|
REEP5
Receptor expression-enhancing protein 5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''REEP5'' gene. Receptor Expression Enhancing Protein is a protein encoded for in Humans by the REEP5 gene. Gene REEP5 is located on chromosome 5 between base pairs 112876385 to 112922289 on the minus strand. The gene includes five exons. The genes DCP2 and SRP19 are located upstream and downstream of REEP5 in humans. Protein The protein is a member of the REEP family, which generally facilitate intracellular trafficking through alterations to the endoplasmic reticulum, and which have the ability to enhance activity of G-protein coupled receptors. The human protein is 189 amino acids in length, containing two transmembrane regions and one named region- TB2_DP1_HVA22, The pre-modification protein mass is 21.5 kdal. Compared to the SwissProt collection of human proteins, REEP5 is composed of normal percentages of all amino acids. Aside from a long stretch of electrically neutral amino acids, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
REEP5 Comparative Evolutionary Rate
Receptor expression-enhancing protein 5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''REEP5'' gene. Receptor Expression Enhancing Protein is a protein encoded for in Humans by the REEP5 gene. Gene REEP5 is located on chromosome 5 between base pairs 112876385 to 112922289 on the minus strand. The gene includes five exons. The genes DCP2 and SRP19 are located upstream and downstream of REEP5 in humans. Protein The protein is a member of the REEP family, which generally facilitate intracellular trafficking through alterations to the endoplasmic reticulum, and which have the ability to enhance activity of G-protein coupled receptors. The human protein is 189 amino acids in length, containing two transmembrane regions and one named region- TB2_DP1_HVA22, The pre-modification protein mass is 21.5 kdal. Compared to the SwissProt collection of human proteins, REEP5 is composed of normal percentages of all amino acids. Aside from a long stretch of electrically neutral amino acids, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Humans
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, and language. Humans are highly social and tend to live in complex social structures composed of many cooperating and competing groups, from families and kinship networks to political states. Social interactions between humans have established a wide variety of values, social norms, and rituals, which bolster human society. Its intelligence and its desire to understand and influence the environment and to explain and manipulate phenomena have motivated humanity's development of science, philosophy, mythology, religion, and other fields of study. Although some scientists equate the term ''humans'' with all members of the genus ''Homo'', in common usage, it generally refers to ''Homo sapiens'', the only extant member. Anatomically ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DCP2
mRNA-decapping enzyme 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''DCP2'' gene In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a b .... DCP2 is a key component of an mRNA-decapping complex required for removal of the 5-prime cap from mRNA prior to its degradation from the 5-prime end (Fenger-Gron et al., 2005). upplied by OMIMref name="entrez" /> Interactions DCP2 has been shown to interact with DCP1A and UPF1. References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{gene-5-stub Nudix hydrolases ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transmembrane Regions Of REEP5
A transmembrane protein (TP) is a type of integral membrane protein that spans the entirety of the cell membrane. Many transmembrane proteins function as gateways to permit the transport of specific substances across the membrane. They frequently undergo significant conformational changes to move a substance through the membrane. They are usually highly hydrophobic and aggregate and precipitate in water. They require detergents or nonpolar solvents for extraction, although some of them (beta-barrels) can be also extracted using denaturing agents. The peptide sequence that spans the membrane, or the transmembrane segment, is largely hydrophobic and can be visualized using the hydropathy plot. Depending on the number of transmembrane segments, transmembrane proteins can be classified as single-span (or bitopic) or multi-span (polytopic). Some other integral membrane proteins are called monotopic, meaning that they are also permanently attached to the membrane, but do not pass t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HPA RNA-sequencing Data For REEP5
HPA may refer to: Organizations * Harry Potter Alliance, a charity * Halifax Port Authority, Canada * Hamburg Port Authority, Germany * Hawaii Preparatory Academy, a school in Hawaii, US * Health Protection Agency, UK * Heerespersonalamt, the German Army Personnel Agency 1920-1944 * Hollywood Post Alliance, an American trade organization * Houston Peace Academy of the Islamic Education Institute of Texas, US * Hurlingham Polo Association, UK polo governing body * HPA Toucan human-powered aircraft built by Hertfordshire Pedal Aeronauts People *Hans Peter Anvin (born 1972), Swedish computer programmer *Howlin' Pelle Almqvist (Born 1978), Swedish lead singer of garage rock band The Hives Science * Hectopascal (hPa), a unit of pressure * Human platelet antigen * Human Protein Atlas * Hydrogen pinch analysis * Hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis in physiology Technology *High-performance addressing, in LCD displays *Host protected area of computer data storage *Human-powered a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
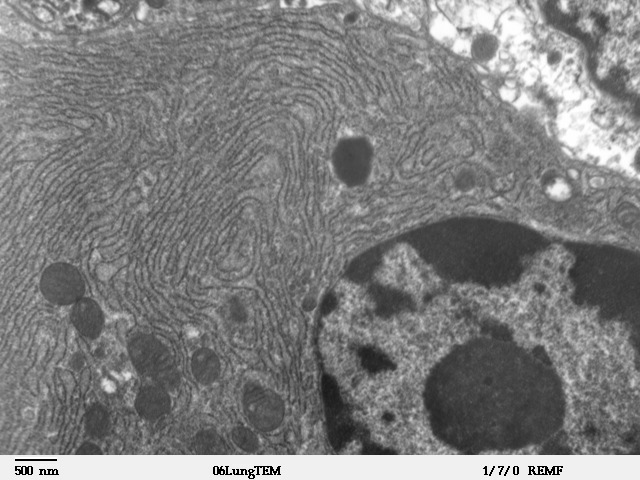
Endoplasmic Reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is, in essence, the transportation system of the eukaryotic cell, and has many other important functions such as protein folding. It is a type of organelle made up of two subunits – rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER), and smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER). The endoplasmic reticulum is found in most eukaryotic cells and forms an interconnected network of flattened, membrane-enclosed sacs known as cisternae (in the RER), and tubular structures in the SER. The membranes of the ER are continuous with the outer nuclear membrane. The endoplasmic reticulum is not found in red blood cells, or spermatozoa. The two types of ER share many of the same proteins and engage in certain common activities such as the synthesis of certain lipids and cholesterol. Different types of cells contain different ratios of the two types of ER depending on the activities of the cell. RER is found mainly toward the nucleus of cell and SER towards the cell membrane or plasma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Post-translational Modification
Post-translational modification (PTM) is the covalent and generally enzymatic modification of proteins following protein biosynthesis. This process occurs in the endoplasmic reticulum and the golgi apparatus. Proteins are synthesized by ribosomes translating mRNA into polypeptide chains, which may then undergo PTM to form the mature protein product. PTMs are important components in cell signaling, as for example when prohormones are converted to hormones. Post-translational modifications can occur on the amino acid side chains or at the protein's C- or N- termini. They can extend the chemical repertoire of the 20 standard amino acids by modifying an existing functional group or introducing a new one such as phosphate. Phosphorylation is a highly effective mechanism for regulating the activity of enzymes and is the most common post-translational modification. Many eukaryotic and prokaryotic proteins also have carbohydrate molecules attached to them in a process called glycosyla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
O-GlcNAc
''O''-GlcNAc (short for ''O''-linked GlcNAc or ''O''-linked β-''N''-acetylglucosamine) is a reversible enzymatic post-translational modification that is found on serine and threonine residues of nucleocytoplasmic proteins. The modification is characterized by a β-glycosidic bond between the hydroxyl group of serine or threonine side chains and ''N''-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc). ''O''-GlcNAc differs from other forms of protein glycosylation: (i) ''O''-GlcNAc is not elongated or modified to form more complex glycan structures, (ii) ''O''-GlcNAc is almost exclusively found on nuclear and cytoplasmic proteins rather than membrane proteins and secretory proteins, and (iii) ''O''-GlcNAc is a highly dynamic modification that turns over more rapidly than the proteins which it modifies. ''O''-GlcNAc is conserved across metazoans. Due to the dynamic nature of ''O''-GlcNAc and its presence on serine and threonine residues, ''O''-GlcNAcylation is similar to protein phosphorylation in some r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‑CoV‑2) is a strain of coronavirus that causes COVID-19 (coronavirus disease 2019), the respiratory illness responsible for the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic. The virus previously had a Novel coronavirus, provisional name, 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV), and has also been called the human coronavirus 2019 (HCoV-19 or hCoV-19). First identified in the city of Wuhan, Hubei, China, the World Health Organization declared the outbreak a public health emergency of international concern on January 30, 2020, and a pandemic on March 11, 2020. SARS‑CoV‑2 is a positive-sense single-stranded RNA virus that is Contagious disease, contagious in humans. SARS‑CoV‑2 is a virus of the species ''severe acute respiratory syndrome–related coronavirus'' (SARSr-CoV), related to the Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 1, SARS-CoV-1 virus that caused the 2002–2004 SARS outbreak. Despite its close relation to SARS-CoV-1, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |