|
Quebec History
Quebec was first called '' Canada'' between 1534 and 1763. It was the most developed colony of New France as well as New France's centre, responsible for a variety of dependencies (ex. Acadia, Plaisance, Louisiana, and the Pays d'en Haut). Common themes in Quebec's early history as ''Canada'' include the fur trade -because it was the main industry- as well as the exploration of North America, war against the English, and alliances or war with Native American groups. Following the Seven Years' War, Quebec became a British colony in the British Empire. It was first known as the Province of Quebec (1763–1791), then as Lower Canada (1791–1841), and then as Canada East (1841–1867) as a result of the Lower Canada Rebellion. During this period, the inferior socio-economic status of francophones (because anglophones dominated the natural resources and industries of Quebec), the Catholic church, resistance against cultural assimilation, and isolation from non English-s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Montreal From Mount Royal4
Montreal ( ; officially Montréal, ) is the second-most populous city in Canada and most populous city in the Canadian province of Quebec. Founded in 1642 as '' Ville-Marie'', or "City of Mary", it is named after Mount Royal, the triple-peaked hill around which the early city of Ville-Marie is built. The city is centred on the Island of Montreal, which obtained its name from the same origin as the city, and a few much smaller peripheral islands, the largest of which is Île Bizard. The city is east of the national capital Ottawa, and southwest of the provincial capital, Quebec City. As of 2021, the city had a population of 1,762,949, and a metropolitan population of 4,291,732, making it the second-largest city, and second-largest metropolitan area in Canada. French is the city's official language. In 2021, it was spoken at home by 59.1% of the population and 69.2% in the Montreal Census Metropolitan Area. Overall, 85.7% of the population of the city of Montreal consider ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ontario
Ontario ( ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada.Ontario is located in the geographic eastern half of Canada, but it has historically and politically been considered to be part of Central Canada. Located in Central Canada, it is Canada's most populous province, with 38.3 percent of the country's population, and is the second-largest province by total area (after Quebec). Ontario is Canada's fourth-largest jurisdiction in total area when the territories of the Northwest Territories and Nunavut are included. It is home to the nation's capital city, Ottawa, and the nation's most populous city, Toronto, which is Ontario's provincial capital. Ontario is bordered by the province of Manitoba to the west, Hudson Bay and James Bay to the north, and Quebec to the east and northeast, and to the south by the U.S. states of (from west to east) Minnesota, Michigan, Ohio, Pennsylvania, and New York. Almost all of Ontario's border with the United States f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atikamekw
The Atikamekw are the Indigenous inhabitants of the subnational country or territory they call ('Our Land'), in the upper Saint-Maurice River valley of Quebec (about north of Montreal), Canada. Their current population is around 8,000. One of the main communities is Manawan, about northeast of Montreal. They have a tradition of agriculture as well as fishing, hunting and gathering. They have close traditional ties with the Innu people, who were their historical allies against the Inuit. The Atikamekw language, usually considered a variety of Cree in the Algonquian family, is closely related to that of the Innu. It is still in everyday use, being among the indigenous languages least threatened with extinction. Their traditional ways of life are endangered, however, as their homeland has largely been taken over by logging companies. Their name, which literally means 'lake whitefish', is sometimes also spelt , , , or . The French colonists referred to them as , meaning 'Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algonquin People
The Algonquin people are an Indigenous people who now live in Eastern Canada. They speak the Algonquin language, which is part of the Algonquian language family. Culturally and linguistically, they are closely related to the Odawa, Potawatomi, Ojibwe (including Oji-Cree), Mississauga and Nipissing, with whom they form the larger Anicinàpe (Anishinaabeg). Algonquins call themselves Omàmiwinini (plural: Omàmiwininiwak) or the more generalised name of Anicinàpe. Though known by several names in the past, such as ''Algoumequin'', the most common term "Algonquin" has been suggested to derive from the Maliseet word (): "they are our relatives/allies." The much larger heterogeneous group of Algonquian-speaking peoples, who, according to Brian Conwell, stretch from Virginia to the Rocky Mountains and north to Hudson Bay, was named after the tribe. Most Algonquins live in Quebec. The nine recognized status Algonquin bands in that province and one in Ontario have a combined ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
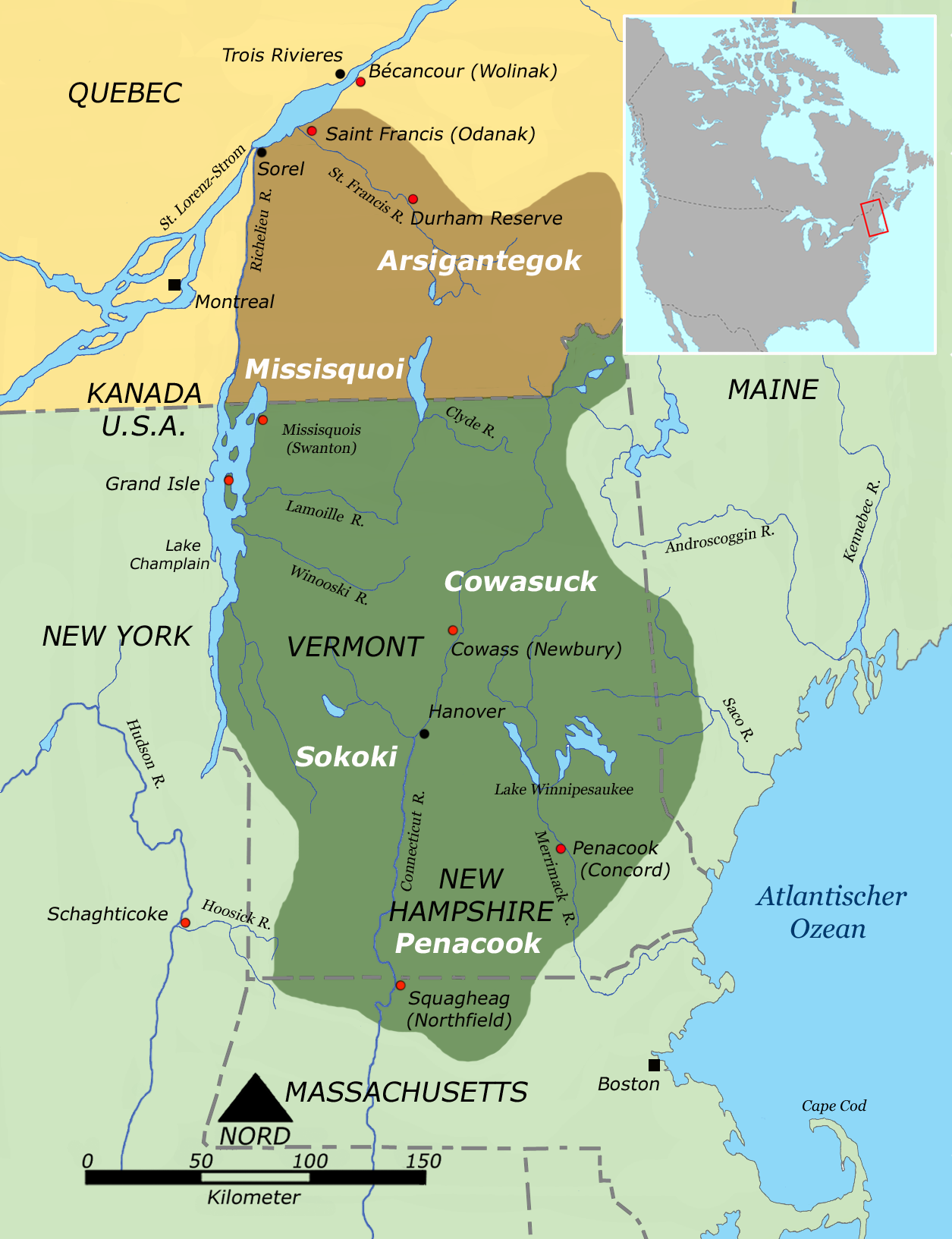
Abenaki People
The Abenaki (Abenaki: ''Wαpánahki'') are an Indigenous peoples of the Northeastern Woodlands of Canada and the United States. They are an Algonquian-speaking people and part of the Wabanaki Confederacy. The Eastern Abenaki language was predominantly spoken in Maine, while the Western Abenaki language was spoken in Quebec, Vermont, and New Hampshire. While Abenaki peoples have shared cultural traits, they did not historically have a centralized government. They came together as a post-contact community after their original tribes were decimated by colonization, disease, and warfare. Names The word ''Abenaki'' and its syncope, ''Abnaki,'' are both derived from ''Wabanaki'', or ''Wôbanakiak,'' meaning "People of the Dawn Land" in the Abenaki language. While the two terms are often confused, the Abenaki are one of several tribes in the Wabanaki Confederacy. The name is spelled several ways including Abnaki, Abinaki, and Alnôbak. ''Wôbanakiak'' is derived from ''wôban'' ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Nations In Canada
First Nations (french: Premières Nations) is a term used to identify those Indigenous Canadian peoples who are neither Inuit nor Métis. Traditionally, First Nations in Canada were peoples who lived south of the tree line, and mainly south of the Arctic Circle. There are 634 recognized First Nations governments or bands across Canada. Roughly half are located in the provinces of Ontario and British Columbia. Under Charter jurisprudence, First Nations are a "designated group," along with women, visible minorities, and people with physical or mental disabilities. First Nations are not defined as a visible minority by the criteria of Statistics Canada. North American indigenous peoples have cultures spanning thousands of years. Some of their oral traditions accurately describe historical events, such as the Cascadia earthquake of 1700 and the 18th-century Tseax Cone eruption. Written records began with the arrival of European explorers and colonists during the Age of Dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inuit
Inuit (; iu, ᐃᓄᐃᑦ 'the people', singular: Inuk, , dual: Inuuk, ) are a group of culturally similar indigenous peoples inhabiting the Arctic and subarctic regions of Greenland, Labrador, Quebec, Nunavut, the Northwest Territories, and Alaska. Inuit languages are part of the Eskimo–Aleut languages, also known as Inuit-Yupik-Unangan, and also as Eskaleut. Inuit Sign Language is a critically endangered language isolate used in Nunavut. Inuit live throughout most of Northern Canada in the territory of Nunavut, Nunavik in the northern third of Quebec, Nunatsiavut and NunatuKavut in Labrador, and in various parts of the Northwest Territories, particularly around the Arctic Ocean, in the Inuvialuit Settlement Region. With the exception of NunatuKavut, these areas are known, primarily by Inuit Tapiriit Kanatami, as Inuit Nunangat. In Canada, sections 25 and 35 of the Constitution Act of 1982 classify Inuit as a distinctive group of Aboriginal Canadians wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coat Of Arms Of Quebec
The coat of arms of Quebec (french: armoiries du Québec) was adopted by order-in-council of the Government of Quebec on 9 December 1939,Justice Québec. Les armoiries du Québec replacing the arms assigned by royal warrant of on 26 May 1868. Symbolism The is divided into three horizontal fields: * ''Top'' — three |
Quebec Sovereignty Movement
The Quebec sovereignty movement (french: Mouvement souverainiste du Québec) is a political movement whose objective is to achieve the sovereignty of Quebec, a province of Canada since 1867, including in all matters related to any provision of Quebec's public order that is applicable on its territory. Sovereignists suggest that the people of Quebec make use of their right to self-determination – a principle that includes the possibility of choosing between integration with a third state, political association with another state or independence – so that Quebecois, collectively and by democratic means, give themselves a sovereign state with its own independent constitution. Quebec sovereigntists believe that such a sovereign state, the Quebec nation, will be better equipped to promote its own economic, social, ecological and cultural development. Quebec's sovereignist movement is based on Quebec nationalism. Overview Ultimately, the goal of Quebec's sovereignist movement ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Canadians
French Canadians (referred to as Canadiens mainly before the twentieth century; french: Canadiens français, ; feminine form: , ), or Franco-Canadians (french: Franco-Canadiens), refers to either an ethnic group who trace their ancestry to French people, French colonists who settled in Canada (New France), Canada beginning in the 17th century or to French-speaking or Francophone Canadians of any ethnic origin. During the 17th century, French settlers originating mainly from the west and north of France settled Canada (New France), Canada. It is from them that the French Canadian ethnicity was born. During the 17th to 18th centuries, French Canadians expanded across North America and colonized various regions, cities, and towns. As a result people of French Canadian descent can be found across North America. Between 1840 and 1930, many French Canadians immigrated to New England, an event known as the Grande Hémorragie. Etymology French Canadians get their name from ''Canada, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quiet Revolution
The Quiet Revolution (french: Révolution tranquille) was a period of intense socio-political and socio-cultural change in French Canada which started in Quebec after the election of 1960, characterized by the effective secularization of government, the creation of a state-run welfare state (''état-providence''), as well as realignment of politics into federalist and sovereigntist (or separatist) factions and the eventual election of a pro-sovereignty provincial government in the 1976 election. The Quiet Revolution typically refers to the efforts made by the Liberal government of Jean Lesage (elected in 1960) and sometimes Robert Bourassa (elected in 1970 after the Union Nationale's Daniel Johnson in 1966), though given the profound effect of the changes, most provincial governments since the early 1960s have maintained an orientation based on core concepts developed and implemented in that era. A primary change was an effort by the provincial government to take more dire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grande Noirceur
The Grande Noirceur (, English, Great Darkness) refers to the regime of conservative policies undertaken by the governing body of Quebec Premier Maurice Le Noblet Duplessis from 1936 to 1939 and from 1944 to 1959. Rural areas Duplessis favoured rural areas over city development and introduced various agricultural credits during his first term. He also was noted for meagre investment in social services. Duplessis also opposed military conscription and Canadian involvement in World War II. Support from the Catholic Church In 1936, Duplessis hung a crucifix in the Quebec legislature. It was replaced by a second crucifix in 1982, which was removed on 10 July 2019. His party, the Union Nationale, often had the active support of the Roman Catholic Church during political campaigns, using the slogan ''Le ciel est bleu; l'enfer est rouge'' ("Heaven is blue; hell is red"; red is the colour of the Liberal party, and blue was the colour of the Union Nationale). However, the 1950s labo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |