Phenyltropane on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Phenyltropanes (PTs) were originally developed to reduce
Phenyltropanes (PTs) were originally developed to reduce

 Phenyltropanes (PTs) were originally developed to reduce
Phenyltropanes (PTs) were originally developed to reduce cocaine
Cocaine (from , from , ultimately from Quechuan languages, Quechua: ''kúka'') is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant mainly recreational drug use, used recreationally for its euphoria, euphoric effects. It is primarily obtained from t ...
addiction and dependency. In general these compounds act as inhibitors of the plasmalemmal
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane (PM) or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment (th ...
monoamine
Monoamine neurotransmitters are neurotransmitters and neuromodulators that contain one amino group connected to an aromatic ring by a two-carbon chain (such as -CH2-CH2-). Examples are dopamine, norepinephrine and serotonin.
All monoamines ar ...
reuptake
Reuptake is the reabsorption of a neurotransmitter by a neurotransmitter transporter located along the plasma membrane of an axon terminal (i.e., the Synapse, pre-synaptic neuron at a synapse) or glial cell after it has performed its function of ...
transporters. Although RTI holds a strong position in this field, they are not the ''only'' researchers that have prepared these analogues. This research has spanned beyond the last couple decades, and has picked up its pace in recent times, creating numerous phenyltropanes as research into cocaine analogues garners interest to treat addiction.
Uses
Addiction
The phenyltropane compounds were initially discovered by R. Clarke et al. during research to try and dissociate the stimulant properties of cocaine from its abuse and dependence liability. The first simple phenyltropanes to be made (WIN 35065-2 and WIN 34,428) were shown to be active in behavioral assays only for the ββ-isomers. The activity of the corresponding αβ-isomers was disappointing. It was later shown that WIN 35065-2 and WIN 34,428 are mostlydopamine
Dopamine (DA, a contraction of 3,4-dihydroxyphenethylamine) is a neuromodulatory molecule that plays several important roles in cells. It is an organic compound, organic chemical of the catecholamine and phenethylamine families. Dopamine const ...
selective reuptake inhibitors with some residual actions at the norepinephrine transporter
The norepinephrine transporter (NET), also known as noradrenaline transporter (NAT), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the solute carrier family 6 member 2 (SLC6A2) gene.
NET is a monoamine transporter and is responsible for the sodium- ...
(NET) and serotonin transporter
The serotonin transporter (SERT or 5-HTT) also known as the sodium-dependent serotonin transporter and solute carrier family 6 member 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC6A4 gene. SERT is a type of monoamine transporter protein tha ...
(SERT). The neurotransmitter dopamine is a key candidate for explanation of reinforcing actions drugs. It's unclear to which extent NET is involved in the reinforcing actions of cocaine
Cocaine (from , from , ultimately from Quechuan languages, Quechua: ''kúka'') is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant mainly recreational drug use, used recreationally for its euphoria, euphoric effects. It is primarily obtained from t ...
(an SNDRI). Animal studies show evidence that inhibiting the SERT might reduce cocaine intake.
Animal studies on monkeys and rats have tried to assess the self-administration propensity of phenyltropane analogs alongside cocaine. Frequently the analogs are administered prior to the start of a session to see if they can suppress cocaine lever responding. Most of the analogs behave in ways that might be considered typical for a DRI. In particular, they tend to stimulate locomotor activity, and cause nonselective reductions in cocaine intake relative to food. At the dose that can reduce cocaine intake, most of the analogs require a high DAT occupancy. This would mean that the agonists would need to be behaviorally active at the dose that can bring about reductions in cocaine craving. Most of the analogs will readily substitute for cocaine, although most do not elicit as many lever responses per session because of pharmacokinetic factors. Since these agonists function as reinforcers, there is an obvious concern surrounding their abuse liability.
