|
Quedlinburg Chronicle
The ''Annals of Quedlinburg'' ( lat, Annales Quedlinburgenses; german: Quedlinburger Annalen) were written between 1008 and 1030 in the convent of Quedlinburg Abbey. In recent years a consensus has emerged that it is likely that the annalist was a woman. The annals are mostly dedicated to the history of the Holy Roman Empire; they also contain the first written mention of the name of Lithuania ("Litua"), dated to March, 1009. The original document has disappeared, surviving only as a 16th-century copy held in Dresden, but its contents endure as a scholarly resource. Background The city of Quedlinburg, Germany, was first mentioned in writing in a document dated to 922. Saint Mathilda founded Quedlinburg Abbey, a religious community for women, there in 936, leading it until her death in 966. The abbey became a premier educational institution for the female nobles of Saxony, and maintained its mission for nearly 900 years. The city served as an imperial palatinate of the Saxon em ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Name Of Lithuania
The first known record of the name of Lithuania ( lt, Lietuva) is in a 9 March 1009 story of Saint Bruno recorded in the Quedlinburg Chronicle ( la, Annales Quedlinburgenses). The Chronicle recorded a Latinized form of the Old Church Slavonic word for Lithuania— (''Litva'')—Latinized as ''Litva'' (pronounced ). Although it is clear the name originated from a Baltic language, scholars still debate the meaning of the word. Historic usage During the 13th century the Duchy of Lithuania was bordered by Slavic lands. The Slavs did not create the name; they used the existing Lithuanian ethnonym. The Lithuanian diphthong -''ie''- has, in Slavic languages, shifted to the vowel -''i''- (), and the short -''u''- became extra-short (reduced) -''ŭ''- () which, being unstressed, later disappeared from the East Slavic, hence ''Litva''. This is evidence that the Slavs borrowed this ethnonym from Lithuanians a long time ago. During the next century, Lithuania's name was recorded in o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Third Council Of Constantinople
The Third Council of Constantinople, counted as the Sixth Ecumenical Council by the Eastern Orthodox and Catholic Churches, as well by certain other Western Churches, met in 680–681 and condemned monoenergism and monothelitism as heretical and defined Jesus Christ as having two energies and two wills (divine and human).George Ostrogorsky, ''History of the Byzantine State'' (Rutgers University Press, 1995), 127. Background The council settled a set of theological controversies that went back to the sixth century but had intensified under the emperors Heraclius () and Constans II (). Heraclius had set out to recover much of the part of his empire lost to the Persians and had attempted to bridge the controversy with monophysitism, which was particularly strong in Syria and Egypt, by proposing a moderate theological position that had as good support in the tradition as any other. The result was first monoenergism, i.e. that Christ, though existing in two natures (divin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Climate Variability
Climate variability includes all the variations in the climate that last longer than individual weather events, whereas the term climate change only refers to those variations that persist for a longer period of time, typically decades or more. ''Climate change'' may refer to any time in Earth's history, but the term is now commonly used to describe contemporary climate change. Since the Industrial Revolution, the climate has increasingly been affected by human activities. The climate system receives nearly all of its energy from the sun and radiates energy to outer space. The balance of incoming and outgoing energy and the passage of the energy through the climate system is Earth's energy budget. When the incoming energy is greater than the outgoing energy, Earth's energy budget is positive and the climate system is warming. If more energy goes out, the energy budget is negative and Earth experiences cooling. The energy moving through Earth's climate system finds expressi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franks
The Franks ( la, Franci or ) were a group of Germanic peoples whose name was first mentioned in 3rd-century Roman sources, and associated with tribes between the Lower Rhine and the Ems River, on the edge of the Roman Empire.H. Schutz: Tools, Weapons and Ornaments: Germanic Material Culture in Pre-Carolingian Central Europe, 400-750. BRILL, 2001, p.42. Later the term was associated with Romanization (cultural), Romanized Germanic dynasties within the collapsing Western Roman Empire, who eventually commanded the whole region between the rivers Loire and Rhine. They imposed power over many other post-Roman kingdoms and Germanic peoples. Beginning with Charlemagne in 800, Frankish rulers were given recognition by the Catholic Church as successors to the old rulers of the Western Roman Empire. Although the Frankish name does not appear until the 3rd century, at least some of the original Frankish tribes had long been known to the Romans under their own names, both as allies providi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beowulf
''Beowulf'' (; ang, Bēowulf ) is an Old English Epic poetry, epic poem in the tradition of Germanic heroic legend consisting of 3,182 Alliterative verse, alliterative lines. It is one of the most important and List of translations of Beowulf, most often translated works of Old English literature. The date of composition is a matter of contention among scholars; the only certain dating is for the manuscript, which was produced between 975 and 1025. Scholars call the anonymous author the "''Beowulf'' poet". The story is set in pagan Scandinavia in the 6th century. Beowulf (hero), Beowulf, a hero of the Geats, comes to the aid of Hrothgar, the king of the Danes (Germanic tribe), Danes, whose mead hall in Heorot has been under attack by the monster Grendel. After Beowulf slays him, Grendel's mother attacks the hall and is then defeated. Victorious, Beowulf goes home to Geatland and becomes king of the Geats. Fifty years later, Beowulf defeats a The Dragon (Beowulf), dragon, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germans
, native_name_lang = de , region1 = , pop1 = 72,650,269 , region2 = , pop2 = 534,000 , region3 = , pop3 = 157,000 3,322,405 , region4 = , pop4 = 21,000 3,000,000 , region5 = , pop5 = 125,000 982,226 , region6 = , pop6 = 900,000 , region7 = , pop7 = 142,000 840,000 , region8 = , pop8 = 9,000 500,000 , region9 = , pop9 = 357,000 , region10 = , pop10 = 310,000 , region11 = , pop11 = 36,000 250,000 , region12 = , pop12 = 25,000 200,000 , region13 = , pop13 = 233,000 , region14 = , pop14 = 211,000 , region15 = , pop15 = 203,000 , region16 = , pop16 = 201,000 , region17 = , pop17 = 101,000 148,00 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saga
is a series of science fantasy role-playing video games by Square Enix. The series originated on the Game Boy in 1989 as the creation of Akitoshi Kawazu at Square. It has since continued across multiple platforms, from the Super NES to the PlayStation 2. The series is notable for its emphasis on open world exploration, non-linear branching plots, and occasionally unconventional gameplay. This distinguishes the games from most of Square's other franchises. Development The ''SaGa'' series was created by game designer Akitoshi Kawazu, whose contributions prior to the franchise's introduction include ''Final Fantasy'' and ''Final Fantasy II''. At a time when Nintendo's Game Boy was becoming popular worldwide due to the puzzle game ''Tetris'', then-Square president Masashi Miyamoto requested that a development team create a game for the handheld console. Kawazu and fellow designer Koichi Ishii suggested that the company develop a role-playing video game, thus making ''Makai T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Felice Lifshitz
Felice Lifshitz is an American academic historian, who specialises in medieval European history. She is a former editor-in-chief of the peer-reviewed journal ''History Compass'', and serves on the editorial board for ''The Historian''. Education Lifshitz graduated from Barnard College (1981) and a Masters (1983) and Ph.D. (1988) from Columbia University Columbia University (also known as Columbia, and officially as Columbia University in the City of New York) is a private research university in New York City. Established in 1754 as King's College on the grounds of Trinity Church in Manha .... Selected works * Reviews of ''Why the Middle Ages Matter'': * * * * References External linksFlorida International University staff profile Living people American medievalists Women medievalists Academic journal editors Barnard College alumni Columbia University alumni American women historians Year of birth missing (living people) 21st-century American women ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
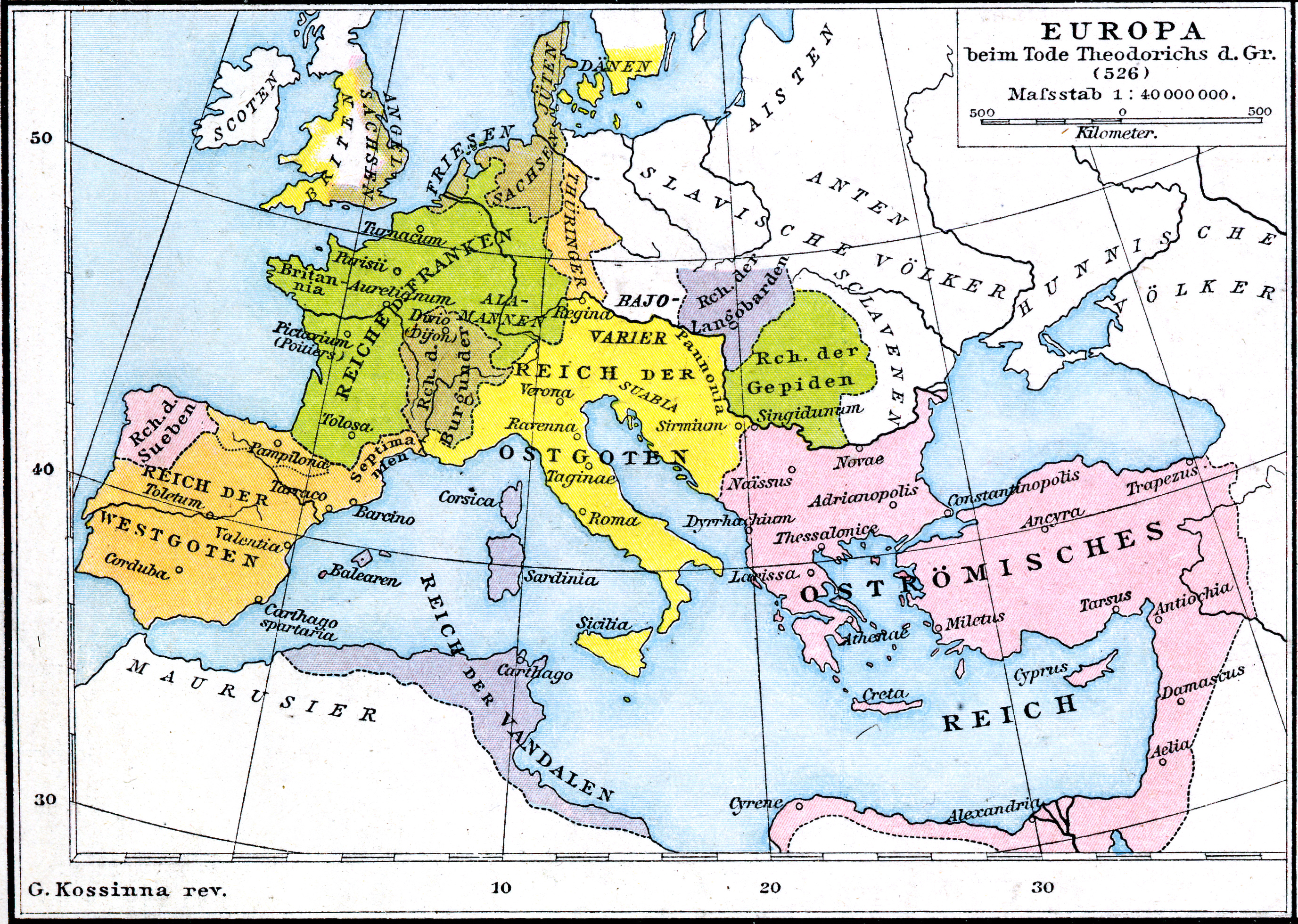
Dietrich Of The Goths
Theodoric (or Theoderic) the Great (454 – 30 August 526), also called Theodoric the Amal ( got, , *Þiudareiks; Greek: , romanized: ; Latin: ), was king of the Ostrogoths (471–526), and ruler of the independent Ostrogothic Kingdom of Italy between 493 and 526, regent of the Visigoths (511–526), and a patrician of the Eastern Roman Empire. As ruler of the combined Gothic realms, Theodoric controlled an empire stretching from the Atlantic Ocean to the Adriatic Sea. Though Theodoric himself only used the title 'king' (''rex''), some scholars characterize him as a Western Roman Emperor in all but name, since he ruled large parts of the former Western Roman Empire, had received the former Western imperial regalia from Constantinople in 497, and was referred to by the title ''augustus'' by some of his subjects. As a young child of an Ostrogothic nobleman, Theodoric was taken as a hostage to Constantinople, where he spent his formative years and received an East Roman education ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attila The Hun
Attila (, ; ), frequently called Attila the Hun, was the ruler of the Huns from 434 until his death in March 453. He was also the leader of a tribal empire consisting of Huns, Ostrogoths, Alans, and Bulgars, among others, in Central and Eastern Europe. During his reign, he was one of the most feared enemies of the Western and Eastern Roman Empires. He crossed the Danube twice and plundered the Balkans, but was unable to take Constantinople. His unsuccessful campaign in Persia was followed in 441 by an invasion of the Eastern Roman (Byzantine) Empire, the success of which emboldened Attila to invade the West. He also attempted to conquer Roman Gaul (modern France), crossing the Rhine in 451 and marching as far as Aurelianum ( Orléans), before being stopped in the Battle of the Catalaunian Plains. He subsequently invaded Italy, devastating the northern provinces, but was unable to take Rome. He planned for further campaigns against the Romans, but died in 453. Af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, , is a country in Central Europe. Poland is divided into Voivodeships of Poland, sixteen voivodeships and is the fifth most populous member state of the European Union (EU), with over 38 million people, and the List of European countries by area, seventh largest EU country, covering a combined area of . It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south, bordering seven countries. The territory is characterised by a varied landscape, diverse ecosystems, and Temperate climate, temperate transitional climate. The capital and List of cities and towns in Poland, largest city is Warsaw; other major cities include Kraków, Wrocław, Łódź, Poznań, and Gdańsk. Prehistory and protohistory of Poland, Humans have been present on Polish soil since the Lower Paleolithic, with continuous settlement since the end of the Last Glacial Period over 12,000 years ago. Culturally diverse throughout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mieszko II Lambert
Mieszko II Lambert (; c. 990 – 10/11 May 1034) was King of Poland from 1025 to 1031, and Duke from 1032 until his death. He was the second son of Bolesław I the Brave, but the eldest born from his third wife Emnilda of Lusatia. He was probably named after his paternal grandfather, Mieszko I. His second name, Lambert, sometimes erroneously considered to be a sobriquet, was given to him as a reference to Saint Lambert. However, it is also probable that the name was chosen after Bolesław's half-brother Lambert Mieszkowic. It is thought that the choice of this name for his son was an expression of warming relations between Bolesław I and his stepmother Oda of Haldensleben. He organized two devastating invasions of Saxony in 1028 and 1030. Then, Mieszko II ran a defensive war against Germany, Bohemia and the Kievan princes. Mieszko II was forced to escape from the country in 1031 after an attack by Yaroslav I the Wise, who installed Mieszko's older half-brother Bezprym ont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |