|
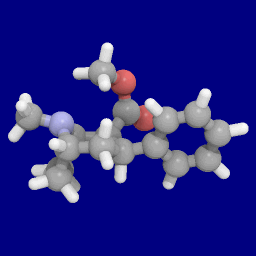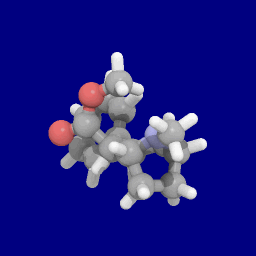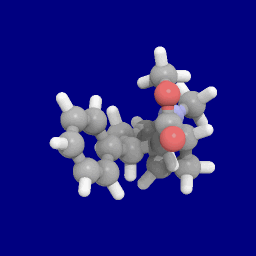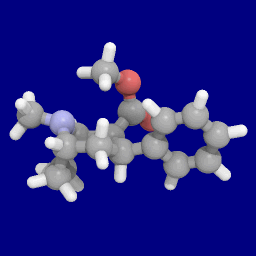
RTI-112
RTI(-''4229'')-112 (2β-carbomethoxy-3β-(3-methyl-4-chlorophenyl)tropane) is a synthetic stimulant drug from the phenyltropane family. In contrast to RTI-113, which is DAT selective, RTI-112 is a nonselective triple reuptake inhibitor. ''In vitro'' tests show a very similar serotonin transporter (SERT)/dopamine transporter (DAT)/norepinephrine transporter (NET) selectivity to cocaine, although in vivo behaviour is different: "The nonselective monoamine transporter inhibitor RTI-126 and the DAT-selective inhibitors RTI-150 and RTI-336 both had a faster rate of onset (30 min) and a short duration of action (4h). In contrast, the nonselective monoamine transporter inhibitor RTI-112 had a slower rate of onset (30–60 min) and a longer duration of action (10h). The DAT-selective inhibitors RTI-171 and RTI-177 also had slower rates of onset (30–120 min), but RTI-171 had a short duration of action (2.5 h) while RTI-177 had a very long duration of action (20 h)." The efficac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serotonin–norepinephrine–dopamine Reuptake Inhibitor
A serotonin–norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitor (SNDRI), also known as a triple reuptake inhibitor (TRI), is a type of drug that acts as a combined reuptake inhibitor of the monoamine neurotransmitters serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine. It does this by concomitantly inhibiting the serotonin transporter (SERT), norepinephrine transporter (NET), and dopamine transporter (DAT), respectively. Inhibition of the reuptake of these neurotransmitters increases their extracellular concentrations and, therefore, results in an increase in serotonergic, adrenergic, and dopaminergic neurotransmission. SNDRIs were developed as potential antidepressants and treatments for other disorders, such as obesity, cocaine addiction, attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), and chronic pain. They are an extension of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) whereby the addition of dopaminergic action is thought ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenyltropane
Phenyltropanes (PTs) were originally developed to reduce cocaine addiction and dependency. In general these compounds act as inhibitors of the plasmalemmal monoamine reuptake transporters. Although RTI holds a strong position in this field, they are not the ''only'' researchers that have prepared these analogues. This research has spanned beyond the last couple decades, and has picked up its pace in recent times, creating numerous phenyltropanes as research into cocaine analogues garners interest to treat addiction. Uses Addiction The phenyltropane compounds were initially discovered by R. Clarke et al. during research to try and dissociate the stimulant properties of cocaine from its abuse and dependence liability. The first simple phenyltropanes to be made (WIN 35065-2 and WIN 34,428) were shown to be active in behavioral assays only for the ββ-isomers. The activity of the corresponding αβ-isomers was disappointing. It was later shown that WIN 35065-2 and WIN 34,428 ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RTI-177
RTI(-''4229'')-177 (2β-(3-phenylisoxazol-5-yl)-3β-(4-chlorophenyl)tropane, β-CPPIT) is a synthetic stimulant drug from the phenyltropane family, which acts as a DRI with micromolar affinity for the SERT. RTI-177 has an unusually long duration of action of 20 hours or more, substantially longer than the related compound RTI-336 from which it differs in molecular structure only by the absence of a ''p''-methyl group. "the nonselective monoamine transporter inhibitor RTI-126 and the DAT-selective inhibitors RTI-150 and RTI-336 both had a faster rate of onset (30 min) and a short duration of action (4h). In contrast, the nonselective monoamine transporter inhibitor RTI-112 had a slower rate of onset (30–60 min) and a longer duration of action (10h). The DAT-selective inhibitors RTI-171 and RTI-177 also had slower rates of onset (30–120 min), but RTI-171 had a short duration of action (2.5 h) while RTI-177 had a very long duration of action (20 h)." Update [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stimulant
Stimulants (also often referred to as psychostimulants or colloquially as uppers) is an overarching term that covers many drugs including those that increase activity of the central nervous system and the body, drugs that are pleasurable and invigorating, or drugs that have Sympathomimetic drug, sympathomimetic effects. Stimulants are widely used throughout the world as prescription medicines as well as without a prescription (either legally or Prohibition (drugs), illicitly) as performance-enhancing substance, performance-enhancing or recreational drug use, recreational drugs. Among narcotics, stimulants produce a noticeable crash or ''Comedown (drugs), comedown'' at the end of their effects. The most frequently prescribed stimulants as of 2013 were lisdexamfetamine (Vyvanse), methylphenidate (Ritalin), and amphetamine (Adderall). It was estimated in 2015 that the percentage of the world population that had used cocaine during a year was 0.4%. For the category "amphetamines and p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RTI-336
RTI(-''4229'')-336, (LS-193,309, (−)-2β-(3-(4-methylphenyl)isoxazol-5-yl)-3β-(4-chlorophenyl)tropane) is a phenyltropane derivative which acts as a potent and selective dopamine reuptake inhibitor and stimulant drug. It binds to the dopamine transporter with around 20x the affinity of cocaine, however it produces relatively mild stimulant effects, with a slow onset and long duration of action. (however other sources class it as having among the faster onsets of action from among phenyltropanes) These characteristics make it a potential candidate for treatment of cocaine addiction, as a possible substitute drug analogous to how methadone is used for treating heroin abuse. RTI-336 fully substitutes for cocaine in addicted monkeys and supports self-administration, and significantly reduces rates of cocaine use, especially when combined with SSRIs, and research is ongoing to determine whether it could be a viable substitute drug in human cocaine addicts. Update [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RTI Compounds
RTI or Rti may refer to: Broadcasters * Radiodiffusion Television Ivoirienne, state broadcaster of Ivory Coast * Radio Taiwan International, a radio station in Taiwan * Reti Televisive Italiane, an Italian broadcaster and subsidiary of Mediaset Other businesses * RTI International, formerly Research Triangle Institute, a not-for-profit American research organization * RTI International Metals, an American company producing titanium * RTI Producciones, a Colombian television production company In science and technology In computing and telecommunications * Run-time infrastructure (simulation) In medicine * Reproductive tract infection * Respiratory tract infection * Reverse-transcriptase inhibitor, a class of antiretroviral drug Other uses in science and technology * Ramp travel index, a measure of an off road vehicle articulation, ability to keep all wheels in contact with the ground over uneven terrain * Rayleigh–Taylor instability, an instability of an interfa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropanes
Tropane alkaloids are a class of bicyclic .2.1alkaloids and secondary metabolites that contain a tropane ring in their chemical structure. Tropane alkaloids occur naturally in many members of the plant family Solanaceae. Certain tropane alkaloids such as cocaine and scopolamine are notorious for their psychoactive effects, related usage and cultural associations. Particular tropane alkaloids such as these have pharmacological properties and can act as anticholinergics or stimulants. Classification Anticholinergics Anticholinergic drugs and deliriants: * Atropine, racemic hyoscyamine, from the deadly nightshade (''Atropa belladonna'') * Hyoscyamine, the ''levo''-isomer of atropine, from henbane (''Hyoscyamus niger''), mandrake (''Mandragora officinarum'') and the sorcerers' tree (''Latua pubiflora''). * Scopolamine, from henbane and ''Datura'' species (Jimson weed) All three acetylcholine-inhibiting chemicals can also be found in the leaves, stems, and flowers in varying, un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlorobenzenes
Chlorobenzene is an aromatic organic compound with the chemical formula C6H5Cl. This colorless, flammable liquid is a common solvent and a widely used intermediate in the manufacture of other chemicals. Uses Historical The major use of chlorobenzene is as an intermediate in the production of herbicides, dyestuffs, and rubber. Chlorobenzene is also used as a high-boiling solvent in industrial applications as well as in the laboratory. Chlorobenzene is nitrated on a large scale to give a mixture of 2-nitrochlorobenzene and 4-nitrochlorobenzene, which are separated. These mononitrochlorobenzenes are converted to related 2-nitrophenol, 2-nitroanisole, bis(2-nitrophenyl)disulfide, and 2-nitroaniline by nucleophilic displacement of the chloride, with respectively sodium hydroxide, sodium methoxide, sodium disulfide, and ammonia. The conversions of the 4-nitro derivative are similar. Chlorobenzene once was used in the manufacture of pesticides, most notably DDT, by reaction with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
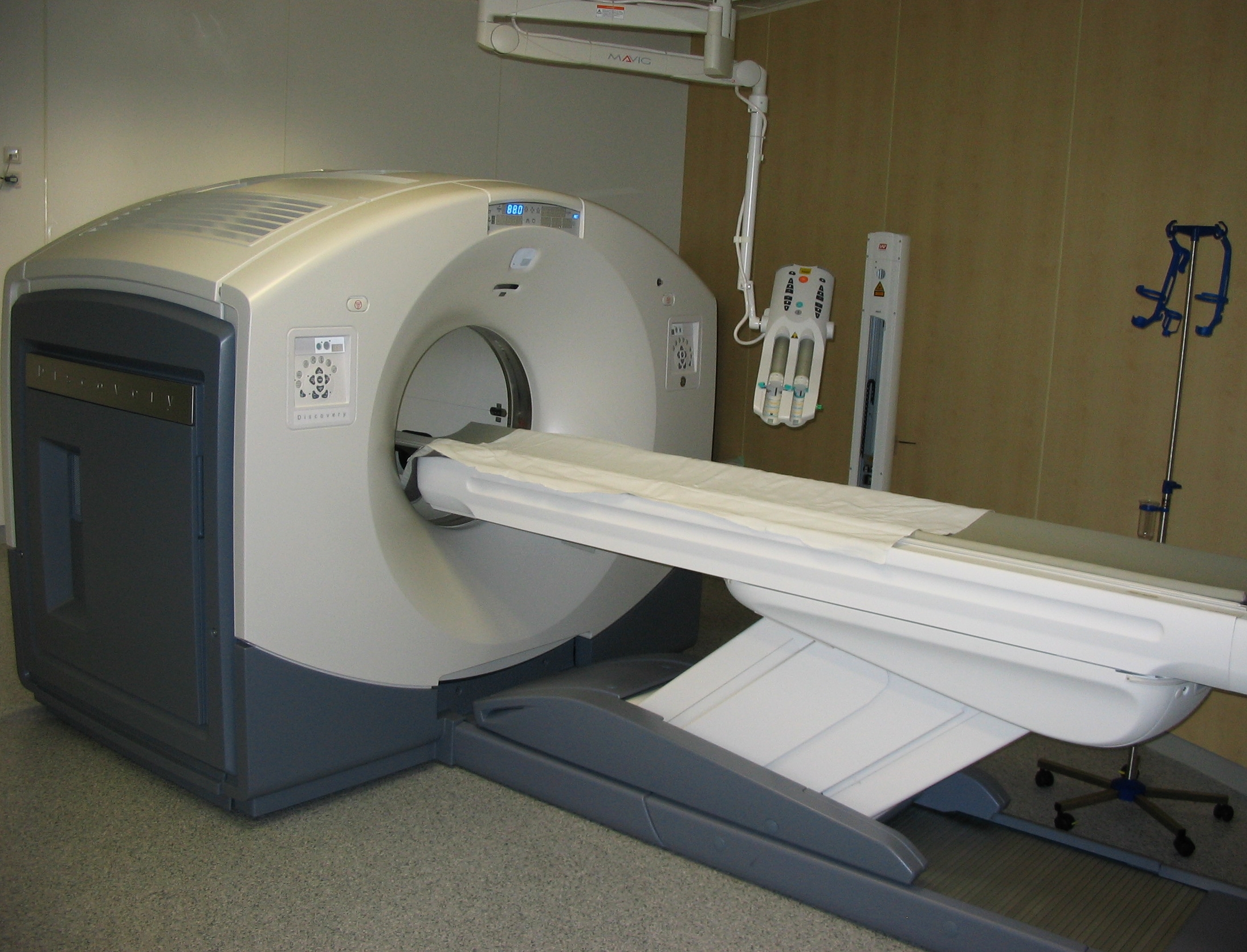
PET Scan
Positron emission tomography (PET) is a functional imaging technique that uses radioactive substances known as radiotracers to visualize and measure changes in metabolic processes, and in other physiological activities including blood flow, regional chemical composition, and absorption. Different tracers are used for various imaging purposes, depending on the target process within the body. For example, -FDG is commonly used to detect cancer, NaF is widely used for detecting bone formation, and oxygen-15 is sometimes used to measure blood flow. PET is a common imaging technique, a medical scintillography technique used in nuclear medicine. A radiopharmaceutical — a radioisotope attached to a drug — is injected into the body as a tracer. When the radiopharmaceutical undergoes beta plus decay, a positron is emitted, and when the positron collides with an ordinary electron, the two particles annihilate and gamma rays are emitted. These gamma rays are detected by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dopamine Reuptake Inhibitor
A dopamine reuptake inhibitor (DRI) is a class of drug which acts as a reuptake inhibitor of the monoamine neurotransmitter dopamine by blocking the action of the dopamine transporter (DAT). Reuptake inhibition is achieved when extracellular dopamine not absorbed by the postsynaptic neuron is blocked from re-entering the presynaptic neuron. This results in increased extracellular concentrations of dopamine and increase in dopaminergic neurotransmission. DRIs are used in the treatment of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and narcolepsy for their psychostimulant effects, and in the treatment of obesity and binge eating disorder for their appetite suppressant effects. They are sometimes used as antidepressants in the treatment of mood disorders, but their use as antidepressants is limited given that strong DRIs have a high abuse potential and legal restrictions on their use. Lack of dopamine reuptake and the increase in extracellular levels of dopamine have been lin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RTI-171
(–)-2β-(3-Methylisoxazol-5-yl)-3β-(p-tolyl)tropane (RTI-''4229''-171) is a phenyltropane derivative which acts as a selective dopamine reuptake inhibitor, with a relatively slow onset of action and short duration of effects found in animal studies. However, other studies have shown it to have the most pronounced effects in terms of speed of onset and rate of stimulation among many differing phenyltropanes. See also * List of phenyltropanes * RTI-126 * O-4210 References Tropanes RTI compounds Dopamine reuptake inhibitors {{nervous-system-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RTI-126
RTI-126 (RTI-''4229''-126 or (–)-2β-(1,2,4-oxadiazol-5-methyl)-3β-phenyltropane) is a phenyltropane derivative which acts as a potent monoamine reuptake inhibitor and stimulant drug, and has been sold as a designer drug. It is around 5 times more potent than cocaine at inhibiting monoamine reuptake ''in vitro'', but is relatively unselective. It binds to all three monoamine transporters, although still with some selectivity for the dopamine transporter. RTI-126 has a fast onset of effects and short duration of action, and its pharmacological profile in animals is among the closest to cocaine itself out of all the drugs in the RTI series. Its main application in scientific research has been in studies investigating the influence of pharmacokinetics on the abuse potential of stimulant drugs, with its rapid entry into the brain thought to be a key factor in producing its high propensity for development of dependence in animals. The structurally related compound (–)-2β-(3-met ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |