|
Reaction Center
A photosynthetic reaction center is a complex of several proteins, pigments and other co-factors that together execute the primary energy conversion reactions of photosynthesis. Molecular excitations, either originating directly from sunlight or transferred as excitation energy via light-harvesting antenna systems, give rise to electron transfer reactions along the path of a series of protein-bound co-factors. These co-factors are light-absorbing molecules (also named chromophores or pigments) such as chlorophyll and pheophytin, as well as quinones. The energy of the photon is used to excite an electron of a pigment. The free energy created is then used, via a chain of nearby electron acceptors, for a transfer of hydrogen atoms (as protons and electrons) from H2O or hydrogen sulfide towards carbon dioxide, eventually producing glucose. These electron transfer steps ultimately result in the conversion of the energy of photons to chemical energy. Transforming light energy into cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit soil, water, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria are vital in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients such as the fixation of nitrogen from the atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, such as hydrogen sulphide and methane, to energy. Bacteria also live in symbiotic and parasitic re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloroplast
A chloroplast () is a type of membrane-bound organelle known as a plastid that conducts photosynthesis mostly in plant and algal cells. The photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll captures the energy from sunlight, converts it, and stores it in the energy-storage molecules ATP and NADPH while freeing oxygen from water in the cells. The ATP and NADPH is then used to make organic molecules from carbon dioxide in a process known as the Calvin cycle. Chloroplasts carry out a number of other functions, including fatty acid synthesis, amino acid synthesis, and the immune response in plants. The number of chloroplasts per cell varies from one, in unicellular algae, up to 100 in plants like '' Arabidopsis'' and wheat. A chloroplast is characterized by its two membranes and a high concentration of chlorophyll. Other plastid types, such as the leucoplast and the chromoplast, contain little chlorophyll and do not carry out photosynthesis. Chloroplasts are highly dynamic—they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protons
A proton is a stable subatomic particle, symbol , H+, or 1H+ with a positive electric charge of +1 ''e'' elementary charge. Its mass is slightly less than that of a neutron and 1,836 times the mass of an electron (the proton–electron mass ratio). Protons and neutrons, each with masses of approximately one atomic mass unit, are jointly referred to as "nucleons" (particles present in atomic nuclei). One or more protons are present in the nucleus of every atom. They provide the attractive electrostatic central force which binds the atomic electrons. The number of protons in the nucleus is the defining property of an element, and is referred to as the atomic number (represented by the symbol ''Z''). Since each element has a unique number of protons, each element has its own unique atomic number, which determines the number of atomic electrons and consequently the chemical characteristics of the element. The word ''proton'' is Greek for "first", and this name was given ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as well as with other compounds. Oxygen is Earth's most abundant element, and after hydrogen and helium, it is the third-most abundant element in the universe. At standard temperature and pressure, two atoms of the element bind to form dioxygen, a colorless and odorless diatomic gas with the formula . Diatomic oxygen gas currently constitutes 20.95% of the Earth's atmosphere, though this has changed considerably over long periods of time. Oxygen makes up almost half of the Earth's crust in the form of oxides.Atkins, P.; Jones, L.; Laverman, L. (2016).''Chemical Principles'', 7th edition. Freeman. Many major classes of organic molecules in living organisms contain oxygen atoms, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and fats ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NADPH