Nevertheless, a slow onset, long-duration agonist seems like a reasonable approach. Phenyltropanes are widely used in animal studies of drug addiction
Addiction is a neuropsychological disorder characterized by a persistent and intense urge to engage in certain behaviors, one of which is the usage of a drug, despite substantial harm and other negative consequences. Repetitive drug use of ...
as they share the stimulant properties and reinforcing effects of cocaine, but with higher potency, less non-specific binding which avoids the cardiotoxicity
Cardiotoxicity is the occurrence of heart dysfunction as electric or muscle damage, resulting in heart toxicity. The heart becomes weaker and is not as efficient in pumping blood. Cardiotoxicity may be caused by chemotherapy (a usual example is th ...
associated with cocaine.

RTI-336
RTI(-''4229'')-336, (LS-193,309, (−)-2β-(3-(4-methylphenyl)isoxazol-5-yl)-3β-(4-chlorophenyl)tropane) is a phenyltropane derivative which acts as a potent and selective dopamine reuptake inhibitor and stimulant drug. It binds to the dopamine ...
is an interesting example of a phenyltropane that is being explored in the context of a treatment for cocaine addiction. RTI-336 is a DRI and thus specifically targets the DAT which is responsible for the addictive properties of cocaine. Although there may be a role for NET inhibition and acetylcholinergic actions, clearly it is DA which is the critical neurotransmitter. Dopamine is a biological precursor to noradrenaline. DA is made from tyrosine
-Tyrosine or tyrosine (symbol Tyr or Y) or 4-hydroxyphenylalanine is one of the 20 standard amino acids that are used by cells to synthesize proteins. It is a non-essential amino acid with a polar side group. The word "tyrosine" is from the Gr ...
, which is a non-essential amino acid
An essential amino acid, or indispensable amino acid, is an amino acid that cannot be synthesized from scratch by the organism fast enough to supply its demand, and must therefore come from the diet. Of the 21 amino acids common to all life form ...
given that it can be made from phenylalanine.
The more greatly attested habit creating methamphetamine is more serotonergic than the lesser reinforcing amphetamine. Most modern research suggests that 5-HT is ''negatively'' correlated with the addiction forming potential of psychostimulants, this is not saying that SRI properties cannot be considered beneficial. In fact, the above was proven by Rothman for releasing agents under the PAL-287 program of related molecules. What was somewhat interesting is that although the reason for the lack of reinforcement of RTI-112
RTI(-''4229'')-112 (2β-carbomethoxy-3β-(3-methyl-4-chlorophenyl)tropane) is a synthetic stimulant drug from the phenyltropane family. In contrast to RTI-113, which is DAT selective, RTI-112 is a nonselective triple reuptake inhibitor.
''In ...
is now well established, closely related RTI-111
Dichloropane ((−)-2β-Carbomethoxy-3β-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)tropane, RTI-111, O-401) is a stimulant of the phenyltropane class that acts as a serotonin–norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitor (SNDRI) with IC50 values of 3.13, 0.79 and ...
was able to behave in ways that might be typical for a nonselective SNDRI such as cocaine. The role of the NET is not completely deleterious. In a recent paper by Rothman on transporter substrates, he establishes that for releasers that are amphetamine-like, discrimination stimulus is more accurately dictated by NE release than DA release. This argument does not mitigate a case against the importance of DA, but is suggestive that catecholamine ''in general'' is important. the exact ratio being 50:50 in the case of methylphenidate.
Desipramine
Desipramine, sold under the brand name Norpramin among others, is a tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) used in the treatment of depression. It acts as a relatively selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor, though it does also have other activiti ...
and atomoxetine
Atomoxetine, sold under the brand name Strattera, among others, is a medication used to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). It may be used alone or along with psychostimulants. It is also used as a cognitive enhancer to impro ...
are not reliably self-administered though, whereas most selective DRIs are. SSRIs are not self-administered either. Hence, it should be borne in mind that these neurotransmitters are unlikely to be involved in the addiction forming properties of cocaine and related stimulants. Nevertheless, they are still behaviorally active and will contribute to the effects that such drugs elicit in their users.
Promiscuity among transporters is worth bearing in mind. Monoamine transporters can transport neurotransmitters other than their "native" neurotransmitter. As an example, in the prefrontal cortex
In mammalian brain anatomy, the prefrontal cortex (PFC) covers the front part of the frontal lobe of the cerebral cortex. The PFC contains the Brodmann areas BA8, BA9, BA10, BA11, BA12, BA13, BA14, BA24, BA25, BA32, BA44, BA45, BA46 ...
where DATs are lower in number, DA is transported mostly by the NET instead. Hence, selective NRIs such as atomoxetine are able to increase the concentration of supracellular (synaptic) DA in this brain region via NET blockade.
Weeding out SERT and NET affinity is desirable in the context that these molecular targets are less relevant to the goals of the treatment program, which is to reduce cocaine intake. It can be clearly seen that RTI-336 has fewer metabolically labile sites than cocaine, and therefore has a longer duration span.
Binding ligands
These compounds are primarily used in scientific research, as their highbinding affinity
In biochemistry and pharmacology, a ligand is a substance that forms a complex with a biomolecule to serve a biological purpose. The etymology stems from ''ligare'', which means 'to bind'. In protein-ligand binding, the ligand is usually a m ...
for monoamine transporters, and the wide range of radiolabelled
Isotopic labeling (or isotopic labelling) is a technique used to track the passage of an isotope (an atom with a detectable variation in neutron count) through a reaction, metabolic pathway, or cell. The reactant is 'labeled' by replacing specific ...
phenyltropane compounds available with different binding specificities makes them very useful for mapping the distribution of the various monoamine transporters in the brain.
Other uses
Some phenyltropane derivatives have also been researched for medical use in the treatment of conditions such asParkinson's disease
Parkinson's disease (PD), or simply Parkinson's, is a long-term degenerative disorder of the central nervous system that mainly affects the motor system. The symptoms usually emerge slowly, and as the disease worsens, non-motor symptoms becom ...
and Alzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegeneration, neurodegenerative disease that usually starts slowly and progressively worsens. It is the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in short-term me ...
, depression, and their strong appetite suppressant
An anorectic or anorexic is a drug which reduces appetite, resulting in lower food consumption, leading to weight loss. By contrast, an appetite stimulant is referred to as orexigenic.
The term is (from the Greek ''ἀν-'' (an-) = "without" ...
effects makes them promising candidates for facilitating weight loss in the treatment of obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, sometimes considered a disease, in which excess body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it may negatively affect health. People are classified as obese when their body mass index (BMI)—a person's we ...
.
Structure-activity relationships
Transporter selectivity
Compounds are known with a pronounced selectivity for each MAT –dopamine
Dopamine (DA, a contraction of 3,4-dihydroxyphenethylamine) is a neuromodulatory molecule that plays several important roles in cells. It is an organic compound, organic chemical of the catecholamine and phenethylamine families. Dopamine const ...
, noradrenaline
Norepinephrine (NE), also called noradrenaline (NA) or noradrenalin, is an organic chemical in the catecholamine family that functions in the brain and body as both a hormone and neurotransmitter. The name "noradrenaline" (from Latin '' ad'', ...
and the serotonin transporter
The serotonin transporter (SERT or 5-HTT) also known as the sodium-dependent serotonin transporter and solute carrier family 6 member 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC6A4 gene. SERT is a type of monoamine transporter protein tha ...
.
Phenyltropane-based " SNDRI's" are another possibility.
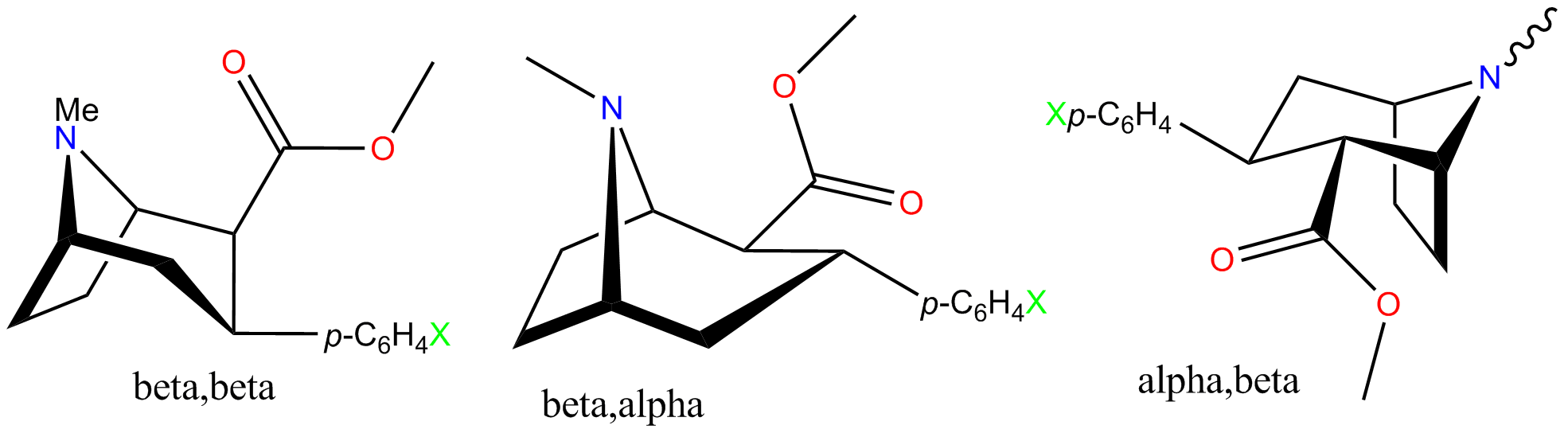
Isomers study
All of the tables and graphs shown beneath is from an article published by FIC, et al. 2004. In summary the following observations can be made: Troparil, WIN35428 and RTI-32 are insufficiently potent. This observation is mainly based on the fact that at 100 mg/kg both troparil and WIN35428 produce convulsions. The twist-boat isomers are insufficiently potent in all cases. The ''trans'' isomers (alpha,beta) are too weak and might actually be dangerous and cause death. RTI-55, while highly potent, still causes death at a dose of 100 mg/kg. It is advised to considerRTI-229
RTI-229, also known as (–)-3β-(4-iodophenyl)tropane-2β-pyrrolidine carboxamide and RTI-''4229''-229, is a potent and long-lasting stimulant drug which was developed in the 1990s as part of a large group of related analogues from the phenylt ...
. RTI-31 is the most potent isomers for the DAT and was "safe" (on a relative scale) even in the event of overdose at 100 mg/kg. RTI-51 also looks like a "good" compound, although its synthesis is slightly more difficult than for RTI-31. RTI-51 is less selective for the DAT than RTI-31 and has appreciable SERT affinity also.

MAT binding affinities
LMA, D.D. and G.B.
See also:Related compounds
Closely related compounds have a variedaryl
In organic chemistry, an aryl is any functional group or substituent derived from an aromaticity, aromatic ring, usually an aromatic hydrocarbon, such as phenyl and naphthyl. "Aryl" is used for the sake of abbreviation or generalization, and "Ar ...
fragment, like naphthyl
Naphthalene is an organic compound with formula . It is the simplest polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon, and is a white crystalline solid with a characteristic odor that is detectable at concentrations as low as 0.08 ppm by mass. As an aromati ...
, or a varied tropane fragment like with exchanged heteroatom
In chemistry, a heteroatom () is, strictly, any atom that is not carbon or hydrogen.
Organic chemistry
In practice, the term is usually used more specifically to indicate that non-carbon atoms have replaced carbon in the backbone of the molecula ...
, trop-2-enes, quinuclidine
Quinuclidine is an organic compound and a bicyclic amine and used as a catalyst and a chemical building block. It is a strong base with p''K''a of the conjugate acid of 11.0.{{cite journal , title=Azatriquinanes: Synthesis, Structure, and Reacti ...
s, piperidine
Piperidine is an organic compound with the molecular formula (CH2)5NH. This heterocyclic amine consists of a six-membered ring containing five methylene bridges (–CH2–) and one amine bridge (–NH–). It is a colorless liquid with an odor de ...
s.
References
{{stimulants Tropanes Serotonin–norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitors Stimulants Substance dependence