|
Rana Sangram Singh
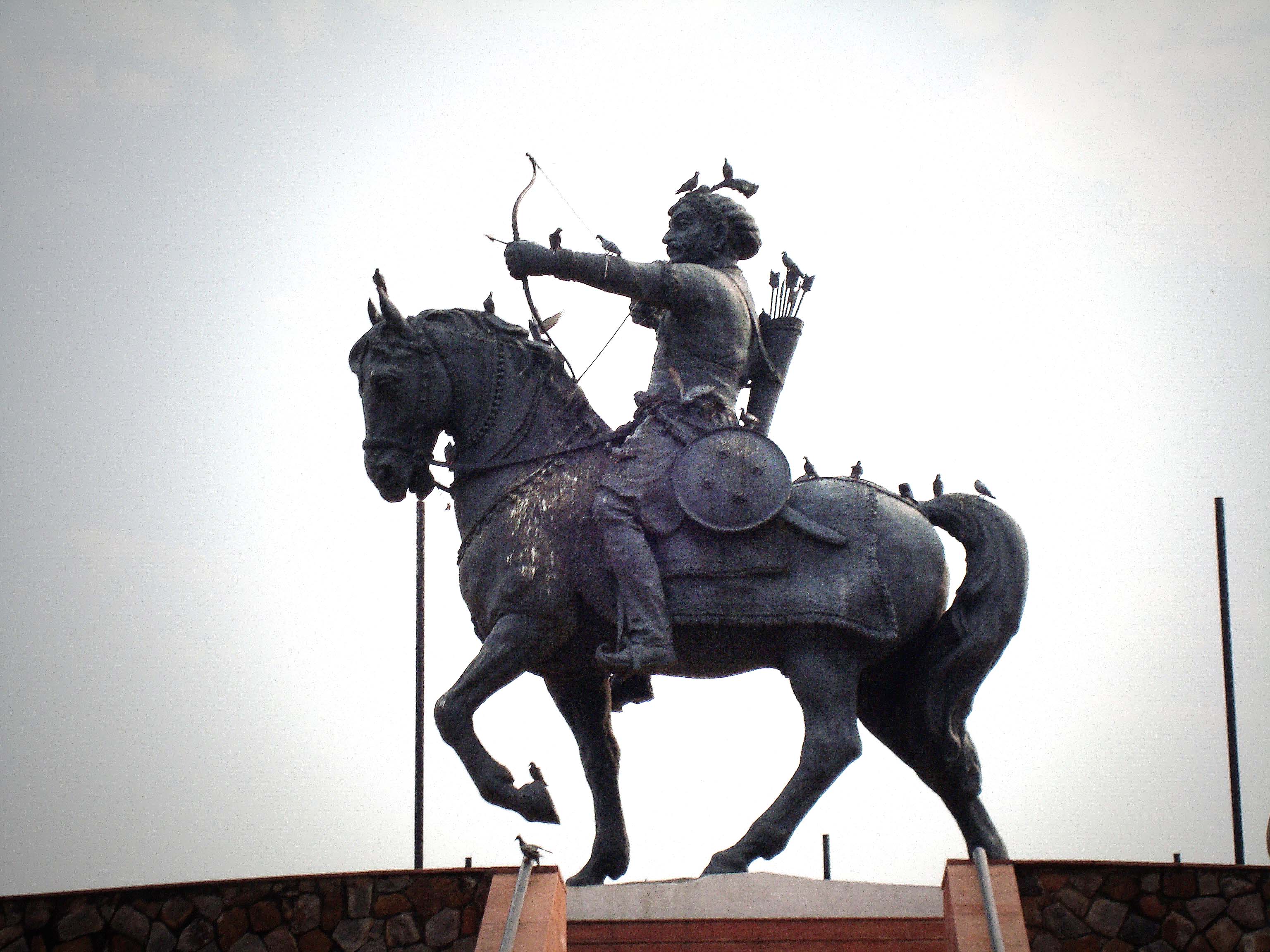
Sangram Singh I (IAST: Rāṇā Saṅgrāma Siṃha; c. 1482 – 1528 CE), popularly known as Rana Sanga or Maharana Sanga, was an Indian ruler from the Sisodia dynasty. He ruled Mewar, the traditional territory of Guhilas (Sisodias) in present-day north-western India. However, through his capable rule his kingdom turned into one of the greatest power of Northern India in early sixteenth century. He controlled parts of present-day Rajasthan, Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh with capital at Chittor. His reign was admired by several of contemporaries including Babur, who described him the "greatest Indian king" of that time along with Krishnadevaraya of South India. The Mughal historian Al-Badayuni called Sanga as the bravest of all Rajputs along with Prithviraj Chauhan. Rana Sanga was the last independent Hindu king of Northern India to control a significant territory before the Mughal Era. In some contemporary texts is described as the ''Hindu Emperor'' in Northern In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maharana
Maharana is a variation on the Indian royal title Rana. Maharana denotes ' king of kings', similar to the word "Maharaja". Ruler title in British India Salute states (all in present India) The gun salutes enjoyed by the states that acceded to the Dominion of India on 14 August 1947, included the following Maharanas: *Hereditary salute of 19-guns (21-guns local): the Maharana of Udaipur State (Mewar) *Hereditary salute of 13-guns the Maharana of Rajpipla *Hereditary salute of 11-guns: the Maharana of Barwani Hereditary salutes of 9-guns: *The Maharana of Danta *The Maharana of Wadhwan *The Maharana of Sant Some of the rulers were granted increased gun salutes after the independence, e.g. the above-listed Maharana of Mewar (Hindu; at Udaipur, Maharajpramukh in Rajasthan) was raised to first place in the Order of Precedence, displacing the Nizam of Hyderabad and Berar (Muslim), and all 9-gun states were permitted the use of the style of Highness. Non-salute states ruled by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
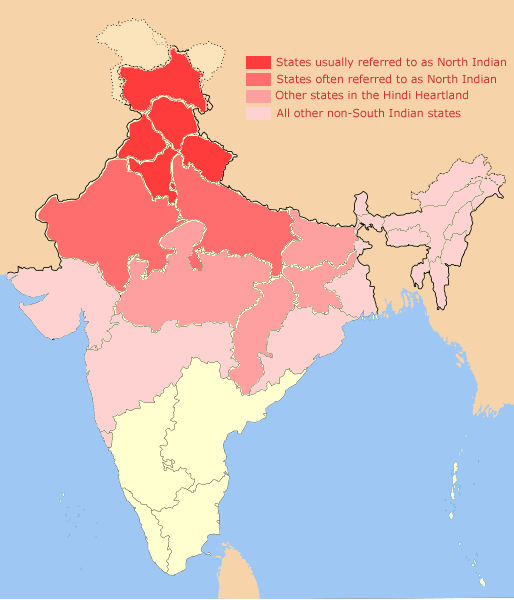
Northern India
North India is a loosely defined region consisting of the northern part of India. The dominant geographical features of North India are the Indo-Gangetic Plain and the Himalayas, which demarcate the region from the Tibetan Plateau and Central Asia. The term North India has varying definitions. The Ministry of Home Affairs in its Northern Zonal Council Administrative division included the states of Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Punjab and Rajasthan and Union Territories of Chandigarh, Delhi, Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh. The Ministry of Culture in its ''North Culture Zone'' includes the state of Uttarakhand but excludes Delhi whereas the Geological Survey of India includes Uttar Pradesh and Delhi but excludes Rajasthan and Chandigarh. Other states sometimes included are Bihar, Gujarat, Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh and West Bengal. North India has been the historical centre of the Mughal Empire, the Delhi Sultanate and the British Indian Empire. It has a diverse culture, and includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timurid Dynasty
