|
Raphe Int
Raphe (; from Greek ῥαφή, "seam"Liddell, H.G. & Scott, R. (1940). ''A Greek-English Lexicon. revised and augmented throughout by Sir Henry Stuart Jones. with the assistance of. Roderick McKenzie.'' Oxford: Clarendon Press.) has several different meanings in science. In botany and planktology it is commonly used when describing a seam or ridge on diatoms or seeds. In animal anatomy it is used to describe a ridged union of continuous biological tissue. There are several different significant anatomical raphes: * The raphe nucleus is a moderate-size cluster of nuclei found in the brain stem that releases serotonin to the rest of the brain. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) antidepressants are believed to act at these nuclei. * The buccal raphe, which is on the cheek and evidence of the fusion of the Maxillary prominence, maxillary and mandibular processes * The lingual raphe on the tongue. Obvious physical evidence of the lingual raphe includes the Frenulum of tong ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Botany
Botany, also called , plant biology or phytology, is the science of plant life and a branch of biology. A botanist, plant scientist or phytologist is a scientist who specialises in this field. The term "botany" comes from the Ancient Greek word (''botanē'') meaning " pasture", " herbs" "grass", or " fodder"; is in turn derived from (), "to feed" or "to graze". Traditionally, botany has also included the study of fungi and algae by mycologists and phycologists respectively, with the study of these three groups of organisms remaining within the sphere of interest of the International Botanical Congress. Nowadays, botanists (in the strict sense) study approximately 410,000 species of land plants of which some 391,000 species are vascular plants (including approximately 369,000 species of flowering plants), and approximately 20,000 are bryophytes. Botany originated in prehistory as herbalism with the efforts of early humans to identify – and later cultivate – ed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palate
The palate () is the roof of the mouth in humans and other mammals. It separates the oral cavity from the nasal cavity. A similar structure is found in crocodilians, but in most other tetrapods, the oral and nasal cavities are not truly separated. The palate is divided into two parts, the anterior, bony hard palate and the posterior, fleshy soft palate (or velum). Structure Innervation The maxillary nerve branch of the trigeminal nerve supplies sensory innervation to the palate. Development The hard palate forms before birth. Variation If the fusion is incomplete, a cleft palate results. Function When functioning in conjunction with other parts of the mouth, the palate produces certain sounds, particularly velar, palatal, palatalized, postalveolar, alveolopalatal, and uvular consonants. History Etymology The English synonyms palate and palatum, and also the related adjective palatine (as in palatine bone), are all from the Latin ''palatum'' via Old French ''palat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lateral Palpebral Raphe
The lateral palpebral raphe is a ligamentous band near the eye. Its existence is contentious, and many sources describe it as the continuation of nearby muscles. It is formed from the lateral ends of the orbicularis oculi muscle. It connects the orbicularis oculi muscle, the frontosphenoidal process of the zygomatic bone, and the tarsi of the eyelids. Structure The lateral palpebral raphe is formed from the lateral ends of the orbicularis oculi muscle. It may also be formed from the pretarsal muscles of the eyelids. It is attached to the margin of the frontosphenoidal process of the zygomatic bone. It passes towards the midline to the lateral commissure of the eyelids. Here, it divides into two slips, which are attached to the margins of the respective tarsi of the eyelids. The lateral palpebral ligament has a tensile strength of around 12 newtons. Relations The lateral palpebral raphe is a much weaker structure than the medial palpebral ligament on the other side of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pterygomandibular Raphe
The pterygomandibular raphe (pterygomandibular ligament) is a ligamentous band of the buccopharyngeal fascia. It is attached superiorly to the pterygoid hamulus of the medial pterygoid plate, and inferiorly to the posterior end of the mylohyoid line of the mandible. It connects the buccinator muscle in front to the superior pharyngeal constrictor muscle behind. Structure The pterygomandibular raphe is a ligament that forms from the buccopharyngeal fascia. It is a paired structure, with one on each side of the mouth. Superiorly, it is attached to the pterygoid hamulus of the medial pterygoid plate of the sphenoid bone. Inferiorly, it is attached to the posterior end of the mylohyoid line of the mandible. * Its ''medial surface'' is covered by the mucous membrane of the mouth. * Its ''lateral surface'' is separated from the ramus of the mandible by a quantity of adipose tissue. * Its ''posterior border'' gives attachment to the superior pharyngeal constrictor muscle. * Its ''an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iliococcygeal Raphe
The iliococcygeal raphe is a raphe representing the midline location where the levatores ani converge. See also * Anococcygeal body The anococcygeal body (anococcygeal ligament, or anococcygeal raphe) is a fibrous median raphe in the floor of the pelvis, which extends between the coccyx and the margin of the anus. It is composed of fibers of the levator ani muscle that unite w ... References Pelvis {{anatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anococcygeal Body
The anococcygeal body (anococcygeal ligament, or anococcygeal raphe) is a fibrous median raphe in the floor of the pelvis, which extends between the coccyx and the margin of the anus. It is composed of fibers of the levator ani muscle that unite with the muscle of the opposite side, muscle fibres from external anal sphincter, and fibrous connective tissue.Daftary, Shirish; Chakravarti, Sudip (2011). Manual of Obstetrics, 3rd Edition. Elsevier. pp. 1-16. . The fibers of the levator ani pass downward and backward to the middle line of the floor of the pelvis; the most posterior are inserted into the side of the last two segments of the coccyx; those placed more anteriorly unite with the muscle of the opposite side, in the anococcygeal body. See also * Iliococcygeal raphe References External links Image at rsnajnls.org (Peer-reviewed medical chapter, available free online at eMedicine) Musculoskeletal system {{musculoskeletal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
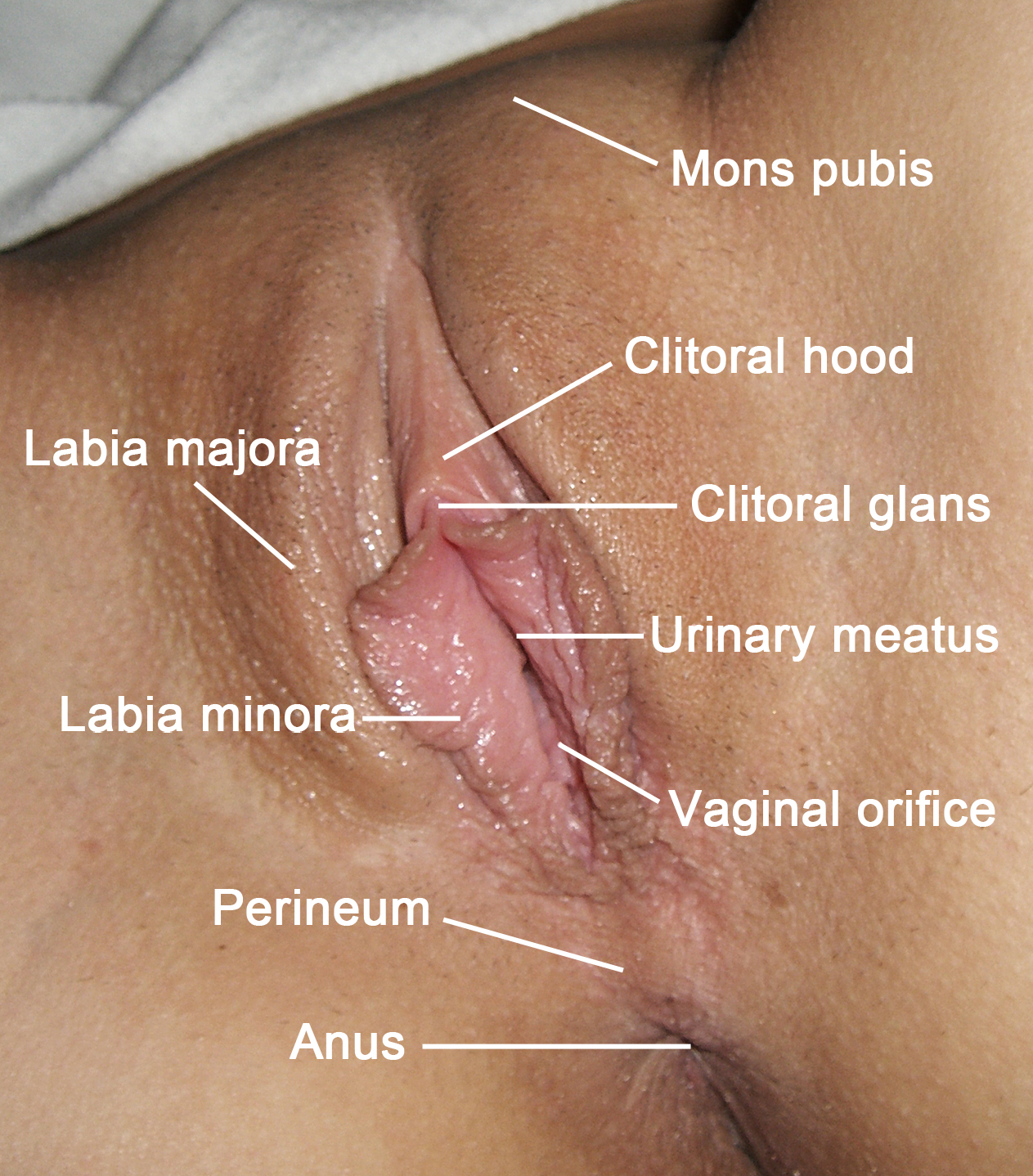
Labia Majora
The labia majora (singular: ''labium majus'') are two prominent longitudinal cutaneous folds that extend downward and backward from the mons pubis to the perineum. Together with the labia minora they form the labia of the vulva. The labia majora are homologous to the male scrotum. Etymology ''Labia majora'' is the Latin plural for big ("major") lips; the singular is ''labium majus.'' The Latin term ''labium/labia'' is used in anatomy for a number of usually paired parallel structures, but in English it is mostly applied to two pairs of parts of female external genitals (vulva)—labia majora and labia minora. Labia majora are commonly known as the outer lips, while labia minora (Latin for ''small lips''), which run alongside between them, are referred to as the inner lips. Traditionally, to avoid confusion with other lip-like structures of the body, the labia of female genitals were termed by anatomists in Latin as ''labia majora (''or ''minora) pudendi.'' Embryology Embryolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perineum
The perineum in humans is the space between the anus and scrotum in the male, or between the anus and the vulva in the female. The perineum is the region of the body between the pubic symphysis (pubic arch) and the coccyx (tail bone), including the perineal body and surrounding structures. There is some variability in how the boundaries are defined. The perineal raphe is visible and pronounced to varying degrees. The perineum is an erogenous zone. The word perineum entered English from late Latin via Greek περίναιος ~ περίνεος ''perinaios, perineos'', itself from περίνεος, περίνεοι 'male genitals' and earlier περίς ''perís'' 'penis' through influence from πηρίς ''pērís'' 'scrotum'. The term was originally understood as a purely male body-part with the perineal raphe seen as a continuation of the scrotal septum since masculinization causes the development of a large anogenital distance in men, in comparison to the corresponding lack ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penis
A penis (plural ''penises'' or ''penes'' () is the primary sexual organ that male animals use to inseminate females (or hermaphrodites) during copulation. Such organs occur in many animals, both vertebrate and invertebrate, but males do not bear a penis in every animal species, and in those species in which the male does bear a so-called penis, the penises in the various species are not necessarily homologous. The term ''penis'' applies to many intromittent organs, but not to all. As an example, the intromittent organ of most cephalopoda is the hectocotylus, a specialized arm, and male spiders use their pedipalps. Even within the Vertebrata there are morphological variants with specific terminology, such as Hemipenis, hemipenes. In most species of animals in which there is an organ that might reasonably be described as a penis, it has no major function other than intromission, or at least conveying the sperm to the female, but in the Eutheria, placental mammals the peni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
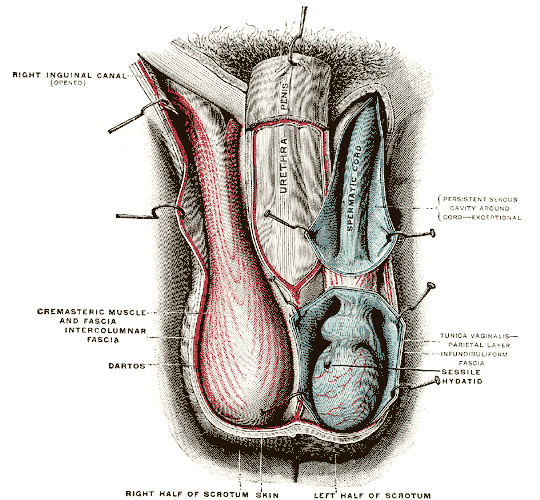
Scrotum
The scrotum or scrotal sac is an anatomical male reproductive structure located at the base of the penis that consists of a suspended dual-chambered sac of skin and smooth muscle. It is present in most terrestrial male mammals. The scrotum contains the external spermatic fascia, testes, epididymis, and ductus deferens. It is a distention of the perineum and carries some abdominal tissues into its cavity including the testicular artery, testicular vein, and pampiniform plexus. The perineal raphe is a small, vertical, slightly raised ridge of scrotal skin under which is found the scrotal septum. It appears as a thin longitudinal line that runs front to back over the entire scrotum. In humans and some other mammals the scrotum becomes covered with pubic hair at puberty. The scrotum will usually tighten during penile erection and when exposed to cold temperatures. One testis is typically lower than the other to avoid compression in the event of an impact. The scrotum is biologicall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anus
The anus (Latin, 'ring' or 'circle') is an opening at the opposite end of an animal's digestive tract from the mouth. Its function is to control the expulsion of feces, the residual semi-solid waste that remains after food digestion, which, depending on the type of animal, includes: matter which the animal cannot digest, such as bones; Summary at food material after the nutrients have been extracted, for example cellulose or lignin; ingested matter which would be toxic if it remained in the digestive tract; and dead or excess gut bacteria and other endosymbionts. Amphibians, reptiles, and birds use the same orifice (known as the cloaca) for excreting liquid and solid wastes, for copulation and egg-laying. Monotreme mammals also have a cloaca, which is thought to be a feature inherited from the earliest amniotes via the therapsids. Marsupials have a single orifice for excreting both solids and liquids and, in females, a separate vagina for reproduction. Female placental mamm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perineal Raphe
The perineal raphe is a visible line or ridge of tissue on the body that extends from the anus through the perineum to scrotum (male) or labia majora (female). It is found in both males and females, arises from the fusion of the urogenital folds, and is visible running medial through anteroposterior, to the anus where it resolves in a small knot of skin of varying size. In males, this structure continues through the midline of the scrotum (scrotal raphe) and upwards through the posterior midline aspect of the penis (penile raphe). It also exists deeper through the scrotum where it is called the scrotal septum. It is the result of a fetal developmental phenomenon whereby the scrotum and penis close toward the midline and fuse. See also * Raphe * Linea nigra * Embryonic and prenatal development of the male reproductive system in humans * Frenulum of prepuce of penis The frenulum of prepuce of penis, often known simply as the frenulum, is a highly erogenous elastic band of tissu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)