Colorado at a young age, and then to Anniston, Alabama, which he considered his hometown. Byron began racing in 1932 and was successful in racing at Talladega and Anniston by the start of the 1940s. Byron then made his way to Lakewood Speedway, where he raced any ride he could find. While racing at Lakewood Speedway, he was noticed by Raymond Parks, a former ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States between the East Coast of the United States, Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The state's List of capitals in the United States, capital is Richmond, Virginia, Richmond and its most populous city is Virginia Beach, Virginia, Virginia Beach. Its most populous subdivision is Fairfax County, Virginia, Fairfax County, part of Northern Virginia, where slightly over a third of Virginia's population of more than 8.8million live. Eastern Virginia is part of the Atlantic Plain, and the Middle Peninsula forms the mouth of the Chesapeake Bay. Central Virginia lies predominantly in the Piedmont (United States), Piedmont, the foothill region of the Blue Ridge Mountains, which cross the western and southwestern parts of the state. The fertile Shenandoah Valley fosters the state's mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charlotte Speedway
Charlotte Speedway was the site of NASCAR's first Strictly Stock Series (now NASCAR Cup Series) race on June 19, 1949. The Daytona Beach Road Course held the first race sanctioned by NASCAR in 1948. The track was a few miles west of the NASCAR Hall of Fame, on Little Rock Road. It was owned by Carl C. Allison Sr. and his wife, Catherine Montgomery Allison. The track was forced to close when construction of Interstate 85 took its parking area. Event details Charlotte Speedway was a three-quarter mile long dirt track. The first event in 1949 was a race. Other events were 100, 113, or long. NASCAR history Twelve events were held at the track between 1949 and 1956. Winners at the track include: Jim Roper (1), Tim Flock (1), Curtis Turner (2), Herb Thomas (2), Dick Passwater (1), Buck Baker (3), Fonty Flock (1), and Speedy Thompson (1). 1949 Bob Flock won the pole. Glenn Dunaway was declared the original winner, but a post-race inspection revealed that his car was fit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rum-running
Rum-running, or bootlegging, is the illegal business of smuggling alcoholic beverages where such transportation is forbidden by law. The term ''rum-running'' is more commonly applied to smuggling over water; ''bootlegging'' is applied to smuggling over land. Smuggling circumvents alcohol taxes and outright prohibition of alcohol sales. Alcohol smuggling today In the United States, the smuggling of alcohol did not end with the repeal of prohibition. In the Appalachian United States, for example, the demand for moonshine was at an all-time high in the 1920s, but an era of rampant bootlegging in dry areas continued into the 1970s. Although the well-known bootleggers of the day may no longer be in business, bootlegging still exists, even if on a smaller scale. The state of Virginia has reported that it loses up to $20 million a year from illegal whiskey smuggling. The Government of the United Kingdom fails to collect an estimated £900 million in taxes due to alcohol smuggling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raymond Parks (auto Racing)
Raymond Parks (June 5, 1914 – June 20, 2010) was an American stock car racing team owner. He was the owner of Red Byron's car which won the inaugural NASCAR Strictly Stock Series championship in 1949. Parks was announced as one of the members of the 2017 NASCAR Hall of Fame class. Background Parks was the first child of Alfred and Leila Parks and great-great-nephew of settler Benny Parks, who found gold in the state of Georgia in the early nineteenth century. Born in Dawsonville, Georgia, on June 5, 1914, Raymond was the oldest of his father's sixteen children, six of whom were born to Leila, and ten of whom were born to Leila's sister, Ila. Parks left home at age 14 and began hauling moonshine. He served nine months of a one-year and one-day sentence in the federal penitentiary in Chillicothe, Ohio, from 1936 to 1937. Parks served in World War II during the famous Battle of the Bulge in Belgium. He served in the 99th Infantry Division and was briefly stationed at Fort Ben ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lakewood Speedway
Lakewood Speedway was a race track located south of Atlanta, Georgia, in Lakewood, just north of the eastern arm of Langford Parkway (formerly Lakewood Freeway). The track held many kinds of races between 1919 and 1979, including events sanctioned by AAA/ USAC, IMCA, and NASCAR. It was a one-mile (1.6 km) dirt track which was located adjacent to Lakewood Fairgrounds. Lakewood Speedway was considered the "Indianapolis of the South" as it was located in the largest city in the Southern United States and it held an annual race of the Indy cars. History In 1916, Atlanta officials chose the Lakewood Fairgrounds as the site for agricultural fairs. They built a one-mile (1.6 km) horse racing track around a lake at the fairgrounds. The first events were held at the track on July 4, 1917. The feature events were a horse race and motorcycle race, before 23,000 spectators. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Talladega, Alabama
Talladega (, also ) is the county seat of Talladega County, Alabama, United States. It was incorporated in 1835. At the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, the population was 15,861. Talladega is approximately east of one of the state's largest cities, Birmingham, Alabama, Birmingham. The city is home to the Alabama Institute for the Deaf and Blind and the Talladega Municipal Airport, a public general aviation airport. The Talladega Superspeedway, Talladega College and the International Motorsports Hall of Fame are located nearby. The First National Bank of Talladega (now First Bank of Alabama) is the oldest bank in the State of Alabama, being founded in 1848. Etymology The name Talladega is derived from a Muscogee language, a Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Native American language of the Muscogee. It comes from the word ''Tvlvtēke'', from Muscogee ''tvlwv'', meaning "town", and ''vtēke'', meaning "border", indicating its location on the border between Muscogee an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
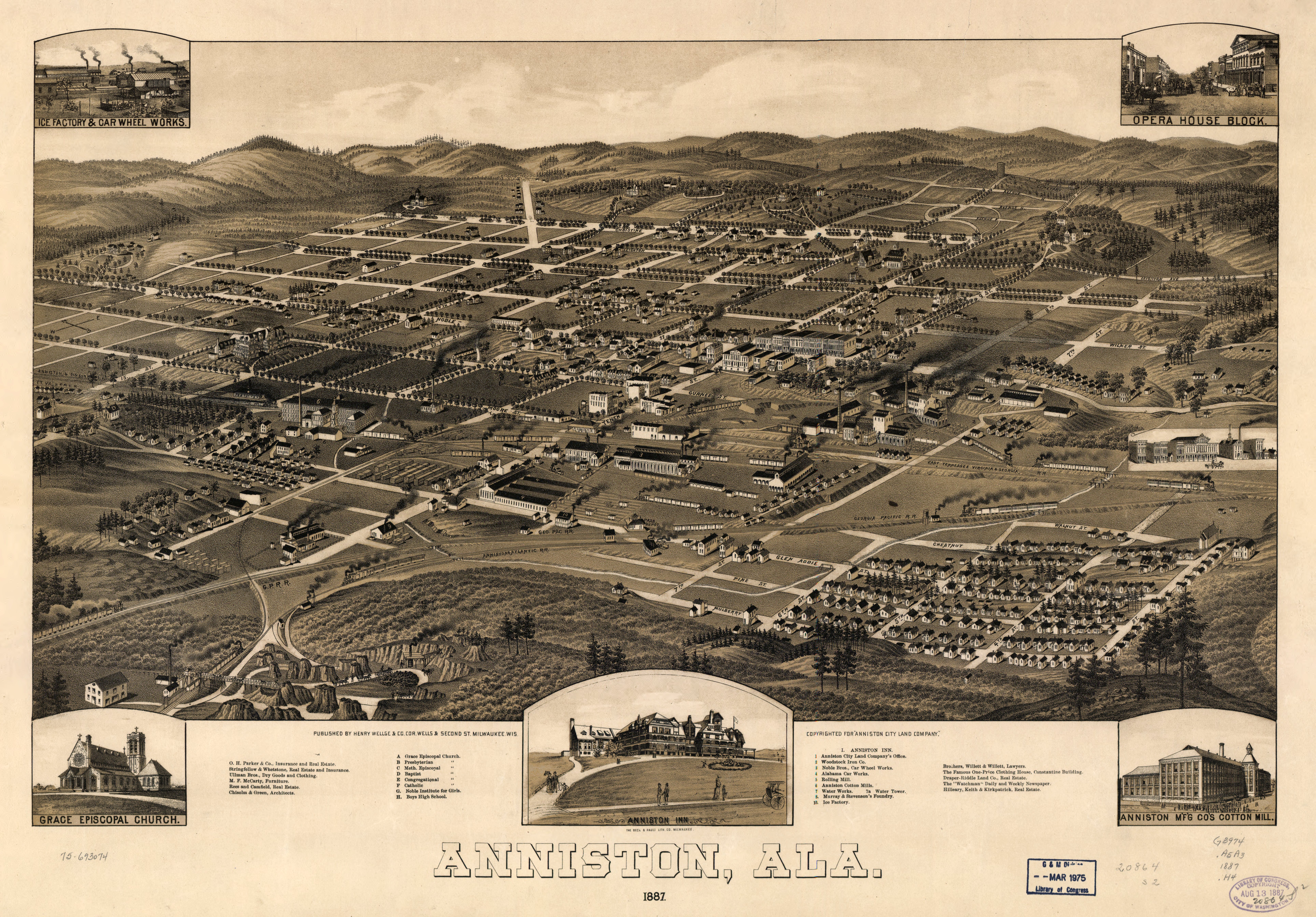
Anniston, Alabama
Anniston is a city and the county seat of Calhoun County, Alabama, Calhoun County in Alabama, United States, and is one of two urban centers/principal cities of and included in the Anniston–Oxford metropolitan area, Anniston–Oxford Metropolitan Statistical Area. As of the 2010 United States Census, 2010 census, the population of the city was 23,106. According to 2019 United States Census Bureau, Census estimates, the city had a population of 21,287. Named "The Model City" by Atlanta newspaperman Henry W. Grady for its careful planning in the late 19th century, the city is situated on the slope of Blue Mountain. History Civil War Though the surrounding area was settled much earlier, the mineral resources in the area of Anniston were not exploited until the American Civil War, Civil War. The Confederate States of America operated an iron furnace near present-day downtown Anniston, until it was destroyed by raiding Union Army, Union cavalry in early 1865. Later, cast iron for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colorado
Colorado is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States. It is one of the Mountain states, sharing the Four Corners region with Arizona, New Mexico, and Utah. It is also bordered by Wyoming to the north, Nebraska to the northeast, Kansas to the east, and Oklahoma to the southeast. Colorado is noted for its landscape of mountains, forests, High Plains (United States), high plains, mesas, canyons, plateaus, rivers, and desert lands. It encompasses most of the Southern Rocky Mountains, as well as the northeastern portion of the Colorado Plateau and the western edge of the Great Plains. Colorado is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, eighth-largest U.S. state by area and the List of U.S. states and territories by population, 21st by population. The United States Census Bureau estimated the population of Colorado to be 5,957,493 as of July 1, 2024, a 3.2% increase from the 2020 United States census. The region has been inhabited by Native Americans in the United St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Washington County, Virginia
Washington County is a county located in the Commonwealth of Virginia. As of the 2020 United States census, the population was 53,935. Its county seat is Abingdon. Washington County is part of the Kingsport–Bristol–Bristol, TN-VA Metropolitan Statistical Area, which is a component of the Johnson City–Kingsport–Bristol, TN-VA Combined Statistical Area, commonly known as the " Tri-Cities" region, which includes Bristol TN-VA, Kingsport TN, and Johnson City TN. History For thousands of years, indigenous peoples of varying cultures lived in the area. At the time of European massacre, the Chiska had a chief village near what is now Saltville, destroyed by the Spaniards in 1568. The Cherokee annexed the region from the Xualae around 1671, and ceded it to the Virginia Colony in 1770 at the Treaty of Lochaber. The county was formed by Virginians in 1776 from Fincastle County. It was named for George Washington, who was then commander-in-chief of the Continental ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daytona Beach And Road Course
The Ormond Beach and Road Course was a motorsport race track that was instrumental in the formation of the NASCAR, National Association for Stock Car Auto Racing. It originally became famous as the location where 15 land speed record, world land speed records were set. Beach and road course Track layout The course started on the pavement of highway State Road A1A (Florida), A1A (at 4511 South Atlantic Avenue, Ponce Inlet ). A restaurant named "Racing's North Turn" now stands at that location. It went south parallel to the ocean on A1A (S. Atlantic Ave) to the end of the road, where the drivers accessed the beach at the south turn at the Beach Street approach , returned north on the sandy beach surface, and returned to A1A at the north turn. The lap length in early events was , and it was lengthened to in the late 1940s. In the video game ''NASCAR Thunder 2004'' by EA Sports, the course is shortened to about half its distance, but still shows how the basic course was set up. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bob Flock
Robert Newman Flock (April 16, 1918 – May 16, 1964) was an American stock car racing, stock car racer. He qualified on the pole position for NASCAR's 1949 NASCAR Strictly Stock Series inaugural race, first Strictly Stock (now NASCAR Cup Series) race and, along with Red Byron, is considered one of the two best drivers from that era. Flock died of a heart attack in 1964. Flock family He was the brother of NASCAR pioneers Tim Flock and Fonty Flock, and the second female NASCAR driver Ethel Mobley. The four raced at the July 10, 1949 race at the Daytona Beach Road Course, which was the first event to feature a brother and a sister, and the only NASCAR event to feature four siblings. Ethel beat Fonty and Bob by finishing in eleventh. Moonshine business The Flock family had an illegal moonshine business. The federal agents discovered that Flock would be running a race in Atlanta, and they staked out the place to make an arrest. A gate opened as the race was beginning, and he drov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stock Car Racing
Stock car racing is a form of Auto racing, automobile racing run on oval track racing, oval tracks and road courses. It originally used Production vehicle, production-model cars, hence the name "stock car", but is now run using cars specifically built for racing. It originated in the Culture of the Southern United States, southern United States and later spread to Japan; its largest governing body is NASCAR. Its NASCAR Cup Series is the premier top-level series of professional stock car racing. Canada, Mexico, Brazil, Argentina and Chile also have forms of stock car racing in the Americas. Other countries, such as Australia, New Zealand and the United Kingdom, have forms of stock car racing worldwide as well. Top-level races typically range between in length. Top-level stock cars exceed at speedway tracks and on superspeedway tracks such as Daytona International Speedway and Talladega Superspeedway. Contemporary NASCAR-spec top-level cars produce maximum power outputs of 860� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |