Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‑CoV‑2) is a strain of First identified in the city of SARS‑CoV‑2 is a
 During the initial outbreak in
During the initial outbreak in
 No
No  Bats are considered the most likely natural reservoir of SARS‑CoV‑2. Differences between the bat coronavirus and SARS‑CoV‑2 suggest that humans may have been infected via an intermediate host; although the source of introduction into humans remains unknown.
Although the role of
Bats are considered the most likely natural reservoir of SARS‑CoV‑2. Differences between the bat coronavirus and SARS‑CoV‑2 suggest that humans may have been infected via an intermediate host; although the source of introduction into humans remains unknown.
Although the role of
SARS‑CoV‑2 belongs to the broad family of viruses known as 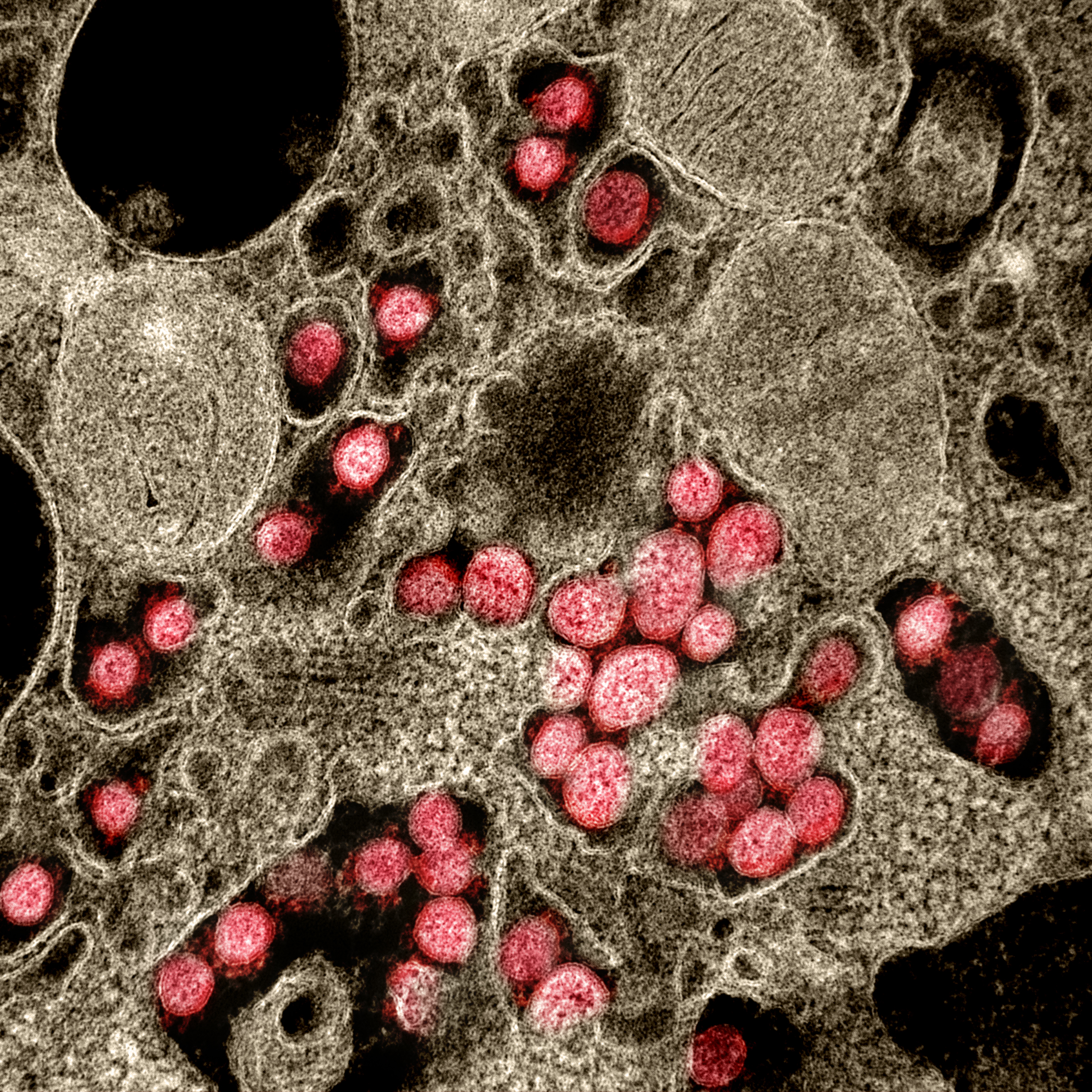 A distinguishing feature of SARS‑CoV‑2 is its incorporation of a polybasic site cleaved by
A distinguishing feature of SARS‑CoV‑2 is its incorporation of a polybasic site cleaved by It was suggested that the acquisition of the furin-cleavage site in the SARS-CoV-2 S protein was essential for zoonotic transfer to humans. The furin In SARS-CoV-2 the recognition site is formed by the incorporated 12 Genetic code, codon nucleotide sequence CCT CGG CGG GCA which corresponds to the amino acid sequence P RR A. This sequence is upstream of an arginine and serine which forms the S1/S2 cleavage site ( P RR A R↓ S) of the spike protein. Although such sites are a common naturally-occurring feature of other viruses within the Subfamily Orthocoronavirinae, it appears in few other viruses from the Beta-CoV genus, and it is unique among members of its subgenus for such a site. The furin cleavage site PRRAR↓ is identical to that of the
In July 2020, scientists reported that a more infectious SARS‑CoV‑2 variant with
 There are many thousands of variants of SARS-CoV-2, which can be grouped into the much larger
There are many thousands of variants of SARS-CoV-2, which can be grouped into the much larger
 Each SARS-CoV-2
Each SARS-CoV-2 
coronavirus
Coronaviruses are a group of related RNA viruses that cause diseases in mammals and birds. In humans and birds, they cause respiratory tract infections that can range from mild to lethal. Mild illnesses in humans include some cases of the com ...
that causes COVID-19
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a contagious disease caused by a virus, the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The first known case was COVID-19 pandemic in Hubei, identified in Wuhan, China, in December ...
(coronavirus disease 2019), the respiratory illness
Respiratory diseases, or lung diseases, are pathological conditions affecting the organs and tissues that make gas exchange difficult in air-breathing animals. They include conditions of the respiratory tract including the trachea, bronchi, bron ...
responsible for the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the coronavirus pandemic, is an ongoing global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The novel virus was first identif ...
. The virus previously had a provisional name, 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV), and has also been called the human coronavirus 2019 (HCoV-19 or hCoV-19). Wuhan
Wuhan (, ; ; ) is the capital of Hubei, Hubei Province in the China, People's Republic of China. It is the largest city in Hubei and the most populous city in Central China, with a population of over eleven million, the List of cities in China ...
, Hubei
Hubei (; ; alternately Hupeh) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China, and is part of the Central China region. The name of the province means "north of the lake", referring to its position north of Dongting Lake. The prov ...
, China, the World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level of h ...
declared the outbreak a public health emergency of international concern
A public health emergency of international concern (PHEIC) is a formal declaration by the World Health Organization (WHO) of "an extraordinary event which is determined to constitute a public health risk to other States through the internatio ...
on January 30, 2020, and a pandemic
A pandemic () is an epidemic of an infectious disease that has spread across a large region, for instance multiple continents or worldwide, affecting a substantial number of individuals. A widespread endemic (epidemiology), endemic disease wi ...
on March 11, 2020.positive-sense single-stranded RNA virus
Positive-strand RNA viruses (+ssRNA viruses) are a group of related viruses that have positive-sense, single-stranded genomes made of ribonucleic acid. The positive-sense genome can act as messenger RNA (mRNA) and can be directly translated into ...
that is contagious
Contagious may refer to:
* Contagious disease
Literature
* Contagious (magazine), a marketing publication
* ''Contagious'' (novel), a science fiction thriller novel by Scott Sigler
Music
Albums
*''Contagious'' (Peggy Scott-Adams album), 1997
* ...
in humans.
SARS‑CoV‑2 is a virus of the species ''severe acute respiratory syndrome–related coronavirus
''Severe acute respiratory syndrome–related coronavirus'' (SARSr-CoV or SARS-CoV)The terms ''SARSr-CoV'' and ''SARS-CoV'' are sometimes used interchangeably, especially prior to the discovery of SARS-CoV-2. This may cause confusion when some ...
'' (SARSr-CoV), related to the SARS-CoV-1
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 1 (SARS-CoV-1; or Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus, SARS-CoV) is a strain of coronavirus that causes severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), the respiratory illness responsible for ...
virus that caused the 2002–2004 SARS outbreak
The 2002–2004 outbreak of SARS, caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV or SARS-CoV-1), infected over 8,000 people from 29 countries and territories, and resulted in at least 774 deaths worldwide.
The outbreak wa ...
. Despite its close relation to SARS-CoV-1, its closest known relatives, with which it forms a sister group, are the derived SARS viruses BANAL-52 and RaTG13. Available evidence indicates that it is most likely of zoonotic
A zoonosis (; plural zoonoses) or zoonotic disease is an infectious disease of humans caused by a pathogen (an infectious agent, such as a bacterium, virus, parasite or prion) that has jumped from a non-human (usually a vertebrate) to a human. ...
origin and has close genetic similarity to bat coronaviruses, suggesting it emerged from a bat-borne virus
The bat virome is the group of viruses associated with bats. Bats host a diverse array of viruses, including all seven types described by the Baltimore classification system: (I) double-stranded DNA viruses; (II) single-stranded DNA viruses; ...
. Research is ongoing as to whether SARS‑CoV‑2 came directly from bats or indirectly through any intermediate hosts. The virus shows little genetic diversity
Genetic diversity is the total number of genetic characteristics in the genetic makeup of a species, it ranges widely from the number of species to differences within species and can be attributed to the span of survival for a species. It is dis ...
, indicating that the spillover event introducing SARS‑CoV‑2 to humans is likely to have occurred in late 2019.
Epidemiological
Epidemiology is the study and analysis of the distribution (who, when, and where), patterns and determinants of health and disease conditions in a defined population.
It is a cornerstone of public health, and shapes policy decisions and evidenc ...
studies estimate that, in the December 2019–September 2020 period, each infection resulted in an average of 2.4–3.4 new infections when no members of the community are immune
In biology, immunity is the capability of multicellular organisms to resist harmful microorganisms. Immunity involves both specific and nonspecific components. The nonspecific components act as barriers or eliminators of a wide range of pathogens ...
and no preventive measures are taken. However, some subsequent variants have become more infectious. The virus primarily spreads between people through close contact and via aerosols
An aerosol is a suspension of fine solid particles or liquid droplets in air or another gas. Aerosols can be natural or anthropogenic. Examples of natural aerosols are fog or mist, dust, forest exudates, and geyser steam. Examples of anthrop ...
and respiratory droplets
A respiratory droplet is a small aqueous droplet produced by exhalation, consisting of saliva or mucus and other matter derived from respiratory tract surfaces. Respiratory droplets are produced naturally as a result of breathing, speaking, snee ...
that are exhaled when talking, breathing, or otherwise exhaling, as well as those produced from coughs and sneezes. It enters human cells by binding to angiotensin-converting enzyme 2
Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) is an enzyme that can be found either attached to the membrane of cells (mACE2) in the intestines, kidney, testis, gallbladder, and heart or in a soluble form (sACE2). Both membrane bound and soluble ACE2 a ...
(ACE2), a membrane protein that regulates the renin–angiotensin system.
Terminology
 During the initial outbreak in
During the initial outbreak in Wuhan
Wuhan (, ; ; ) is the capital of Hubei, Hubei Province in the China, People's Republic of China. It is the largest city in Hubei and the most populous city in Central China, with a population of over eleven million, the List of cities in China ...
, China, various names were used for the virus; some names used by different sources included "the coronavirus" or "Wuhan coronavirus". In January 2020, the World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level of h ...
(WHO) recommended "2019 novel coronavirus" (2019-nCoV) as the provisional name for the virus. This was in accordance with WHO's 2015 guidance against using geographical locations, animal species, or groups of people in disease and virus names.
On 11 February 2020, the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses
The International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) authorizes and organizes the taxonomic classification of and the nomenclatures for viruses. The ICTV has developed a universal taxonomic scheme for viruses, and thus has the means to app ...
adopted the official name "severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2" (SARS‑CoV‑2). To avoid confusion with the disease SARS
Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) is a viral respiratory disease of zoonotic origin caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV or SARS-CoV-1), the first identified strain of the SARS coronavirus species, ''sever ...
, the WHO sometimes refers to SARS‑CoV‑2 as "the COVID-19 virus" in public health communications and the name HCoV-19 was included in some research articles. Referring to COVID-19 as the "Wuhan virus" has been described as dangerous by WHO officials, and as xenophobic
Xenophobia () is the fear or dislike of anything which is perceived as being foreign or strange. It is an expression of perceived conflict between an in-group and out-group and may manifest in suspicion by the one of the other's activities, a ...
by University of California at Berkeley Asian American studies lecturer Harvey Dong.
Infection and transmission
Human-to-humantransmission
Transmission may refer to:
Medicine, science and technology
* Power transmission
** Electric power transmission
** Propulsion transmission, technology allowing controlled application of power
*** Automatic transmission
*** Manual transmission
*** ...
of SARS‑CoV‑2 was confirmed on 20 January 2020 during the COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the coronavirus pandemic, is an ongoing global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The novel virus was first identif ...
. Transmission was initially assumed to occur primarily via respiratory droplet
A respiratory droplet is a small aqueous droplet produced by exhalation, consisting of saliva or mucus and other matter derived from respiratory tract surfaces. Respiratory droplets are produced naturally as a result of breathing, speaking, snee ...
s from coughs and sneezes within a range of about . Laser light scattering experiments suggest that speaking
Speech is a human vocal communication using language. Each language uses phonetic combinations of vowel and consonant sounds that form the sound of its words (that is, all English words sound different from all French words, even if they are th ...
is an additional mode of transmission and a far-reaching one, indoors, with little air flow. Other studies have suggested that the virus may be airborne
Airborne or Airborn may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
Films
* ''Airborne'' (1962 film), a 1962 American film directed by James Landis
* ''Airborne'' (1993 film), a comedy–drama film
* ''Airborne'' (1998 film), an action film sta ...
as well, with aerosols
An aerosol is a suspension of fine solid particles or liquid droplets in air or another gas. Aerosols can be natural or anthropogenic. Examples of natural aerosols are fog or mist, dust, forest exudates, and geyser steam. Examples of anthrop ...
potentially being able to transmit the virus. During human-to-human transmission, between 200 and 800 infectious SARS‑CoV‑2 virion
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea.
Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's 1 ...
s are thought to initiate a new infection. If confirmed, aerosol transmission has biosafety implications because a major concern associated with the risk of working with emerging viruses in the laboratory is the generation of aerosols from various laboratory activities which are not immediately recognizable and may affect other scientific personnel. Indirect contact via contaminated surfaces is another possible cause of infection. Preliminary research indicates that the virus may remain viable on plastic (polypropylene
Polypropylene (PP), also known as polypropene, is a thermoplastic polymer used in a wide variety of applications. It is produced via chain-growth polymerization from the monomer propylene.
Polypropylene
belongs to the group of polyolefins and ...
) and stainless steel
Stainless steel is an alloy of iron that is resistant to rusting and corrosion. It contains at least 11% chromium and may contain elements such as carbon, other nonmetals and metals to obtain other desired properties. Stainless steel's corros ...
( AISI 304) for up to three days, but it does not survive on cardboard for more than one day or on copper for more than four hours. The virus is inactivated by soap, which destabilizes its lipid bilayer
The lipid bilayer (or phospholipid bilayer) is a thin polar membrane made of two layers of lipid molecules. These membranes are flat sheets that form a continuous barrier around all cells. The cell membranes of almost all organisms and many vir ...
. Viral RNA
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule essential in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation and expression of genes. RNA and deoxyribonucleic acid ( DNA) are nucleic acids. Along with lipids, proteins, and carbohydra ...
has also been found in stool sample
A stool test is a medical diagnostic technique that involves the collection and analysis of fecal matter. Microbial analysis (culturing), microscopy and chemical tests are among the tests performed on stool samples.
Collection
Stool samples shoul ...
s and semen from infected individuals.
The degree to which the virus is infectious during the incubation period
Incubation period (also known as the latent period or latency period) is the time elapsed between exposure to a pathogenic organism, a chemical, or radiation, and when symptoms and signs are first apparent. In a typical infectious disease, the i ...
is uncertain, but research has indicated that the pharynx
The pharynx (plural: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity, and above the oesophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its struc ...
reaches peak viral load
Viral load, also known as viral burden, is a numerical expression of the quantity of virus in a given volume of fluid, including biological and environmental specimens. It is not to be confused with viral titre or viral titer, which depends on the ...
approximately four days after infection or in the first week of symptoms and declines thereafter. The duration of SARS-CoV-2 RNA shedding is generally between 3 and 46 days after symptom onset.
A study by a team of researchers from the University of North Carolina
The University of North Carolina is the multi-campus public university system for the state of North Carolina. Overseeing the state's 16 public universities and the NC School of Science and Mathematics, it is commonly referred to as the UNC Sy ...
found that the nasal cavity
The nasal cavity is a large, air-filled space above and behind the nose in the middle of the face. The nasal septum divides the cavity into two cavities, also known as fossae. Each cavity is the continuation of one of the two nostrils. The nasal c ...
is seemingly the dominant initial site of infection, with subsequent aspiration-mediated virus-seeding into the lungs in SARS‑CoV‑2 pathogenesis. They found that there was an infection gradient from high in proximal towards low in distal pulmonary epithelial cultures, with a focal infection in ciliated cells and type 2 pneumocytes in the airway and alveolar regions respectively.
Studies have identified a range of animals—such as cats, ferrets, hamsters, non-human primates, minks, tree shrews, raccoon dogs, fruit bats, and rabbits—that are susceptible and permissive to SARS-CoV-2 infection. Some institutions have advised that those infected with SARS‑CoV‑2 restrict their contact with animals.
Asymptomatic and presymptomatic transmission
On 1February 2020, theWorld Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level of h ...
(WHO) indicated that "transmission from asymptomatic
In medicine, any disease is classified asymptomatic if a patient tests as carrier for a disease or infection but experiences no symptoms. Whenever a medical condition fails to show noticeable symptoms after a diagnosis it might be considered asy ...
cases is likely not a major driver of transmission". One meta-analysis found that 17% of infections are asymptomatic, and asymptomatic individuals were 42% less likely to transmit the virus.
However, an epidemiological model of the beginning of the outbreak in China suggested that "pre-symptomatic shedding may be typical among documented infections" and that subclinical infection
A subclinical infection—sometimes called a preinfection or inapparent infection—is an infection that, being subclinical, is nearly or completely asymptomatic (no signs or symptoms). A subclinically infected person is thus a paucisymptomatic ...
s may have been the source of a majority of infections. That may explain how out of 217 on board a cruise liner
Cruise ships are large passenger ships used mainly for vacationing. Unlike ocean liners, which are used for transport, cruise ships typically embark on round-trip voyages to various ports-of-call, where passengers may go on tours known as "sho ...
that docked at Montevideo
Montevideo () is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Uruguay, largest city of Uruguay. According to the 2011 census, the city proper has a population of 1,319,108 (about one-third of the country's total population) in an area of . M ...
, only 24 of 128 who tested positive for viral RNA showed symptoms. Similarly, a study of ninety-four patients hospitalized in January and February 2020 estimated patients began shedding virus two to three days before symptoms appear and that "a substantial proportion of transmission probably occurred before first symptoms in the index case
The index case or patient zero is the first documented patient in a disease epidemic within a population, or the first documented patient included in an epidemiological study.
It can also refer to the first case of a condition or syndrome (not n ...
". The authors later published a correction that showed that shedding began earlier than first estimated, four to five days before symptoms appear.
Reinfection
There is uncertainty about reinfection and long-term immunity. It is not known how common reinfection is, but reports have indicated that it is occurring with variable severity. The first reported case of reinfection was a 33-year-old man from Hong Kong who first tested positive on 26 March 2020, was discharged on 15 April 2020 after two negative tests, and tested positive again on 15 August 2020 (142 days later), which was confirmed by whole-genome sequencing showing that the viral genomes between the episodes belong to differentclade
A clade (), also known as a monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that are monophyletic – that is, composed of a common ancestor and all its lineal descendants – on a phylogenetic tree. Rather than the English term, ...
s. The findings had the implications that herd immunity
Herd immunity (also called herd effect, community immunity, population immunity, or mass immunity) is a form of indirect protection that applies only to contagious diseases. It occurs when a sufficient percentage of a population has become imm ...
may not eliminate the virus if reinfection is not an uncommon occurrence and that vaccines
A vaccine is a biological preparation that provides active acquired immunity
The adaptive immune system, also known as the acquired immune system, is a subsystem of the immune system that is composed of specialized, systemic cells and pro ...
may not be able to provide lifelong protection against the virus.
Another case study described a 25-year-old man from Nevada who tested positive for SARS‑CoV‑2 on 18 April 2020 and on 5 June 2020 (separated by two negative tests). Since genomic analyses showed significant genetic differences between the SARS‑CoV‑2 variant sampled on those two dates, the case study authors determined this was a reinfection. The man's second infection was symptomatically more severe than the first infection, but the mechanisms that could account for this are not known.
Reservoir and origin
 No
No natural reservoir
In infectious disease ecology and epidemiology, a natural reservoir, also known as a disease reservoir or a reservoir of infection, is the population of organisms or the specific environment in which an infectious pathogen naturally lives and rep ...
for SARS-CoV-2 has been identified. Prior to the emergence of SARS-CoV-2 as a pathogen infecting humans, there had been two previous zoonosis
A zoonosis (; plural zoonoses) or zoonotic disease is an infectious disease of humans caused by a pathogen (an infectious agent, such as a bacterium, virus, parasite or prion) that has jumped from a non-human (usually a vertebrate) to a human. ...
-based coronavirus epidemics, those caused by SARS-CoV-1
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 1 (SARS-CoV-1; or Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus, SARS-CoV) is a strain of coronavirus that causes severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), the respiratory illness responsible for ...
and MERS-CoV
''Middle East respiratory syndrome–related coronavirus'' (''MERS-CoV''), or EMC/2012 ( HCoV-EMC/2012), is the virus that causes Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS). It is a species of coronavirus which infects humans, bats, and camels. Th ...
.
The first known infections from SARS‑CoV‑2 were discovered in Wuhan, China. The original source of viral transmission to humans remains unclear, as does whether the virus became pathogen
In biology, a pathogen ( el, πάθος, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of") in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a germ ...
ic before or after the spillover event. Because many of the early infectees were workers at the Huanan Seafood Market
The Wuhan Huanan Seafood Wholesale Market (), simply known as the Huanan Seafood Market (''Huanan'' means ' South China'), was a live animal and seafood market in Jianghan District, Wuhan City, the capital of Hubei Province in Central China.
...
, it has been suggested that the virus might have originated from the market. However, other research indicates that visitors may have introduced the virus to the market, which then facilitated rapid expansion of the infections. A March 2021 WHO-convened report stated that human spillover via an intermediate animal host was the most likely explanation, with direct spillover from bats next most likely. Introduction through the food supply chain and the Huanan Seafood Market was considered another possible, but less likely, explanation. An analysis in November 2021, however, said that the earliest-known case had been misidentified and that the preponderance of early cases linked to the Huanan Market argued for it being the source.
For a virus recently acquired through a cross-species transmission, rapid evolution is expected. The mutation rate estimated from early cases of SARS-CoV-2 was of per site per year. Coronaviruses in general have high genetic plasticity
Plasticity may refer to:
Science
* Plasticity (physics), in engineering and physics, the propensity of a solid material to undergo permanent deformation under load
* Neuroplasticity, in neuroscience, how entire brain structures, and the brain it ...
, but SARS-CoV-2's viral evolution is slowed by the RNA proofreading capability of its replication machinery. For comparison, the viral mutation rate in vivo of SARS-CoV-2 has been found to be lower than that of influenza.
Research into the natural reservoir of the virus that caused the 2002–2004 SARS outbreak
The 2002–2004 outbreak of SARS, caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV or SARS-CoV-1), infected over 8,000 people from 29 countries and territories, and resulted in at least 774 deaths worldwide.
The outbreak wa ...
has resulted in the discovery of many SARS-like bat coronaviruses, most originating in horseshoe bat
Horseshoe bats are bats in the family Rhinolophidae. In addition to the single living genus, ''Rhinolophus'', which has about 106 species, the extinct genus '' Palaeonycteris'' has been recognized. Horseshoe bats are closely related to the Old ...
s. The closest match by far, published on ''Nature (journal)
''Nature'' is a British weekly scientific journal founded and based in London, England. As a multidisciplinary publication, ''Nature'' features peer-reviewed research from a variety of academic disciplines, mainly in science and technology. ...
'' in February 2022, were viruses BANAL-52 (96.8% resemblance to SARS‑CoV‑2), BANAL-103 and BANAL-236, collected in three different species of bats in Feuang, Laos. An earlier source published in February 2020 identified the virus RaTG13
Bat coronavirus RaTG13 is a SARS-like betacoronavirus that infects the horseshoe bat '' Rhinolophus affinis''. It was discovered in 2013 in bat droppings from a mining cave near the town of Tongguan in Mojiang county in Yunnan, China. In Februar ...
, collected in bats in Mojiang, Yunnan, China to be the closest to SARS‑CoV‑2, with 96.1% resemblance. None of the above are its direct ancestor.
 Bats are considered the most likely natural reservoir of SARS‑CoV‑2. Differences between the bat coronavirus and SARS‑CoV‑2 suggest that humans may have been infected via an intermediate host; although the source of introduction into humans remains unknown.
Although the role of
Bats are considered the most likely natural reservoir of SARS‑CoV‑2. Differences between the bat coronavirus and SARS‑CoV‑2 suggest that humans may have been infected via an intermediate host; although the source of introduction into humans remains unknown.
Although the role of pangolins
Pangolins, sometimes known as scaly anteaters, are mammals of the order Pholidota (, from Ancient Greek ϕολιδωτός – "clad in scales"). The one extant family, the Manidae, has three genera: ''Manis'', ''Phataginus'', and ''Smutsia'' ...
as an intermediate host was initially posited (a study published in July 2020 suggested that pangolins are an intermediate host of SARS‑CoV‑2-like coronaviruses), subsequent studies have not substantiated their contribution to the spillover. Evidence against this hypothesis includes the fact that pangolin virus samples are too distant to SARS-CoV-2: isolates obtained from pangolins seized in Guangdong
Guangdong (, ), alternatively romanized as Canton or Kwangtung, is a coastal province in South China on the north shore of the South China Sea. The capital of the province is Guangzhou. With a population of 126.01 million (as of 2020) ...
were only 92% identical in sequence to the SARS‑CoV‑2 genome (matches above 90 percent may sound high, but in genomic terms it is a wide evolutionary gap). In addition, despite similarities in a few critical amino acids, pangolin virus samples exhibit poor binding to the human ACE2 receptor.
Phylogenetics and taxonomy
coronavirus
Coronaviruses are a group of related RNA viruses that cause diseases in mammals and birds. In humans and birds, they cause respiratory tract infections that can range from mild to lethal. Mild illnesses in humans include some cases of the com ...
es. It is a positive-sense single-stranded RNA (+ssRNA) virus, with a single linear RNA segment. Coronaviruses infect humans, other mammals, including livestock and companion animals, and avian species. Human coronaviruses are capable of causing illnesses ranging from the common cold
The common cold or the cold is a viral infectious disease of the upper respiratory tract that primarily affects the respiratory mucosa of the nose, throat, sinuses, and larynx. Signs and symptoms may appear fewer than two days after exposu ...
to more severe diseases such as Middle East respiratory syndrome
Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS) is a viral respiratory infection caused by ''Middle East respiratory syndrome–related coronavirus'' (MERS-CoV). Symptoms may range from none, to mild, to severe. Typical symptoms include fever, cough, ...
(MERS, fatality rate ~34%). SARS-CoV-2 is the seventh known coronavirus to infect people, after 229E, NL63, OC43, HKU1, MERS-CoV
''Middle East respiratory syndrome–related coronavirus'' (''MERS-CoV''), or EMC/2012 ( HCoV-EMC/2012), is the virus that causes Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS). It is a species of coronavirus which infects humans, bats, and camels. Th ...
, and the original SARS-CoV
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 1 (SARS-CoV-1; or Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus, SARS-CoV) is a strain of coronavirus that causes severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), the respiratory illness responsible for ...
.
Like the SARS-related coronavirus implicated in the 2003 SARS outbreak, SARS‑CoV‑2 is a member of the subgenus ''Sarbecovirus
''Severe acute respiratory syndrome–related coronavirus'' (SARSr-CoV or SARS-CoV)The terms ''SARSr-CoV'' and ''SARS-CoV'' are sometimes used interchangeably, especially prior to the discovery of SARS-CoV-2. This may cause confusion when some ...
'' ( beta-CoV lineage B). Coronaviruses undergo frequent recombination. The mechanism of recombination in unsegmented RNA viruses such as SARS-CoV-2 is generally by copy-choice replication, in which gene material switches from one RNA template molecule to another during replication. The SARS-CoV-2 RNA sequence is approximately 30,000 bases in length, relatively long for a coronavirus—which in turn carry the largest genomes among all RNA families. Its genome consists nearly entirely of protein-coding sequences, a trait shared with other coronaviruses.
 A distinguishing feature of SARS‑CoV‑2 is its incorporation of a polybasic site cleaved by
A distinguishing feature of SARS‑CoV‑2 is its incorporation of a polybasic site cleaved by furin
Furin is a protease, a proteolytic enzyme that in humans and other animals is encoded by the ''FURIN'' gene. Some proteins are inactive when they are first synthesized, and must have sections removed in order to become active. Furin cleaves these s ...
, which appears to be an important element enhancing its virulence.protease
A protease (also called a peptidase, proteinase, or proteolytic enzyme) is an enzyme that catalyzes (increases reaction rate or "speeds up") proteolysis, breaking down proteins into smaller polypeptides or single amino acids, and spurring the ...
recognizes the canonical peptide
Peptides (, ) are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. Long chains of amino acids are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty amino acids are called oligopeptides, and include dipeptides, tripeptides, and tetrapeptides.
A ...
sequence RX R/ R/Lysine">K.html" ;"title="Lysine.html" ;"title="nowiki/> R/Lysine">K">Lysine.html" ;"title="nowiki/> R/Lysine">K R↓X where the cleavage site is indicated by a down arrow and X is any amino acid.feline coronavirus
Feline coronavirus (FCoV) is a positive-stranded RNA virus that infects cats worldwide. It is a coronavirus of the species '' Alphacoronavirus 1'' which includes canine coronavirus (CCoV) and porcine transmissible gastroenteritis coronavirus (T ...
, an alphacoronavirus 1
''Alphacoronavirus 1'' is a species of coronavirus that infects cats, dogs and pigs. It includes the virus strains feline coronavirus, canine coronavirus, and transmissible gastroenteritis virus.' It is an Viral envelope, enveloped, positive-s ...
strain.
Viral genetic sequence data can provide critical information about whether viruses separated by time and space are likely to be epidemiologically linked. With a sufficient number of sequenced genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding ge ...
s, it is possible to reconstruct a phylogenetic tree
A phylogenetic tree (also phylogeny or evolutionary tree Felsenstein J. (2004). ''Inferring Phylogenies'' Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA.) is a branching diagram or a tree showing the evolutionary relationships among various biological spec ...
of the mutation history of a family of viruses. By 12 January 2020, five genomes of SARS‑CoV‑2 had been isolated from Wuhan and reported by the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention
The Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CCDC; ) is an institution directly under the National Health Commission, based in Changping District, Beijing, China.
Established in 1983, it works to protect public health and safety ...
(CCDC) and other institutions; the number of genomes increased to 42 by 30 January 2020. A phylogenetic analysis of those samples showed they were "highly related with at most seven mutations relative to a common ancestor
Common descent is a concept in evolutionary biology applicable when one species is the ancestor of two or more species later in time. All living beings are in fact descendants of a unique ancestor commonly referred to as the last universal comm ...
", implying that the first human infection occurred in November or December 2019. Examination of the topology of the phylogenetic tree at the start of the pandemic also found high similarities between human isolates. 3,422 SARS‑CoV‑2 genomes, belonging to 19 strains, sampled on all continents except Antarctica were publicly available.
On 11 February 2020, the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses
The International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) authorizes and organizes the taxonomic classification of and the nomenclatures for viruses. The ICTV has developed a universal taxonomic scheme for viruses, and thus has the means to app ...
announced that according to existing rules that compute hierarchical relationships among coronaviruses based on five conserved sequence
In evolutionary biology, conserved sequences are identical or similar sequences in nucleic acids ( DNA and RNA) or proteins across species ( orthologous sequences), or within a genome ( paralogous sequences), or between donor and receptor taxa ...
s of nucleic acids, the differences between what was then called 2019-nCoV and the virus from the 2003 SARS outbreak were insufficient to make them separate viral species
Virus classification is the process of naming viruses and placing them into a taxonomic system similar to the classification systems used for cellular organisms.
Viruses are classified by phenotypic characteristics, such as morphology, nucleic ...
. Therefore, they identified 2019-nCoV as a virus of ''Severe acute respiratory syndrome–related coronavirus
''Severe acute respiratory syndrome–related coronavirus'' (SARSr-CoV or SARS-CoV)The terms ''SARSr-CoV'' and ''SARS-CoV'' are sometimes used interchangeably, especially prior to the discovery of SARS-CoV-2. This may cause confusion when some ...
''.spike protein
In virology, a spike protein or peplomer protein is a protein that forms a large structure known as a spike or peplomer projecting from the surface of an enveloped virus. as cited in The proteins are usually glycoproteins that form dimers or ...
variant G614 has replaced D614 as the dominant form in the pandemic.
Coronavirus genomes and subgenomes encode six open reading frame
In molecular biology, open reading frames (ORFs) are defined as spans of DNA sequence between the start and stop codons. Usually, this is considered within a studied region of a prokaryotic DNA sequence, where only one of the six possible readin ...
s (ORFs). In October 2020, researchers discovered a possible overlapping gene
An overlapping gene (or OLG) is a gene whose expressible Nucleic acid sequence, nucleotide sequence partially overlaps with the expressible nucleotide sequence of another gene. In this way, a nucleotide sequence may make a contribution to the func ...
named ''ORF3d'', in the SARS‑CoV‑2 genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding ge ...
. It is unknown if the protein produced by ''ORF3d'' has any function, but it provokes a strong immune response. ''ORF3d'' has been identified before, in a variant of coronavirus that infects pangolin
Pangolins, sometimes known as scaly anteaters, are mammals of the order Pholidota (, from Ancient Greek ϕολιδωτός – "clad in scales"). The one extant family, the Manidae, has three genera: '' Manis'', '' Phataginus'', and '' Smut ...
s.
Phylogenetic tree
Variants
 There are many thousands of variants of SARS-CoV-2, which can be grouped into the much larger
There are many thousands of variants of SARS-CoV-2, which can be grouped into the much larger clade
A clade (), also known as a monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that are monophyletic – that is, composed of a common ancestor and all its lineal descendants – on a phylogenetic tree. Rather than the English term, ...
s. Several different clade nomenclatures have been proposed. Nextstrain divides the variants into five clades (19A, 19B, 20A, 20B, and 20C), while GISAID
GISAID (Global Initiative on Sharing Avian Influenza Data) is a global science initiative and primary source established in 2008 that provides open access to genomic data of influenza viruses and the coronavirus responsible for the COVID-19 pan ...
divides them into seven (L, O, V, S, G, GH, and GR).
Several notable variants of SARS-CoV-2 emerged in late 2020. The World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level of h ...
has currently declared five variants of concern, which are as follows:
* Alpha
Alpha (uppercase , lowercase ; grc, ἄλφα, ''álpha'', or ell, άλφα, álfa) is the first letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of one. Alpha is derived from the Phoenician letter aleph , whic ...
: Lineage B.1.1.7 emerged in the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and North ...
in September 2020, with evidence of increased transmissibility and virulence. Notable mutations include N501Y
There are many variants of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the virus that causes coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Some are believed, or have been stated, to be of particular importance due to their potential ...
and P681H
There are many variants of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the virus that causes coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Some are believed, or have been stated, to be of particular importance due to their potenti ...
.
** An E484K
There are many variants of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the virus that causes coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Some are believed, or have been stated, to be of particular importance due to their potenti ...
mutation in some lineage B.1.1.7 virions has been noted and is also tracked by various public health agencies.
* Beta
Beta (, ; uppercase , lowercase , or cursive ; grc, βῆτα, bē̂ta or ell, βήτα, víta) is the second letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of 2. In Modern Greek, it represents the voiced labiod ...
: Lineage B.1.351 emerged in South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the north by the neighbouring countri ...
in May 2020, with evidence of increased transmissibility and changes to antigenicity, with some public health officials raising alarms about its impact on the efficacy of some vaccines. Notable mutations include K417N
There are many variants of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the virus that causes coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Some are believed, or have been stated, to be of particular importance due to their potential ...
, E484K and N501Y.
* Gamma
Gamma (uppercase , lowercase ; ''gámma'') is the third letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 3. In Ancient Greek, the letter gamma represented a voiced velar stop . In Modern Greek, this letter re ...
: Lineage P.1 emerged in Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
in November 2020, also with evidence of increased transmissibility and virulence, alongside changes to antigenicity. Similar concerns about vaccine efficacy have been raised. Notable mutations also include K417N, E484K and N501Y.
* Delta
Delta commonly refers to:
* Delta (letter) (Δ or δ), a letter of the Greek alphabet
* River delta, at a river mouth
* D ( NATO phonetic alphabet: "Delta")
* Delta Air Lines, US
* Delta variant of SARS-CoV-2 that causes COVID-19
Delta may also ...
: Lineage B.1.617.2 emerged in India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
in October 2020. There is also evidence of increased transmissibility and changes to antigenicity.
* Omicron
Omicron (; uppercase Ο, lowercase ο, ell, όμικρον) is the 15th letter of the Greek alphabet. This letter is derived from the Phoenician letter ayin: . In classical Greek, omicron represented the close-mid back rounded vowel in contras ...
: Lineage B.1.1.529 emerged in Botswana
Botswana (, ), officially the Republic of Botswana ( tn, Lefatshe la Botswana, label=Setswana, ), is a landlocked country in Southern Africa. Botswana is topographically flat, with approximately 70 percent of its territory being the Kalahar ...
in November 2021.
Other notable variants include 6 other WHO-designated variants under investigation and Cluster 5
Cluster 5 is a designation used by the Danish Statens Serum Institut for a virus variant described by the institute in autumn 2020, in connection with investigations of SARS-CoV-2 infection among mink and humans in the north of Jutland, Denmark. ...
, which emerged among mink
Mink are dark-colored, semiaquatic, carnivorous mammals of the genera ''Neogale'' and '' Mustela'' and part of the family Mustelidae, which also includes weasels, otters, and ferrets. There are two extant species referred to as "mink": the A ...
in Denmark and resulted in a mink euthanasia campaign rendering it virtually extinct.
Virology
Structure
virion
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea.
Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's 1 ...
is in diameter; its mass within the global human populace has been estimated as being between 0.1 and 10 kilograms. Like other coronaviruses, SARS-CoV-2 has four structural proteins, known as the S (spike
Spike, spikes, or spiking may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
Books
* ''The Spike'' (novel), a novel by Arnaud de Borchgrave
* ''The Spike'' (book), a nonfiction book by Damien Broderick
* ''The Spike'', a starship in Peter F. Hamilto ...
), E (envelope
An envelope is a common packaging item, usually made of thin, flat material. It is designed to contain a flat object, such as a letter or card.
Traditional envelopes are made from sheets of paper cut to one of three shapes: a rhombus, a shor ...
), M (membrane
A membrane is a selective barrier; it allows some things to pass through but stops others. Such things may be molecules, ions, or other small particles. Membranes can be generally classified into synthetic membranes and biological membranes. B ...
), and N (nucleocapsid
A capsid is the protein shell of a virus, enclosing its genetic material. It consists of several oligomeric (repeating) structural subunits made of protein called protomers. The observable 3-dimensional morphological subunits, which may or may ...
) proteins; the N protein holds the RNA genome, and the S, E, and M proteins together create the viral envelope
A viral envelope is the outermost layer of many types of viruses. It protects the genetic material in their life cycle when traveling between host cells. Not all viruses have envelopes.
Numerous human pathogenic viruses in circulation are encase ...
. Coronavirus S proteins are glycoprotein
Glycoproteins are proteins which contain oligosaccharide chains covalently attached to amino acid side-chains. The carbohydrate is attached to the protein in a cotranslational or posttranslational modification. This process is known as glycos ...
s and also type I membrane protein
Membrane proteins are common proteins that are part of, or interact with, biological membranes. Membrane proteins fall into several broad categories depending on their location. Integral membrane proteins are a permanent part of a cell membrane ...
s (membranes containing a single transmembrane domain
A transmembrane domain (TMD) is a membrane-spanning protein domain. TMDs generally adopt an alpha helix topological conformation, although some TMDs such as those in porins can adopt a different conformation. Because the interior of the lipid bil ...
oriented on the extracellular side). They are divided into two functional parts (S1 and S2). In SARS-CoV-2, the spike protein, which has been imaged at the atomic level using cryogenic electron microscopy
Cryogenic electron microscopy (cryo-EM) is a cryomicroscopy technique applied on samples cooled to cryogenic temperatures. For biological specimens, the structure is preserved by embedding in an environment of vitreous ice. An aqueous sample so ...
, is the protein responsible for allowing the virus to attach to and fuse with the membrane
A membrane is a selective barrier; it allows some things to pass through but stops others. Such things may be molecules, ions, or other small particles. Membranes can be generally classified into synthetic membranes and biological membranes. B ...
of a host cell; specifically, its S1 subunit catalyzes attachment, the S2 subunit fusion.

Genome
As of early 2022, about 7 million SARS-CoV-2 genomes had been sequenced and deposited into public databases and another 800,000 or so were added each month. SARS-CoV-2 has a linear,positive-sense
In molecular biology and genetics, the sense of a nucleic acid molecule, particularly of a strand of DNA or RNA, refers to the nature of the roles of the strand and its complement in specifying a sequence of amino acids. Depending on the context, ...
, single-stranded RNA genome about 30,000 bases long. Its genome has a bias against cytosine (C) and guanine (G) nucleotides, like other coronaviruses. The genome has the highest composition of U (32.2%), followed by A (29.9%), and a similar composition of G (19.6%) and C (18.3%). The nucleotide bias arises from the mutation of guanines and cytosines to adenosines and uracil
Uracil () (symbol U or Ura) is one of the four nucleobases in the nucleic acid RNA. The others are adenine (A), cytosine (C), and guanine (G). In RNA, uracil binds to adenine via two hydrogen bonds. In DNA, the uracil nucleobase is replaced by ...
s, respectively. The mutation of CG dinucleotides is thought to arise to avoid the zinc finger antiviral protein related defense mechanism of cells, and to lower the energy to unbind the genome during replication and translation
Translation is the communication of the Meaning (linguistic), meaning of a #Source and target languages, source-language text by means of an Dynamic and formal equivalence, equivalent #Source and target languages, target-language text. The ...
(adenosine and uracil base pair
A base pair (bp) is a fundamental unit of double-stranded nucleic acids consisting of two nucleobases bound to each other by hydrogen bonds. They form the building blocks of the DNA double helix and contribute to the folded structure of both DNA ...
via two hydrogen bond
In chemistry, a hydrogen bond (or H-bond) is a primarily electrostatic force of attraction between a hydrogen (H) atom which is covalently bound to a more electronegative "donor" atom or group (Dn), and another electronegative atom bearing a ...
s, cytosine and guanine via three). The depletion of CG dinucleotides in its genome has led the virus to have a noticeable codon usage bias
Codon usage bias refers to differences in the frequency of occurrence of synonymous codons in coding DNA. A codon is a series of three nucleotides (a triplet) that encodes a specific amino acid residue in a polypeptide chain or for the terminatio ...
. For instance, arginine's six different codons have a relative synonymous codon usage of AGA (2.67), CGU (1.46), AGG (.81), CGC (.58), CGA (.29), and CGG (.19). A similar codon usage bias trend is seen in other SARS–related coronaviruses.
Replication cycle
Virus infections start when viral particles bind to host surface cellular receptors. Protein modeling experiments on the spike protein of the virus soon suggested that SARS‑CoV‑2 has sufficient affinity to the receptorangiotensin converting enzyme 2
Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) is an enzyme that can be found either attached to the membrane of cells (mACE2) in the intestines, kidney, testis, gallbladder, and heart or in a soluble form (sACE2). Both membrane bound and soluble ACE2 a ...
(ACE2) on human cells to use them as a mechanism of cell entry. By 22 January 2020, a group in China working with the full virus genome and a group in the United States using reverse genetics
Reverse genetics is a method in molecular genetics that is used to help understand the function(s) of a gene by analysing the phenotypic effects caused by genetically engineering specific nucleic acid sequences within the gene. The process proce ...
methods independently and experimentally demonstrated that ACE2 could act as the receptor for SARS‑CoV‑2. Studies have shown that SARS‑CoV‑2 has a higher affinity to human ACE2 than the original SARS virus. SARS‑CoV‑2 may also use basigin
Basigin (BSG) also known as extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer (EMMPRIN) or cluster of differentiation 147 (CD147) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''BSG'' gene. This protein is a determinant for the Ok blood group syste ...
to assist in cell entry.
Initial spike protein priming by transmembrane protease, serine 2 (TMPRSS2) is essential for entry of SARS‑CoV‑2. The host protein neuropilin 1
Neuropilin-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''NRP1'' gene. In humans, the neuropilin 1 gene is located at 10p11.22. This is one of two human neuropilins.
Function
NRP1 is a membrane-bound coreceptor to a tyrosine kinase recepto ...
(NRP1) may aid the virus in host cell entry using ACE2. After a SARS‑CoV‑2 virion attaches to a target cell, the cell's TMPRSS2 cuts open the spike protein of the virus, exposing a fusion peptide
Membrane fusion proteins (not to be confused with chimeric or fusion proteins) are proteins that cause fusion of biological membranes. Membrane fusion is critical for many biological processes, especially in eukaryotic development and viral entry ...
in the S2 subunit, and the host receptor ACE2. After fusion, an endosome
Endosomes are a collection of intracellular sorting organelles in eukaryotic cells. They are parts of endocytic membrane transport pathway originating from the trans Golgi network. Molecules or ligands internalized from the plasma membrane can ...
forms around the virion, separating it from the rest of the host cell. The virion escapes when the pH of the endosome drops or when cathepsin
Cathepsins (Ancient Greek ''kata-'' "down" and ''hepsein'' "boil"; abbreviated CTS) are proteases (enzymes that degrade proteins) found in all animals as well as other organisms. There are approximately a dozen members of this family, which are di ...
, a host cysteine
Cysteine (symbol Cys or C; ) is a semiessential proteinogenic amino acid with the formula . The thiol side chain in cysteine often participates in enzymatic reactions as a nucleophile.
When present as a deprotonated catalytic residue, sometime ...
protease, cleaves it. The virion then releases RNA into the cell and forces the cell to produce and disseminate copies of the virus, which infect more cells.
SARS‑CoV‑2 produces at least three virulence factor
Virulence factors (preferably known as pathogenicity factors or effectors in plant science) are cellular structures, molecules and regulatory systems that enable microbial pathogens (bacteria, viruses, fungi, and protozoa) to achieve the following ...
s that promote shedding of new virions from host cells and inhibit immune response
An immune response is a reaction which occurs within an organism for the purpose of defending against foreign invaders. These invaders include a wide variety of different microorganisms including viruses, bacteria, parasites, and fungi which could ...
. Whether they include downregulation
In the biological context of organisms' production of gene products, downregulation is the process by which a cell decreases the quantity of a cellular component, such as RNA or protein, in response to an external stimulus. The complementary proc ...
of ACE2, as seen in similar coronaviruses, remains under investigation (as of May 2020).
Treatment and drug development
Very few drugs are known to effectively inhibit SARS‑CoV‑2.Masitinib
Masitinib is a tyrosine-kinase inhibitor used in the treatment of mast cell tumours in animals, specifically dogs.Information abouMasivetat the European pharmacy agency website Since its introduction in November 2008 it has been distributed und ...
is a clinically safe drug and was recently found to inhibit its main protease
A protease (also called a peptidase, proteinase, or proteolytic enzyme) is an enzyme that catalyzes (increases reaction rate or "speeds up") proteolysis, breaking down proteins into smaller polypeptides or single amino acids, and spurring the ...
, 3CLpro and showed >200-fold reduction in viral titers in the lungs and nose in mice. However, it is not approved for the treatment of COVID-19 in humans as of August 2021. In December 2021, the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
granted emergency use authorization
An Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) in the United States is an authorization granted to the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) under sections of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act as added to and amended by various Act of Congress, Acts of ...
to Nirmatrelvir/ritonavir
Nirmatrelvir/ritonavir, sold under the brand name Paxlovid, is a co-packaged Oral administration, oral medication, developed by Pfizer and used as a treatment for COVID-19. It contains the antiviral medications nirmatrelvir and ritonavir.
Sid ...
for the treatment of the virus; the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been des ...
, United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and North ...
, and Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
followed suit with full authorization soon after. Text was copied from this source which is copyright European Medicines Agency. Reproduction is authorized provided the source is acknowledged. One study found that Nirmatrelvir/ritonavir reduced the risk of hospitalization and death by 88%.
COVID Moonshot is an international collaborative open-science project started in March 2020 with the goal of developing an un-patented
A patent is a type of intellectual property that gives its owner the legal right to exclude others from making, using, or selling an invention for a limited period of time in exchange for publishing an enabling disclosure of the invention."A p ...
oral
The word oral may refer to:
Relating to the mouth
* Relating to the mouth, the first portion of the alimentary canal that primarily receives food and liquid
**Oral administration of medicines
** Oral examination (also known as an oral exam or or ...
antiviral drug
Antiviral drugs are a class of medication used for treating viral infections. Most antivirals target specific viruses, while a broad-spectrum antiviral is effective against a wide range of viruses. Unlike most antibiotics, antiviral drugs do n ...
for treatment of SARS-CoV-2.
Epidemiology
Retrospective tests collected within the Chinese surveillance system revealed no clear indication of substantial unrecognized circulation of SARS‑CoV‑2 in Wuhan during the latter part of 2019. A meta-analysis from November 2020 estimated thebasic reproduction number
In epidemiology, the basic reproduction number, or basic reproductive number (sometimes called basic reproduction ratio or basic reproductive rate), denoted R_0 (pronounced ''R nought'' or ''R zero''), of an infection is the expected number of ...
() of the virus to be between 2.39 and 3.44. This means each infection from the virus is expected to result in 2.39 to 3.44 new infections when no members of the community are immune
In biology, immunity is the capability of multicellular organisms to resist harmful microorganisms. Immunity involves both specific and nonspecific components. The nonspecific components act as barriers or eliminators of a wide range of pathogens ...
and no preventive measures are taken. The reproduction number may be higher in densely populated conditions such as those found on cruise ship
Cruise ships are large passenger ships used mainly for vacationing. Unlike ocean liners, which are used for transport, cruise ships typically embark on round-trip voyages to various ports-of-call, where passengers may go on tours known as "s ...
s. Human behavior affects the R0 value and hence estimates of R0 differ between different countries, cultures, and social norms. For instance, one study found relatively low R0 (~3.5) in Sweden, Belgium and the Netherlands, while Spain and the US had significantly higher R0 values (5.9 to 6.4, respectively).
There have been about 96,000 confirmed cases of infection in mainland China. While the proportion of infections that result in confirmed cases or progress to diagnosable disease remains unclear, one mathematical model estimated that 75,815 people were infected on 25 January 2020 in Wuhan alone, at a time when the number of confirmed cases worldwide was only 2,015. Before 24 February 2020, over 95% of all deaths from COVID-19
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a contagious disease caused by a virus, the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The first known case was COVID-19 pandemic in Hubei, identified in Wuhan, China, in December ...
worldwide had occurred in Hubei province
Hubei (; ; alternately Hupeh) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China, and is part of the Central China region. The name of the province means "north of the lake", referring to its position north of Dongting Lake. The prov ...
, where Wuhan is located. As of , the percentage had decreased to .
As of , there have been total confirmed cases of SARS‑CoV‑2 infection in the ongoing pandemic. The total number of deaths attributed to the virus is .
See also
*3C-like protease
The 3C-like protease (3CLpro) or main protease (Mpro), formally known as C30 endopeptidase or 3-chymotrypsin-like protease, is the main protease found in coronaviruses. It cleaves the coronavirus polyprotein at eleven conserved sites. It is a cy ...
(NS5)
References
Further reading
* * * * *External links
* * * * * * * * {{Authority control Chiroptera-borne diseases Infraspecific virus taxa SARS-related coronavirus Zoonoses 2019 in biology