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, abbreviated NADP or, in older notation, TPN (triphosphopyridine nucleotide), is a cofactor used in anabolic reactions, such as the Calvin cycle and lipid and nucleic acid syntheses, which require NADPH as a reducing agent ('hydrogen source'). It is used by all forms of cellular life. NADPH is the reduced form of NADP. NADP differs from NAD by the presence of an additional phosphate group on the 2' position of the ribose ring that carries the adenine moiety. This extra phosphate is added by NAD+ kinase and removed by NADP+ phosphatase. Biosynthesis NADP In general, NADP+ is synthesized before NADPH is. Such a reaction usually starts with NAD+ from either the de-novo or the salvage pathway, with NAD+ kinase adding the extra phosphate group. ADP-ribosyl cyclase allows for synthesis from nicotinamide in the salvage pathway, and NADP+ phosphatase can convert NADPH back to NADH to maintain a balance. Some forms of the NAD+ kinase, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferredoxin
Ferredoxins (from Latin ''ferrum'': iron + redox, often abbreviated "fd") are iron–sulfur proteins that mediate electron transfer in a range of metabolic reactions. The term "ferredoxin" was coined by D.C. Wharton of the DuPont Co. and applied to the "iron protein" first purified in 1962 by Mortenson, Valentine, and Carnahan from the anaerobic bacterium '' Clostridium pasteurianum''. Another redox protein, isolated from spinach chloroplasts, was termed "chloroplast ferredoxin". The chloroplast ferredoxin is involved in both cyclic and non-cyclic photophosphorylation reactions of photosynthesis. In non-cyclic photophosphorylation, ferredoxin is the last electron acceptor thus reducing the enzyme NADP+ reductase. It accepts electrons produced from sunlight- excited chlorophyll and transfers them to the enzyme ferredoxin: NADP+ oxidoreductase . Ferredoxins are small proteins containing iron and sulfur atoms organized as iron–sulfur clusters. These biological " capacitors" ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytochrome B6f Complex
The cytochrome ''b''6''f'' complex (plastoquinol—plastocyanin reductase; ) is an enzyme found in the thylakoid membrane in chloroplasts of plants, cyanobacteria, and green algae, that catalyzes the transfer of electrons from plastoquinol to plastocyanin. The reaction is analogous to the reaction catalyzed by cytochrome bc1 (Complex III) of the mitochondrial electron transport chain. During photosynthesis, the cytochrome b6f complex is one step along the chain that transfers electrons from Photosystem II to Photosystem I, and at the same time pumps protons into the thylakoid space, contributing to the generation of an electrochemical (energy) gradient that is later used to synthesize ATP from ADP. Enzyme structure The cytochrome b6f complex is a dimer, with each monomer composed of eight subunits. These consist of four large subunits: a 32 kDa cytochrome f with a c-type cytochrome, a 25 kDa cytochrome b6 with a low- and high-potential heme group, a 19 kDa Rieske iro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
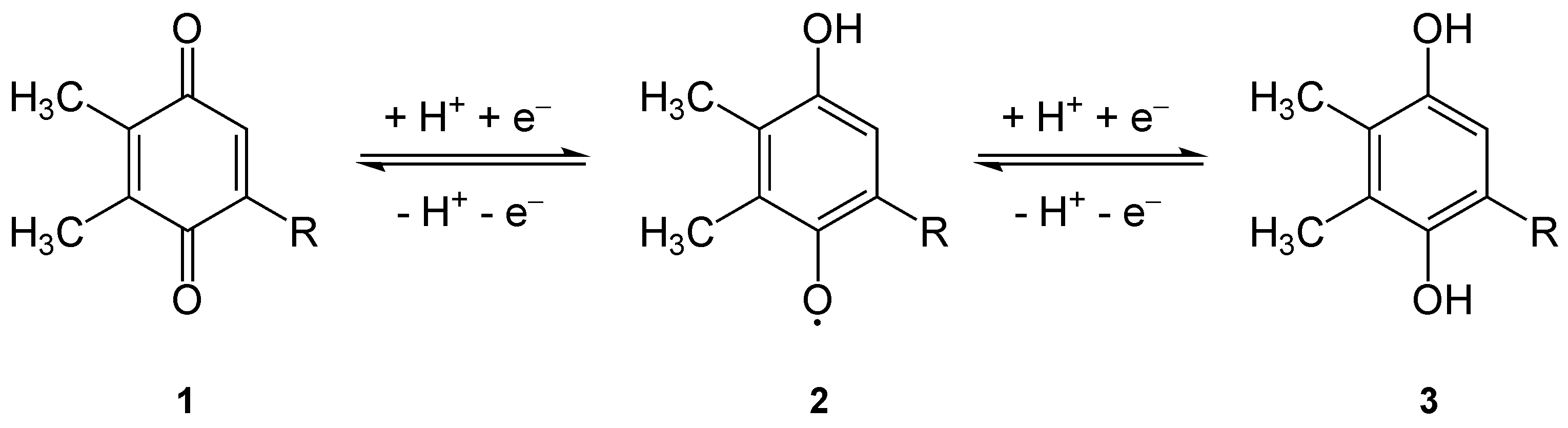
Plastoquinone
Plastoquinone (PQ) is an isoprenoid quinone molecule involved in the electron transport chain in the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis. The most common form of plastoquinone, known as PQ-A or PQ-9, is a 2,3-dimethyl-1,4- benzoquinone molecule with a side chain of nine isoprenyl units. There are other forms of plastoquinone, such as ones with shorter side chains like PQ-3 (which has 3 isoprenyl side units instead of 9) as well as analogs such as PQ-B, PQ-C, and PQ-D, which differ in their side chains. The benzoquinone and isoprenyl units are both nonpolar, anchoring the molecule within the inner section of a lipid bilayer, where the hydrophobic tails are usually found. Plastoquinones are very structurally similar to ubiquinone, or coenzyme Q10, differing by the length of the isoprenyl side chain, replacement of the methoxy groups with methyl groups, and removal of the methyl group in the 2 position on the quinone. Like ubiquinone, it can come in several oxidation states ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quinone
The quinones are a class of organic compounds that are formally "derived from aromatic compounds benzene.html" ;"title="uch as benzene">uch as benzene or naphthalene] by conversion of an even number of –CH= groups into –C(=O)– groups with any necessary rearrangement of double bonds, resulting in "a fully Conjugated system, conjugated cyclic diketone, dione structure". The archetypical member of the class is 1,4-benzoquinone or cyclohexadienedione, often called simply "quinone" (thus the name of the class). Other important examples are 1,2-benzoquinone (''ortho''-quinone), 1,4-naphthoquinone and 9,10-anthraquinone. The name is derived from that of quinic acid (with the suffix "-one" indicating a ketone), since it is one of the compounds obtained upon oxidation of quinic acid. Quinic acid, like quinine is obtained from cinchona bark, called quinaquina in the indigenous languages of Peruvian tribes. Properties Quinones are oxidized derivatives of aromatic compounds and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron Transport Chain
An electron transport chain (ETC) is a series of protein complexes and other molecules that transfer electrons from electron donors to electron acceptors via redox reactions (both reduction and oxidation occurring simultaneously) and couples this electron transfer with the transfer of protons (H+ ions) across a membrane. The electrons that transferred from NADH and FADH2 to the ETC involves 4 multi-subunit large enzymes complexes and 2 mobile electron carriers. Many of the enzymes in the electron transport chain are membrane-bound. The flow of electrons through the electron transport chain is an exergonic process. The energy from the redox reactions creates an electrochemical proton gradient that drives the synthesis of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In aerobic respiration, the flow of electrons terminates with molecular oxygen as the final electron acceptor. In anaerobic respiration, other electron acceptors are used, such as sulfate. In an electron transport chain, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polypeptide Chain
Peptides (, ) are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. Long chains of amino acids are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty amino acids are called oligopeptides, and include dipeptides, tripeptides, and tetrapeptides. A polypeptide is a longer, continuous, unbranched peptide chain. Hence, peptides fall under the broad chemical classes of biological polymers and oligomers, alongside nucleic acids, oligosaccharides, polysaccharides, and others. A polypeptide that contains more than approximately 50 amino acids is known as a protein. Proteins consist of one or more polypeptides arranged in a biologically functional way, often bound to ligands such as coenzymes and cofactors, or to another protein or other macromolecule such as DNA or RNA, or to complex macromolecular assemblies. Amino acids that have been incorporated into peptides are termed residues. A water molecule is released during formation of each amide bond.. All peptides except cy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_cyt6bf_mutant.jpg)