|
Qazançı, Nakhchivan
Qazançı (also rendered as Gazanchy, Gazanchi, Ghazanchi), also known as Shahkert (), is a village and municipality in the Julfa District of Nakhchivan, Azerbaijan. It is located 43 km in the north from the district center, on the right bank of the Alinjachay River, on the slope of the Zangezur ridge. History The village is located in the ancient Armenian province of Goght. Its alternative name means coppersmiths (ghazanchetsi) in Armenian and the village was famous for the quality of the copper utensils produced there. In the 19th century, Armenians from Shahkert migrated to Shusha where they continued their trade as coppersmiths. The Ghazanchetsots Cathedral in Shusha is named after this village. Historical and archaeological monuments Surp Amenaprkich Monastery Within the village (until at least the 1990s) was an Armenian church that was originally part of a monastery called '' Surp Amenaprkich''. Ayvazian dates it to the 12th century, with additions from the 17th cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
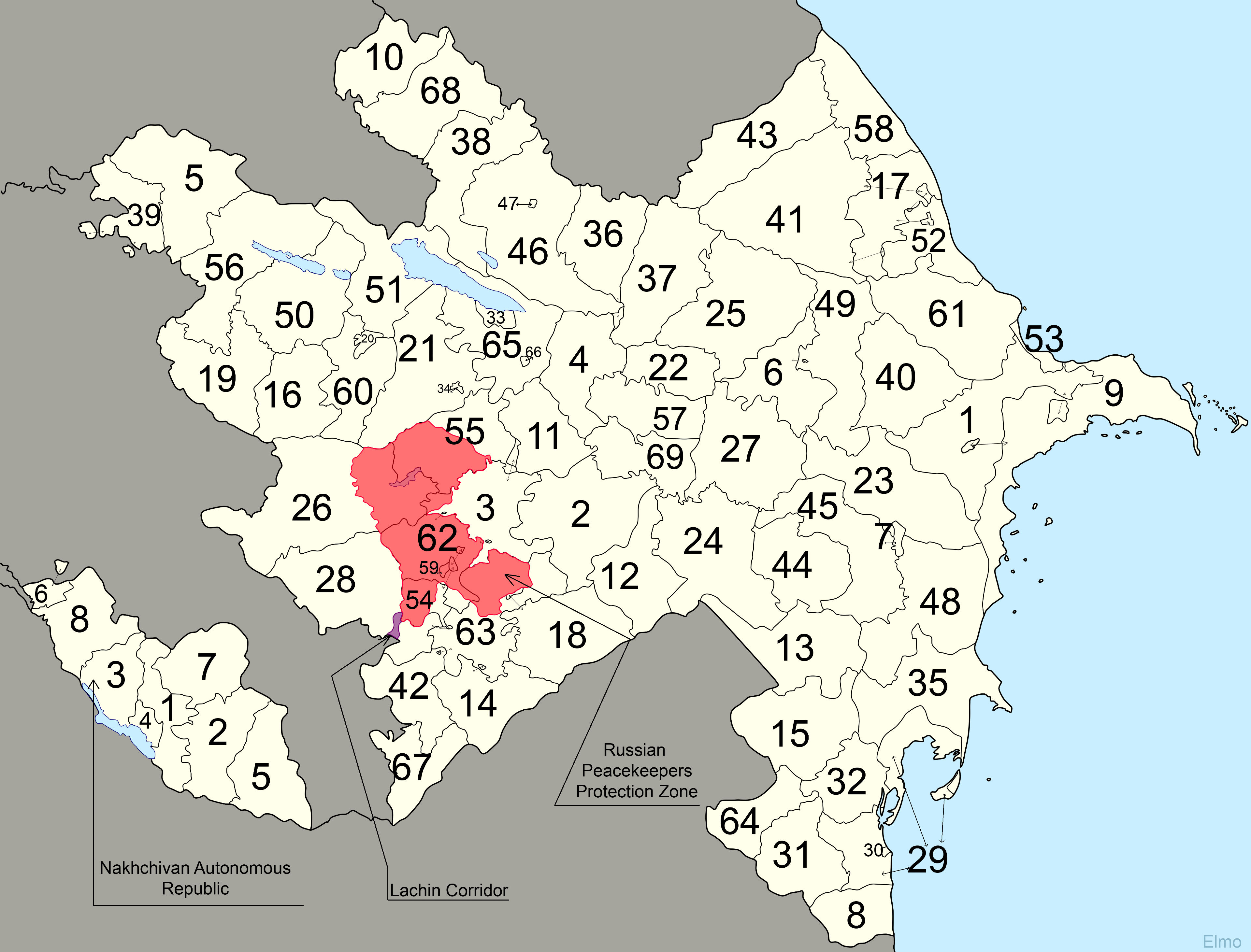
Administrative Divisions Of Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan is administratively divided into 66 districts () and 11 cities () that are subordinate to the Republic. Out of these, 7 districts and 1 city is located within the Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic. The districts are further divided into municipalities (). Additionally, the districts of Azerbaijan are grouped into 14 Economic Regions (). On July 7, 2021, the President of Azerbaijan Ilham Aliyev signed Decree "On the new division of economic regions in the Republic of Azerbaijan". Administrative divisions Contiguous Azerbaijan The territory of former Nagorno-Karabakh Autonomous Oblast presently consists of the districts of Khojavend, Shusha, Khojaly, the eastern portion of Kalbajar and the western portion of Tartar. The Autonomous Oblast was abolished on 26 November 1991, by the Supreme Soviet of the Azerbaijan SSR. Since then, the territory of the autonomous oblast has been administratively split between the aforementioned districts. As a result of the First N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic
The Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic ( az, Naxçıvan Muxtar Respublikası, ), is a landlocked exclave of the Republic of Azerbaijan. The region covers Official portal of Nakhchivan Autonomous RepublicNakhchivan Autonomous Republic with a population of 459,600 bordered by Armenia to the east and north, Iran to the southwest, and Turkey to the west. The republic, especially the capital city of Nakhchivan, has a long history dating back to about 1500 BCE. ''Nakhijevan'' was one the cantons of the historical Armenian province of Vaspurakan in the Kingdom of Armenia. Historically though, the Persians, Armenians, Mongols, and Turks all competed for the region. The area that is now Nakhchivan became part of Safavid Iran in the 16th century. In 1828, after the last Russo-Persian War and the Treaty of Turkmenchay, the Nakhchivan Khanate passed from Iranian into Imperial Russian possession. After the 1917 February Revolution, Nakhchivan and its surrounding region were under the autho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Julfa District
Julfa District ( az, Culfa rayonu) is one of the 7 districts of the Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic of Azerbaijan. The district borders the districts of Ordubad, Babek, Shahbuz, as well as the Syunik Province of Armenia and the East Azerbaijan Province of Iran. Its capital and largest city is Julfa. As of 2020, the district had a population of 47,000. History Established in 1930 and initially named Abragunus, it has been called Julfa District since 1950. The names, Jolfa/Julfa are also used for several regions in neighboring Iran. On November 28, 2014, by the decree of the President of Azerbaijan Republic, the Nahajir and Goynuk villages of Julfa District were removed and added to the territory of Babek District. Geography The district borders Armenia to the North-East, and Iran to the South. Julfa District is in the east from Nakhchivan city. ''Damirlidagh Mountain'' (3368 m) is the highest point of the district. Summer of the district is hot and dry, but winter is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azerbaijan Time
Azerbaijan Time ( az, Azərbaycanda vaxt), abbreviated as AZT, is the standard time zone in Azerbaijan, four hours ahead of UTC ( UTC+04:00). The daylight saving time adjustment, Azerbaijan Summer Time (AZST), was one hour ahead at UTC+05:00 and was introduced in 1997 and discontinued in March 2016. Azerbaijan Time is the same as Samara Time (Russia), United Arab Emirates Standard Time, Georgia Time, Armenia Time and Seychelles Time. IANA time zone database The IANA time zone database The tz database is a collaborative compilation of information about the world's time zones, primarily intended for use with computer programs and operating systems. Paul Eggert is its current editor and maintainer, with the organizational backi ... contains one zone for Azerbaijan in the file zone.tab, named Asia/Baku. References Time in Azerbaijan {{Azerbaijan-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan (, ; az, Azərbaycan ), officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, , also sometimes officially called the Azerbaijan Republic is a transcontinental country located at the boundary of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is a part of the South Caucasus region and is bounded by the Caspian Sea to the east, Russia (Republic of Dagestan) to the north, Georgia to the northwest, Armenia and Turkey to the west, and Iran to the south. Baku is the capital and largest city. The Azerbaijan Democratic Republic proclaimed its independence from the Transcaucasian Democratic Federative Republic in 1918 and became the first secular democratic Muslim-majority state. In 1920, the country was incorporated into the Soviet Union as the Azerbaijan SSR. The modern Republic of Azerbaijan proclaimed its independence on 30 August 1991, shortly before the dissolution of the Soviet Union in the same year. In September 1991, the ethnic Armenian majority of the Nagorno-Karabakh region formed the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ghazanchetsots Cathedral
Holy Savior Cathedral ( hy, Սուրբ Ամենափրկիչ մայր տաճար, ''Surb Amenap′rkich mayr tachar''), commonly referred to as Ghazanchetsots ( hy, Ղազանչեցոց),), ''Kazanchetsots'' (russian: Казанчецоц). In Azerbaijani: ''Kazançetsots''/''Qazançetsots'' or ''Qazançı kilsəsi''. is an Armenian Apostolic cathedral in Shusha (also known as ''Shushi'') in Azerbaijan, in the disputed region of Nagorno-Karabakh. It is the '' cathedra'' of the Diocese of Artsakh of the Armenian Apostolic Church. Standing high, Ghazanchetsots is one of the largest Armenian churches in the world. A landmark of Shusha and the Karabakh region, and of Armenian cultural and religious identity, it is listed as cultural and historical monument of the breakaway Republic of Artsakh. Built between 1868 and 1887, the cathedral was consecrated in 1888. It was damaged during the March 1920 massacre of the city's Armenians—and the destruction of their half of the city� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amenaprkich Monastery (Gazanchy)
Amenaprkich Monastery was an Armenian monastery in Gazanchy village (Julfa District) of the Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic of Azerbaijan. The monastery was located in the center of the village.Ayvazyan, Argam. ''The Historical Monuments of Nakhichevan.'' Transl. Krikor H. Maksoudian. Detroit: Wayne State University Press, 1990, p. 85. History The monastery was founded in the 12–13th centuries and was rebuilt in 1654, according to an Armenian inscription on a ''khachkar'' set above the lintel A lintel or lintol is a type of beam (a horizontal structural element) that spans openings such as portals, doors, windows and fireplaces. It can be a decorative architectural element, or a combined ornamented structural item. In the case of w ... of the doorway.Ayvazyan, Argam. ''Nakhijevani ISSH haykakan hushardzannery. Hamahavak tsutsak''. Yerevan: Hayastan, 1986, pp. 72–73. Architecture In the late Soviet years, the outer walls of the monastery complex, the porch attache ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azerbaijan Republic
Azerbaijan (, ; az, Azərbaycan ), officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, , also sometimes officially called the Azerbaijan Republic is a transcontinental country located at the boundary of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is a part of the South Caucasus region and is bounded by the Caspian Sea to the east, Russia (Republic of Dagestan) to the north, Georgia to the northwest, Armenia and Turkey to the west, and Iran to the south. Baku is the capital and largest city. The Azerbaijan Democratic Republic proclaimed its independence from the Transcaucasian Democratic Federative Republic in 1918 and became the first secular democratic Muslim-majority state. In 1920, the country was incorporated into the Soviet Union as the Azerbaijan SSR. The modern Republic of Azerbaijan proclaimed its independence on 30 August 1991, shortly before the dissolution of the Soviet Union in the same year. In September 1991, the ethnic Armenian majority of the Nagorno-Karabakh region formed the se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ghazan
Mahmud Ghazan (5 November 1271 – 11 May 1304) (, Ghazan Khan, sometimes archaically spelled as Casanus by the Westerners) was the seventh ruler of the Mongol Empire's Ilkhanate division in modern-day Iran from 1295 to 1304. He was the son of Arghun, grandson of Abaqa Khan and great-grandson of Hulagu Khan, continuing a long line of rulers who were direct descendants of Genghis Khan. Considered the most prominent of the Ilkhans, he is perhaps best known for converting to Islam and meeting Imam Ibn Taymiyya in 1295 when he took the throne, marking a turning point for the dominant religion of the Mongols in Western Asia (Iran, Iraq, Anatolia and Transcaucasia). One of his many principal wives was Kököchin, a Mongol princess (originally betrothed to Ghazan's father Arghun before his death) sent by his great-uncle Kublai Khan. Military conflicts during Ghazan's reign included war with the Egyptian Mamluks for control of Syria, and battles with the Turko-Mongol Chagatai Khanate. G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Book Of Dede Korkut
The ''Book of Dede Korkut'' or ''Book of Korkut Ata'' ( az, Kitabi-Dədə Qorqud, ; tk, Kitaby Dädem Gorkut; tr, Dede Korkut Kitabı) is the most famous among the epic stories of the Oghuz Turks. The stories carry morals and values significant to the social lifestyle of the nomadic Turkic peoples and their pre-Islamic beliefs. The book's mythic narrative is part of the cultural heritage of the peoples of Oghuz Turkic origin, mainly of Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Turkmenistan. Only two manuscripts of the text, one in the Vatican and one in Dresden, were known until 2018, when the Gonbad manuscript was discovered. The epic tales of ''Dede Korkut'' are some of the best-known Turkic dastans from among a total of well over 1,000 recorded epics among the Mongolian and Turkic language families. Origin and synopsis of the epic ''Dede Korkut'' is a heroic dastan (legend), also known as ''Oghuz-nameh'' among the Oghuz Turkic people, which starts out in Central Asia, continues in Ana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and transitioned into the Renaissance and the Age of Discovery. The Middle Ages is the middle period of the three traditional divisions of Western history: classical antiquity, the medieval period, and the modern period. The medieval period is itself subdivided into the Early, High, and Late Middle Ages. Population decline, counterurbanisation, the collapse of centralized authority, invasions, and mass migrations of tribes, which had begun in late antiquity, continued into the Early Middle Ages. The large-scale movements of the Migration Period, including various Germanic peoples, formed new kingdoms in what remained of the Western Roman Empire. In the 7th century, North Africa and the Middle East—most recently part of the Eastern Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |