|
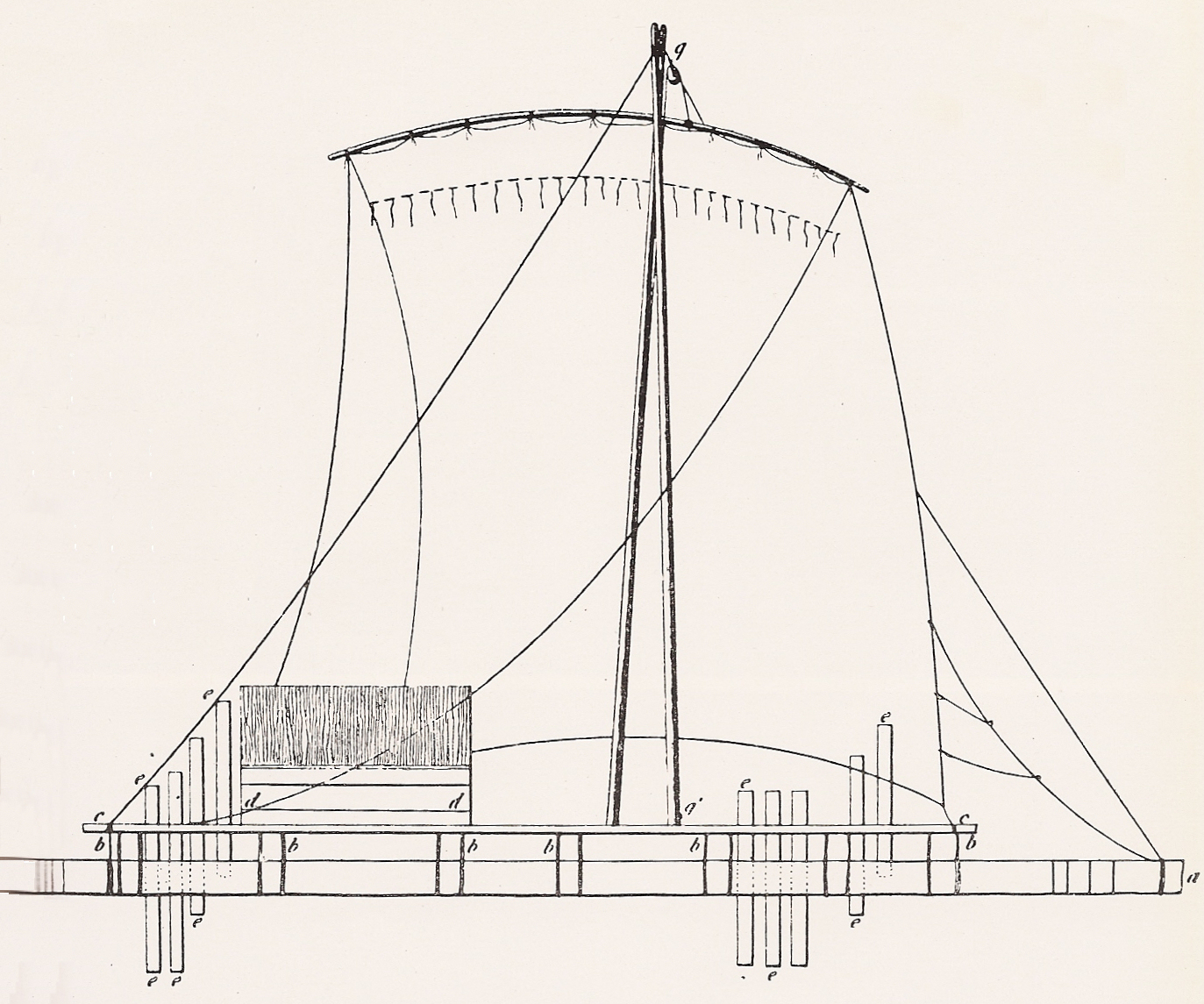
RAFT (chemistry)
A raft is any flat structure for support or transportation over water. It is usually of basic design, characterized by the absence of a hull. Rafts are usually kept afloat by using any combination of buoyant materials such as wood, sealed barrels, or inflated air chambers (such as pontoons), and are typically not propelled by an engine. Rafts are an ancient mode of transport; naturally-occurring rafts such as entwined vegetation and pieces of wood have been used to traverse water since the dawn of humanity. Human-made rafts Traditional or primitive rafts were constructed of wood or reeds. Modern rafts may also use pontoons, drums, or extruded polystyrene blocks. Inflatable rafts up to the 20th century used flotation chambers made of goat- or buffalo-skins, but most now use durable, multi-layered rubberized fabrics. Depending on its use and size, it may have a superstructure, masts, or rudders. Timber rafting is used by the logging industry for the transportation of logs, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whitewater
Whitewater forms in a rapid context, in particular, when a river's gradient changes enough to generate so much turbulence that air is trapped within the water. This forms an unstable current that froths, making the water appear opaque and white. The term "whitewater" also has a broader meaning, applying to any river or creek that has a significant number of rapids. The term is also used as an adjective describing boating on such rivers, such as whitewater canoeing or whitewater kayaking. Fast rivers Four factors, separately or in combination, can create rapids: gradient, constriction, obstruction, and flow rate. Gradient, constriction, and obstruction are streambed topography factors and are relatively consistent. Flow rate is dependent upon both seasonal variation in precipitation and snowmelt and upon release rates of upstream dams. Streambed topography Streambed topography is the primary factor in creating rapids, and is generally consistent over time. Increased f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammal
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur or hair, and three middle ear bones. These characteristics distinguish them from reptiles (including birds) from which they diverged in the Carboniferous, over 300 million years ago. Around 6,400 extant species of mammals have been described divided into 29 orders. The largest orders, in terms of number of species, are the rodents, bats, and Eulipotyphla (hedgehogs, moles, shrews, and others). The next three are the Primates (including humans, apes, monkeys, and others), the Artiodactyla ( cetaceans and even-toed ungulates), and the Carnivora (cats, dogs, seals, and others). In terms of cladistics, which reflects evolutionary history, mammals are the only living members of the Synapsida (synapsids); this clade, together with Saur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oceanic Dispersal
Oceanic dispersal is a type of biological dispersal that occurs when terrestrial organisms transfer from one land mass to another by way of a sea crossing. Island hopping is the crossing of an ocean by a series of shorter journeys between islands, as opposed to a single journey directly to the destination. Often this occurs via large rafts of floating vegetation such as are sometimes seen floating down major rivers in the tropics and washing out to sea, occasionally with animals trapped on them. Dispersal via such a raft is sometimes referred to as a rafting event. Colonization of land masses by plants can also occur via long-distance oceanic dispersal of floating seeds. History Rafting has played an important role in the colonization of isolated land masses by mammals. Prominent examples include Madagascar, which has been isolated for ~120 million years ( Ma), and South America, which was isolated for much of the Cenozoic. Both land masses, for example, appear to have received ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decomposition
Decomposition or rot is the process by which dead organic substances are broken down into simpler organic or inorganic matter such as carbon dioxide, water, simple sugars and mineral salts. The process is a part of the nutrient cycle and is essential for recycling the finite matter that occupies physical space in the biosphere. Bodies of living organisms begin to decompose shortly after death. Animals, such as worms, also help decompose the organic materials. Organisms that do this are known as decomposers or detritivores. Although no two organisms decompose in the same way, they all undergo the same sequential stages of decomposition. The science which studies decomposition is generally referred to as ''taphonomy'' from the Greek word ''taphos'', meaning tomb. Decomposition can also be a gradual process for organisms that have extended periods of dormancy. One can differentiate abiotic decomposition from biotic decomposition (biodegradation). The former means "the degradation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wave
In physics, mathematics, and related fields, a wave is a propagating dynamic disturbance (change from equilibrium) of one or more quantities. Waves can be periodic, in which case those quantities oscillate repeatedly about an equilibrium (resting) value at some frequency. When the entire waveform moves in one direction, it is said to be a ''traveling wave''; by contrast, a pair of superimposed periodic waves traveling in opposite directions makes a '' standing wave''. In a standing wave, the amplitude of vibration has nulls at some positions where the wave amplitude appears smaller or even zero. Waves are often described by a ''wave equation'' (standing wave field of two opposite waves) or a one-way wave equation for single wave propagation in a defined direction. Two types of waves are most commonly studied in classical physics. In a ''mechanical wave'', stress and strain fields oscillate about a mechanical equilibrium. A mechanical wave is a local deformation (strain) in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
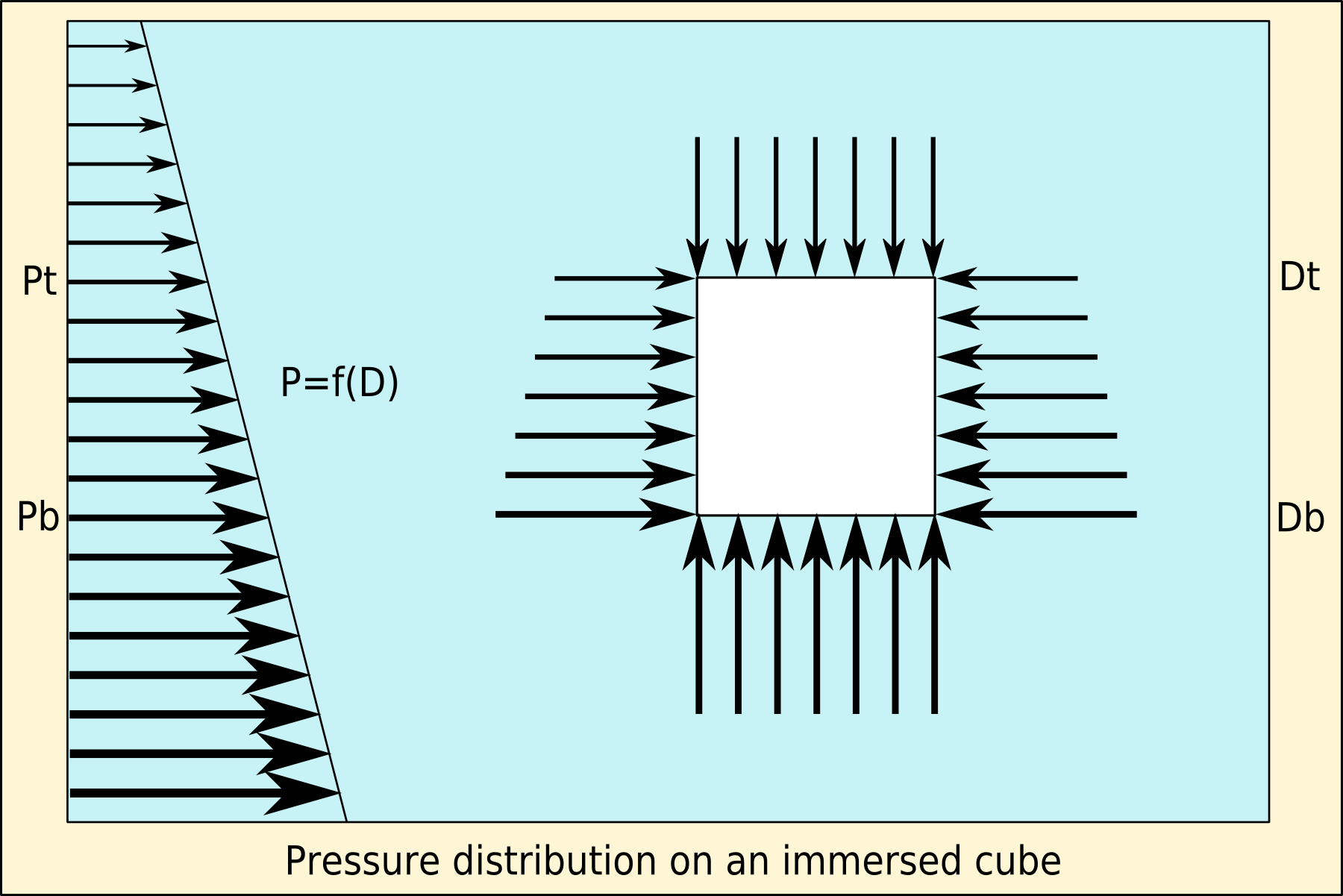
Buoyancy
Buoyancy (), or upthrust, is an upward force exerted by a fluid that opposes the weight of a partially or fully immersed object. In a column of fluid, pressure increases with depth as a result of the weight of the overlying fluid. Thus the pressure at the bottom of a column of fluid is greater than at the top of the column. Similarly, the pressure at the bottom of an object submerged in a fluid is greater than at the top of the object. The pressure difference results in a net upward force on the object. The magnitude of the force is proportional to the pressure difference, and (as explained by Archimedes' principle) is equivalent to the weight of the fluid that would otherwise occupy the submerged volume of the object, i.e. the displaced fluid. For this reason, an object whose average density is greater than that of the fluid in which it is submerged tends to sink. If the object is less dense than the liquid, the force can keep the object afloat. This can occur only in a no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flotsam And Jetsam
In maritime law, flotsam'','' jetsam'','' lagan'','' and derelict are specific kinds of shipwreck. The words have specific nautical meanings, with legal consequences in the law of admiralty and marine salvage. A shipwreck is defined as the remains of a ship that has been wrecked—a destroyed ship at sea, whether it has sunk or is floating on the surface of the water. Overview A wreck is categorized as property belonging to no apparent owner that either sinks to the seabed or floats on the surface of the water, whether it be intentionally cast overboard or as the result of an accident. The term encompasses the hull of the vessel and its fixtures as well as any other form of object on board, such as cargo and stores, and personal effects of the crew and passengers. This also encompasses the narrower definition of salvage, that is, property that has been recovered from a wreckage, or the recovery of the ship itself. There are a number of factors that contribute to the formati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earthquake
An earthquake (also known as a quake, tremor or temblor) is the shaking of the surface of the Earth resulting from a sudden release of energy in the Earth's lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, from those that are so weak that they cannot be felt, to those violent enough to propel objects and people into the air, damage critical infrastructure, and wreak destruction across entire cities. The seismic activity of an area is the frequency, type, and size of earthquakes experienced over a particular time period. The seismicity at a particular location in the Earth is the average rate of seismic energy release per unit volume. The word ''tremor'' is also used for Episodic tremor and slip, non-earthquake seismic rumbling. At the Earth's surface, earthquakes manifest themselves by shaking and displacing or disrupting the ground. When the epicenter of a large earthquake is located offshore, the seabed may be displaced sufficiently to cause ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tide
Tides are the rise and fall of sea levels caused by the combined effects of the gravity, gravitational forces exerted by the Moon (and to a much lesser extent, the Sun) and are also caused by the Earth and Moon orbiting one another. Tide tables can be used for any given locale to find the predicted times and amplitude (or "tidal range"). The predictions are influenced by many factors including the alignment of the Sun and Moon, the #Phase and amplitude, phase and amplitude of the tide (pattern of tides in the deep ocean), the amphidromic systems of the oceans, and the shape of the coastline and near-shore bathymetry (see ''#Timing, Timing''). They are however only predictions, the actual time and height of the tide is affected by wind and atmospheric pressure. Many shorelines experience semi-diurnal tides—two nearly equal high and low tides each day. Other locations have a diurnal cycle, diurnal tide—one high and low tide each day. A "mixed tide"—two uneven magnitude ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
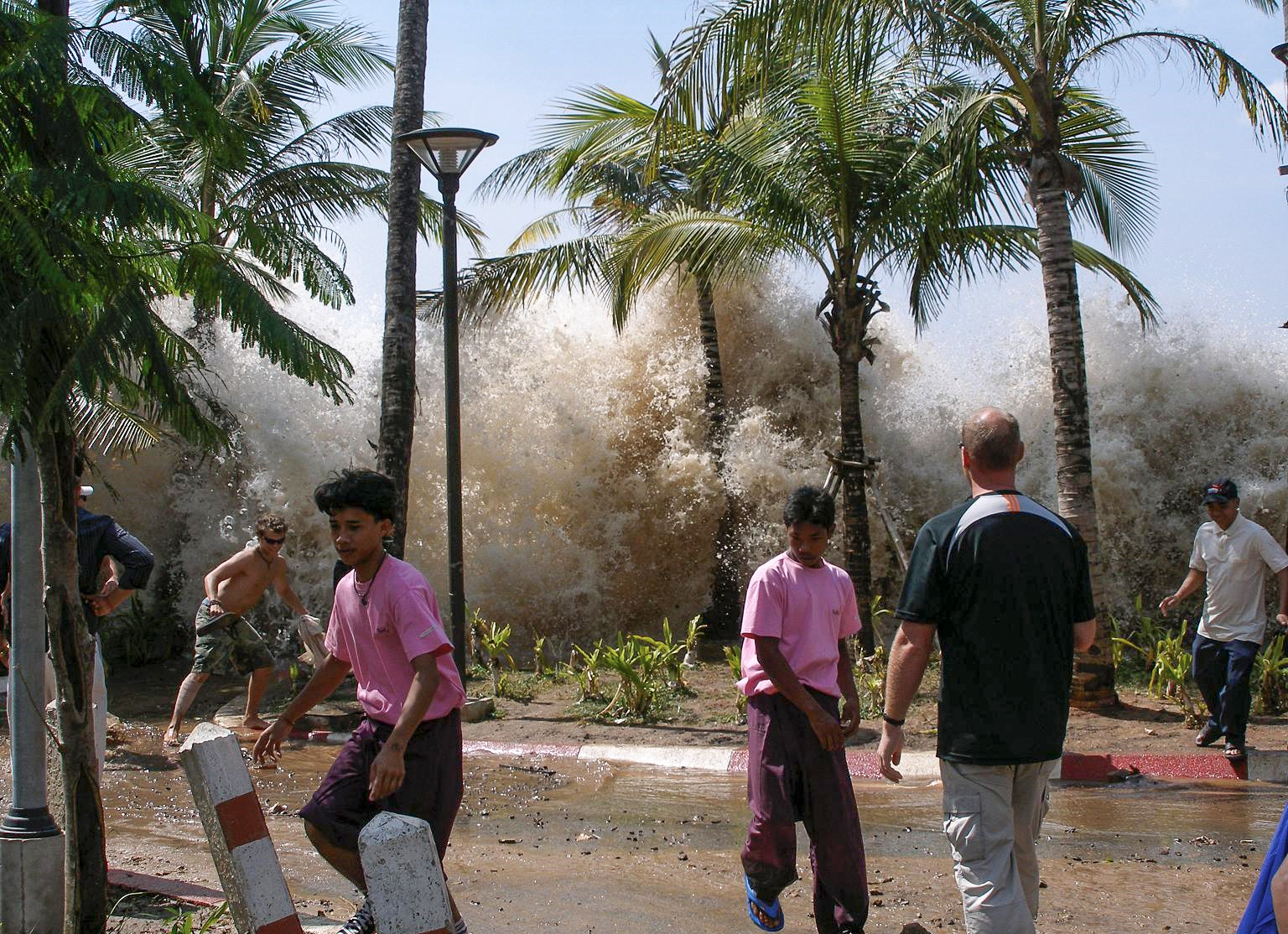
Tsunami
A tsunami ( ; from ja, 津波, lit=harbour wave, ) is a series of waves in a water body caused by the displacement of a large volume of water, generally in an ocean or a large lake. Earthquakes, volcanic eruptions and other underwater explosions (including detonations, landslides, glacier calvings, meteorite impacts and other disturbances) above or below water all have the potential to generate a tsunami. Unlike normal ocean waves, which are generated by wind, or tides, which are in turn generated by the gravitational pull of the Moon and the Sun, a tsunami is generated by the displacement of water from a large event. Tsunami waves do not resemble normal undersea currents or sea waves because their wavelength is far longer. Rather than appearing as a breaking wave, a tsunami may instead initially resemble a rapidly rising tide. For this reason, it is often referred to as a tidal wave, although this usage is not favoured by the scientific community because it might give ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Storm
A storm is any disturbed state of the natural environment or the atmosphere An atmosphere () is a layer of gas or layers of gases that envelop a planet, and is held in place by the gravity of the planetary body. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A s ... of an Astronomy, astronomical body. It may be marked by significant disruptions to normal conditions such as strong wind, tornadoes, hail, thunder and lightning (a thunderstorm), heavy Precipitation (meteorology), precipitation (snowstorm, rainstorm), heavy freezing rain (ice storm), strong winds (tropical cyclone, windstorm), wind transporting some Chemical substance, substance through the Earth's atmosphere, atmosphere such as in a dust storm, among other forms of severe weather. Storms have the potential to harm lives and property via storm surge, heavy rain or snow causing flooding or road impassibility, lightning, wildfires, and vertical and horizont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)