The Timurid dynasty ( chg, , fa, ), self-designated as Gurkani ( chg, , translit=Küregen, fa, , translit=Gūrkāniyān), was a Sunni Muslim dynasty or clan of Turco-Mongol originB.F. Manz, ''"Tīmūr Lang"'', in Encyclopaedia of Islam, Online Edition, 2006''Encyclopædia Britannica'',Timurid Dynasty, Online Academic Edition, 2007. (Quotation: "Turkic dynasty descended from the conqueror Timur (Tamerlane), renowned for its brilliant revival of artistic and intellectual life in Iran and Central Asia. ... Trading and artistic communities were brought into the capital city of Herat, where a library was founded, and the capital became the centre of a renewed and artistically brilliant Persian culture.") descended from the warlord Timur (also known as Tamerlane). The word "Gurkani" derives from "Gurkan", a Persianized form of the Mongolian word "Kuragan" meaning "son-in-law". This was an honorific title used by the dynasty as the Timurids were in-laws of the line of Genghis Khan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Battle Of Tarain
The Second Battle of Tarain was fought in 1192 between the Ghurid forces of Muhammad Ghuri and the Rajput Confederacy of Prithviraj Chauhan. It took place near Tarain (modern Taraori), which is , north of Delhi. The battle ended in a decisive victory for the invading Ghurids and their successful penetration in north Indian plain. The battle is regarded as a watershed event in Medieval India history as it led to the destruction of Rajput powers for a while and laid the foundation of Muslim rule in North India, which led to the establishment of Delhi Sultanate. Background Prithviraj Chauhan's forces had defeated the Ghurids at the First Battle of Tarain in 1191. The Ghurid king Mu'izz al-Din, who was seriously injured in the battle, returned to Ghazni, and made preparations to avenge his defeat. Historians generally date the second battle of Tarain to 1192, although there is a possibility that it happened in late 1191. Size of the forces According to the 16th-17th cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rajput
Rajput (from Sanskrit ''raja-putra'' 'son of a king') is a large multi-component cluster of castes, kin bodies, and local groups, sharing social status and ideology of genealogical descent originating from the Indian subcontinent. The term Rajput covers various patrilineal clans historically associated with warriorhood: several clans claim Rajput status, although not all claims are universally accepted. According to modern scholars, almost all Rajput clans originated from peasant or pastoral communities. Over time, the Rajputs emerged as a social class comprising people from a variety of ethnic and geographical backgrounds. During the 16th and 17th centuries, the membership of this class became largely hereditary, although new claims to Rajput status continued to be made in the later centuries. Several Rajput-ruled kingdoms played a significant role in many regions of central and northern India from seventh century onwards. The Rajput population and the former Rajput stat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delhi Sultanate
The Delhi Sultanate was an Islamic empire based in Delhi that stretched over large parts of the Indian subcontinent for 320 years (1206–1526).Delhi Sultanate Encyclopædia Britannica Following the invasion of by the , five dynasties ruled over the Delhi Sultanate sequentially: the Mamluk dynasty (1206–1290), the Khalji dynasty (1290–1320), the |
Lodi Dynasty
The Lodi dynasty ( ps, لودي سلسله; fa, سلسله لودی) was an Afghan dynasty that ruled the Delhi Sultanate from 1451 to 1526. It was the fifth and final dynasty of the Delhi Sultanate, and was founded by Bahlul Khan Lodi when he replaced the Sayyid dynasty. Bahlul Lodi Bahlul Khan Lodi () was the nephew and son-in-law of Malik Sultan Shah Lodi, the governor of Sirhind in (Punjab), India and succeeded him as the governor of Sirhind during the reign of Sayyid dynasty ruler Muhammad Shah. Muhammad Shah raised him to the status of an Tarun-Bin-Sultan. He was the most powerful of the Punjab chiefs and a vigorous leader, holding together a loose confederacy of Afghan and Turkish chiefs with his strong personality. He reduced the turbulent chiefs of the provinces to submission and infused some vigour into the government. After the last Sayyid ruler of Delhi, Alauddin Alam Shah voluntarily abdicated in favour of him, Bahlul Khan Lodi ascended the throne of the Delhi sult ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prithviraj Chauhan
Prithviraja III (IAST: Pṛthvī-rāja; reign. – 1192 CE), popularly known as Prithviraj Chauhan or Rai Pithora, was a king from the Chauhan (Chahamana) dynasty who ruled the territory of Sapadalaksha, with his capital at Ajmer in present-day Rajasthan. Ascending the throne as a minor in 1177 CE, Prithviraj inherited a kingdom which stretched from Thanesar in the north to Jahazpur (Mewar) in the south, which he aimed to expand by military actions against neighbouring kingdoms, most notably defeating the Chandelas. Prithviraj led a coalition of several Rajput kings and defeated the Ghurid army led by Muhammad Ghori near Taraori in 1191 AD. However, in 1192 CE, Ghori returned with an army of Turkish mounted archers and defeated the Rajput army on the same battlefield. Prithviraj fled the battlefield, but was captured near Sirsa and executed. His defeat at Tarain is seen as a landmark event in the Islamic conquest of India, and has been described in several semi-legendar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Krishnadevaraya
Krishnadevaraya (17 January 1471 – 17 October 1529) was an emperor of the Vijayanagara Empire, also known as the Karnata Empire, reigning from 1509 to 1529. He was the third monarch of the Tuluva dynasty, and is considered to be one of the greatest rulers in Indian history. He ruled the largest empire in India after the decline of the Delhi Sultanate.Keay, John, India: A History, New York: Harper Collins, 2000, p.302 Presiding over the empire at its zenith, he is regarded as an icon by many Indians. Krishnadevaraya earned the titles ''Karnatakaratna Simhasanadeeshwara'' (lit. "Lord of the Jewelled Throne of Karnataka"), ''Yavana Rajya Pratistapanacharya'' (lit. "Establishment of the King to Bahmani Throne"), ''Kannada Rajya Rama Ramana'' (lit. "Lord of the Kannada Empire), ''Andhra Bhoja'' (lit. "Scholar of Andhra"), ''Gaubrahmana Pratipalaka'' (lit. "Protector of Brahmins and Cows") and ''Mooru Rayara Ganda'' (lit. "Lord of Three Kings"). He became the dominant ruler of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Babur
Babur ( fa, , lit= tiger, translit= Bābur; ; 14 February 148326 December 1530), born Mīrzā Zahīr ud-Dīn Muhammad, was the founder of the Mughal Empire in the Indian subcontinent. He was a descendant of Timur and Genghis Khan through his father and mother respectively.F. LehmannẒahīr-al-Dīn Moḥammad Bābor In Encyclopædia Iranica. Online Ed. December 1988 (updated August 2011). "Bābor, Ẓahīr-al-Dīn Moḥammad son of Umar Sheikh Mirza, (6 Moḥarram 886-6 Jomādā I 937/14 February 1483 – 26 December 1530), Timurid prince, military genius, and literary craftsman who escaped the bloody political arena of his Central Asian birthplace to found the Mughal Empire in India. His origin, milieu, training, and education were steeped in Muslim culture and so Bābor played significant role for the fostering of this culture by his descendants, the Mughals of India, and for the expansion of Islam in the Indian subcontinent, with brilliant literary, artistic, and histo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh (; , 'Northern Province') is a state in northern India. With over 200 million inhabitants, it is the most populated state in India as well as the most populous country subdivision in the world. It was established in 1950 after India had become a republic. It was a successor to the United Provinces (UP) during the period of the Dominion of India (1947–1950), which in turn was a successor to the United Provinces (UP) established in 1935, and eventually of the United Provinces of Agra and Oudh established in 1902 during the British Raj. The state is divided into 18 divisions and 75 districts, with the state capital being Lucknow, and Prayagraj serving as the judicial capital. On 9 November 2000, a new state, Uttaranchal (now Uttarakhand), was created from Uttar Pradesh's western Himalayan hill region. The two major rivers of the state, the Ganges and its tributary Yamuna, meet at the Triveni Sangam in Prayagraj, a Hindu pilgrimage site. Ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |