|
QuickPath
The Intel QuickPath Interconnect (QPI) is a point-to-point processor interconnect developed by Intel which replaced the front-side bus (FSB) in Xeon, Itanium, and certain desktop platforms starting in 2008. It increased the scalability and available bandwidth. Prior to the name's announcement, Intel referred to it as Common System Interface (CSI). Earlier incarnations were known as Yet Another Protocol (YAP) and YAP+. QPI 1.1 is a significantly revamped version introduced with Sandy Bridge-EP ( Romley platform). QPI was replaced by Intel Ultra Path Interconnect (UPI) in Skylake-SP Xeon processors based on LGA 3647 socket. Background Although sometimes called a "bus", QPI is a point-to-point interconnect. It was designed to compete with HyperTransport that had been used by Advanced Micro Devices (AMD) since around 2003. Intel developed QPI at its Massachusetts Microprocessor Design Center (MMDC) by members of what had been the Alpha Development Group, which Intel had acquired ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sandy Bridge-EP
Intel Sandy Bridge-based Xeon microprocessors (often referred to as Sandy Bridge-E) are microprocessors based on the Intel's 32 nm Sandy Bridge architecture for servers, workstations, and high-end desktops. It succeeds the six-core Gulftown/Westmere-EP processor which used the older LGA 1366 package, and uses LGA 2011, LGA 1356 and LGA 1155 socket depending on the package. Overview There are five different families of Xeon processors that were based on Sandy Bridge architecture: * Sandy Bridge-E (LGA 2011) targeted high-end desktop (HEDT) enthusiast segment. It was branded as Core i7 Extreme Edition and Core i7 processors, despite sharing many similarities with Xeon models. * Sandy Bridge-EP (LGA 2011) branded as Xeon E5 models aimed at high-end servers and workstations. It supported motherboards equipped with up to 4 sockets. * Sandy Bridge-EN (LGA 1356) uses a smaller socket for low-end and dual-processor servers on certain Xeon E5 and Pentium branded models. * Sandy Bridge X ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
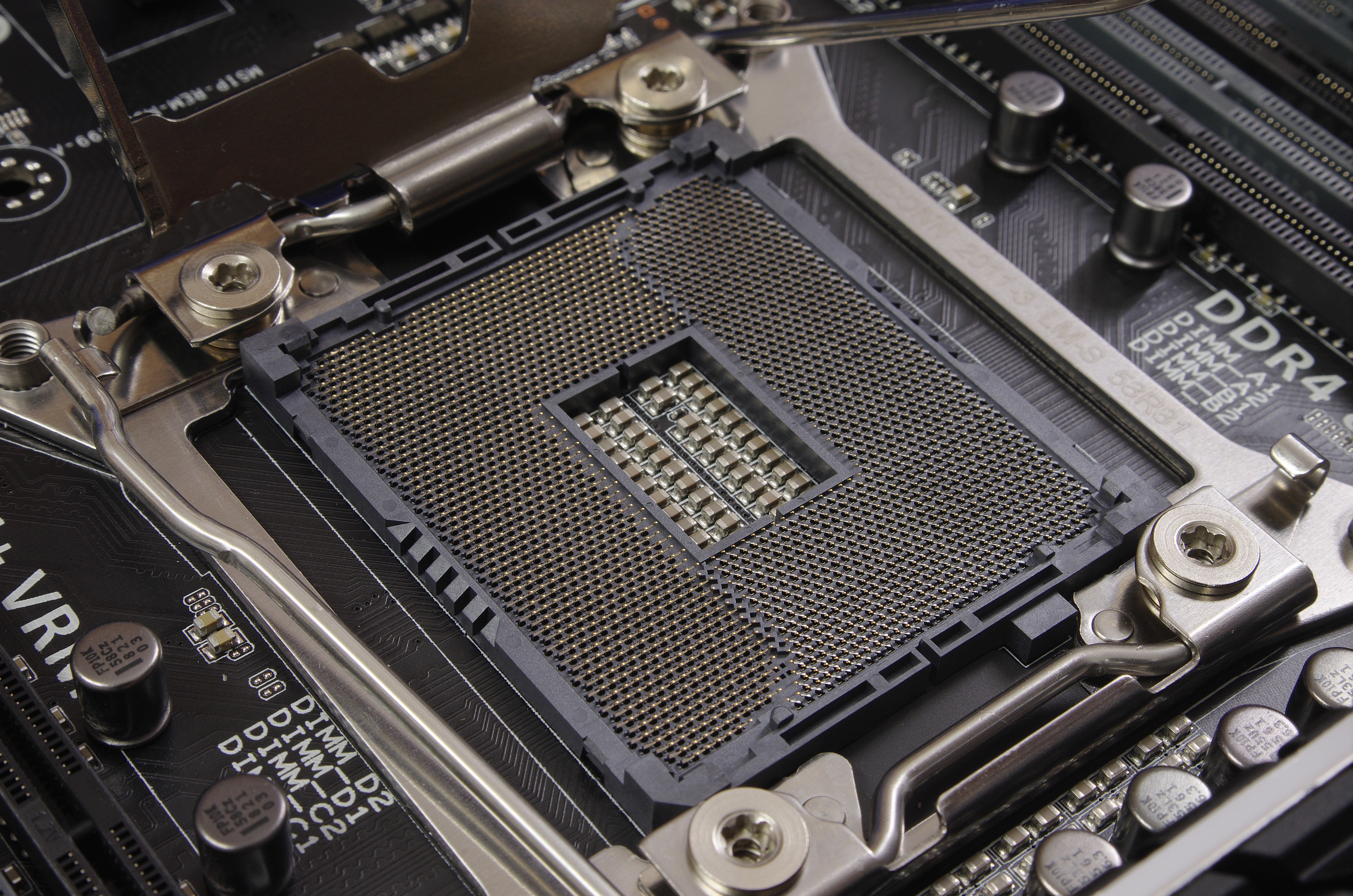
Romley
LGA 2011, also called ''Socket R'', is a CPU socket by Intel released on November 14, 2011. It launched along with LGA 1356 to replace its predecessor, LGA 1366 (Socket B) and LGA 1567. While LGA 1356 was designed for dual-processor or low-end servers, LGA 2011 was designed for high-end desktops and high-performance servers. The socket has 2011 protruding pins that touch contact points on the underside of the processor. The LGA 2011 socket uses QPI to connect the CPU to additional CPUs. DMI 2.0 is used to connect the processor to the PCH. The memory controller and 40 PCI Express (PCIe) lanes are integrated on the CPU. On a secondary processor an extra ×4 PCIe interface replaces the DMI interface. As with its predecessor LGA 1366, there is no provisioning for integrated graphics. This socket supports four DDR3 or DDR4 SDRAM memory channels with up to three unbuffered or registered DIMMs per channel, as well as up to 40 PCI Express 2.0 or 3.0 lanes. LGA&nb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bloomfield (microprocessor)
Bloomfield is the code name for Intel high-end desktop processors sold as Core i7-9xx and single-processor servers sold as Xeon 35xx., in almost identical configurations, replacing the earlier Yorkfield processors. The Bloomfield core is closely related to the dual-processor Gainestown, which has the same CPUID value of 0106Ax (family 6, model 26) and which uses the same socket. Bloomfield uses a different socket than the later Lynnfield and Clarksfield processors based on the same 45 nm Nehalem microarchitecture, even though some of these share the same Intel Core i7 brand. Features Bloomfield has many new features that represent significant changes from Yorkfield: * The new LGA 1366 socket is incompatible with earlier processors. * On- die memory controller: the memory is directly connected to the processor. It is called the uncore part and runs at a different clock (uncore clock) than the execution cores. ** Three channel memory: each channel can support up to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xeon
Xeon ( ) is a brand of x86 microprocessors designed, manufactured, and marketed by Intel, targeted at the non-consumer workstation, server, and embedded system markets. It was introduced in June 1998. Xeon processors are based on the same architecture as regular desktop-grade CPUs, but have advanced features such as support for ECC memory, higher core counts, more PCI Express lanes, support for larger amounts of RAM, larger cache memory and extra provision for enterprise-grade reliability, availability and serviceability (RAS) features responsible for handling hardware exceptions through the Machine Check Architecture. They are often capable of safely continuing execution where a normal processor cannot due to these extra RAS features, depending on the type and severity of the machine-check exception (MCE). Some also support multi-socket systems with two, four, or eight sockets through use of the Ultra Path Interconnect (UPI) bus. Overview The ''Xeon'' brand has been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intel X58
The Intel X58 ( codenamed ''Tylersburg'') is an Intel chip designed to connect Intel processors with Intel QuickPath Interconnect (QPI) interface to peripheral devices. Supported processors implement the Nehalem microarchitecture and therefore have an integrated memory controller (IMC), so the X58 does not have a memory interface. Initially supported processors were the Core i7, but the chip also supported Nehalem and Westmere-based Xeon processors. Description The QuickPath architecture differs considerably from earlier Intel architectures, and is much closer to AMD's HyperTransport architecture. Except for the lack of a memory interface, the X58 is similar to the traditional northbridge: it communicates with the processor(s) via the high bandwidth QuickPath Interconnect, it communicates with the southbridge via Direct Media Interface (DMI), and it communicates with high bandwidth peripherals via PCI Express (PCIe). The X58 is not a ''memory controller hub'' (MCH), be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Front-side Bus
A front-side bus (FSB) is a computer communication interface (bus) that was often used in Intel-chip-based computers during the 1990s and 2000s. The EV6 bus served the same function for competing AMD CPUs. Both typically carry data between the central processing unit (CPU) and a memory controller hub, known as the northbridge. Depending on the implementation, some computers may also have a back-side bus that connects the CPU to the cache. This bus and the cache connected to it are faster than accessing the system memory (or RAM) via the front-side bus. The speed of the front side bus is often used as an important measure of the performance of a computer. The original front-side bus architecture has been replaced by HyperTransport, Intel QuickPath Interconnect or Direct Media Interface in modern volume CPUs. History The term came into use by Intel Corporation about the time the Pentium Pro and Pentium II products were announced, in the 1990s. "Front side" refers to the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Itanium
Itanium ( ) is a discontinued family of 64-bit Intel microprocessors that implement the Intel Itanium architecture (formerly called IA-64). Launched in June 2001, Intel marketed the processors for enterprise servers and high-performance computing systems. The Itanium architecture originated at Hewlett-Packard (HP), and was later jointly developed by HP and Intel. Itanium-based systems were produced by HP/Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE) (the HPE Integrity Servers line) and several other manufacturers. In 2008, Itanium was the fourth-most deployed microprocessor architecture for enterprise-class systems, behind x86-64, Power ISA, and SPARC. In February 2017, Intel released the final generation, Kittson, to test customers, and in May began shipping in volume. It was used exclusively in mission-critical servers from Hewlett Packard Enterprise. In 2019, Intel announced that new orders for Itanium would be accepted until January 30, 2020, and shipments would cease by July ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-uniform Memory Access
Non-uniform memory access (NUMA) is a computer memory design used in multiprocessing, where the memory access time depends on the memory location relative to the processor. Under NUMA, a processor can access its own local memory faster than non-local memory (memory local to another processor or memory shared between processors). The benefits of NUMA are limited to particular workloads, notably on servers where the data is often associated strongly with certain tasks or users. NUMA architectures logically follow in scaling from symmetric multiprocessing (SMP) architectures. They were developed commercially during the 1990s by Unisys, Convex Computer (later Hewlett-Packard), Honeywell Information Systems Italy (HISI) (later Groupe Bull), Silicon Graphics (later Silicon Graphics International), Sequent Computer Systems (later IBM), Data General (later EMC, now Dell Technologies), and Digital (later Compaq, then HP, now HPE). Techniques developed by these companies later ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intel Core I7
The following is a list of Intel Core i7 brand microprocessors. Introduced in 2008, the Core i7 line of microprocessors are intended to be used by high-end users. Desktop processors Nehalem microarchitecture (1st generation) "Bloomfield" (45 nm) * All models support: MMX, SSE, SSE2, SSE3, SSSE3, SSE4.1, SSE4.2, Enhanced Intel SpeedStep Technology (EIST), Intel 64, XD bit (an NX bit implementation), Intel VT-x, Hyper-threading, Turbo Boost, Smart Cache. * FSB has been replaced with QPI. * Transistors: 731 million * Die size: 263 mm * Steppings: C0, D0 "Lynnfield" (45 nm) * All models support: MMX, SSE, SSE2, SSE3, SSSE3, SSE4.1, SSE4.2, Enhanced Intel SpeedStep Technology (EIST), Intel 64, XD bit (an NX bit implementation), TXT, Intel VT-x, Intel VT-d, Hyper-threading, Turbo Boost, Smart Cache. * Core i7-875K features an unlocked multiplier and does not support Intel TXT and Intel VT-d. * FSB has been replaced with DMI. *Mov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nehalem (microarchitecture)
Nehalem is the codename for Intel's 45 nm microarchitecture released in November 2008. It was used in the first-generation of the Intel Core i5 and i7 processors, and succeeds the older Core microarchitecture used on Core 2 processors. The term "Nehalem" comes from the Nehalem River. Nehalem is built on the 45 nm process, is able to run at higher clock speeds, and is more energy-efficient than Penryn microprocessors. Hyper-threading is reintroduced, along with a reduction in L2 cache size, as well as an enlarged L3 cache that is shared among all cores. Nehalem is an architecture that differs radically from Netburst, while retaining some of the latter's minor features. Nehalem later received a die-shrink to 32 nm with Westmere, and was fully succeeded by "second-generation" Sandy Bridge in January 2011. Technology * Cache line block on L2/L3 cache was reduced from 128 bytes in Netburst & Conroe/Penryn to 64 bytes per line in this generation (same size as Yonah a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uncore
"Uncore" is a term used by Intel to describe the functions of a microprocessor that are not in the core, but which must be closely connected to the core to achieve high performance. It has been called "system agent" since the release of the Sandy Bridge microarchitecture. Details The core contains the components of the processor involved in executing instructions, including the ALU, FPU, L1 and L2 cache. Uncore functions include QPI controllers, L3 cache, snoop agent pipeline, on-die memory controller, on-die PCI Express Root Complex, and Thunderbolt controller. Other bus controllers such as SPI and LPC are part of the chipset. The Intel uncore design stems from its origin as the northbridge. The design of the Intel uncore reorganizes the functions critical to the core, making them physically closer to the core on-die, thereby reducing their access latency. Specifically, the microarchitecture of the Intel uncore is broken down into a number of modular units. The main uncore ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
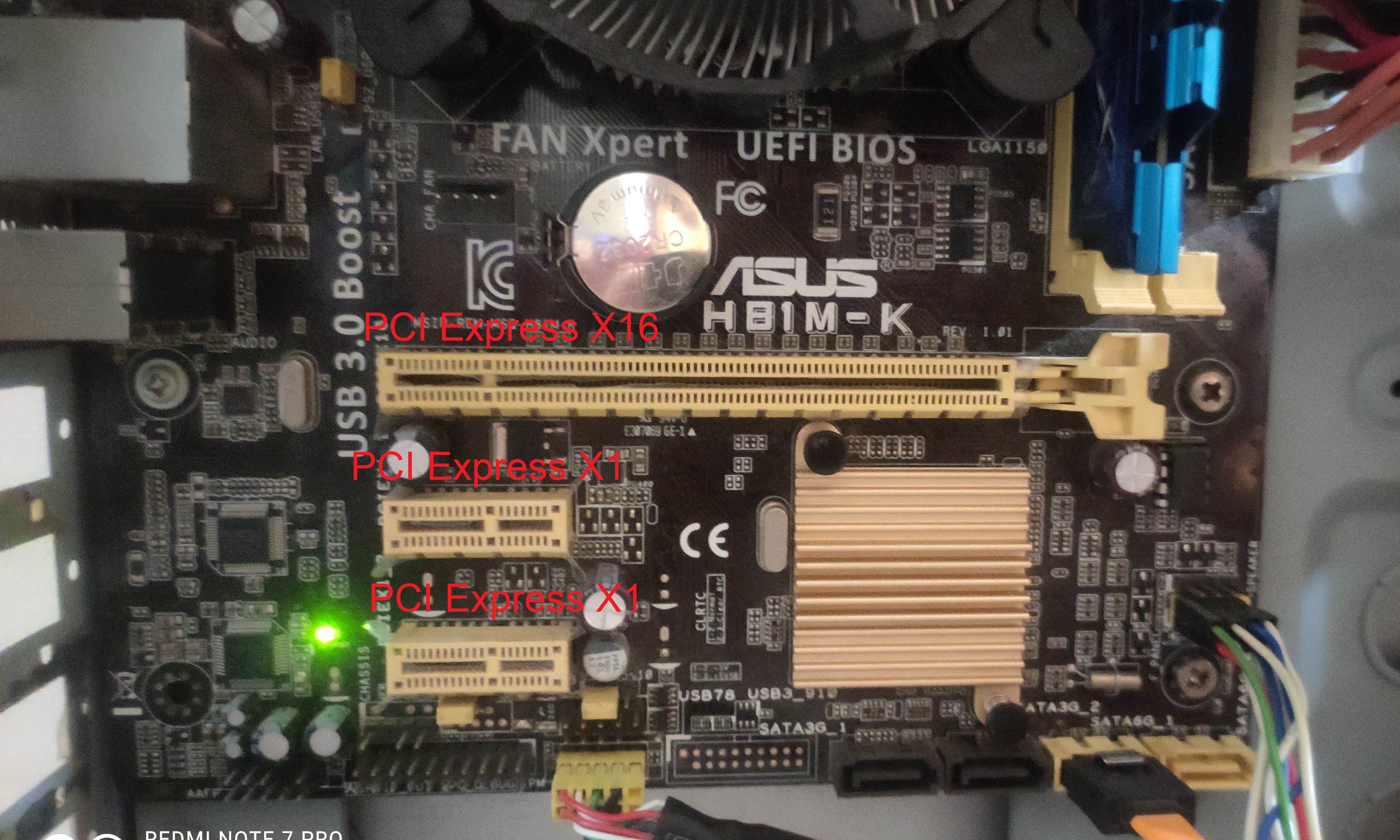
PCI Express
PCI Express (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express), officially abbreviated as PCIe or PCI-e, is a high-speed serial computer expansion bus standard, designed to replace the older PCI, PCI-X and AGP bus standards. It is the common motherboard interface for personal computers' graphics cards, hard disk drive host adapters, SSDs, Wi-Fi and Ethernet hardware connections. PCIe has numerous improvements over the older standards, including higher maximum system bus throughput, lower I/O pin count and smaller physical footprint, better performance scaling for bus devices, a more detailed error detection and reporting mechanism (Advanced Error Reporting, AER), and native hot-swap functionality. More recent revisions of the PCIe standard provide hardware support for I/O virtualization. The PCI Express electrical interface is measured by the number of simultaneous lanes. (A lane is a single send/receive line of data. The analogy is a highway with traffic in both direc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |