Azerbaijan Republic on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Azerbaijan (, ; az, Azərbaycan ), officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, , also sometimes officially called the Azerbaijan Republic is a
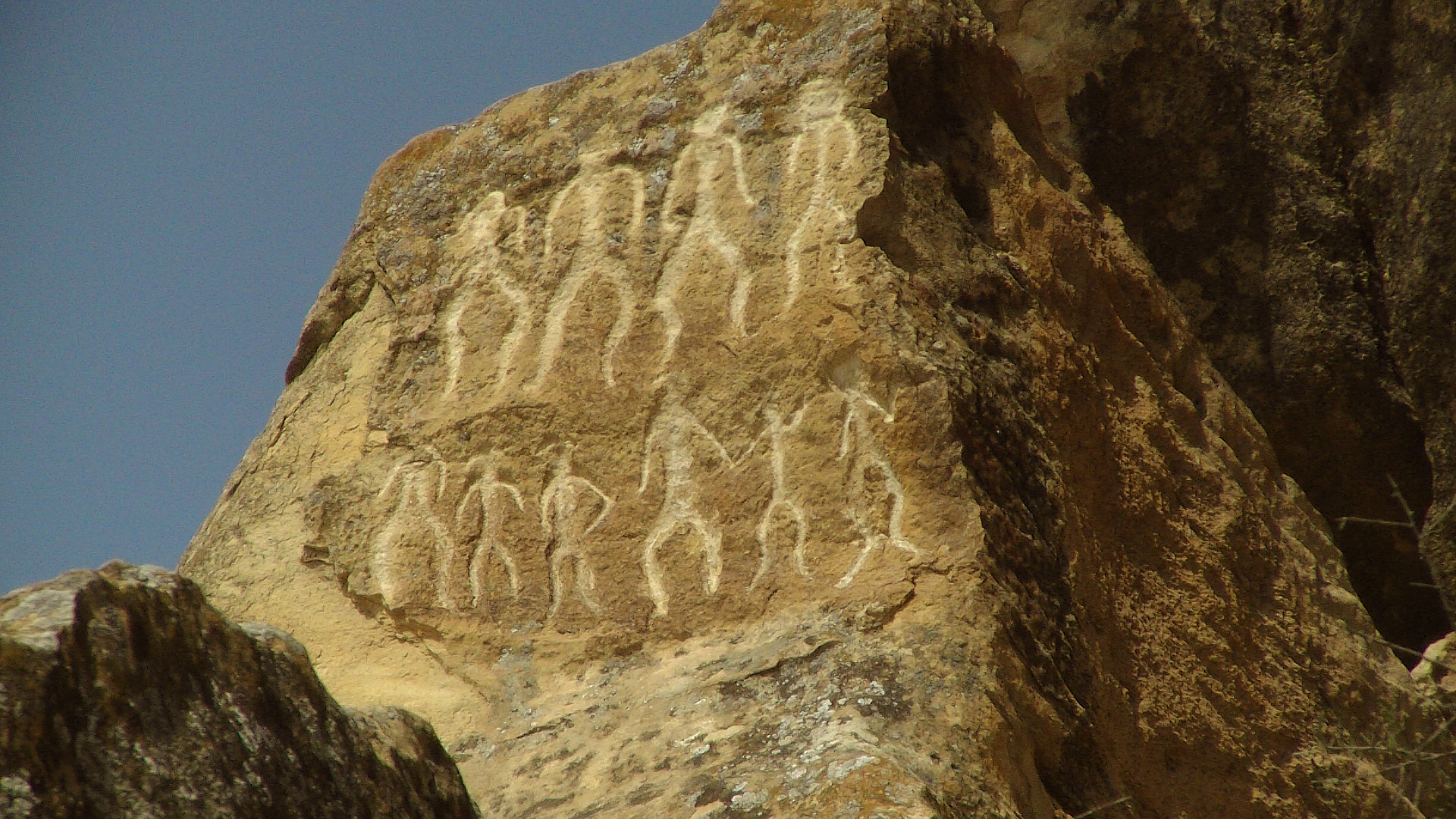 The earliest evidence of human settlement in the territory of Azerbaijan dates back to the late Stone Age and is related to the Guruchay culture of Azykh Cave.
Early settlements included the
The earliest evidence of human settlement in the territory of Azerbaijan dates back to the late Stone Age and is related to the Guruchay culture of Azykh Cave.
Early settlements included the
 After the
After the
''Russia at War: From the Mongol Conquest to Afghanistan, Chechnya, and Beyond''
pp. 728–729 ABC-CLIO, The area to the north of the river Aras, amongst which territory lies the contemporary Republic of Azerbaijan, was Iranian territory until Russia occupied it in the 19th century. About a decade later, in violation of the Gulistan treaty, the Russians invaded Iran's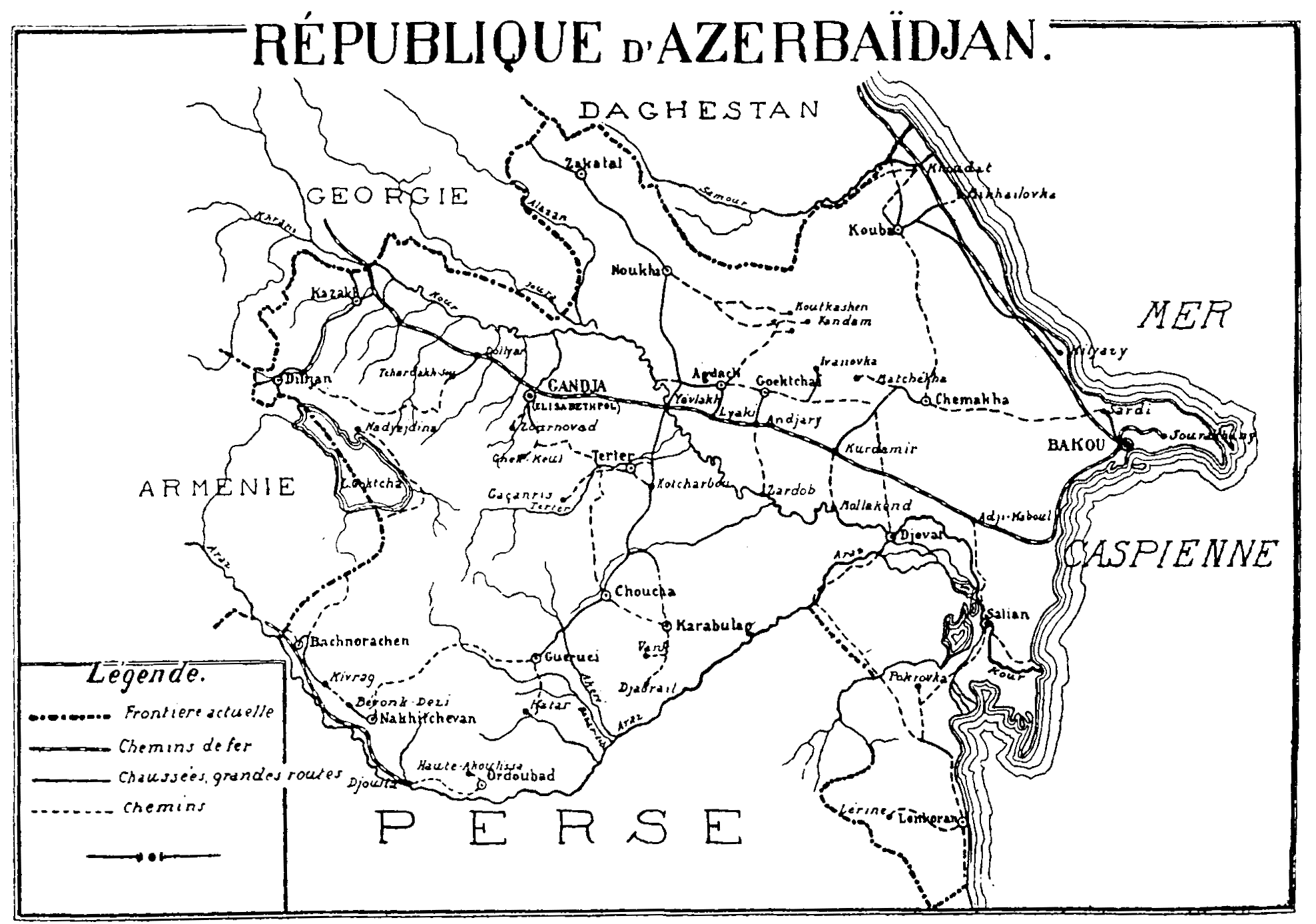 By March 1920, it was obvious that Soviet Russia would attack Baku.
By March 1920, it was obvious that Soviet Russia would attack Baku.
 Following the politics of ''
Following the politics of ''
 In 1993, democratically elected president
In 1993, democratically elected president
 Geographically, Azerbaijan is located in the
Geographically, Azerbaijan is located in the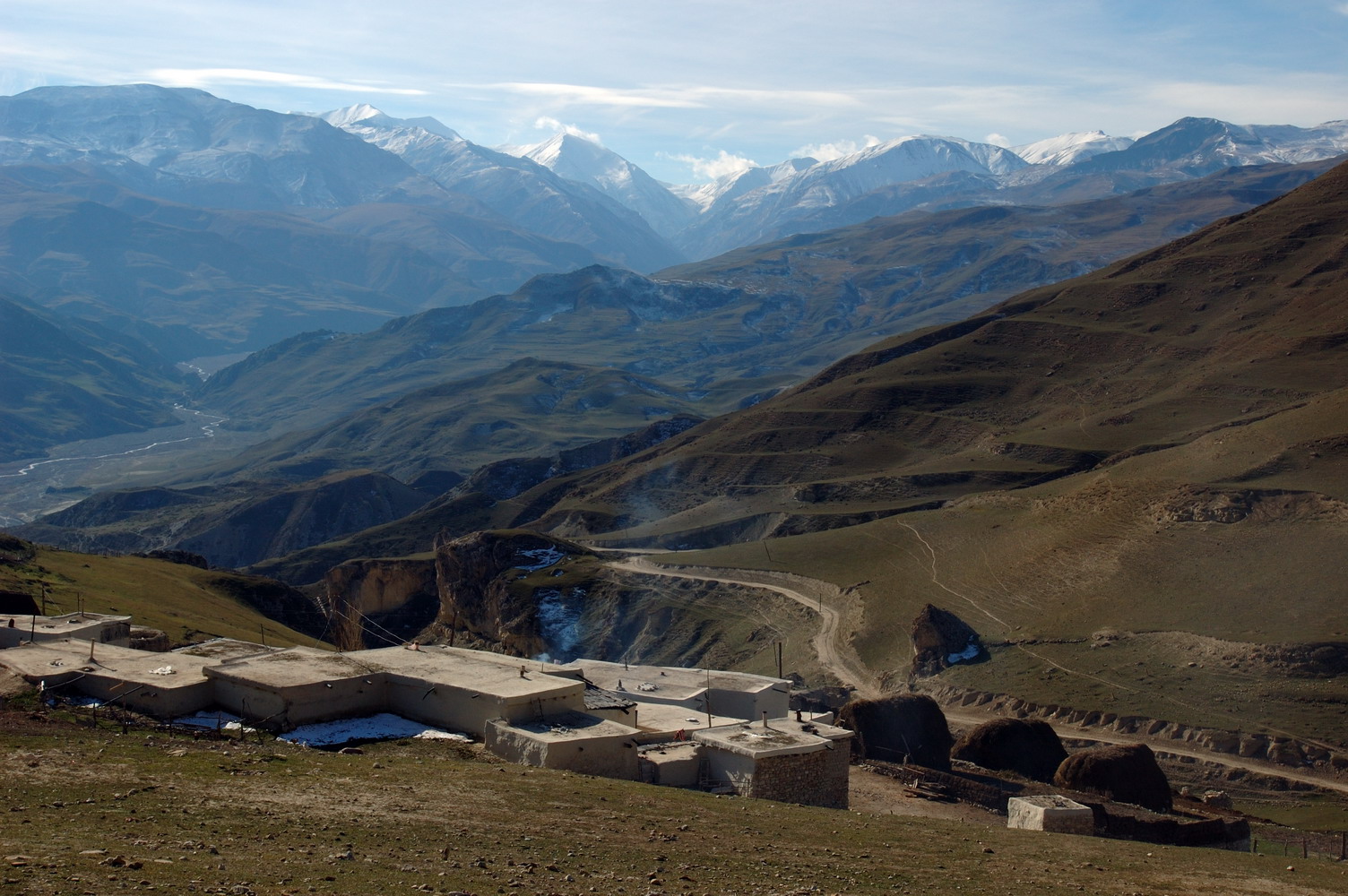  Three physical features dominate Azerbaijan: the Caspian Sea, whose shoreline forms a natural boundary to the east; the
Three physical features dominate Azerbaijan: the Caspian Sea, whose shoreline forms a natural boundary to the east; the
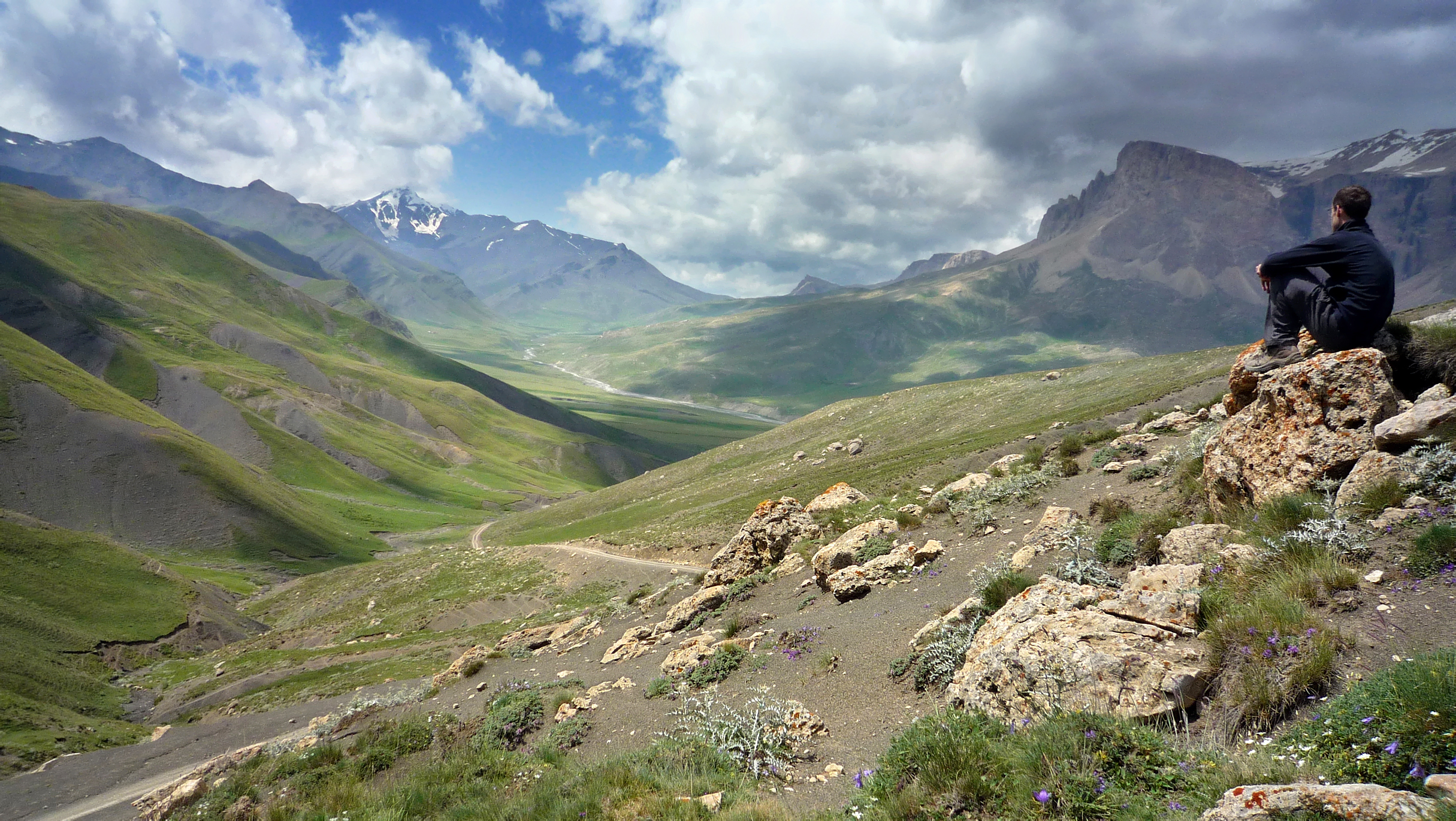
 Azerbaijan is home to a wide variety of landscapes. Over half of Azerbaijan's landmass consists of
Azerbaijan is home to a wide variety of landscapes. Over half of Azerbaijan's landmass consists of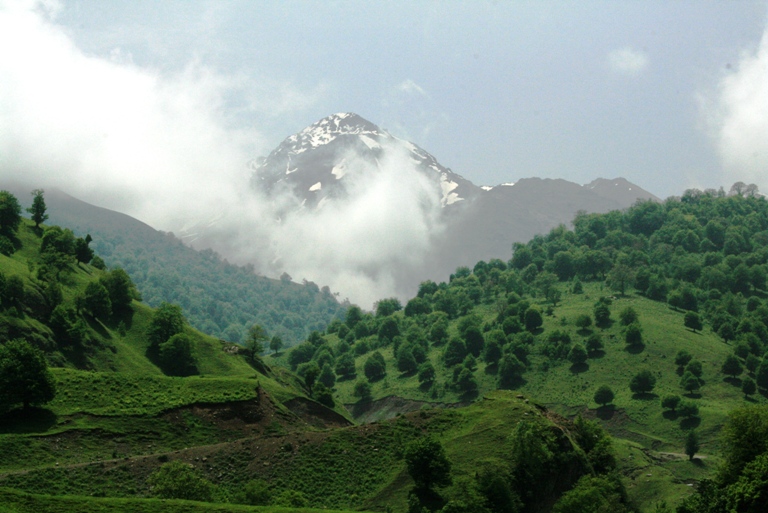  Rivers and lakes form the principal part of the water systems of Azerbaijan, they were formed over a long geological timeframe and changed significantly throughout that period. This is particularly evidenced by remnants of ancient rivers found throughout the country. The country's water systems are continually changing under the influence of natural forces and human-introduced industrial activities. Artificial rivers (canals) and ponds are a part of Azerbaijan's water systems. In terms of water supply, Azerbaijan is below the average in the world with approximately per year of water per square kilometer. All big water reservoirs are built on Kur. The hydrography of Azerbaijan basically belongs to the
Rivers and lakes form the principal part of the water systems of Azerbaijan, they were formed over a long geological timeframe and changed significantly throughout that period. This is particularly evidenced by remnants of ancient rivers found throughout the country. The country's water systems are continually changing under the influence of natural forces and human-introduced industrial activities. Artificial rivers (canals) and ponds are a part of Azerbaijan's water systems. In terms of water supply, Azerbaijan is below the average in the world with approximately per year of water per square kilometer. All big water reservoirs are built on Kur. The hydrography of Azerbaijan basically belongs to the
 The first reports on the richness and diversity of animal life in Azerbaijan can be found in travel notes of Eastern travelers. Animal carvings on architectural monuments, ancient rocks, and stones survived up to the present times. The first information on flora and fauna of Azerbaijan was collected during the visits of naturalists to Azerbaijan in the 17th century.
There are 106 species of mammals, 97 species of fish, 363 species of birds, 10 species of amphibians, and 52 species of reptiles which have been recorded and classified in Azerbaijan. The national animal of Azerbaijan is the Karabakh horse, a mountain-steppe racing and riding horse endemic to Azerbaijan. The Karabakh horse has a reputation for its good temper, speed, elegance, and intelligence. It is one of the oldest breeds, with ancestry dating to the ancient world, but today the horse is an endangered species.
Azerbaijan's flora consists of more than 4,500 species of higher plants. Due to the unique climate in Azerbaijan, the flora is much richer in the number of species than the flora of the other republics of the South Caucasus. 66 percent of the species growing in the whole
The first reports on the richness and diversity of animal life in Azerbaijan can be found in travel notes of Eastern travelers. Animal carvings on architectural monuments, ancient rocks, and stones survived up to the present times. The first information on flora and fauna of Azerbaijan was collected during the visits of naturalists to Azerbaijan in the 17th century.
There are 106 species of mammals, 97 species of fish, 363 species of birds, 10 species of amphibians, and 52 species of reptiles which have been recorded and classified in Azerbaijan. The national animal of Azerbaijan is the Karabakh horse, a mountain-steppe racing and riding horse endemic to Azerbaijan. The Karabakh horse has a reputation for its good temper, speed, elegance, and intelligence. It is one of the oldest breeds, with ancestry dating to the ancient world, but today the horse is an endangered species.
Azerbaijan's flora consists of more than 4,500 species of higher plants. Due to the unique climate in Azerbaijan, the flora is much richer in the number of species than the flora of the other republics of the South Caucasus. 66 percent of the species growing in the whole
 The executive power is held by the
The executive power is held by the
// Freedom Files Analytical Centre (Civic Solidarity Platform), March 2017
 The short-lived Azerbaijan Democratic Republic succeeded in establishing diplomatic relations with six countries, sending diplomatic representatives to Germany and Finland. The process of international recognition of Azerbaijan's independence from the collapsing Soviet Union lasted roughly one year. The most recent country to recognize Azerbaijan was Bahrain, on 6 November 1996. Full diplomatic relations, including mutual exchanges of missions, were first established with Turkey, Pakistan, the United States, Iran and Israel. Azerbaijan has placed a particular emphasis on its "
The short-lived Azerbaijan Democratic Republic succeeded in establishing diplomatic relations with six countries, sending diplomatic representatives to Germany and Finland. The process of international recognition of Azerbaijan's independence from the collapsing Soviet Union lasted roughly one year. The most recent country to recognize Azerbaijan was Bahrain, on 6 November 1996. Full diplomatic relations, including mutual exchanges of missions, were first established with Turkey, Pakistan, the United States, Iran and Israel. Azerbaijan has placed a particular emphasis on its " Foreign policy priorities of Azerbaijan include, first of all, the restoration of its territorial integrity; elimination of the consequences of occupation of Nagorno-Karabakh and seven other regions of Azerbaijan surrounding Nagorno-Karabakh; integration into European and Euro-Atlantic structure; contribution to international security; cooperation with international organizations; regional cooperation and bilateral relations; strengthening of defense capability; promotion of security by domestic policy means; strengthening of democracy; preservation of ethnic and religious tolerance; scientific, educational, and cultural policy and preservation of moral values; economic and social development; enhancing internal and border security; and migration, energy, and transportation security policy.
Azerbaijan is an active member of international coalitions fighting international terrorism. Azerbaijan was one of the first countries to offer support after the
Foreign policy priorities of Azerbaijan include, first of all, the restoration of its territorial integrity; elimination of the consequences of occupation of Nagorno-Karabakh and seven other regions of Azerbaijan surrounding Nagorno-Karabakh; integration into European and Euro-Atlantic structure; contribution to international security; cooperation with international organizations; regional cooperation and bilateral relations; strengthening of defense capability; promotion of security by domestic policy means; strengthening of democracy; preservation of ethnic and religious tolerance; scientific, educational, and cultural policy and preservation of moral values; economic and social development; enhancing internal and border security; and migration, energy, and transportation security policy.
Azerbaijan is an active member of international coalitions fighting international terrorism. Azerbaijan was one of the first countries to offer support after the
Azerbaijan: Is War Over Nagornyy Karabakh a Realistic Option? Advanced Research and Assessment Group. Caucasus Series 08/17. – Defense Academy of the United Kingdom, 2008, p. 12
The armed forces have three branches: the Land Forces, the Air Forces and the
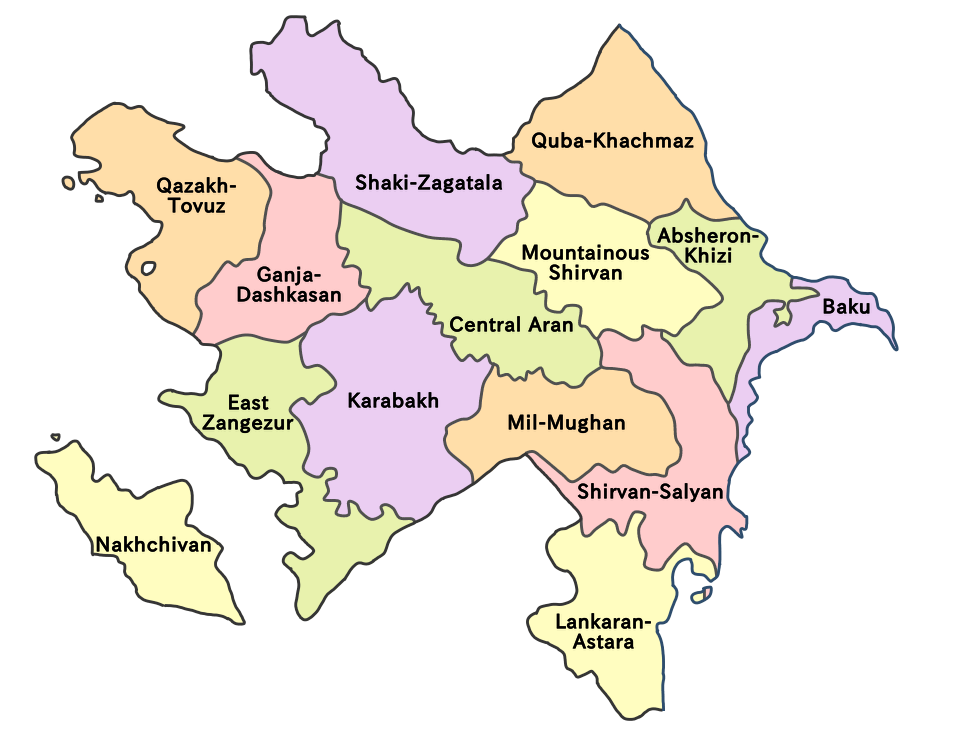 Azerbaijan is administratively divided into 14 economic regions; 66 rayons (, singular ) and 11 cities (, singular ) under the direct authority of the republic. Moreover, Azerbaijan includes the
Azerbaijan is administratively divided into 14 economic regions; 66 rayons (, singular ) and 11 cities (, singular ) under the direct authority of the republic. Moreover, Azerbaijan includes the
 After gaining independence in 1991, Azerbaijan became a member of the
After gaining independence in 1991, Azerbaijan became a member of the  In the early 2000s, chronically high inflation was brought under control. This led to the launch of a new currency, the new Azerbaijani manat, on 1 January 2006, to cement the economic reforms and erase the vestiges of an unstable economy.
Azerbaijan is also ranked 57th in the
In the early 2000s, chronically high inflation was brought under control. This led to the launch of a new currency, the new Azerbaijani manat, on 1 January 2006, to cement the economic reforms and erase the vestiges of an unstable economy.
Azerbaijan is also ranked 57th in the
 Two-thirds of Azerbaijan is rich in oil and natural gas.
The history of the oil industry of Azerbaijan dates back to the ancient period. Arabian historian and traveler Ahmad Al-Baladhuri discussed the economy of the Absheron peninsula in antiquity, mentioning its oil in particular. There are many pipelines in Azerbaijan. The goal of the Southern Gas Corridor, which connects the giant
Two-thirds of Azerbaijan is rich in oil and natural gas.
The history of the oil industry of Azerbaijan dates back to the ancient period. Arabian historian and traveler Ahmad Al-Baladhuri discussed the economy of the Absheron peninsula in antiquity, mentioning its oil in particular. There are many pipelines in Azerbaijan. The goal of the Southern Gas Corridor, which connects the giant  Access to biocapacity in Azerbaijan is less than world average. In 2016, Azerbaijan had 0.8 global hectares of biocapacity per person within its territory, half the world average of 1.6 global hectares per person. In 2016 Azerbaijan used 2.1 global hectares of biocapacity per person – their
Access to biocapacity in Azerbaijan is less than world average. In 2016, Azerbaijan had 0.8 global hectares of biocapacity per person within its territory, half the world average of 1.6 global hectares per person. In 2016 Azerbaijan used 2.1 global hectares of biocapacity per person – their
 Tourism is an important part of the economy of Azerbaijan. The country was a well-known tourist spot in the 1980s. The fall of the Soviet Union, and the First Nagorno-Karabakh War during the 1990s, damaged the tourist industry and the image of Azerbaijan as a tourist destination.
It was not until the 2000s that the tourism industry began to recover, and the country has since experienced a high rate of growth in the number of tourist visits and overnight stays. In the recent years, Azerbaijan has also become a popular destination for religious, spa, and
Tourism is an important part of the economy of Azerbaijan. The country was a well-known tourist spot in the 1980s. The fall of the Soviet Union, and the First Nagorno-Karabakh War during the 1990s, damaged the tourist industry and the image of Azerbaijan as a tourist destination.
It was not until the 2000s that the tourism industry began to recover, and the country has since experienced a high rate of growth in the number of tourist visits and overnight stays. In the recent years, Azerbaijan has also become a popular destination for religious, spa, and
 In the 21st century, a new oil and gas boom helped improve the situation in Azerbaijan's science and technology sectors. The government launched a campaign aimed at modernization and
In the 21st century, a new oil and gas boom helped improve the situation in Azerbaijan's science and technology sectors. The government launched a campaign aimed at modernization and
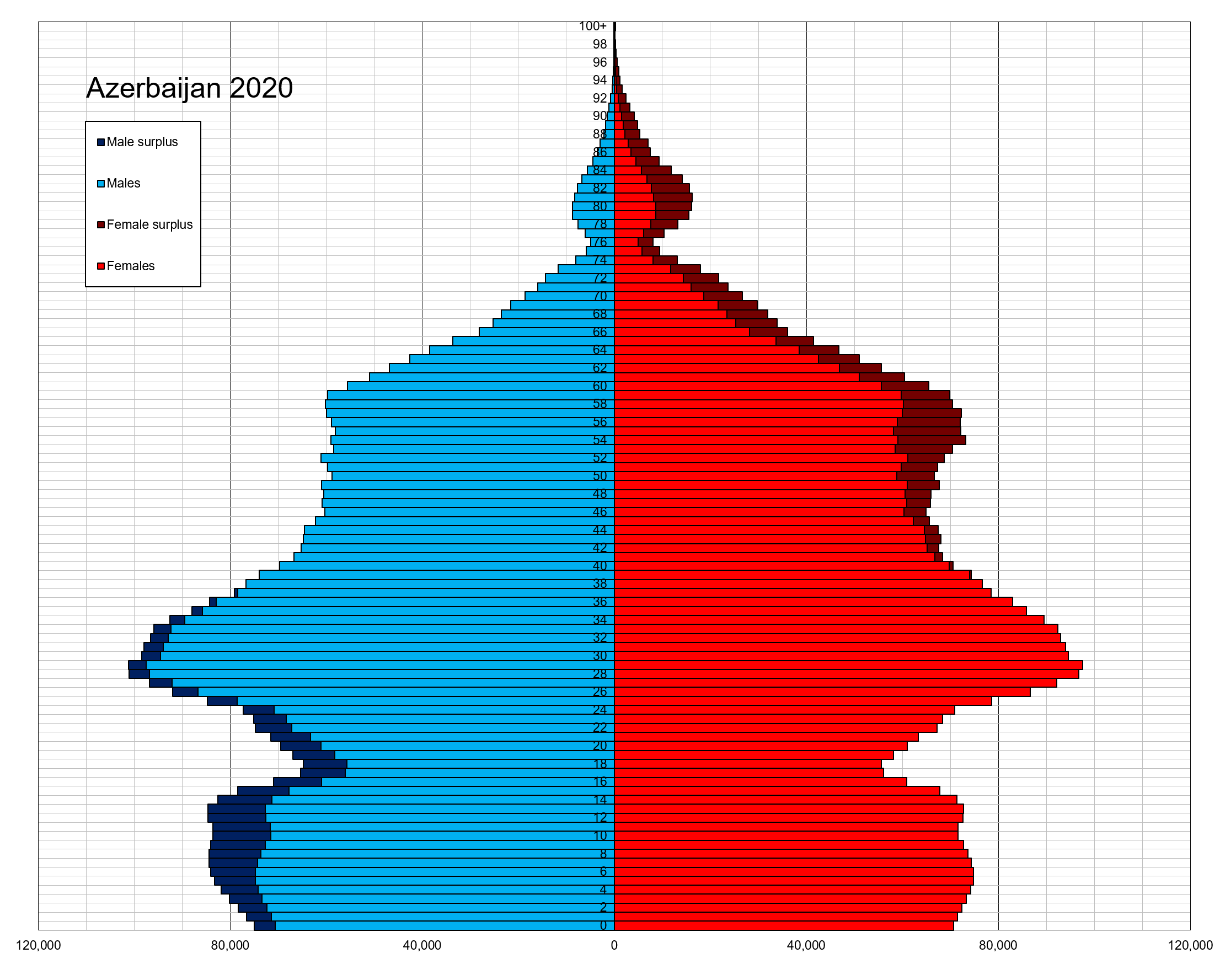 As of March 2022, 52.9% of Azerbaijan's total population of 10,164,464 is urban, with the remaining 47.1% being rural. In January 2019, the 50.1% of the total population was female. The
As of March 2022, 52.9% of Azerbaijan's total population of 10,164,464 is urban, with the remaining 47.1% being rural. In January 2019, the 50.1% of the total population was female. The
transcontinental
Transcontinental may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
* "Transcontinental", a song by the band Pedro the Lion from the album ''Achilles Heel''
* TC Transcontinental, a publishing, media and marketing company based in Canada, a subsidiary o ...
country located at the boundary of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is a part of the South Caucasus
The South Caucasus, also known as Transcaucasia or the Transcaucasus, is a geographical region on the border of Eastern Europe and Western Asia, straddling the southern Caucasus Mountains. The South Caucasus roughly corresponds to modern Arme ...
region and is bounded by the Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, often described as the List of lakes by area, world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia; east of the Caucasus, west of the broad s ...
to the east, Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eigh ...
(Republic of Dagestan
Dagestan ( ; rus, Дагеста́н, , dəɡʲɪˈstan, links=yes), officially the Republic of Dagestan (russian: Респу́блика Дагеста́н, Respúblika Dagestán, links=no), is a republic of Russia situated in the North C ...
) to the north, Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to t ...
to the northwest, Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ...
and Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a list of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolia, Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with ...
to the west, and Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkm ...
to the south. Baku is the capital and largest city.
The Azerbaijan Democratic Republic
The Azerbaijan Democratic Republic), or simply as Azerbaijan in Paris Peace Conference, 1919–1920,''Bulletin d'Information de l'Azerbaidjan'', No. I, September 1, 1919, pp. 6–7''125 H.C.Debs.'', 58., February 24, 1920, p. 1467. Caucasian Az ...
proclaimed its independence from the Transcaucasian Democratic Federative Republic in 1918 and became the first secular
Secularity, also the secular or secularness (from Latin ''saeculum'', "worldly" or "of a generation"), is the state of being unrelated or neutral in regards to religion. Anything that does not have an explicit reference to religion, either negativ ...
democratic Muslim-majority state. In 1920, the country was incorporated into the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
as the Azerbaijan SSR. The modern Republic of Azerbaijan proclaimed its independence on 30 August 1991, shortly before the dissolution of the Soviet Union in the same year. In September 1991, the ethnic Armenian
Armenian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Armenia, a country in the South Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Armenians, the national people of Armenia, or people of Armenian descent
** Armenian Diaspora, Armenian communities across the ...
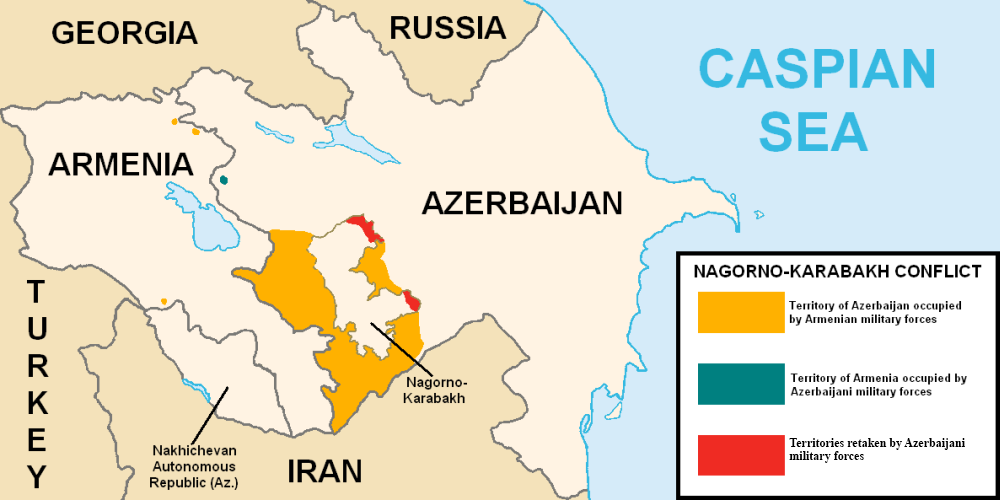
majority of the Nagorno-Karabakh
Nagorno-Karabakh ( ) is a landlocked region in the South Caucasus, within the mountainous range of Karabakh, lying between Lower Karabakh and Syunik, and covering the southeastern range of the Lesser Caucasus mountains. The region is mos ...
region formed the self-proclaimed Republic of Artsakh
Artsakh, officially the Republic of Artsakh () or the Nagorno-Karabakh Republic (),, is a breakaway state in the South Caucasus whose territory is internationally recognised as part of Azerbaijan. Artsakh controls a part of the former ...
. The region and seven surrounding districts are internationally recognized as part of Azerbaijan pending a solution to the status of the Nagorno-Karabakh through negotiations facilitated by the OSCE
The Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE) is the world's largest regional security-oriented intergovernmental organization with observer status at the United Nations. Its mandate includes issues such as arms control, prom ...
, although became ''de facto'' independent with the end of the First Nagorno-Karabakh War in 1994. Following the Second Nagorno-Karabakh War
The Second Nagorno-Karabakh War was an armed conflict in 2020 that took place in the disputed region of Nagorno-Karabakh and the surrounding territories. It was a major escalation of an unresolved conflict over the region, involving Azerba ...
in 2020, the seven districts and parts of Nagorno-Karabakh
Nagorno-Karabakh ( ) is a landlocked region in the South Caucasus, within the mountainous range of Karabakh, lying between Lower Karabakh and Syunik, and covering the southeastern range of the Lesser Caucasus mountains. The region is mos ...
were returned to Azerbaijani control.
Azerbaijan is a unitary semi-presidential
A semi-presidential republic, is a republic in which a president exists alongside a prime minister and a cabinet, with the latter two being responsible to the legislature of the state. It differs from a parliamentary republic in that it has ...
republic. It is one of six independent Turkic states and an active member of the Organization of Turkic States and the TÜRKSOY
The International Organization of Turkic Culture tr, Uluslararası Türk Kültürü Teşkilatı or TURKSOY is an international cultural organization of countries with Turkic populations, speaking languages belonging to the Turkic language fami ...
community. Azerbaijan has diplomatic relations with 182 countries and holds membership in 38 international organizations, including the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmonizi ...
, the Council of Europe, the Non-Aligned Movement
The Non-Aligned Movement (NAM) is a forum of 120 countries that are not formally aligned with or against any major power bloc. After the United Nations, it is the largest grouping of states worldwide.
The movement originated in the aftermath ...
, the OSCE
The Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE) is the world's largest regional security-oriented intergovernmental organization with observer status at the United Nations. Its mandate includes issues such as arms control, prom ...
, and the NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
PfP program. It is one of the founding members of GUAM
Guam (; ch, Guåhan ) is an organized, unincorporated territory of the United States in the Micronesia subregion of the western Pacific Ocean. It is the westernmost point and territory of the United States (reckoned from the geographic ce ...
, the CIS, and the OPCW
The Organisation for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons (OPCW) is an intergovernmental organisation and the implementing body for the Chemical Weapons Convention (CWC), which entered into force on 29 April 1997. The OPCW, with its 193 member ...
. Azerbaijan is also an observer state of the WTO.
The vast majority of the country's population (97%) is nominally Muslim, but the constitution
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organisation or other type of entity and commonly determine how that entity is to be governed.
When these princip ...
does not declare an official religion and all major political forces in the country are secularist
Secularism is the principle of seeking to conduct human affairs based on secular, naturalistic considerations.
Secularism is most commonly defined as the separation of religion from civil affairs and the state, and may be broadened to a si ...
. Azerbaijan is a developing country and ranks 88th on the Human Development Index
The Human Development Index (HDI) is a statistic composite index of life expectancy, Education Index, education (mean years of schooling completed and expected years of schooling upon entering the Educational system, education system), ...
. It has a high rate of economic development
In the economics study of the public sector, economic and social development is the process by which the economic well-being and quality of life of a nation, region, local community, or an individual are improved according to targeted goals a ...
, literacy
Literacy in its broadest sense describes "particular ways of thinking about and doing reading and writing" with the purpose of understanding or expressing thoughts or ideas in written form in some specific context of use. In other words, hum ...
, and a low rate of unemployment
Unemployment, according to the OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development), is people above a specified age (usually 15) not being in paid employment or self-employment but currently available for work during the refer ...
. However, the ruling New Azerbaijan Party
The New Azerbaijan Party ( az, Yeni Azərbaycan Partiyası, YAP) is the ruling political party in Azerbaijan, founded on 21 November 1992 under the leadership of Heydar Aliyev. After his election as President of Azerbaijan on 3 October 1993, ...
, in power since 1993, has been accused of authoritarian
Authoritarianism is a political system characterized by the rejection of political plurality, the use of strong central power to preserve the political ''status quo'', and reductions in the rule of law, separation of powers, and democratic votin ...
leadership under the leadership of both Heydar Aliyev
Heydar Alirza oghlu Aliyev ( az, Һејдәр Әлирза оғлу Әлијев, italic=no, Heydər Əlirza oğlu Əliyev, ; , ; 10 May 1923 – 12 December 2003) was a Soviet and Azerbaijani politician who served as the third president of Azer ...
and his son Ilham Aliyev
Ilham Heydar oghlu Aliyev ( az, İlham Heydər oğlu Əliyev, ; born 24 December 1961) is the fourth president of Azerbaijan, serving in the post since 31 October 2003.
The son and second child of the former Azerbaijani leader Heydar Aliyev ...
, and deteriorating the country's human rights record, including increasing restrictions on civil liberties, particularly on press freedom and political repression.
Etymology
According to a modern etymology, the term ''Azerbaijan'' derives from that of '' Atropates'', a Persiansatrap
A satrap () was a governor of the provinces of the ancient Median and Achaemenid Empires and in several of their successors, such as in the Sasanian Empire and the Hellenistic empires.
The satrap served as viceroy to the king, though with cons ...
under the Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was contemporarily the largest em ...
, who was later reinstated as the satrap of Media
Media may refer to:
Communication
* Media (communication), tools used to deliver information or data
** Advertising media, various media, content, buying and placement for advertising
** Broadcast media, communications delivered over mass el ...
under Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
.Nevertheless, "despite being one of the chief vassals of Sasanian ''Shahanshah
Shah (; fa, شاه, , ) is a royal title that was historically used by the leading figures of Iranian monarchies.Yarshater, EhsaPersia or Iran, Persian or Farsi, ''Iranian Studies'', vol. XXII no. 1 (1989) It was also used by a variety of ...
'', the Albanian king had only a semblance of authority, and the Sassanid marzban
Marzbān, or Marzpān (Middle Persian transliteration: mrzwpn, derived from ''marz'' "border, boundary" and the suffix ''-pān'' "guardian"; Modern Persian: ''Marzbān'') were a class of margraves, warden of the marches, and by extension milita ...
(military governor) held most civil, religious, and military authority. The original etymology of this name is thought to have its roots in the once-dominant Zoroastrianism
Zoroastrianism is an Iranian religion and one of the world's oldest organized faiths, based on the teachings of the Iranian-speaking prophet Zoroaster. It has a dualistic cosmology of good and evil within the framework of a monotheistic ont ...
. In the Avesta
The Avesta () is the primary collection of religious texts of Zoroastrianism, composed in the Avestan language.
The Avesta texts fall into several different categories, arranged either by dialect, or by usage. The principal text in the li ...
's ''Frawardin Yasht
The Yashts are a collection of twenty-one hymns in the Younger Avestan language. Each of these hymns invokes a specific Zoroastrian divinity or concept. ''Yasht'' chapter and verse pointers are traditionally abbreviated as ''Yt.''
Overview
The wo ...
'' ("Hymn to the Guardian Angels"), there is a mention of , which literally translates from Avestan
Avestan (), or historically Zend, is an umbrella term for two Old Iranian languages: Old Avestan (spoken in the 2nd millennium BCE) and Younger Avestan (spoken in the 1st millennium BCE). They are known only from their conjoined use as the scri ...
as "we worship the fravashi
Fravashi ( ae, 𐬟𐬭𐬀𐬎𐬎𐬀𐬴𐬌, translit=fravaṣ̌i, ) is the Avestan language term for the Zoroastrian concept of a personal spirit of an individual, whether dead, living, or yet-unborn. The ''fravashi'' of an individual sends o ...
of the holy Atropatene". The name "Atropates" itself is the Greek transliteration of an Old Iranian, probably Median, compounded name with the meaning "Protected by the (Holy) Fire" or "The Land of the (Holy) Fire". The Greek name was mentioned by Diodorus Siculus
Diodorus Siculus, or Diodorus of Sicily ( grc-gre, Διόδωρος ; 1st century BC), was an ancient Greek historian. He is known for writing the monumental universal history '' Bibliotheca historica'', in forty books, fifteen of which ...
and Strabo. Over the span of millennia, the name evolved to (Middle Persian
Middle Persian or Pahlavi, also known by its endonym Pārsīk or Pārsīg () in its later form, is a Western Middle Iranian language which became the literary language of the Sasanian Empire. For some time after the Sasanian collapse, Middle Per ...
), then to , , (New Persian) and present-day ''Azerbaijan''.
The name ''Azerbaijan'' was first adopted for the area of the present-day Republic of Azerbaijan by the government of Musavat in 1918, after the collapse of the Russian Empire, when the independent Azerbaijan Democratic Republic
The Azerbaijan Democratic Republic), or simply as Azerbaijan in Paris Peace Conference, 1919–1920,''Bulletin d'Information de l'Azerbaidjan'', No. I, September 1, 1919, pp. 6–7''125 H.C.Debs.'', 58., February 24, 1920, p. 1467. Caucasian Az ...
was established. Until then, the designation had been used exclusively to identify the adjacent region of contemporary northwestern Iran, while the area of the Azerbaijan Democratic Republic was formerly referred to as '' Arran'' and ''Shirvan
Shirvan (from fa, شروان, translit=Shirvān; az, Şirvan; Tat: ''Şirvan''), also spelled as Sharvān, Shirwan, Shervan, Sherwan and Šervān, is a historical Iranian region in the eastern Caucasus, known by this name in both pre-Islam ...
''. On that basis Iran protested the newly adopted country name.
During the Soviet rule, the country was also spelled in Latin from the Russian transliteration as ' ( rus, Азербайджа́н). The country's name was also spelled in Cyrillic script from 1940 to 1991 as '.
History
Antiquity
 The earliest evidence of human settlement in the territory of Azerbaijan dates back to the late Stone Age and is related to the Guruchay culture of Azykh Cave.
Early settlements included the
The earliest evidence of human settlement in the territory of Azerbaijan dates back to the late Stone Age and is related to the Guruchay culture of Azykh Cave.
Early settlements included the Scythia
Scythia ( Scythian: ; Old Persian: ; Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ) or Scythica (Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ), also known as Pontic Scythia, was a kingdom created by the Scythians during the 6th to 3rd centuries BC in the Pontic–Caspian steppe.
...
ns during the 9th century BC. Following the Scythians, Iranian Medes
The Medes (Old Persian: ; Akkadian: , ; Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ) were an ancient Iranian people who spoke the Median language and who inhabited an area known as Media between western and northern Iran. Around the 11th century BC, th ...
came to dominate the area to the south of the Aras river
, az, Araz, fa, ارس, tr, Aras
The Aras (also known as the Araks, Arax, Araxes, or Araz) is a river in the Caucasus. It rises in eastern Turkey and flows along the borders between Turkey and Armenia, between Turkey and the Nakhchivan excl ...
. The Medes forged a vast empire between 900 and 700 BC, which was integrated into the Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was contemporarily the largest em ...
around 550 BC. The area was conquered by the Achaemenids leading to the spread of Zoroastrianism
Zoroastrianism is an Iranian religion and one of the world's oldest organized faiths, based on the teachings of the Iranian-speaking prophet Zoroaster. It has a dualistic cosmology of good and evil within the framework of a monotheistic ont ...
.
From the Sasanid period to the Safavid period
The Sasanian Empire turnedCaucasian Albania
Caucasian Albania is a modern exonym for a former state located in ancient times in the Caucasus: mostly in what is now Azerbaijan (where both of its capitals were located). The modern endonyms for the area are ''Aghwank'' and ''Aluank'', amon ...
into a vassal state
A vassal state is any state that has a mutual obligation to a superior state or empire, in a status similar to that of a vassal in the feudal system in medieval Europe. Vassal states were common among the empires of the Near East, dating back ...
in 252, while King Urnayr officially adopted Christianity as the state religion in the 4th century. Despite Sassanid rule, Albania
Albania ( ; sq, Shqipëri or ), or , also or . officially the Republic of Albania ( sq, Republika e Shqipërisë), is a country in Southeastern Europe. It is located on the Adriatic
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the ...
remained an entity in the region until the 9th century, while fully subordinate to Sassanid Iran, and retained its monarchy. Despite being one of the chief vassals of the Sasanian emperor, the Albanian king had only a semblance of authority, and the Sasanian marzban
Marzbān, or Marzpān (Middle Persian transliteration: mrzwpn, derived from ''marz'' "border, boundary" and the suffix ''-pān'' "guardian"; Modern Persian: ''Marzbān'') were a class of margraves, warden of the marches, and by extension milita ...
(military governor) held most civil, religious, and military authority.
In the first half of the 7th century, Caucasian Albania
Caucasian Albania is a modern exonym for a former state located in ancient times in the Caucasus: mostly in what is now Azerbaijan (where both of its capitals were located). The modern endonyms for the area are ''Aghwank'' and ''Aluank'', amon ...
, as a vassal of the Sasanians, came under nominal Muslim rule due to the Muslim conquest of Persia
The Muslim conquest of Persia, also known as the Arab conquest of Iran, was carried out by the Rashidun Caliphate from 633 to 654 AD and led to the fall of the Sasanian Empire as well as the eventual decline of the Zoroastrian religion.
The ...
. The Umayyad Caliphate
The Umayyad Caliphate (661–750 CE; , ; ar, ٱلْخِلَافَة ٱلْأُمَوِيَّة, al-Khilāfah al-ʾUmawīyah) was the second of the four major caliphates established after the death of Muhammad. The caliphate was ruled by the ...
repulsed both the Sasanians and Byzantines from the South Caucasus
The South Caucasus, also known as Transcaucasia or the Transcaucasus, is a geographical region on the border of Eastern Europe and Western Asia, straddling the southern Caucasus Mountains. The South Caucasus roughly corresponds to modern Arme ...
and turned Caucasian Albania
Caucasian Albania is a modern exonym for a former state located in ancient times in the Caucasus: mostly in what is now Azerbaijan (where both of its capitals were located). The modern endonyms for the area are ''Aghwank'' and ''Aluank'', amon ...
into a vassal state after Christian resistance led by King Javanshir
Javanshir (alternate spellings: Javansher, Juansher, Ĵovenšēr, Jivanshir; '' pal, Juvānšēr''; literally "young lion"), was the prince of Caucasian Albania from 637 to 680, hailing from the region of Gardman. His life and deeds were the subj ...
was suppressed in 667. The power vacuum left by the decline of the Abbasid Caliphate
The Abbasid Caliphate ( or ; ar, الْخِلَافَةُ الْعَبَّاسِيَّة, ') was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Mutta ...
was filled by numerous local dynasties such as the Sallarids
The Sallarid dynasty ( fa, سالاریان), (also known as the Musafirids or Langarids) was a Muslim dynasty, of Daylami origin, which ruled in Tarom, Samiran, Daylam, Gilan and subsequently Azerbaijan, Arran, and some districts in Eastern Arm ...
, Sajids, and Shaddadids
The Shaddadids were a Kurdish Sunni Muslim dynasty. who ruled in various parts of Armenia and Arran from 951 to 1199 AD. They were established in Dvin. Through their long tenure in Armenia, they often intermarried with the Bagratuni royal famil ...
. At the beginning of the 11th century, the territory was gradually seized by the waves of Oghuz Turks
The Oghuz or Ghuzz Turks (Middle Turkic: ٱغُز, ''Oγuz'', ota, اوغوز, Oġuz) were a western Turkic people that spoke the Oghuz branch of the Turkic language family. In the 8th century, they formed a tribal confederation conven ...
from Central Asia, who adopted a Turkoman ethnonym at the time. The first of these Turkic dynasties established was the Seljuk Empire
The Great Seljuk Empire, or the Seljuk Empire was a high medieval, culturally Turko-Persian, Sunni Muslim empire, founded and ruled by the Qïnïq branch of Oghuz Turks. It spanned a total area of from Anatolia and the Levant in the west to ...
, which entered the area now known as Azerbaijan by 1067.
The pre-Turkic population that lived on the territory of modern Azerbaijan spoke several Indo-European
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, ...
and Caucasian languages, among them Armenian
Armenian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Armenia, a country in the South Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Armenians, the national people of Armenia, or people of Armenian descent
** Armenian Diaspora, Armenian communities across the ...
Моисей Хоренский. Армянская География VII в. Перевод Патканова К.П. СПб., 1877. стр. 40,17 and an Iranian language
The Iranian languages or Iranic languages are a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages in the Indo-European language family that are spoken natively by the Iranian peoples, predominantly in the Iranian Plateau.
The Iranian languages are grouped ...
, Old Azeri, which was gradually replaced by a Turkic language
The Turkic languages are a language family of over 35 documented languages, spoken by the Turkic peoples of Eurasia from Eastern Europe and Southern Europe to Central Asia, East Asia, North Asia (Siberia), and Western Asia. The Turkic languag ...
, the early precursor of the Azerbaijani language
Azerbaijani () or Azeri (), also referred to as Azeri Turkic or Azeri Turkish, is a Turkic language from the Oghuz sub-branch spoken primarily by the Azerbaijani people, who live mainly in the Republic of Azerbaijan where the North Azerbaij ...
of today. Some linguists have also stated that the Tati dialects of Iranian Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan or Azarbaijan ( fa, آذربایجان, ''Āzarbāijān'' ; az-Arab, آذربایجان, ''Āzerbāyjān'' ), also known as Iranian Azerbaijan, is a historical region in northwestern Iran that borders Iraq, Turkey, the Nakhchivan ...
and the Republic of Azerbaijan, like those spoken by the Tats, are descended from Old Azeri.
Locally, the possessions of the subsequent Seljuk Empire were ruled by Eldiguzids
The Ildegizids, EldiguzidsC.E. Bosworth, "Ildenizids or Eldiguzids", Encyclopaedia of Islam, Edited by P.J. Bearman, Th. Bianquis, C.E. Bosworth, E. van Donzel and W.P. Heinrichs et al., Encyclopædia of Islam, 2nd Edition., 12 vols. with index ...
, technically vassals of the Seljuk sultans, but sometimes ''de facto'' rulers themselves. Under the Seljuks, local poets such as Nizami Ganjavi
Nizami Ganjavi ( fa, نظامی گنجوی, lit=Niẓāmī of Ganja, Azerbaijan, Ganja, translit=Niẓāmī Ganjavī; c. 1141–1209), Nizami Ganje'i, Nizami, or Nezāmi, whose formal name was ''Jamal ad-Dīn Abū Muḥammad Ilyās ibn-Yūsuf ...
and Khaqani
Afzal al-Dīn Badīl ibn ʿAlī ibn ʿOthmān, commonly known as Khāqānī ( fa, خاقانی, , – 1199), was a major Persian poet and prose-writer. He was born in Transcaucasia in the historical region known as Shirvan, where he served a ...
gave rise to a blossoming of Persian literature
Persian literature ( fa, ادبیات فارسی, Adabiyâte fârsi, ) comprises oral compositions and written texts in the Persian language and is one of the world's oldest literatures. It spans over two-and-a-half millennia. Its sources h ...
on the territory of present-day Azerbaijan.
The local dynasty of the Shirvanshah
''Shirvanshah'' ( fa, شروانشاه), also spelled as ''Shīrwān Shāh'' or ''Sharwān Shāh'', was the title of the rulers of Shirvan from the mid-9th century to the early 16th century. The title remained in a single family, the Yazidids, ...
s became a vassal
A vassal or liege subject is a person regarded as having a mutual obligation to a lord or monarch, in the context of the feudal system in medieval Europe. While the subordinate party is called a vassal, the dominant party is called a suzerain. ...
state of Timur's empire and assisted him in his war with the ruler of the Golden Horde
The Golden Horde, self-designated as Ulug Ulus, 'Great State' in Turkic, was originally a Mongol and later Turkicized khanate established in the 13th century and originating as the northwestern sector of the Mongol Empire. With the fragment ...
Tokhtamysh
Tokhtamysh ( kz, Тоқтамыс, tt-Cyrl, Тухтамыш, translit=Tuqtamış, fa, توقتمش),The spelling of Tokhtamysh varies, but the most common spelling is Tokhtamysh. Tokhtamısh, Toqtamysh, ''Toqtamış'', ''Toqtamıs'', ''Toktamy ...
. Following Timur's death, two independent and rival states emerged: Qara Qoyunlu
The Qara Qoyunlu or Kara Koyunlu ( az, Qaraqoyunlular , fa, قره قویونلو), also known as the Black Sheep Turkomans, were a culturally Persianate, Muslim Turkoman "Kara Koyunlu, also spelled Qara Qoyunlu, Turkish Karakoyunlular, En ...
and Aq Qoyunlu
The Aq Qoyunlu ( az, Ağqoyunlular , ) was a culturally Persianate,Kaushik Roy, ''Military Transition in Early Modern Asia, 1400–1750'', (Bloomsbury, 2014), 38; "Post-Mongol Persia and Iraq were ruled by two tribal confederations: Akkoyunlu (W ...
. The Shirvanshahs returned, maintaining for numerous centuries to come a high degree of autonomy as local rulers and vassals as they had done since 861. In 1501, the Safavid dynasty of Iran subdued the Shirvanshahs and gained its possessions. In the course of the next century, the Safavids converted the formerly Sunni population to Shia Islam, as they did with the population in what is modern-day Iran. The Safavids allowed the Shirvanshahs to remain in power, under Safavid suzerainty, until 1538, when Safavid king Tahmasp I
Tahmasp I ( fa, طهماسب, translit=Ṭahmāsb or ; 22 February 1514 – 14 May 1576) was the second shah of Safavid Iran from 1524 to 1576. He was the eldest son of Ismail I and his principal consort, Tajlu Khanum. Ascending the throne after t ...
(r. 1524–1576) completely deposed them, and made the area into the Safavid province of Shirvan
Shirvan (from fa, شروان, translit=Shirvān; az, Şirvan; Tat: ''Şirvan''), also spelled as Sharvān, Shirwan, Shervan, Sherwan and Šervān, is a historical Iranian region in the eastern Caucasus, known by this name in both pre-Islam ...
. The Sunni Ottomans briefly managed to occupy parts of present-day Azerbaijan as a result of the Ottoman–Safavid War of 1578–1590; by the early 17th century, they were ousted by Safavid Iranian ruler Abbas I (r. 1588–1629). In the wake of the demise of the Safavid Empire, Baku and its environs were briefly occupied by the Russians as a consequence of the Russo-Persian War of 1722–1723. Despite brief intermissions such as these by Safavid Iran's neighboring rivals, the land of what is today Azerbaijan remained under Iranian rule from the earliest advent of the Safavids up to the course of the 19th century.
Contemporary history
 After the
After the Safavid
Safavid Iran or Safavid Persia (), also referred to as the Safavid Empire, '. was one of the greatest Iranian empires after the 7th-century Muslim conquest of Persia, which was ruled from 1501 to 1736 by the Safavid dynasty. It is often consid ...
s, the area was ruled by the Iranian Afsharid dynasty
The Afsharid dynasty ( fa, افشاریان) was an Iranian dynasty founded by Nader Shah () of the Qirqlu clan of the Turkoman Afshar tribe
Afshar ( az, Əfşar افشار; tr, Avşar, ''Afşar''; tk, Owşar; fa, اَفشار, Āfshār) i ...
. After the death of Nader Shah
Nader Shah Afshar ( fa, نادر شاه افشار; also known as ''Nader Qoli Beyg'' or ''Tahmāsp Qoli Khan'' ) (August 1688 – 19 June 1747) was the founder of the Afsharid dynasty of Iran and one of the most powerful rulers in Iranian ...
(r. 1736–1747), many of his former subjects capitalized on the eruption of instability. Numerous self-ruling khanate
A khaganate or khanate was a polity ruled by a khan, khagan, khatun, or khanum. That political territory was typically found on the Eurasian Steppe and could be equivalent in status to tribal chiefdom, principality, kingdom or empire.
...
s with various forms of autonomy emerged in the area. The rulers of these khanates were directly related to the ruling dynasties of Iran and were vassals
A vassal or liege subject is a person regarded as having a mutual obligation to a lord or monarch, in the context of the feudal system in medieval Europe. While the subordinate party is called a vassal, the dominant party is called a suzerain. ...
and subjects of the Iranian shah. The khanates exercised control over their affairs via international trade routes between Central Asia and the West.
Thereafter, the area was under the successive rule of the Iranian Zands and Qajars. From the late 18th century, Imperial Russia switched to a more aggressive geo-political stance towards its two neighbors and rivals to the south, namely Iran and the Ottoman Empire. Russia now actively tried to gain possession of the Caucasus region which was, for the most part, in the hands of Iran.
In 1804, the Russians invaded and sacked the Iranian town of Ganja, sparking the Russo-Persian War of 1804–1813. The militarily superior Russians ended the Russo-Persian War of 1804–1813 with a victory.
Following Qajar Iran's loss in the 1804–1813 war, it was forced to concede suzerainty over most of the khanates, along with Georgia and Dagestan to the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the List of Russian monarchs, Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended th ...
, per the Treaty of Gulistan
The Treaty of Gulistan (russian: Гюлистанский договор; fa, عهدنامه گلستان) was a peace treaty concluded between the Russian Empire and Iran on 24 October 1813 in the village of Gulistan (now in the Goranboy Distr ...
.Timothy C. Dowling (2014)''Russia at War: From the Mongol Conquest to Afghanistan, Chechnya, and Beyond''
pp. 728–729 ABC-CLIO, The area to the north of the river Aras, amongst which territory lies the contemporary Republic of Azerbaijan, was Iranian territory until Russia occupied it in the 19th century. About a decade later, in violation of the Gulistan treaty, the Russians invaded Iran's
Erivan Khanate
The Erivan Khanate ( fa, خانات ایروان, translit=Xānāt-e Iravān; hy, Երեւանի խանութիւն, translit=Yerevani xanut'iwn; az, ایروان خانلیغی, translit=İrəvan xanlığı), also known as Chokhur-e Sa'd, was ...
. This sparked the final bout of hostilities between the two, the Russo-Persian War of 1826–1828. The resulting Treaty of Turkmenchay
The Treaty of Turkmenchay ( fa, عهدنامه ترکمنچای; russian: Туркманчайский договор) was an agreement between Qajar Iran and the Russian Empire, which concluded the Russo-Persian War (1826–28). It was second o ...
, forced Qajar Iran
Qajar Iran (), also referred to as Qajar Persia, the Qajar Empire, '. Sublime State of Persia, officially the Sublime State of Iran ( fa, دولت علیّه ایران ') and also known then as the Guarded Domains of Iran ( fa, ممالک م� ...
to cede sovereignty over the Erivan Khanate, the Nakhchivan Khanate
The Nakhichevan Khanate ( fa, خانات نخجوان, translit=Khānāt-e Nakhchevān; Azerbaijani:ناخچیوان خانلیغی,Naxçıvan xanlığı; hy, Նախիջեւանի խանութիւն, translit=Naxijewani xanowt'iwn) was a khanate ...
and the remainder of the Talysh Khanate, comprising the last parts of the soil of the contemporary Azerbaijani Republic that were still in Iranian hands. After the incorporation of all Caucasian territories from Iran into Russia, the new border between the two was set at the Aras River
, az, Araz, fa, ارس, tr, Aras
The Aras (also known as the Araks, Arax, Araxes, or Araz) is a river in the Caucasus. It rises in eastern Turkey and flows along the borders between Turkey and Armenia, between Turkey and the Nakhchivan excl ...
, which, upon the Soviet Union's disintegration, subsequently became part of the border between Iran and the Azerbaijan Republic.
Qajar Iran was forced to cede its Caucasian territories to Russia in the 19th century, which thus included the territory of the modern-day Azerbaijan Republic, while as a result of that cession, the Azerbaijani ethnic group is nowadays parted between two nations: Iran and Azerbaijan.
Despite the Russian conquest, throughout the entire 19th century, preoccupation with Iranian culture
The culture of Iran () or culture of PersiaYarshater, Ehsa, ''Iranian Studies'', vol. XXII no. 1 (1989) is among the most influential in the world. Iran, also known as Persia, is widely considered to be one of the cradles of civilization. Due ...
, literature
Literature is any collection of written work, but it is also used more narrowly for writings specifically considered to be an art form, especially prose fiction, drama, and poetry. In recent centuries, the definition has expanded to inclu ...
, and language remained widespread amongst Shia and Sunni intellectuals in the Russian-held cities of Baku, Ganja
Ganja (, ; ) is one of the oldest and most commonly used synonyms for marijuana. Its usage in English dates to before 1689.
Etymology
''Ganja'' is borrowed from Hindi/Urdu ( hi, गांजा, links=no, ur, , links=no, IPA: �aːɲd͡� ...
and Tiflis (Tbilisi
Tbilisi ( ; ka, თბილისი ), in some languages still known by its pre-1936 name Tiflis ( ), is the capital and the largest city of Georgia, lying on the banks of the Kura River with a population of approximately 1.5 million p ...
, now Georgia). Within the same century, in post-Iranian Russian-held East Caucasia, an Azerbaijani national identity emerged at the end of the 19th century.
After the collapse of the Russian Empire during World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
, the short-lived Transcaucasian Democratic Federative Republic was declared, constituting the present-day republics of Azerbaijan, Georgia, and Armenia.
It was followed by the March Days massacres that took place between 30 March and 2 April 1918 in the city of Baku and adjacent areas of the Baku Governorate
The Baku Governorate, known before 1859 as the Shemakha Governorate, was a province ('' guberniya'') of the Caucasus Viceroyalty of the Russian Empire, with its center in the booming metropolis and Caspian Sea port of Baku. Area (1897): 34,400 ...
of the Russian Empire. When the republic dissolved in May 1918, the leading Musavat party declared independence as the Azerbaijan Democratic Republic
The Azerbaijan Democratic Republic), or simply as Azerbaijan in Paris Peace Conference, 1919–1920,''Bulletin d'Information de l'Azerbaidjan'', No. I, September 1, 1919, pp. 6–7''125 H.C.Debs.'', 58., February 24, 1920, p. 1467. Caucasian Az ...
(ADR), adopting the name of "Azerbaijan" for the new republic; a name that prior to the proclamation of the ADR was solely used to refer to the adjacent northwestern region of contemporary Iran. The ADR was the first modern parliamentary republic
A parliamentary republic is a republic that operates under a parliamentary system of government where the executive branch (the government) derives its legitimacy from and is accountable to the legislature (the parliament). There are a number ...
in the Muslim world. Among the important accomplishments of the Parliament was the extension of suffrage to women, making Azerbaijan the first Muslim nation to grant women equal political rights with men. Another important accomplishment of ADR was the establishment of Baku State University
Baku State University (BSU) ( az, Bakı Dövlət Universiteti (BDU)) is a public university located in Baku, Azerbaijan. Established in 1919 by the Parliament of Azerbaijan Democratic Republic, the university started with faculties of history an ...
, which was the first modern-type university founded in the Muslim East.
 By March 1920, it was obvious that Soviet Russia would attack Baku.
By March 1920, it was obvious that Soviet Russia would attack Baku. Vladimir Lenin
Vladimir Ilyich Ulyanov. ( 1870 – 21 January 1924), better known as Vladimir Lenin,. was a Russian revolutionary, politician, and political theorist. He served as the first and founding head of government of Soviet Russia from 1917 to 1 ...
said that the invasion was justified as Soviet Russia
The Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, Russian SFSR or RSFSR ( rus, Российская Советская Федеративная Социалистическая Республика, Rossíyskaya Sovétskaya Federatívnaya Soci ...
could not survive without Baku's oil
An oil is any nonpolar chemical substance that is composed primarily of hydrocarbons and is hydrophobic (does not mix with water) & lipophilic (mixes with other oils). Oils are usually flammable and surface active. Most oils are unsaturate ...
. Independent Azerbaijan lasted only 23 months until the Bolshevik
The Bolsheviks (russian: Большевики́, from большинство́ ''bol'shinstvó'', 'majority'),; derived from ''bol'shinstvó'' (большинство́), "majority", literally meaning "one of the majority". also known in English ...
11th Soviet Red Army
The 11th Army was a field army of the Red Army during the Russian Civil War, which fought on the Caspian-Caucasian Front. It took a prominent part in the sovietization of the three republics of the southern Caucasus in 1920–21, when Azerbaijan, ...
invaded it, establishing the Azerbaijan SSR on 28 April 1920. Although the bulk of the newly formed Azerbaijani army was engaged in putting down an Armenian revolt that had just broken out in Karabakh
Karabakh ( az, Qarabağ ; hy, Ղարաբաղ, Ġarabaġ ) is a geographic region in present-day southwestern Azerbaijan and eastern Armenia, extending from the highlands of the Lesser Caucasus down to the lowlands between the rivers Kura and A ...
, Azerbaijanis did not surrender their brief independence of 1918–20 quickly or easily. As many as 20,000 Azerbaijani soldiers died resisting what was effectively a Russian reconquest. Within the ensuing early Soviet period, the Azerbaijani national identity was finally forged.
On 13 October 1921, the Soviet republics of Russia, Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Georgia signed an agreement with Turkey known as the Treaty of Kars
The Treaty of Kars ( tr, Kars Antlaşması, rus, Карсский договор, Karskii dogovor, ka, ყარსის ხელშეკრულება, hy, Կարսի պայմանագիր, az, Qars müqaviləsi) was a treaty that est ...
. The previously independent Republic of Aras
The Republic of Aras ( az, Araz Respublikası; also known as the Republic of Araks or the Araxi Republic) was a short-lived and unrecognized state in the South Caucasus, roughly corresponding with the territory that is now the Nakhchivan Autonomous ...
would also become the Nakhchivan Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic
The Nakhichevan Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic, abbreviated as Nakhichevan ASSR was an autonomous republic within the Azerbaijan SSR, itself a republic within the Soviet Union. It was formed on 16 March 1921 and became a part of the Aze ...
within the Azerbaijan SSR by the treaty of Kars. On the other hand, Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ...
was awarded the region of Zangezur
Zangezur ( hy, Զանգեզուր) is a historical and geographical region in Eastern Armenia on the slopes of the Zangezur Mountains which largely corresponds to the Syunik Province of the Republic of Armenia. It was ceded to Russia by Qajar Ir ...
and Turkey agreed to return Gyumri
Gyumri ( hy, Գյումրի, ) is an urban municipal community and the second-largest city in Armenia, serving as the administrative center of Shirak Province in the northwestern part of the country. By the end of the 19th century, when the city w ...
(then known as Alexandropol).
During World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, Azerbaijan played a crucial role in the strategic energy policy of the Soviet Union, with 80 percent of the Soviet Union's oil on the Eastern Front being supplied by Baku. By the Decree of the Supreme Soviet of the USSR
The Supreme Soviet of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics ( rus, Верховный Совет Союза Советских Социалистических Республик, r=Verkhovnyy Sovet Soyuza Sovetskikh Sotsialisticheskikh Respubl ...
in February 1942, the commitment of more than 500 workers and employees of the oil industry
The petroleum industry, also known as the oil industry or the oil patch, includes the global processes of exploration, extraction, refining, transportation (often by oil tankers and pipelines), and marketing of petroleum products. The larg ...
of Azerbaijan were awarded orders and medals. Operation Edelweiss carried out by the German Wehrmacht
The ''Wehrmacht'' (, ) were the unified armed forces of Nazi Germany from 1935 to 1945. It consisted of the ''Heer'' (army), the ''Kriegsmarine'' (navy) and the ''Luftwaffe'' (air force). The designation "''Wehrmacht''" replaced the previou ...
targeted Baku because of its importance as the energy (petroleum) dynamo of the USSR. A fifth of all Azerbaijanis fought in the Second World War from 1941 to 1945. Approximately 681,000 people with over 100,000 of them women, went to the front, while the total population of Azerbaijan was 3.4 million at the time. Some 250,000 people from Azerbaijan were killed on the front. More than 130 Azerbaijanis were named Heroes of the Soviet Union
The title Hero of the Soviet Union (russian: Герой Советского Союза, translit=Geroy Sovietskogo Soyuza) was the highest distinction in the Soviet Union, awarded together with the Order of Lenin personally or collectively for ...
. Azerbaijani Major-General Azi Aslanov
Hazi Aslanov ( az, Həzi Əhəd oğlu Aslanov; russian: Ази Агад оглы Асланов; commonly described as Azi Aslanov and A. A. Aslanov,Aleksander A. Maslov, David M. Glantz, ''Fallen Soviet Generals: Soviet General Officers Killed i ...
was twice awarded the Hero of the Soviet Union.
Independence
 Following the politics of ''
Following the politics of ''glasnost
''Glasnost'' (; russian: link=no, гласность, ) has several general and specific meanings – a policy of maximum openness in the activities of state institutions and freedom of information, the inadmissibility of hushing up problems, ...
'', initiated by Mikhail Gorbachev, civil unrest and ethnic strife grew in various regions of the Soviet Union, including Nagorno-Karabakh
Nagorno-Karabakh ( ) is a landlocked region in the South Caucasus, within the mountainous range of Karabakh, lying between Lower Karabakh and Syunik, and covering the southeastern range of the Lesser Caucasus mountains. The region is mos ...
, an autonomous region of the Azerbaijan SSR. The disturbances in Azerbaijan, in response to Moscow's indifference to an already heated conflict, resulted in calls for independence and secession, which culminated in the Black January
Black January ( az, Qara Yanvar), also known as Black Saturday or the January Massacre, was a violent crackdown on the civilian population of Baku on 19–20 January 1990, as part of a state of emergency during the dissolution of the Soviet Unio ...
events in Baku. Later in 1990, the Supreme Council of the Azerbaijan SSR dropped the words "Soviet Socialist" from the title, adopted the "Declaration of Sovereignty of the Azerbaijan Republic" and restored the flag of the Azerbaijan Democratic Republic as the state flag. As a consequence of the failed 1991 Soviet coup d'état attempt in Moscow, the Supreme Council of Azerbaijan adopted a Declaration of Independence on 18 October 1991, which was affirmed by a nationwide referendum in December 1991, while the Soviet Union officially ceased to exist on 26 December 1991. The country now celebrates its Independence Day
An independence day is an annual event commemorating the anniversary of a nation's independence or statehood, usually after ceasing to be a group or part of another nation or state, or more rarely after the end of a military occupation. Man ...
on 18 October.
The early years of independence were overshadowed by the First Nagorno-Karabakh war with the ethnic Armenian majority of Nagorno-Karabakh backed by Armenia. By the end of the hostilities in 1994, Armenians controlled up to 14–16 percent of Azerbaijani territory, including Nagorno-Karabakh itself. De Waal, Thomas (2013). ''Black Garden: Armenia And Azerbaijan Through Peace and War''. New York: New York University Press, p. 286. . During the war many atrocities and pogroms by both sides were committed including the massacre
A massacre is the killing of a large number of people or animals, especially those who are not involved in any fighting or have no way of defending themselves. A massacre is generally considered to be morally unacceptable, especially when per ...
s at Malibeyli and Gushchular, the Garadaghly massacre
The Capture of Garadaghly ( az, Qaradağlının işğalı) was the seizure of Garadaghly, an Azerbaijani-populated village in Khojavend district of Nagorno-Karabakh by Armenian volunteer units on 17 February 1992, in the First Nagorno-Karabakh ...
and the Khojaly massacres, along with the Baku pogrom
The Baku pogrom ( hy, Բաքվի ջարդեր, ) was a pogrom directed against the ethnic Armenian inhabitants of Baku, Azerbaijan SSR. From January 12, 1990, a seven-day pogrom broke out against the Armenian civilian population in Baku during ...
, the Maraga massacre and the Kirovabad pogrom. Furthermore, an estimated 30,000 people have been killed and more than a million people have been displaced, more than 800,000 Azerbaijanis and 300,000 Armenians. Four United Nations Security Council
The United Nations Security Council (UNSC) is one of the Organs of the United Nations, six principal organs of the United Nations (UN) and is charged with ensuring international security, international peace and security, recommending the admi ...
Resolutions ( 822, 853, 874, and 884
__NOTOC__
Year 884 ( DCCCLXXXIV) was a leap year starting on Wednesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar.
Events
By place Europe
* March 1 – Diego Rodríguez Porcelos, count of Castile, founds and repo ...
) demand for "the immediate withdrawal of all Armenian forces from all occupied territories of Azerbaijan." Many Russians and Armenians left and fled Azerbaijan as refugees during the 1990s. According to the 1970 census, there were 510,000 ethnic Russians
, native_name_lang = ru
, image =
, caption =
, population =
, popplace =
118 million Russians in the Russian Federation (2002 ''Winkler Prins'' estimate)
, region1 =
, pop1 ...
and 484,000 Armenians in Azerbaijan.
Heydar Aliyev, 1993–today
 In 1993, democratically elected president
In 1993, democratically elected president Abulfaz Elchibey
Abulfaz Elchibey ( az, Əbülfəz Elçibəy; 24 June 1938, in Nakhchivan – 22 August 2000, in Ankara) was an Azerbaijani political figure and a former Soviet dissident. His real name was Abulfaz Gadirgulu oghlu Aliyev (Azerbaijani: ''Əbülf ...
was overthrown by a military insurrection led by Colonel Surat Huseynov
Surat Davud oghlu Huseynov ( az, Surət Davud oğlu Hüseynov; born 12 February 1959 in Kirovabad) is an Azerbaijani colonel and ex-Prime Minister of Azerbaijan, who rose to prominence during the First Nagorno-Karabakh War. His military career l ...
, which resulted in the rise to power of the former leader of Soviet Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan ( az, Азәрбајҹан, Azərbaycan, italics=no), officially the Azerbaijan Soviet Socialist Republic (Azerbaijan SSR; az, Азәрбајҹан Совет Сосиалист Республикасы, Azərbaycan Sovet Sosialist R ...
, Heydar Aliyev
Heydar Alirza oghlu Aliyev ( az, Һејдәр Әлирза оғлу Әлијев, italic=no, Heydər Əlirza oğlu Əliyev, ; , ; 10 May 1923 – 12 December 2003) was a Soviet and Azerbaijani politician who served as the third president of Azer ...
. In 1994, Surat Huseynov, by that time the prime minister, attempted another military coup against Heydar Aliyev, but he was arrested and charged with treason. A year later, in 1995, another coup was attempted against Aliyev, this time by the commander of the OMON
OMON (russian: ОМОН – Отряд Мобильный Особого Назначения , translit = Otryad Mobil'nyy Osobogo Naznacheniya , translation = Special Purpose Mobile Unit, , previously ru , Отряд Милиции Осо� ...
special unit, Rovshan Javadov. The coup was averted, resulting in the killing of the latter and disbanding of Azerbaijan's OMON units. At the same time, the country was tainted by rampant corruption in the governing bureaucracy. In October 1998, Aliyev was reelected for a second term. Despite the much improved economy, particularly with the exploitation of the Azeri–Chirag–Guneshli oil field and Shah Deniz gas field
Shah Deniz gas field ( az, Şahdəniz) is the largest natural gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amo ...
, Aliyev's presidency was criticized due to suspected election fraud, high levels of economic inequality and domestic corruption.
Ilham Aliyev
Ilham Heydar oghlu Aliyev ( az, İlham Heydər oğlu Əliyev, ; born 24 December 1961) is the fourth president of Azerbaijan, serving in the post since 31 October 2003.
The son and second child of the former Azerbaijani leader Heydar Aliyev ...
, Heydar Aliyev's son, became chairman of the New Azerbaijan Party
The New Azerbaijan Party ( az, Yeni Azərbaycan Partiyası, YAP) is the ruling political party in Azerbaijan, founded on 21 November 1992 under the leadership of Heydar Aliyev. After his election as President of Azerbaijan on 3 October 1993, ...
as well as President of Azerbaijan
The president of the Republic of Azerbaijan is the head of state of Azerbaijan. The Constitution states that the president is the embodiment of executive power, commander-in-chief, "representative of Azerbaijan in home and foreign policies" ...
when his father died in 2003. He was reelected to a third term as president in October 2013. In April 2018, President Ilham Aliyev secured his fourth consecutive term in the election
An election is a formal group decision-making process by which a population chooses an individual or multiple individuals to hold public office.
Elections have been the usual mechanism by which modern representative democracy has opera ...
that was boycotted by the main opposition parties as fraudulent. On 27 September 2020, new clashes in the unresolved Nagorno-Karabakh conflict
The Nagorno-Karabakh conflict is an ethnic and territorial conflict between Armenia and Azerbaijan over the disputed region of Nagorno-Karabakh, inhabited mostly by ethnic Armenians, and seven surrounding districts, inhabited mostly by Azerba ...
resumed along the Nagorno-Karabakh Line of Contact. Both the armed forces of Azerbaijan and Armenia reported military and civilian casualties. The Nagorno-Karabakh ceasefire agreement and the end of the six-week war between Azerbaijan and Armenia was widely celebrated in Azerbaijan, as they made significant territorial gains.
Geography
South Caucasus
The South Caucasus, also known as Transcaucasia or the Transcaucasus, is a geographical region on the border of Eastern Europe and Western Asia, straddling the southern Caucasus Mountains. The South Caucasus roughly corresponds to modern Arme ...
region of Eurasia
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Japanese archipelag ...
, straddling Western Asia
Western Asia, West Asia, or Southwest Asia, is the westernmost subregion of the larger geographical region of Asia, as defined by some academics, UN bodies and other institutions. It is almost entirely a part of the Middle East, and includes A ...
and Eastern Europe. It lies between latitudes 38° and 42° N, and longitudes 44° and 51° E. The total length of Azerbaijan's land borders is , of which are with Armenia, with Iran, 480 kilometers with Georgia, with Russia and with Turkey. The coastline stretches for , and the length of the widest area of the Azerbaijani section of the Caspian Sea is . The country has a landlocked
A landlocked country is a country that does not have territory connected to an ocean or whose coastlines lie on endorheic basins. There are currently 44 landlocked countries and 4 landlocked de facto states. Kazakhstan is the world's largest ...
exclave
An enclave is a territory (or a small territory apart of a larger one) that is entirely surrounded by the territory of one other state or entity. Enclaves may also exist within territorial waters. ''Enclave'' is sometimes used improperly to deno ...
, the Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic
The Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic ( az, Naxçıvan Muxtar Respublikası, ), is a landlocked exclave of the Republic of Azerbaijan. The region covers Official portal of Nakhchivan Autonomous RepublicNakhchivan Autonomous Republic with a popula ...
.
 Three physical features dominate Azerbaijan: the Caspian Sea, whose shoreline forms a natural boundary to the east; the
Three physical features dominate Azerbaijan: the Caspian Sea, whose shoreline forms a natural boundary to the east; the Greater Caucasus
The Greater Caucasus ( az, Böyük Qafqaz, Бөјүк Гафгаз, بيوک قافقاز; ka, დიდი კავკასიონი, ''Didi K’avk’asioni''; russian: Большой Кавказ, ''Bolshoy Kavkaz'', sometimes translat ...
mountain range to the north; and the extensive flatlands at the country's center. There are also three mountain ranges, the Greater and Lesser Caucasus
The Lesser Caucasus, also called Caucasus Minor, is the second of the two main mountain ranges of Caucasus mountains, of length about . The western portion of the Lesser Caucasus overlaps and converges with east Turkey and northwest Iran.
It ru ...
, and the Talysh Mountains
Talysh Mountains ( tly, Tolışə Bandon, script=Latn, fa, کوههای تالش, Kuhhâye Tâleš; az, Talış dağları) is a mountain range in far southeastern Azerbaijan and far northwestern Iran within Ardabil Province and Gilan Provin ...
, together covering approximately 40% of the country. The highest peak of Azerbaijan is Mount Bazardüzü , while the lowest point lies in the Caspian Sea . Nearly half of all the mud volcano
A mud volcano or mud dome is a landform created by the eruption of mud or slurries, water and gases. Several geological processes may cause the formation of mud volcanoes. Mud volcanoes are not true igneous volcanoes as they do not produce l ...
es on Earth are concentrated in Azerbaijan, these volcanoes were also among nominees for the New7Wonders of Nature
New 7 Wonders of Nature (2007–2011) was an initiative started in 2007 to create a list of seven natural wonders chosen by people through a global poll. It was the second in a series of Internet-based polls led by Swiss-born Canadian Bernard Web ...
.
The main water sources are surface waters. Only 24 of the 8,350 rivers are greater than in length. All the rivers drain into the Caspian Sea in the east of the country. The largest lake is Sarysu , and the longest river is Kur
The ancient Mesopotamian underworld, most often known in Sumerian as Kur, Irkalla, Kukku, Arali, or Kigal and in Akkadian as Erṣetu, although it had many names in both languages, was a dark, dreary cavern located deep below the ground, where ...
, which is transboundary with Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ...
. Azerbaijan has several islands along the Caspian sea, mostly located in the Baku Archipelago.
Since the independence of Azerbaijan in 1991, the Azerbaijani government
The Politics of Azerbaijan takes place in a framework of a semi-presidential republic, with the President of Azerbaijan as the head of state, and the Prime Minister of Azerbaijan as head of government. Executive power is exercised by the presi ...
has taken measures to preserve the environment of Azerbaijan. National protection of the environment accelerated after 2001 when the state budget increased due to new revenues provided by the Baku–Tbilisi–Ceyhan pipeline
The Baku–Tbilisi–Ceyhan (BTC) pipeline is a long crude oil pipeline from the Azeri–Chirag–Gunashli oil field in the Caspian Sea to the Mediterranean Sea. It connects Baku, the capital of Azerbaijan and Ceyhan, a port on the south-eas ...
. Within four years, protected areas doubled and now make up eight percent of the country's territory. Since 2001 the government has set up seven large reserves and almost doubled the sector of the budget earmarked for environmental protection.
Landscape
 Azerbaijan is home to a wide variety of landscapes. Over half of Azerbaijan's landmass consists of
Azerbaijan is home to a wide variety of landscapes. Over half of Azerbaijan's landmass consists of mountain ridge
A ridge or a mountain ridge is a geographical feature consisting of a chain of mountains or hills that form a continuous elevated crest for an extended distance. The sides of the ridge slope away from the narrow top on either side. The line ...
s, crests, highland
Highlands or uplands are areas of high elevation such as a mountainous region, elevated mountainous plateau or high hills. Generally speaking, upland (or uplands) refers to ranges of hills, typically from up to while highland (or highlands) is ...
s, and plateaus which rise up to hypsometric levels of 400–1000 meters (including the Middle and Lower lowlands), in some places (Talis, Jeyranchol-Ajinohur and Langabiz-Alat foreranges) up to 100–120 meters, and others from 0–50 meters and up ( Qobustan, Absheron). The rest of Azerbaijan's terrain consists of plains and lowlands. Hypsometric marks within the Caucasus region vary from about −28 meters at the Caspian Sea shoreline up to 4,466 meters (Bazardüzü peak).
The formation of climate in Azerbaijan is influenced particularly by cold arctic
The Arctic ( or ) is a polar region located at the northernmost part of Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean, adjacent seas, and parts of Canada ( Yukon, Northwest Territories, Nunavut), Danish Realm ( Greenland), Finland, Iceland ...
air mass
In meteorology, an air mass is a volume of air defined by its temperature and humidity. Air masses cover many hundreds or thousands of square miles, and adapt to the characteristics of the surface below them. They are classified according to ...
es of Scandinavian anticyclone
An anticyclone is a weather phenomenon defined as a large-scale circulation of winds around a central region of high atmospheric pressure, clockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and counterclockwise in the Southern Hemisphere as viewed from abo ...
, temperate air masses of Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part o ...
n anticyclone, and Central Asian anticyclone. Azerbaijan's diverse landscape affects the ways air masses enter the country. The Greater Caucasus protects the country from direct influences of cold air masses coming from the north. That leads to the formation of subtropical climate
The subtropical zones or subtropics are geographical and climate zones to the north and south of the tropics. Geographically part of the temperate zones of both hemispheres, they cover the middle latitudes from to approximately 35° north a ...
on most foothills and plains of the country. Meanwhile, plains and foothills are characterized by high solar radiation
Solar irradiance is the power per unit area ( surface power density) received from the Sun in the form of electromagnetic radiation in the wavelength range of the measuring instrument.
Solar irradiance is measured in watts per square metre ...
rates.
Nine out of eleven existing climate zones are present in Azerbaijan. Both the absolute minimum temperature ( ) and the absolute maximum temperature were observed in Julfa and Ordubad
Ordubad is the second largest city of Azerbaijan's Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic and the capital of an eponymous district. Ordubad is a medieval city of the Caucasus and in its current capacity of a town was founded in the 18th century. The town ...
– regions of Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic
The Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic ( az, Naxçıvan Muxtar Respublikası, ), is a landlocked exclave of the Republic of Azerbaijan. The region covers Official portal of Nakhchivan Autonomous RepublicNakhchivan Autonomous Republic with a popula ...
. The maximum annual precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravitational pull from clouds. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, sleet, snow, ice pellets, graupel and hai ...
falls in Lankaran
Lankaran ( az, Lənkəran, ) is a city in Azerbaijan, on the coast of the Caspian Sea, near the southern border with Iran. As of 2021, the city had a population of 89,300. It is next to, but independent of, Lankaran District. The city forms a di ...
() and the minimum in Absheron ().
 Rivers and lakes form the principal part of the water systems of Azerbaijan, they were formed over a long geological timeframe and changed significantly throughout that period. This is particularly evidenced by remnants of ancient rivers found throughout the country. The country's water systems are continually changing under the influence of natural forces and human-introduced industrial activities. Artificial rivers (canals) and ponds are a part of Azerbaijan's water systems. In terms of water supply, Azerbaijan is below the average in the world with approximately per year of water per square kilometer. All big water reservoirs are built on Kur. The hydrography of Azerbaijan basically belongs to the
Rivers and lakes form the principal part of the water systems of Azerbaijan, they were formed over a long geological timeframe and changed significantly throughout that period. This is particularly evidenced by remnants of ancient rivers found throughout the country. The country's water systems are continually changing under the influence of natural forces and human-introduced industrial activities. Artificial rivers (canals) and ponds are a part of Azerbaijan's water systems. In terms of water supply, Azerbaijan is below the average in the world with approximately per year of water per square kilometer. All big water reservoirs are built on Kur. The hydrography of Azerbaijan basically belongs to the Caspian Sea basin Caspian can refer to:
*The Caspian Sea
*The Caspian Depression, surrounding the northern part of the Caspian Sea
*The Caspians, the ancient people living near the Caspian Sea
*Caspian languages, collection of languages and dialects of Caspian peopl ...
.
The Kura and Aras are the major rivers in Azerbaijan. They run through the Kura-Aras Lowland
The Kura-Aras Lowland, Kura-Aras Depression or Kura-Aras Basin ( az, Kür-Araz ovalığı) is a vast depression in central-southern Azerbaijan defined by the valleys of the Kura River and Aras River. It is situated by the West shore of the Casp ...
. The rivers that directly flow into the Caspian Sea, originate mainly from the north-eastern slope of the Major Caucasus and Talysh Mountains
Talysh Mountains ( tly, Tolışə Bandon, script=Latn, fa, کوههای تالش, Kuhhâye Tâleš; az, Talış dağları) is a mountain range in far southeastern Azerbaijan and far northwestern Iran within Ardabil Province and Gilan Provin ...
and run along the Samur–Devechi and Lankaran lowlands.
Yanar Dag, translated as "burning mountain", is a natural gas fire which blazes continuously on a hillside on the Absheron Peninsula
The Absheron Peninsula ( az, Abşeron yarımadası) is a peninsula in Azerbaijan. It is the location of Baku, the biggest and the most populous city of the country, and also the Baku metropolitan area, with its satellite cities Sumqayit and Khyr ...
on the Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, often described as the List of lakes by area, world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia; east of the Caucasus, west of the broad s ...
near Baku, which itself is known as the "land of fire." Flames jet out into the air from a thin, porous sandstone layer. It is a tourist attraction to visitors to the Baku area.
Biodiversity
 The first reports on the richness and diversity of animal life in Azerbaijan can be found in travel notes of Eastern travelers. Animal carvings on architectural monuments, ancient rocks, and stones survived up to the present times. The first information on flora and fauna of Azerbaijan was collected during the visits of naturalists to Azerbaijan in the 17th century.
There are 106 species of mammals, 97 species of fish, 363 species of birds, 10 species of amphibians, and 52 species of reptiles which have been recorded and classified in Azerbaijan. The national animal of Azerbaijan is the Karabakh horse, a mountain-steppe racing and riding horse endemic to Azerbaijan. The Karabakh horse has a reputation for its good temper, speed, elegance, and intelligence. It is one of the oldest breeds, with ancestry dating to the ancient world, but today the horse is an endangered species.
Azerbaijan's flora consists of more than 4,500 species of higher plants. Due to the unique climate in Azerbaijan, the flora is much richer in the number of species than the flora of the other republics of the South Caucasus. 66 percent of the species growing in the whole
The first reports on the richness and diversity of animal life in Azerbaijan can be found in travel notes of Eastern travelers. Animal carvings on architectural monuments, ancient rocks, and stones survived up to the present times. The first information on flora and fauna of Azerbaijan was collected during the visits of naturalists to Azerbaijan in the 17th century.
There are 106 species of mammals, 97 species of fish, 363 species of birds, 10 species of amphibians, and 52 species of reptiles which have been recorded and classified in Azerbaijan. The national animal of Azerbaijan is the Karabakh horse, a mountain-steppe racing and riding horse endemic to Azerbaijan. The Karabakh horse has a reputation for its good temper, speed, elegance, and intelligence. It is one of the oldest breeds, with ancestry dating to the ancient world, but today the horse is an endangered species.
Azerbaijan's flora consists of more than 4,500 species of higher plants. Due to the unique climate in Azerbaijan, the flora is much richer in the number of species than the flora of the other republics of the South Caucasus. 66 percent of the species growing in the whole Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, mainly comprising Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia (country), Georgia, and parts of Southern Russia. The Caucasus Mountains, including the Greater Caucasus range ...
can be found in Azerbaijan. The country lies within four ecoregions: Caspian Hyrcanian mixed forests, Caucasus mixed forests
The Caucasus mixed forests is a temperate broadleaf and mixed forests ecoregion in the Caucasus Mountains, as well as the adjacent Lesser Caucasus range and the eastern end of the Pontic Mountains.
Geography
The ecoregion covers an area of ...
, Eastern Anatolian montane steppe
The Eastern Anatolian montane steppe is a temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands ecoregion. It is located in the Armenian Highlands, covering parts of eastern Turkey, Armenia, Azerbaijan, southern Georgia, and northwestern Iran.
...
, and Azerbaijan shrub desert and steppe
The Azerbaijan shrub desert and steppe is a deserts and xeric shrublands ecoregion in western Asia. It lies in the lowlands west of the Caspian Sea, and covers portions of Azerbaijan, Georgia, and Iran.
Geography
The ecoregion lies mostly in the ...
. Azerbaijan had a 2018 Forest Landscape Integrity Index
The Forest Landscape Integrity Index (FLII) is an annual global index of forest condition measured by degree of anthropogenic modification. Created by a team of 48 scientists, the FLII, in its measurement of 300m pixels of forest across the globe ...
mean score of 6.55/10, ranking it 72nd globally out of 172 countries.
Government and politics
The structural formation of Azerbaijan's political system was completed by the adoption of the newConstitution
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organisation or other type of entity and commonly determine how that entity is to be governed.
When these princip ...
on 12 November 1995. According to Article 23 of the Constitution, the state symbols of the Azerbaijan Republic are the flag
A flag is a piece of fabric (most often rectangular or quadrilateral) with a distinctive design and colours. It is used as a symbol, a signalling device, or for decoration. The term ''flag'' is also used to refer to the graphic design emp ...
, the coat of arms
A coat of arms is a heraldic visual design on an escutcheon (i.e., shield), surcoat, or tabard (the latter two being outer garments). The coat of arms on an escutcheon forms the central element of the full heraldic achievement, which in it ...
, and the national anthem
A national anthem is a patriotic musical composition symbolizing and evoking eulogies of the history and traditions of a country or nation. The majority of national anthems are marches or hymns in style. American, Central Asian, and Europe ...
. The state power in Azerbaijan is limited only by law for internal issues, but international affairs are also limited by international agreements' provisions.
The Constitution of Azerbaijan states that it is a presidential republic with three branches of power – Executive, Legislative, and Judicial. The legislative power is held by the unicameral
Unicameralism (from ''uni''- "one" + Latin ''camera'' "chamber") is a type of legislature, which consists of one house or assembly, that legislates and votes as one.
Unicameral legislatures exist when there is no widely perceived need for multi ...
National Assembly
In politics, a national assembly is either a unicameral legislature, the lower house of a bicameral legislature, or both houses of a bicameral legislature together. In the English language it generally means "an assembly composed of the rep ...
and the Supreme National Assembly in the Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic. The Parliament of Azerbaijan, called Milli Majlis, consists of 125 deputies elected based on majority vote
A majority, also called a simple majority or absolute majority to distinguish it from related terms, is more than half of the total.Dictionary definitions of ''majority'' aMerriam-WebsterNew Azerbaijan Party
The New Azerbaijan Party ( az, Yeni Azərbaycan Partiyası, YAP) is the ruling political party in Azerbaijan, founded on 21 November 1992 under the leadership of Heydar Aliyev. After his election as President of Azerbaijan on 3 October 1993, ...
, and independents loyal to the ruling government, currently hold almost all of the Parliament's 125 seats. During the 2010 Parliamentary election, the opposition parties, Musavat and Azerbaijani Popular Front Party, failed to win a single seat. European observers found numerous irregularities in the run-up to the election and on election day.
 The executive power is held by the
The executive power is held by the President
President most commonly refers to:
*President (corporate title)
* President (education), a leader of a college or university
*President (government title)
President may also refer to:
Automobiles
* Nissan President, a 1966–2010 Japanese f ...
, who is elected for a seven-year term by direct elections, and the Prime Minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister is ...
. The president is authorized to form the Cabinet
Cabinet or The Cabinet may refer to:
Furniture
* Cabinetry, a box-shaped piece of furniture with doors and/or drawers
* Display cabinet, a piece of furniture with one or more transparent glass sheets or transparent polycarbonate sheets
* Filing ...
, a collective executive body accountable to both the President and the National Assembly. The Cabinet of Azerbaijan consists primarily of the prime minister, his deputies, and ministers. The 8th Government of Azerbaijan
The 8th Government of Azerbaijan is the current formation of the Cabinet of Azerbaijan.
Prime Minister
* Novruz Mammadov (2018 to 2019)
* Ali Asadov (from 2019)
Deputy Prime Ministers
* Yaqub Eyyubov
* Shahin Mustafayev
* Ali Ahmadov
* ...
is the administration in its current formation. The president does not have the right to dissolve the National Assembly but has the right to veto its decisions. To override the presidential veto, the parliament must have a majority of 95 votes. The judicial power is vested in the Constitutional Court
A constitutional court is a high court that deals primarily with constitutional law. Its main authority is to rule on whether laws that are challenged are in fact unconstitutional, i.e. whether they conflict with constitutionally established ...
, Supreme Court
A supreme court is the highest court within the hierarchy of courts in most legal jurisdictions. Other descriptions for such courts include court of last resort, apex court, and high (or final) court of appeal. Broadly speaking, the decisions of ...
, and the Economic Court. The president nominates the judges in these courts. The European Commission for the Efficiency of Justice The European Commission for the Efficiency of Justice (CEPEJ) is a judicial body, composed of experts from all the 47 member States of the Council of Europe and prepares tools to improve the efficiency and functioning of justice in Europe (includin ...
(CEPEJ) report refers to the Azerbaijani justice model on the selection of new judges as best practice, reflecting the particular features and the course of development towards ensuring the independence and quality of the judiciary in a new democracy.
Azerbaijan's system of governance nominally can be called two-tiered. The top or highest tier of the government is the Executive Power headed by President. The President appoints the Cabinet of Ministers and other high-ranking officials. The Local Executive Authority is merely a continuation of Executive Power. The Provision determines the legal status of local state administration in Azerbaijan on Local Executive Authority (''Yerli Icra Hakimiyati''), adopted 16 June 1999. In June 2012, the President approved the new Regulation, which granted additional powers to Local Executive Authorities, strengthening their dominant position in Azerbaijan's local affairs Chapter 9 of the Constitution of the Azerbaijan Republic addresses major issues of local self-government, such as the legal status of municipalities, types of local self-government bodies, their basic powers and relationships to other official entities. The other nominal tier of governance is municipalities (''Bələdiyə''), and members of municipalities are elected by a general vote in Municipal elections every five years. Currently, there are 1,607 municipalities across the country. The Law on Municipal Elections and the Law on the Status of Municipalities were the first to be adopted in the field of local government (2 July 1999). The Law on Municipal Service regulates the activities of municipal employees, their rights, duties, labor conditions, and social benefits and outlines the structure of the executive apparatus and the organization of municipal service. The Law on the Status of Municipalities regulates the role and structure of municipal bodies and outlines state guarantees of legal and financial autonomy. The law pays special attention to the adoption and execution of municipal programs concerning social protection, social and economic development, and the local environment.
The Security Council is the deliberative body under the president, and he organizes it according to the Constitution. It was established on 10 April 1997. The administrative department is not a part of the president's office but manages the financial, technical and pecuniary activities of both the president and his office.
Called a " dynastic dictatorship", the country has been led by Heydar Aliyev
Heydar Alirza oghlu Aliyev ( az, Һејдәр Әлирза оғлу Әлијев, italic=no, Heydər Əlirza oğlu Əliyev, ; , ; 10 May 1923 – 12 December 2003) was a Soviet and Azerbaijani politician who served as the third president of Azer ...
(who led Soviet Azerbaijan from 1969 to 1982) and then his son Ilham Aliyev
Ilham Heydar oghlu Aliyev ( az, İlham Heydər oğlu Əliyev, ; born 24 December 1961) is the fourth president of Azerbaijan, serving in the post since 31 October 2003.
The son and second child of the former Azerbaijani leader Heydar Aliyev ...
since 1993. Although Azerbaijan has held several elections since regaining its independence and it has many of the formal institutions of democracy, it remains categorised as "not free" by Freedom House
Freedom House is a non-profit, majority U.S. government funded organization in Washington, D.C., that conducts research and advocacy on democracy, political freedom, and human rights. Freedom House was founded in October 1941, and Wendell Wi ...
, who ranked it 9/100 on Global Freedom Score in 2022, calling it a "consolidated authoritarian regime". In recent years, large numbers of Azerbaijani journalists, bloggers, lawyers, and human rights activists have been rounded up and jailed for their criticism of President Aliyev and government authorities. A resolution adopted by the European Parliament in September 2015 described Azerbaijan as "having suffered the greatest decline in democratic governance in all of Eurasia over the past ten years," noting as well that its dialogue with the country on human rights has "not made any substantial progress." On 17 March 2016, the President of Azerbaijan signed a decree pardoning more than a dozen of the persons regarded as political prisoners by some NGOs. This decree was welcomed as a positive step by the US State Department. On 16 March 2017 another pardon decree was signed, which led to the release of additional persons regarded as political prisoners.
Azerbaijan has been harshly criticized for bribing foreign officials and diplomats to promote its causes abroad and legitimize its elections at home, a practice termed caviar diplomacy
Caviar diplomacy is a lobbying strategy of Azerbaijan, consisting of costly invitations to foreign politicians and employees of international organizations to Azerbaijan at the expense of the host country. Caviar diplomacy also includes expensive ...
. However, on 6 March 2017, the European Strategic Intelligence and Security Center
The European Strategic Intelligence and Security Center (ESISC) is a self-described think tank and lobbying group dealing with issues related to terrorism and security. ESISC notes on its website that its "lobbying operations can defend an industri ...
ESISC) published a report called "The Armenian Connection", in which it attacked human rights NGOs and research organisations criticising human rights violations and corruption in Azerbaijan.
ESISC in that report asserted that the "Caviar Diplomacy" report elaborated by ESI aimed to create a climate of suspicion based on slander to form a network of MPs that would engage in a political war against Azerbaijan and that the network, composed of European PMs, Armenian officials, and some NGOs (Human Rights Watch, Amnesty International, "Human Rights House Foundation", "Open Dialog, European Stability Initiative, and Helsinki Committee for Human Rights) was financed by the Soros Foundation. According to Robert Coalson (Radio Free Europe), ESISC is a part of Baku's lobbying efforts to extend the use of front think tanks to shift public opinion. Freedom Files Analytical Centre said that "The report is written in the worst traditions of authoritarian propaganda".An Exploration into Azerbaijan's Sophisticated System of Projecting Its International Influence, Buying Western Politicians and Capturing Intergovernmental Organisations// Freedom Files Analytical Centre (Civic Solidarity Platform), March 2017
Foreign relations
 The short-lived Azerbaijan Democratic Republic succeeded in establishing diplomatic relations with six countries, sending diplomatic representatives to Germany and Finland. The process of international recognition of Azerbaijan's independence from the collapsing Soviet Union lasted roughly one year. The most recent country to recognize Azerbaijan was Bahrain, on 6 November 1996. Full diplomatic relations, including mutual exchanges of missions, were first established with Turkey, Pakistan, the United States, Iran and Israel. Azerbaijan has placed a particular emphasis on its "
The short-lived Azerbaijan Democratic Republic succeeded in establishing diplomatic relations with six countries, sending diplomatic representatives to Germany and Finland. The process of international recognition of Azerbaijan's independence from the collapsing Soviet Union lasted roughly one year. The most recent country to recognize Azerbaijan was Bahrain, on 6 November 1996. Full diplomatic relations, including mutual exchanges of missions, were first established with Turkey, Pakistan, the United States, Iran and Israel. Azerbaijan has placed a particular emphasis on its "special relationship
The Special Relationship is a term that is often used to describe the political, social, diplomatic, cultural, economic, legal, environmental, religious, military and historic relations between the United Kingdom and the United States or its ...
" with Turkey.
Azerbaijan has diplomatic relations with 158 countries so far and holds membership in 38 international organizations. It holds observer status in the Non-Aligned Movement
The Non-Aligned Movement (NAM) is a forum of 120 countries that are not formally aligned with or against any major power bloc. After the United Nations, it is the largest grouping of states worldwide.
The movement originated in the aftermath ...
and World Trade Organization
The World Trade Organization (WTO) is an intergovernmental organization that regulates and facilitates international trade. With effective cooperation
in the United Nations System, governments use the organization to establish, revise, and ...
and is a correspondent at the International Telecommunication Union
The International Telecommunication Union is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for many matters related to information and communication technologies. It was established on 17 May 1865 as the International Telegraph Unio ...
. On 9 May 2006 Azerbaijan was elected to membership in the newly established Human Rights Council
The United Nations Human Rights Council (UNHRC), CDH is a United Nations body whose mission is to promote and protect human rights around the world. The Council has 47 members elected for staggered three-year terms on a regional group basis. ...
by the United Nations General Assembly
The United Nations General Assembly (UNGA or GA; french: link=no, Assemblée générale, AG) is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN), serving as the main deliberative, policymaking, and representative organ of the UN. Cur ...
. The term of office began on 19 June 2006. Azerbaijan was first elected as a non-permanent member of the UN Security Council in 2011 with the support of 155 countries.
 Foreign policy priorities of Azerbaijan include, first of all, the restoration of its territorial integrity; elimination of the consequences of occupation of Nagorno-Karabakh and seven other regions of Azerbaijan surrounding Nagorno-Karabakh; integration into European and Euro-Atlantic structure; contribution to international security; cooperation with international organizations; regional cooperation and bilateral relations; strengthening of defense capability; promotion of security by domestic policy means; strengthening of democracy; preservation of ethnic and religious tolerance; scientific, educational, and cultural policy and preservation of moral values; economic and social development; enhancing internal and border security; and migration, energy, and transportation security policy.
Azerbaijan is an active member of international coalitions fighting international terrorism. Azerbaijan was one of the first countries to offer support after the
Foreign policy priorities of Azerbaijan include, first of all, the restoration of its territorial integrity; elimination of the consequences of occupation of Nagorno-Karabakh and seven other regions of Azerbaijan surrounding Nagorno-Karabakh; integration into European and Euro-Atlantic structure; contribution to international security; cooperation with international organizations; regional cooperation and bilateral relations; strengthening of defense capability; promotion of security by domestic policy means; strengthening of democracy; preservation of ethnic and religious tolerance; scientific, educational, and cultural policy and preservation of moral values; economic and social development; enhancing internal and border security; and migration, energy, and transportation security policy.
Azerbaijan is an active member of international coalitions fighting international terrorism. Azerbaijan was one of the first countries to offer support after the September 11 attacks
The September 11 attacks, commonly known as 9/11, were four coordinated suicide terrorist attacks carried out by al-Qaeda against the United States on Tuesday, September 11, 2001. That morning, nineteen terrorists hijacked four commerc ...
. The country is contributing to peacekeeping efforts in Kosovo, Afghanistan and Iraq. Azerbaijan is an active member of NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
's Partnership for Peace
The Partnership for Peace (PfP; french: Partenariat pour la paix) is a North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) program aimed at creating trust between the member states of NATO and other states mostly in Europe, including post-Soviet states; ...
program. It also maintains good relations with the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been ...
and could potentially one day apply for membership.
On 1 July 2021, the US Congress advanced legislation that will have an impact on the military aid that Washington has sent to Azerbaijan since 2012. This was due to the fact that the packages to Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ...
, instead are significantly smaller.
Military
The history of the modern Azerbaijan army dates back toAzerbaijan Democratic Republic
The Azerbaijan Democratic Republic), or simply as Azerbaijan in Paris Peace Conference, 1919–1920,''Bulletin d'Information de l'Azerbaidjan'', No. I, September 1, 1919, pp. 6–7''125 H.C.Debs.'', 58., February 24, 1920, p. 1467. Caucasian Az ...
in 1918 when the National Army of the newly formed Azerbaijan Democratic Republic was created on 26 June 1918. When Azerbaijan gained independence after the dissolution of the Soviet Union, the Armed Forces of the Republic of Azerbaijan were created according to the Law on the Armed Forces of 9 October 1991. The original date of the establishment of the short-lived National Army is celebrated as Army Day (26 June) in today's Azerbaijan.
As of 2021, Azerbaijan had 126,000 active personnel in its armed forces. There are also 17,000 paramilitary troops and 330,00 reserve personnel.C. W. BlandAzerbaijan: Is War Over Nagornyy Karabakh a Realistic Option? Advanced Research and Assessment Group. Caucasus Series 08/17. – Defense Academy of the United Kingdom, 2008, p. 12
The armed forces have three branches: the Land Forces, the Air Forces and the
Navy
A navy, naval force, or maritime force is the branch of a nation's armed forces principally designated for naval and amphibious warfare; namely, lake-borne, riverine, littoral, or ocean-borne combat operations and related functions. It include ...
. Additionally the armed forces embrace several military sub-groups that can be involved in state defense when needed. These are the Internal Troops
The Internal Troops, full name Internal Troops of the Ministry for Internal Affairs (MVD) (russian: Внутренние войска Министерства внутренних дел, Vnutrenniye Voiska Ministerstva Vnutrennikh Del; abbreviat ...
of the Ministry of Internal Affairs and the State Border Service, which includes the Coast Guard
A coast guard or coastguard is a Maritime Security Regimes, maritime security organization of a particular country. The term embraces wide range of responsibilities in different countries, from being a heavily armed military force with cust ...
as well. The Azerbaijan National Guard
The Azerbaijani National Guard ( az, Azərbaycan Milli Qvardiyası) is an armed force of the Government of Azerbaijan, and operates as a semi-independent entity as well as the a reserve component of the Azerbaijan Army. The Special State Pr ...
is a further paramilitary force. It operates as a semi-independent entity of the Special State Protection Service, an agency subordinate to the President.
Azerbaijan adheres to the Treaty on Conventional Armed Forces in Europe
The original Treaty on Conventional Armed Forces in Europe (CFE) was negotiated and concluded during the last years of the Cold War and established comprehensive limits on key categories of conventional military equipment in Europe (from the Atla ...
and has signed all major international arms and weapons treaties. Azerbaijan closely cooperates with NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
in programs such as Partnership for Peace
The Partnership for Peace (PfP; french: Partenariat pour la paix) is a North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) program aimed at creating trust between the member states of NATO and other states mostly in Europe, including post-Soviet states; ...
and Individual Partnership Action Plan/pfp and ipa. Azerbaijan has deployed 151 of its Peacekeeping Forces in Iraq and another 184 in Afghanistan.
Azerbaijan spent $2.24 billion on its defence budget , which amounted to 5.4% of its total GDP, and some 12.7% of general government expenditure. Azerbaijani defense industry
The arms industry, also known as the arms trade, is a global industry which manufactures and sells weapons and military technology. It consists of a commercial industry involved in the research and development, engineering, production, and ...
manufactures small arms, artillery systems, tanks, armors and noctovision devices, aviation bombs, UAV'S/unmanned aerial vehicle, various military vehicles and military planes and helicopters.
Administrative divisions
 Azerbaijan is administratively divided into 14 economic regions; 66 rayons (, singular ) and 11 cities (, singular ) under the direct authority of the republic. Moreover, Azerbaijan includes the
Azerbaijan is administratively divided into 14 economic regions; 66 rayons (, singular ) and 11 cities (, singular ) under the direct authority of the republic. Moreover, Azerbaijan includes the Autonomous Republic
An autonomous republic is a type of administrative division similar to a province or Federated state, state. A significant number of autonomous republics can be found within the successor states of the Soviet Union, but the majority are located wi ...
() of Nakhchivan. The President of Azerbaijan
The president of the Republic of Azerbaijan is the head of state of Azerbaijan. The Constitution states that the president is the embodiment of executive power, commander-in-chief, "representative of Azerbaijan in home and foreign policies" ...
appoints the governors of these units, while the government of Nakhchivan is elected and approved by the parliament of Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic.
Economy
 After gaining independence in 1991, Azerbaijan became a member of the
After gaining independence in 1991, Azerbaijan became a member of the International Monetary Fund
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is a major financial agency of the United Nations, and an international financial institution, headquartered in Washington, D.C., consisting of 190 countries. Its stated mission is "working to foster gl ...
, the World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and grants to the governments of low- and middle-income countries for the purpose of pursuing capital projects. The World Bank is the collective name for the Inte ...
, the European Bank for Reconstruction and Development
The European Bank for Reconstruction and Development (EBRD) is an international financial institution founded in 1991. As a multilateral developmental investment bank, the EBRD uses investment as a tool to build market economies. Initially fo ...
, the Islamic Development Bank
The Islamic Development Bank ( ar, البنك الإسلامي للتنمية, abbreviated as IsDB) is a multilateral development finance institution that is focused on Islamic finance for infrastructure development and located in Jeddah, Saud ...
, and the Asian Development Bank
The Asian Development Bank (ADB) is a regional development bank established on 19 December 1966, which is headquartered in the Ortigas Center located in the city of Mandaluyong, Metro Manila, Philippines. The bank also maintains 31 field offi ...
.
The banking system of Azerbaijan consists of the Central Bank of Azerbaijan, commercial bank
A commercial bank is a financial institution which accepts deposits from the public and gives loans for the purposes of consumption and investment to make profit.
It can also refer to a bank, or a division of a large bank, which deals with co ...
s, and non-banking credit organizations. The National (now Central) Bank was created in 1992 based on the Azerbaijan State Savings Bank, an affiliate of the former State Savings Bank of the USSR. The Central Bank serves as Azerbaijan's central bank, empowered to issue the national currency, the Azerbaijani manat
The manat ( ISO code: AZN; sign: ₼; abbreviation: m) is the currency of Azerbaijan. It is subdivided into 100 '' gapiks''.
The first iteration of the currency happened in the times of the Azerbaijan Democratic Republic and its successor, the Az ...
, and to supervise all commercial banks. Two major commercial banks are UniBank and the state-owned International Bank of Azerbaijan
ABB (from az, Azərbaycan Beynəlxalq Bankı ; formerly known as International Bank of Azerbaijan), the largest bank in Azerbaijan, is an open joint-stock company whose shares are owned by the Azerbaijan state.
History
ABB OJSC was founded on ...
, run by Abbas Ibrahimov.
Pushed up by spending and demand growth, the 2007 Q1 inflation rate reached 16.6%.
Nominal incomes and monthly wages climbed 29% and 25% respectively against this figure, but price increases in the non-oil industry encouraged inflation. Azerbaijan shows some signs of the so-called "Dutch disease
In economics, the Dutch disease is the apparent causal relationship between the increase in the economic development of a specific sector (for example natural resources) and a decline in other sectors (like the manufacturing sector or agricultu ...
" because of its fast-growing energy sector, which causes inflation and makes non-energy exports more expensive.
Global Competitiveness Report
The ''Global Competitiveness Report'' (GCR) is a yearly report published by the World Economic Forum. Since 2004, the ''Global Competitiveness Report'' ranks countries based on the Global Competitiveness Index, developed by Xavier Sala-i-Martin ...
for 2010–2011, above other CIS countries. By 2012 the GDP of Azerbaijan had increased 20-fold from its 1995 level.
Energy and natural resources
 Two-thirds of Azerbaijan is rich in oil and natural gas.
The history of the oil industry of Azerbaijan dates back to the ancient period. Arabian historian and traveler Ahmad Al-Baladhuri discussed the economy of the Absheron peninsula in antiquity, mentioning its oil in particular. There are many pipelines in Azerbaijan. The goal of the Southern Gas Corridor, which connects the giant
Two-thirds of Azerbaijan is rich in oil and natural gas.
The history of the oil industry of Azerbaijan dates back to the ancient period. Arabian historian and traveler Ahmad Al-Baladhuri discussed the economy of the Absheron peninsula in antiquity, mentioning its oil in particular. There are many pipelines in Azerbaijan. The goal of the Southern Gas Corridor, which connects the giant Shah Deniz gas field
Shah Deniz gas field ( az, Şahdəniz) is the largest natural gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amo ...
in Azerbaijan to Europe, is to reduce European Union's dependency on Russian gas.
The region of the Lesser Caucasus
The Lesser Caucasus, also called Caucasus Minor, is the second of the two main mountain ranges of Caucasus mountains, of length about . The western portion of the Lesser Caucasus overlaps and converges with east Turkey and northwest Iran.
It ru ...
accounts for most of the country's gold, silver, iron, copper, titanium
Titanium is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ti and atomic number 22. Found in nature only as an oxide, it can be reduced to produce a lustrous transition metal with a silver color, low density, and high strength, resista ...
, chromium
Chromium is a chemical element with the symbol Cr and atomic number 24. It is the first element in group 6. It is a steely-grey, lustrous, hard, and brittle transition metal.
Chromium metal is valued for its high corrosion resistance and h ...
, manganese
Manganese is a chemical element with the symbol Mn and atomic number 25. It is a hard, brittle, silvery metal, often found in minerals in combination with iron. Manganese is a transition metal with a multifaceted array of industrial alloy u ...
, cobalt
Cobalt is a chemical element with the symbol Co and atomic number 27. As with nickel, cobalt is found in the Earth's crust only in a chemically combined form, save for small deposits found in alloys of natural meteoric iron. The free element, ...
, molybdenum
Molybdenum is a chemical element with the symbol Mo and atomic number 42 which is located in period 5 and group 6. The name is from Neo-Latin ''molybdaenum'', which is based on Ancient Greek ', meaning lead, since its ores were confused with le ...
, complex ore and antimony
Antimony is a chemical element with the symbol Sb (from la, stibium) and atomic number 51. A lustrous gray metalloid, it is found in nature mainly as the sulfide mineral stibnite (Sb2S3). Antimony compounds have been known since ancient ti ...
. In September 1994, a 30-year contract was signed between the State Oil Company of Azerbaijan Republic (SOCAR) and 13 oil companies, among them Amoco
Amoco () is a brand of fuel stations operating in the United States, and owned by BP since 1998. The Amoco Corporation was an American chemical and oil company, founded by Standard Oil Company in 1889 around a refinery in Whiting, Indiana, a ...
, BP, ExxonMobil
ExxonMobil Corporation (commonly shortened to Exxon) is an American multinational oil and gas corporation headquartered in Irving, Texas. It is the largest direct descendant of John D. Rockefeller's Standard Oil, and was formed on November ...
, Lukoil
The PJSC Lukoil Oil Company ( stylized as LUKOIL or ЛУКОЙЛ in Cyrillic script) is a Russian multinational energy corporation headquartered in Moscow, specializing in the business of extraction, production, transport, and sale of petrol ...
and Equinor
Equinor ASA (formerly Statoil and StatoilHydro) is a Norwegian state-owned multinational energy company headquartered in Stavanger. It is primarily a petroleum company, operating in 36 countries with additional investments in renewable energy. ...
. As Western oil companies are able to tap deepwater oilfields untouched by the Soviet exploitation, Azerbaijan is considered one of the most important spots in the world for oil exploration
Hydrocarbon exploration (or oil and gas exploration) is the search by petroleum geologists and geophysicists for deposits of hydrocarbons, particularly petroleum and natural gas, in the Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun ...
and development. Meanwhile, the State Oil Fund of Azerbaijan was established as an extra-budgetary fund to ensure macroeconomic
Macroeconomics (from the Greek prefix ''makro-'' meaning "large" + ''economics'') is a branch of economics dealing with performance, structure, behavior, and decision-making of an economy
An economy is an area of the production, distributio ...
stability, transparency in the management of oil revenue, and safeguarding of resources for future generations.
ecological footprint
The ecological footprint is a method promoted by the Global Footprint Network to measure human demand on natural capital, i.e. the quantity of nature it takes to support people or an economy. It tracks this demand through an ecological accounti ...
of consumption. This means they use more biocapacity than Azerbaijan contains. As a result, Azerbaijan is running a biocapacity deficit.
Azeriqaz, a sub-company of SOCAR, intends to ensure full gasification of the country by 2021.
Azerbaijan is one of the sponsors of the east–west and north–south energy transport corridors. Baku–Tbilisi–Kars railway line will connect the Caspian region with Turkey, which is expected to be completed in July 2017. The Trans-Anatolian gas pipeline (TANAP) and Trans Adriatic Pipeline
Trans Adriatic Pipeline (TAP) ( sq, Gazsjellësi Trans-Adriatik, el, Διαδριατικός Αγωγός Φυσικού Αερίου - ''Diadriatikós Agogós Fysikoú Aeríou'', it, Gasdotto Trans-Adriatico) is a natural gas pipeline p ...
(TAP) will deliver natural gas from Azerbaijan's Shah Deniz gas to Turkey and Europe.
Azerbaijan extended the agreement on development of ACG until 2050 according to the amended PSA
PSA, PsA, Psa, or psa may refer to:
Biology and medicine
* Posterior spinal artery
* Primary systemic amyloidosis, a disease caused by the accumulation of abnormal proteins
* Prostate-specific antigen, an enzyme used as a blood tracer for prost ...
signed on 14 September 2017 by SOCAR
The State Oil Company of Azerbaijan Republic ( az, Azərbaycan Respublikası Dövlət Neft Şirkəti), largely known as SOCAR is fully state-owned national oil and gas company headquartered in Baku, Azerbaijan. The company produces oil and n ...
and co-ventures ( BP, Chevron, Inpex, Equinor
Equinor ASA (formerly Statoil and StatoilHydro) is a Norwegian state-owned multinational energy company headquartered in Stavanger. It is primarily a petroleum company, operating in 36 countries with additional investments in renewable energy. ...
, ExxonMobil
ExxonMobil Corporation (commonly shortened to Exxon) is an American multinational oil and gas corporation headquartered in Irving, Texas. It is the largest direct descendant of John D. Rockefeller's Standard Oil, and was formed on November ...
, TP, ITOCHU and ONGC Videsh).
Agriculture
Azerbaijan has the largest agricultural basin in the region. About 54.9 percent of Azerbaijan is agricultural land. At the beginning of 2007 there were 4,755,100 hectares of utilized agricultural area. In the same year the total wood resources counted 136 million m3. Azerbaijan's agricultural scientific research institutes are focused on meadows and pastures, horticulture and subtropical crops, green vegetables,viticulture
Viticulture (from the Latin word for ''vine'') or winegrowing (wine growing) is the cultivation and harvesting of grapes. It is a branch of the science of horticulture. While the native territory of ''Vitis vinifera'', the common grape vine, ran ...
and wine-making
Winemaking or vinification is the production of wine, starting with the selection of the fruit, its fermentation into alcohol, and the bottling of the finished liquid. The history of wine-making stretches over millennia. The science of wine and w ...
, cotton growing and medicinal plants
Medicinal plants, also called medicinal herbs, have been discovered and used in traditional medicine practices since prehistoric times. Plants synthesize hundreds of chemical compounds for various functions, including defense and protection ...
. In some areas it is profitable to grow grain, potatoes, sugar beet
A sugar beet is a plant whose root contains a high concentration of sucrose and which is grown commercially for sugar production. In plant breeding, it is known as the Altissima cultivar group of the common beet ('' Beta vulgaris''). Together ...
s, cotton and tobacco. Livestock, dairy products, and wine and spirits are also important farm products. The Caspian fishing industry
The fishing industry includes any industry or activity concerned with taking, culturing, processing, preserving, storing, transporting, marketing or selling fish or fish products. It is defined by the Food and Agriculture Organization as including ...
concentrates on the dwindling stocks of sturgeon and beluga. In 2002 the Azerbaijani merchant marine had 54 ships.
Some products previously imported from abroad have begun to be produced locally. Among them are Coca-Cola by Coca-Cola Bottlers LTD., beer by Baki-Kastel, parquet by Nehir and oil pipes by EUPEC Pipe Coating Azerbaijan.
Tourism
 Tourism is an important part of the economy of Azerbaijan. The country was a well-known tourist spot in the 1980s. The fall of the Soviet Union, and the First Nagorno-Karabakh War during the 1990s, damaged the tourist industry and the image of Azerbaijan as a tourist destination.
It was not until the 2000s that the tourism industry began to recover, and the country has since experienced a high rate of growth in the number of tourist visits and overnight stays. In the recent years, Azerbaijan has also become a popular destination for religious, spa, and
Tourism is an important part of the economy of Azerbaijan. The country was a well-known tourist spot in the 1980s. The fall of the Soviet Union, and the First Nagorno-Karabakh War during the 1990s, damaged the tourist industry and the image of Azerbaijan as a tourist destination.
It was not until the 2000s that the tourism industry began to recover, and the country has since experienced a high rate of growth in the number of tourist visits and overnight stays. In the recent years, Azerbaijan has also become a popular destination for religious, spa, and health care tourism
Medical tourism refers to people traveling abroad to obtain medical treatment. In the past, this usually referred to those who traveled from less-developed countries to major medical centers in highly developed countries for treatment unavailable a ...
. During winter, the Shahdag Mountain Resort offers skiing with state of the art facilities.
The government of Azerbaijan has set the development of Azerbaijan as an elite tourist destination as a top priority. It is a national strategy to make tourism a major, if not the single largest, contributor to the Azerbaijani economy. These activities are regulated by the Ministry of Culture and Tourism of Azerbaijan.
There are 63 countries which have a visa-free score.
E-visa – for a visit of foreigners of visa-required countries to the Republic of Azerbaijan.
According to the Travel and Tourism Competitiveness Report 2015 of the World Economic Forum, Azerbaijan holds 84th place.
According to a report by the World Travel and Tourism Council, Azerbaijan was among the top ten countries showing the strongest growth in visitor exports between 2010 and 2016, In addition, Azerbaijan placed first (46.1%) among countries with the fastest-developing travel and tourism economies, with strong indicators for inbound international visitor spending last year.
Transportation
The convenient location of Azerbaijan on the crossroad of major international traffic arteries, such as the Silk Road and the south–north corridor, highlights the strategic importance of the transportation sector for the country's economy. The transport sector in the country includes roads, railways, aviation, and maritime transport. Azerbaijan is also an important economic hub in the transportation of raw materials. TheBaku–Tbilisi–Ceyhan pipeline
The Baku–Tbilisi–Ceyhan (BTC) pipeline is a long crude oil pipeline from the Azeri–Chirag–Gunashli oil field in the Caspian Sea to the Mediterranean Sea. It connects Baku, the capital of Azerbaijan and Ceyhan, a port on the south-eas ...
(BTC) became operational in May 2006 and extends more than through the territories of Azerbaijan, Georgia, and Turkey. The BTC is designed to transport up to 50 million tons of crude oil annually and carries oil from the Caspian Sea oilfields to global markets. The South Caucasus Pipeline
The South Caucasus Pipeline (also known as Baku–Tbilisi–Erzurum Pipeline, BTE pipeline, or Shah Deniz Pipeline) is a natural gas pipeline from the Shah Deniz gas field in the Azerbaijan sector of the Caspian Sea to Turkey. It runs parallel to ...
, also stretching through the territory of Azerbaijan, Georgia, and Turkey, became operational at the end of 2006 and offers additional gas supplies to the European market from the Shah Deniz gas field
Shah Deniz gas field ( az, Şahdəniz) is the largest natural gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amo ...
. Shah Deniz is expected to produce up to 296 billion cubic meters of natural gas per year. Azerbaijan also plays a major role in the EU-sponsored Silk Road Project.
In 2002, the Azerbaijani government established the Ministry of Transport with a broad range of policy and regulatory functions. In the same year, the country became a member of the Vienna Convention on Road Traffic
The Convention on Road Traffic, commonly known as the Vienna Convention on Road Traffic, is an international treaty designed to facilitate international road traffic and to increase road safety by establishing standard traffic rules among the co ...
. Priorities are upgrading the transport network and improving transportation services to better facilitate the development of other sectors of the economy.
The 2012 construction of Kars–Tbilisi–Baku railway was meant to improve transportation between Asia and Europe by connecting the railways of China and Kazakhstan in the east to the European railway system in the west via Turkey. In 2010 Broad-gauge
A broad-gauge railway is a railway with a track gauge (the distance between the rails) broader than the used by standard-gauge railways.
Broad gauge of , commonly known as Russian gauge, is the dominant track gauge in former Soviet Union ( CI ...
railways and electrified railways stretched for and respectively. By 2010, there were 35 airports and one heliport
A heliport is a small airport suitable for use by helicopters and some other vertical lift aircraft. Designated heliports typically contain one or more touchdown and liftoff areas and may also have limited facilities such as fuel or hangars. I ...
.
Science and technology
 In the 21st century, a new oil and gas boom helped improve the situation in Azerbaijan's science and technology sectors. The government launched a campaign aimed at modernization and
In the 21st century, a new oil and gas boom helped improve the situation in Azerbaijan's science and technology sectors. The government launched a campaign aimed at modernization and innovation
Innovation is the practical implementation of ideas that result in the introduction of new goods or service (economics), services or improvement in offering goods or services. ISO TC 279 in the standard ISO 56000:2020 defines innovation as "a ...
. The government estimates that profits from the information technology and communication industry will grow and become comparable to those from oil production.
Azerbaijan has a large and steadily growing Internet sector, mostly uninfluenced by the financial crisis of 2007–2008
Finance is the study and discipline of money, currency and capital assets. It is related to, but not synonymous with economics, the study of production, distribution, and consumption of money, assets, goods and services (the discipline of ...
; rapid growth is forecast for at least five more years. Azerbaijan was ranked 80th in the Global Innovation Index
The Global Innovation Index is an annual ranking of countries by their capacity for, and success in, innovation, published by the World Intellectual Property Organization. It was started in 2007 by INSEAD and ''World Business'', a British maga ...
in 2021, up from 84th in 2019.
The country has also been making progress in developing its telecoms sector. The Ministry of Communications & Information Technologies (MCIT) and an operator through its role in Aztelekom are both policy-makers and regulators. Public payphones are available for local calls and require the purchase of a token from the telephone exchange or some shops and kiosks. Tokens allow a call of indefinite duration. , there were 1,397,000 main telephone lines and 1,485,000 internet users. There are four GSM providers: Azercell
Azercell is an Azerbaijani telecommunications company based in Baku. It is the largest mobile network operator in Azerbaijan.
Company background
Azercell Telecom LLC was established on 19 January 1996.
Azercell Telecom started its activitie ...
, , Azerfon (Nar Mobile
Nar is a brand for commercial activities of Azerfon, a mobile telecommunications company, located in Baku, Azerbaijan.
Company background
Azerfon LLC launched its commercial activities on 21 March 2007 under brand name Nar Mobile.
Today the n ...
), Nakhtel mobile network operators and one CDMA
Code-division multiple access (CDMA) is a channel access method used by various radio communication technologies. CDMA is an example of multiple access, where several transmitters can send information simultaneously over a single communication ...
.
In the 21st century a number of prominent Azerbaijani geodynamics
Geodynamics is a subfield of geophysics dealing with dynamics of the Earth. It applies physics, chemistry and mathematics to the understanding of how mantle convection leads to plate tectonics and geologic phenomena such as seafloor spreading, ...
and geotectonics scientists, inspired by the fundamental works of Elchin Khalilov and others, designed hundreds of earthquake prediction stations and earthquake-resistant buildings that now constitute the bulk of The Republican Center of Seismic Service.
The Azerbaijan National Aerospace Agency
Azerbaijan National Aerospace Agency (MAKA; az, Azərbaycan Milli Aerokosmik Agentliyi) is a governmental body that coordinates all Azerbaijani space research programs with scientific and commercial goals. National Aerospace Agency has been opera ...
launched its first satellite AzerSat 1 into orbit on 7 February 2013 from Guiana Space Centre
The Guiana Space Centre (french: links=no, Centre spatial guyanais; CSG), also called Europe's Spaceport, is a European spaceport to the northwest of Kourou in French Guiana, a region of France in South America. Kourou is located approximat ...
in French Guiana at orbital positions 46° East. The satellite covers Europe and a significant part of Asia and Africa and serves the transmission of TV and radio broadcasting as well as the Internet. The launching of a satellite into orbit is Azerbaijan's first step in realizing its goal of becoming a nation with its own space industry, capable of successfully implementing more projects in the future.
Demographics
 As of March 2022, 52.9% of Azerbaijan's total population of 10,164,464 is urban, with the remaining 47.1% being rural. In January 2019, the 50.1% of the total population was female. The
As of March 2022, 52.9% of Azerbaijan's total population of 10,164,464 is urban, with the remaining 47.1% being rural. In January 2019, the 50.1% of the total population was female. The sex ratio
The sex ratio (or gender ratio) is usually defined as the ratio of males to females in a population. As explained by Fisher's principle, for evolutionary reasons this is typically about 1:1 in species which reproduce sexually. Many species de ...
in the same year was 0.99 males per female.
The 2011 population growth-rate was 0.85%, compared to 1.09% worldwide. A significant factor restricting population growth is a high level of migration. In 2011 Azerbaijan saw a migration of −1.14/1,000 people.
The Azerbaijani diaspora
The Azerbaijani diaspora are the communities of Azerbaijanis living outside the places of their ethnic origin: Azerbaijan and the Iranian region of Azerbaijan.
According to Ethnologue, there were over 1 million Azerbaijani-speakers of the north ...
is found in 42 countries and in turn there are many centers for ethnic minorities inside Azerbaijan, including the German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ger ...
cultural society "Karelhaus", Slavic cultural center, Azerbaijani-Israeli community, Kurdish cultural center, International Talysh Association, Lezgin national center "Samur", Azerbaijani-Tatar
The Tatars ()Tatar
in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different community,
Stat.gov.az. Retrieved 1 July 2017.
in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different community,
Crimean Tatars
, flag = Flag of the Crimean Tatar people.svg
, flag_caption = Flag of Crimean Tatars
, image = Love, Peace, Traditions.jpg
, caption = Crimean Tatars in traditional clothing in front of the Khan's Palace ...
society, etc.
In total, Azerbaijan has 78 cities, 63 city districts, and one special legal status city. 261 urban-type settlements and 4248 villages follow these.Azərbaycanın əhalisi , Azərbaycan Respublikasının Dövlət Statistika KomitəsiStat.gov.az. Retrieved 1 July 2017.
Ethnicity
The ethnic composition of the population according to the 2009 population census: 91.6%Azerbaijanis
Azerbaijanis (; az, Azərbaycanlılar, ), Azeris ( az, Azərilər, ), or Azerbaijani Turks ( az, Azərbaycan Türkləri, ) are a Turkic peoples, Turkic people living mainly in Azerbaijan (Iran), northwestern Iran and the Azerbaijan, Republi ...
, 2.0% Lezgins
Lezgins or Leks ( lez, Лезгияр, Лекьер. lezgijar) are a Northeast Caucasian ethnic group native predominantly to southern Dagestan, a republic of Russia, and northeastern Azerbaijan. The Lezgin are predominantly Sunni Muslims and ...
, 1.4% Armenians
Armenians ( hy, հայեր, '' hayer'' ) are an ethnic group native to the Armenian highlands of Western Asia. Armenians constitute the main population of Armenia and the ''de facto'' independent Artsakh. There is a wide-ranging diaspora ...
(almost all Armenians live in the break-away region of Nagorno-Karabakh
Nagorno-Karabakh ( ) is a landlocked region in the South Caucasus, within the mountainous range of Karabakh, lying between Lower Karabakh and Syunik, and covering the southeastern range of the Lesser Caucasus mountains. The region is mos ...
), 1.3% Russians
, native_name_lang = ru
, image =
, caption =
, population =
, popplace =
118 million Russians in the Russian Federation (2002 ''Winkler Prins'' estimate)
, region1 =
, pop1 ...
, 1.3% Talysh, 0.6% Avars, 0.4% Turks
Turk or Turks may refer to:
Communities and ethnic groups
* Turkic peoples, a collection of ethnic groups who speak Turkic languages
* Turkish people, or the Turks, a Turkic ethnic group and nation
* Turkish citizen, a citizen of the Republic ...
, 0.3% Tatars
The Tatars ()Tatar
in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different , 0.3% Tats, 0.2%
UN Data. Retrieved 27 August 2016. Russian and
 Azerbaijan is considered the most secular Muslim-majority country. Around 97% of the population are Muslims. 85% of the Muslims are
Azerbaijan is considered the most secular Muslim-majority country. Around 97% of the population are Muslims. 85% of the Muslims are
(PDF). Retrieved 1 July 2017. the Republic of Azerbaijan has the second-highest proportion of Shia Muslims of any country in the world. Other faiths are practised by the country's various ethnic groups. Under article 48 of its
 A relatively high percentage of Azerbaijanis have obtained some form of higher education, most notably in scientific and technical subjects. In the Soviet era, literacy and average education levels rose dramatically from their very low starting point, despite two changes in the standard alphabet, from
A relatively high percentage of Azerbaijanis have obtained some form of higher education, most notably in scientific and technical subjects. In the Soviet era, literacy and average education levels rose dramatically from their very low starting point, despite two changes in the standard alphabet, from
 Music of Azerbaijan builds on folk traditions that reach back nearly a thousand years. For centuries Azerbaijani music has evolved under the badge of
Music of Azerbaijan builds on folk traditions that reach back nearly a thousand years. For centuries Azerbaijani music has evolved under the badge of 
– ''European University Institute, Florence, Italy'' (retrieved 10 August 2006). Ashiqs' songs are semi-improvised around common bases. Azerbaijan's ashiq art was included in the list of Intangible Cultural Heritage by the UNESCO on 30 September 2009. Since the mid-1960s, Western-influenced Azerbaijani pop music, in its various forms, that has been growing in popularity in Azerbaijan, while genres such as Azerbaijani rock, rock and Azerbaijani hip hop, hip hop are widely produced and enjoyed. Azerbaijani pop and Azerbaijani folk music arose with the international popularity of performers like Alim Qasimov, Rashid Behbudov, Vagif Mustafazadeh, Muslim Magomayev (musician), Muslim Magomayev, Shovkat Alakbarova and Rubaba Muradova. Azerbaijan is an enthusiastic participant in the Eurovision Song Contest. Azerbaijan made its debut appearance at the 2008 Eurovision Song Contest 2008, Eurovision Song Contest. The country's Azerbaijan in the Eurovision Song Contest 2009, entry gained third place in 2009 and fifth the following year. Eldar & Nigar, Ell and Nikki won the first place at the Eurovision Song Contest 2011 with the song "Running Scared (Eldar & Nigar song), Running Scared", entitling Azerbaijan to host the contest in Eurovision Song Contest 2012, 2012, in Baku. They have qualified for every Grand Final up until the Eurovision Song Contest 2018, 2018 edition of the contest, entering with X My Heart (song), X My Heart by singer Aisel (singer), Aisel. There are dozens of Azerbaijani folk dances. They are performed at formal celebrations and the dancers wear national clothes like the
 Among the medieval authors born within the territorial limits of modern Azerbaijani Republic was Persian poet and philosopher Nizami Ganjavi, Nizami, called Ganjavi after his place of birth,
Among the medieval authors born within the territorial limits of modern Azerbaijani Republic was Persian poet and philosopher Nizami Ganjavi, Nizami, called Ganjavi after his place of birth,
Encyclopædia Iranica , Articles
Retrieved October 2010. "The Ketāb-e Dede Qorqut, which is a collection of twelve stories reflecting the oral traditions of the Turkmens in the 15th-century eastern Anatolia, is also called Oḡuz-nāma" It is a collection of 12 stories reflecting the oral tradition of Oghuz nomads. The 16th-century poet, Muhammed Fuzuli produced his timeless philosophical and lyrical ''Qazals'' in Arabic, Persian, and Azerbaijani. Benefiting immensely from the fine literary traditions of his environment, and building upon the legacy of his predecessors, Fuzuli was destined to become the leading literary figure of his society. His major works include ''The Divan of Ghazals'' and ''The Qasidas''. In the same century, Azerbaijani literature further flourished with the development of Ashik ( az, Aşıq) poetic genre of bards. During the same period, under the pen-name of Khatāī ( ar, خطائی for ''sinner'') Shah Ismail I wrote about 1400 verses in Azerbaijani, which were later published as his ''Divan''. A unique literary style known as ''qoshma'' ( az, qoşma for ''improvisation'') was introduced in this period, and developed by Shah Ismail and later by his son and successor, Shah
 Azerbaijanis have a rich and distinctive culture, a major part of which is decorative art, decorative and applied art. This art form is represented by a wide range of handicrafts, such as chasing, jeweling, engraving in metal, carving in wood, stone, bone, carpet-making, lasing, pattern weaving and printing, and knitting and embroidery. Each of these types of decorative art, evidence of the endowments of the Azerbaijan nation, is very much in favor here. Many interesting facts pertaining to the development of arts and crafts in Azerbaijan were reported by numerous merchants, travelers, and diplomats who had visited these places at different times.
The Azerbaijani rug, Azerbaijani carpet is a traditional handmade textile of various sizes, with a dense texture and a pile or pile-less surface, whose patterns are characteristic of Azerbaijan's many carpet-making regions. In November 2010 the Azerbaijani carpet was proclaimed a Masterpieces of the Oral and Intangible Heritage of Humanity, Masterpiece of Intangible Heritage by
Azerbaijanis have a rich and distinctive culture, a major part of which is decorative art, decorative and applied art. This art form is represented by a wide range of handicrafts, such as chasing, jeweling, engraving in metal, carving in wood, stone, bone, carpet-making, lasing, pattern weaving and printing, and knitting and embroidery. Each of these types of decorative art, evidence of the endowments of the Azerbaijan nation, is very much in favor here. Many interesting facts pertaining to the development of arts and crafts in Azerbaijan were reported by numerous merchants, travelers, and diplomats who had visited these places at different times.
The Azerbaijani rug, Azerbaijani carpet is a traditional handmade textile of various sizes, with a dense texture and a pile or pile-less surface, whose patterns are characteristic of Azerbaijan's many carpet-making regions. In November 2010 the Azerbaijani carpet was proclaimed a Masterpieces of the Oral and Intangible Heritage of Humanity, Masterpiece of Intangible Heritage by  Azerbaijan has been since ancient times known as a center of a large variety of crafts. The archeological dig on the territory of Azerbaijan testifies to the well-developed agriculture, stock raising, metalworking, pottery, ceramics, and carpet-weaving that date as far back as to the 2nd millennium BC. Archeological sites in Dashbulaq, Hasansu, Zayamchai, and Tovuzchai uncovered from the BTC pipeline have revealed early Iron Age artifacts.
Azerbaijani carpets can be categorized under several large groups and a multitude of subgroups. Scientific research of the Azerbaijani carpet is connected with the name of Latif Karimov, a prominent scientist and artist. It was his classification that related the four large groups of carpets with the four geographical zones of Azerbaijan, Guba-Shirvan, Ganja-Kazakh, Karabakh and Tabriz.
Azerbaijan has been since ancient times known as a center of a large variety of crafts. The archeological dig on the territory of Azerbaijan testifies to the well-developed agriculture, stock raising, metalworking, pottery, ceramics, and carpet-weaving that date as far back as to the 2nd millennium BC. Archeological sites in Dashbulaq, Hasansu, Zayamchai, and Tovuzchai uncovered from the BTC pipeline have revealed early Iron Age artifacts.
Azerbaijani carpets can be categorized under several large groups and a multitude of subgroups. Scientific research of the Azerbaijani carpet is connected with the name of Latif Karimov, a prominent scientist and artist. It was his classification that related the four large groups of carpets with the four geographical zones of Azerbaijan, Guba-Shirvan, Ganja-Kazakh, Karabakh and Tabriz.
 The traditional cuisine is famous for an abundance of vegetables and greens used seasonally in the dishes. Fresh herbs, including mint, cilantro (coriander), dill, basil, parsley, tarragon, leeks, chives, thyme, marjoram, green onion, and watercress, are very popular and often accompany main dishes on the table. Climatic diversity and fertility of the land are reflected in the national dishes, which are based on fish from the
The traditional cuisine is famous for an abundance of vegetables and greens used seasonally in the dishes. Fresh herbs, including mint, cilantro (coriander), dill, basil, parsley, tarragon, leeks, chives, thyme, marjoram, green onion, and watercress, are very popular and often accompany main dishes on the table. Climatic diversity and fertility of the land are reflected in the national dishes, which are based on fish from the
 Azerbaijani architecture typically combines elements of Eastern world, East and Western culture, West. Azerbaijani architecture has heavy influences from Persian architecture. Many ancient architectural treasures such as the Maiden Tower (Baku), Maiden Tower and Palace of the Shirvanshahs in the Baku, Walled City of Baku survive in modern Azerbaijan. Entries submitted on the UNESCO World Heritage tentative list include the Ateshgah of Baku, Momine Khatun Mausoleum, Hirkan National Park, Binagadi asphalt lake, Lökbatan Mud Volcano, Shusha State Historical and Architectural Reserve, Baku Stage Mountain, Caspian Shore Defensive Constructions, Ordubad National Reserve and the Palace of Shaki Khans.
Among other architectural treasures are Quadrangular castle (Mardakan), Quadrangular Castle in Mardakan, Parigala in Yuxarı Çardaqlar, Yukhary Chardaglar, a number of bridges spanning the Aras River, and several mausoleums. In the 19th and early 20th centuries, little monumental architecture was created, but distinctive residences were built in Baku and elsewhere. Among the most recent architectural monuments, the Baku Metro, Baku subways are noted for their lavish decor.
The task for modern Azerbaijani architecture is diverse application of modern aesthetics, the search for an architect's own artistic style and inclusion of the existing historico-cultural environment. Major projects such as Heydar Aliyev Cultural Center, Flame Towers, Baku Crystal Hall, Baku White City and SOCAR Tower have transformed the country's skyline and promotes its contemporary identity.
Azerbaijani architecture typically combines elements of Eastern world, East and Western culture, West. Azerbaijani architecture has heavy influences from Persian architecture. Many ancient architectural treasures such as the Maiden Tower (Baku), Maiden Tower and Palace of the Shirvanshahs in the Baku, Walled City of Baku survive in modern Azerbaijan. Entries submitted on the UNESCO World Heritage tentative list include the Ateshgah of Baku, Momine Khatun Mausoleum, Hirkan National Park, Binagadi asphalt lake, Lökbatan Mud Volcano, Shusha State Historical and Architectural Reserve, Baku Stage Mountain, Caspian Shore Defensive Constructions, Ordubad National Reserve and the Palace of Shaki Khans.
Among other architectural treasures are Quadrangular castle (Mardakan), Quadrangular Castle in Mardakan, Parigala in Yuxarı Çardaqlar, Yukhary Chardaglar, a number of bridges spanning the Aras River, and several mausoleums. In the 19th and early 20th centuries, little monumental architecture was created, but distinctive residences were built in Baku and elsewhere. Among the most recent architectural monuments, the Baku Metro, Baku subways are noted for their lavish decor.
The task for modern Azerbaijani architecture is diverse application of modern aesthetics, the search for an architect's own artistic style and inclusion of the existing historico-cultural environment. Major projects such as Heydar Aliyev Cultural Center, Flame Towers, Baku Crystal Hall, Baku White City and SOCAR Tower have transformed the country's skyline and promotes its contemporary identity.
 The Gamigaya Petroglyphs, which date back to the 1st to 4th millennium BC, are located in Azerbaijan's Ordubad District. They consist of some 1500 dislodged and carved rock paintings with images of deer, goats, bulls, dogs, snakes, birds, fantastic beings, and people, carriages, and various symbols were found on basalt rocks. Norwegian ethnographer and adventurer Thor Heyerdahl was convinced that people from the area went to Scandinavia in about 100 AD, took their boat building skills with them, and transmuted them into the Viking boats in Northern Europe.
Over the centuries, Azerbaijani art has gone through many stylistic changes. Azerbaijani painting is traditionally characterized by a warmth of colour and light, as exemplified in the works of Azim Azimzade and Bahruz Kangarli, and a preoccupation with religious figures and cultural motifs. Azerbaijani painting enjoyed preeminence in Caucasus for hundreds of years, from the Romanesque art, Romanesque and Culture of the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman periods, and through the Socialist realism, Soviet and Baroque periods, the latter two of which saw fruition in Azerbaijan. Other notable artists who fall within these periods include Sattar Bahlulzade, Togrul Narimanbekov, Tahir Salahov, Alakbar Rezaguliyev, Mirza Gadim Iravani, Mikayil Abdullayev and Boyukagha Mirzazade.
The Gamigaya Petroglyphs, which date back to the 1st to 4th millennium BC, are located in Azerbaijan's Ordubad District. They consist of some 1500 dislodged and carved rock paintings with images of deer, goats, bulls, dogs, snakes, birds, fantastic beings, and people, carriages, and various symbols were found on basalt rocks. Norwegian ethnographer and adventurer Thor Heyerdahl was convinced that people from the area went to Scandinavia in about 100 AD, took their boat building skills with them, and transmuted them into the Viking boats in Northern Europe.
Over the centuries, Azerbaijani art has gone through many stylistic changes. Azerbaijani painting is traditionally characterized by a warmth of colour and light, as exemplified in the works of Azim Azimzade and Bahruz Kangarli, and a preoccupation with religious figures and cultural motifs. Azerbaijani painting enjoyed preeminence in Caucasus for hundreds of years, from the Romanesque art, Romanesque and Culture of the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman periods, and through the Socialist realism, Soviet and Baroque periods, the latter two of which saw fruition in Azerbaijan. Other notable artists who fall within these periods include Sattar Bahlulzade, Togrul Narimanbekov, Tahir Salahov, Alakbar Rezaguliyev, Mirza Gadim Iravani, Mikayil Abdullayev and Boyukagha Mirzazade.
File:Shaki khan palace interier.jpg, Usta Gambar Karabakhi – Tree of Life
(Palace of Shaki Khans) File:Portrait of sitting woman by Irevani.jpg, Mirza Gadim Iravani – Portrait of sitting woman
(National Art Museum of Azerbaijan) File:Dağ mənzərəsi – Bəhruz Kəngərli.jpg, Bahruz Kangarli – Landscape with mountains
(National Art Museum of Azerbaijan) File:Ruins of Reichstag.jpg, Azim Azimzade – Ruins of Reichstag
(National Art Museum of Azerbaijan)
 The film industry in Azerbaijan dates back to 1898. Azerbaijan was among the first countries involved in cinematography, with the apparatus first showing up in Baku.Celebrating 100 Years in Film, not 80
The film industry in Azerbaijan dates back to 1898. Azerbaijan was among the first countries involved in cinematography, with the apparatus first showing up in Baku.Celebrating 100 Years in Film, not 80
by Aydin Kazimzade. Azerbaijan International, Autumn 1997 In 1919, during the
 The Constitution of Azerbaijan claims to guarantee freedom of speech, but this is denied in practice. After several years of decline in press and media freedom, in 2014, the media environment in Azerbaijan deteriorated rapidly under a governmental campaign to silence any opposition and criticism, even while the country led the Committee of Ministers of the Council of Europe (May–November 2014). Spurious legal charges and impunity in violence against journalists have remained the norm.Parliamentary Assembly of the Council of Europe
The Constitution of Azerbaijan claims to guarantee freedom of speech, but this is denied in practice. After several years of decline in press and media freedom, in 2014, the media environment in Azerbaijan deteriorated rapidly under a governmental campaign to silence any opposition and criticism, even while the country led the Committee of Ministers of the Council of Europe (May–November 2014). Spurious legal charges and impunity in violence against journalists have remained the norm.Parliamentary Assembly of the Council of Europe
The Protection of media freedom in Europe
.Background report prepared by Mr William Horsley, special representative for media freedom of the Association of European Journalists All foreign broadcasts are banned in the country.
Azerbaijan
2015 Press Freedom report According to the 2013
 Azerbaijan Women's Volleyball Super League is one of the strongest women leagues in the world. Its women's national team came fourth at the 2005 Women's European Volleyball Championship, 2005 European Championship. Over the last years, clubs like Rabita Baku and Azerrail Baku achieved great success at European cups. Azerbaijani volleyball players include likes of Valeriya Korotenko, Oksana Parkhomenko, Inessa Korkmaz, Natalya Mammadova and Alla Hasanova.
Other Azerbaijani athletes are Namig Abdullayev, Toghrul Asgarov, Rovshan Bayramov, Sharif Sharifov, Mariya Stadnik and Farid Mansurov in Amateur wrestling, wrestling, Nazim Huseynov, Elnur Mammadli, Elkhan Mammadov (judoka), Elkhan Mammadov and Rustam Orujov in judo, Rafael Aghayev in karate, Magomedrasul Majidov and Aghasi Mammadov in boxing, Nizami Pashayev in Olympic weightlifting, Azad Asgarov in pankration, Eduard Mammadov in kickboxing, and K-1 fighter Zabit Samedov.
Azerbaijan has a Baku City Circuit, Formula One race-track, made in June 2012, and the country hosted its first 2016 European Grand Prix, Formula One Grand Prix on 19 June 2016 and the Azerbaijan Grand Prix in 2017, 2018, 2019, 2021 and 2022. Other annual sporting events held in the country are the Baku Cup tennis tournament and the Tour d'Azerbaïdjan cycling race.
Azerbaijan hosted several major sport competitions since the late 2000s, including the 2013 F1 Powerboat World Championship season, 2013 F1 Powerboat World Championship, 2012 FIFA U-17 Women's World Cup, 2011 AIBA World Boxing Championships, 2010 European Wrestling Championships, 2009 Rhythmic Gymnastics European Championships, European Taekwondo Championships, 2014 European Taekwondo Championships, 2014 Rhythmic Gymnastics European Championships, and 42nd Chess Olympiad, 2016 World Chess Olympiad. On 8 December 2012, Baku was selected to host the 2015 European Games, the first to be held in the competition's history. Baku also hosted the fourth Islamic Solidarity Games in 2017 and the 2019 European Youth Summer Olympic Festival, and it is also one of the hosts of UEFA Euro 2020, which because of Covid-19 is being held in 2021.
Azerbaijan Women's Volleyball Super League is one of the strongest women leagues in the world. Its women's national team came fourth at the 2005 Women's European Volleyball Championship, 2005 European Championship. Over the last years, clubs like Rabita Baku and Azerrail Baku achieved great success at European cups. Azerbaijani volleyball players include likes of Valeriya Korotenko, Oksana Parkhomenko, Inessa Korkmaz, Natalya Mammadova and Alla Hasanova.
Other Azerbaijani athletes are Namig Abdullayev, Toghrul Asgarov, Rovshan Bayramov, Sharif Sharifov, Mariya Stadnik and Farid Mansurov in Amateur wrestling, wrestling, Nazim Huseynov, Elnur Mammadli, Elkhan Mammadov (judoka), Elkhan Mammadov and Rustam Orujov in judo, Rafael Aghayev in karate, Magomedrasul Majidov and Aghasi Mammadov in boxing, Nizami Pashayev in Olympic weightlifting, Azad Asgarov in pankration, Eduard Mammadov in kickboxing, and K-1 fighter Zabit Samedov.
Azerbaijan has a Baku City Circuit, Formula One race-track, made in June 2012, and the country hosted its first 2016 European Grand Prix, Formula One Grand Prix on 19 June 2016 and the Azerbaijan Grand Prix in 2017, 2018, 2019, 2021 and 2022. Other annual sporting events held in the country are the Baku Cup tennis tournament and the Tour d'Azerbaïdjan cycling race.
Azerbaijan hosted several major sport competitions since the late 2000s, including the 2013 F1 Powerboat World Championship season, 2013 F1 Powerboat World Championship, 2012 FIFA U-17 Women's World Cup, 2011 AIBA World Boxing Championships, 2010 European Wrestling Championships, 2009 Rhythmic Gymnastics European Championships, European Taekwondo Championships, 2014 European Taekwondo Championships, 2014 Rhythmic Gymnastics European Championships, and 42nd Chess Olympiad, 2016 World Chess Olympiad. On 8 December 2012, Baku was selected to host the 2015 European Games, the first to be held in the competition's history. Baku also hosted the fourth Islamic Solidarity Games in 2017 and the 2019 European Youth Summer Olympic Festival, and it is also one of the hosts of UEFA Euro 2020, which because of Covid-19 is being held in 2021.
online
* Thomas Goltz, Goltz, Thomas. ''Azerbaijan Diary : A Rogue Reporter's Adventures in an Oil-Rich, War-Torn, Post-Soviet Republic''. M E Sharpe (1998). * Habibov, Nazim, Betty Jo Barrett, and Elena Chernyak. "Understanding women's empowerment and its determinants in post-communist countries: Results of Azerbaijan national survey." ''Women's Studies International Forum.'' Vol. 62. Pergamon, 2017. * Olukbasi, Suha. ''Azerbaijan: A Political History''. I.B. Tauris (2011). Focus on post-Soviet era.
Azerbaijan International
Heydar Aliyev Foundation
*
Azerbaijan
''The World Factbook''. Central Intelligence Agency.
Azerbaijan
at University of Colorado at Boulder
Country profile
from BBC
Key Development Forecasts for Azerbaijan
from International Futures
Visions of Azerbaijan Journal
of The European Azerbaijan Society * *
President of Azerbaijan website
Azerbaijan State Statistical Committee
United Nations Office in Azerbaijan
Network NEWS Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan Today
Trend News Agency
News.Az
Azerbaijan Tourism Portal
*
Travel in Azerbaijan
in Visions of Azerbaijan Journal {{Good article Azerbaijan, Caucasus Countries in Asia Countries in Europe Eastern European countries Western Asian countries Landlocked countries South Caucasus Republics Member states of the Commonwealth of Independent States Member states of the Council of Europe Member states of the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation Member states of the United Nations States and territories established in 1991 1991 establishments in Asia 1991 establishments in Europe Azerbaijani-speaking countries and territories Russian-speaking countries and territories Transcontinental countries Members of the International Organization of Turkic Culture Member states of the Organization of Turkic States Turkic states
in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different , 0.3% Tats, 0.2%
Ukrainians
Ukrainians ( uk, Українці, Ukraintsi, ) are an East Slavic ethnic group native to Ukraine. They are the seventh-largest nation in Europe. The native language of the Ukrainians is Ukrainian. The majority of Ukrainians are Eastern Or ...
, 0.1% Tsakhurs
The Tsakhur or Caxur ( lez, ЦIахурар, az, Saxurlar, russian: Цахуры) people are a Lezgin sub-ethnic group of northern Azerbaijan and southern Dagestan (Russia). The group numbers around 30,000 people and are called ''yiqy'' (pl. ''yiq ...
, 0.1% Georgians, 0.1% Jew
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""T ...
s, 0.1% Kurds ug:كۇردلار
Kurds ( ku, کورد ,Kurd, italic=yes, rtl=yes) or Kurdish people are an Iranian peoples, Iranian ethnic group native to the mountainous region of Kurdistan in Western Asia, which spans southeastern Turkey, northwestern Ir ...
, other 0.2%.
Languages
The official language isAzerbaijani
Azerbaijani may refer to:
* Something of, or related to Azerbaijan
* Azerbaijanis
* Azerbaijani language
See also
* Azerbaijan (disambiguation)
* Azeri (disambiguation)
* Azerbaijani cuisine
* Culture of Azerbaijan
The culture of Azerbaijan ...
, which is a Turkic language
The Turkic languages are a language family of over 35 documented languages, spoken by the Turkic peoples of Eurasia from Eastern Europe and Southern Europe to Central Asia, East Asia, North Asia (Siberia), and Western Asia. The Turkic languag ...
. Azerbaijani is spoken by approximately 92% of the population as a mother tongue
A first language, native tongue, native language, mother tongue or L1 is the first language or dialect that a person has been exposed to from birth or within the critical period. In some countries, the term ''native language'' or ''mother tong ...
.Population by language, sex and urban/rural residenceUN Data. Retrieved 27 August 2016. Russian and
Armenian
Armenian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Armenia, a country in the South Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Armenians, the national people of Armenia, or people of Armenian descent
** Armenian Diaspora, Armenian communities across the ...
(only in Nagorno-Karabakh) are also spoken, and each are the mother tongue of around 1.5% of the population respectively. There are a dozen other minority languages spoken natively in the country. Avar, Budukh, Georgian, Juhuri, Khinalug, Kryts, Lezgin, Rutul
Rutul may refer to:
* Rutul people, an ethnic group in the Republic of Dagestan, Russia
*Rutul language, their Lezgic language
*Rutul (rural locality), a rural locality (a ''selo'') in the Republic of Dagestan, Russia
See also
*Rutuli, members of ...
, Talysh, Tat, Tsakhur, and Udi are all spoken by small minorities. Some of these language communities are very small and their numbers are decreasing. Armenian was the majority language in Nagorno-Karabakh with around 76% in 1989. After the first Nagorno-Karabakh war, the population is almost exclusively Armenian at around 95%.
Religion
 Azerbaijan is considered the most secular Muslim-majority country. Around 97% of the population are Muslims. 85% of the Muslims are
Azerbaijan is considered the most secular Muslim-majority country. Around 97% of the population are Muslims. 85% of the Muslims are Shia
Shīʿa Islam or Shīʿīsm is the second-largest branch of Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the ...
and 15% Sunni;Administrative Department of the President of the Republic of Azerbaijan – Presidential Library – Religion(PDF). Retrieved 1 July 2017. the Republic of Azerbaijan has the second-highest proportion of Shia Muslims of any country in the world. Other faiths are practised by the country's various ethnic groups. Under article 48 of its
Constitution
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organisation or other type of entity and commonly determine how that entity is to be governed.
When these princip ...
, Azerbaijan is a secular state and ensures religious freedom. In a 2006–2008 Gallup
Gallup may refer to:
*Gallup, Inc., a firm founded by George Gallup, well known for its opinion poll
*Gallup (surname), a surname
*Gallup, New Mexico, a city in New Mexico, United States
**Gallup station, an Amtrak train in downtown Gallup, New Me ...
poll, only 21% of respondents from Azerbaijan stated that religion is an important part of their daily lives.
Of the nation's religious minorities, the estimated 280,000 Christians (3.1%) are mostly Russian and Georgian Orthodox and Armenian Apostolic (almost all Armenians live in the break-away region of Nagorno-Karabakh). In 2003, there were 250 Roman Catholics
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
. Other Christian denominations as of 2002 include Lutherans
Lutheranism is one of the largest branches of Protestantism, identifying primarily with the theology of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German monk and Protestant Reformers, reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practice of the Cathol ...
, Baptists and Molokan
The Molokans ( rus, молокан, p=məlɐˈkan or , "dairy-eater") are a Spiritual Christian sect that evolved from Eastern Orthodoxy in the East Slavic lands. Their traditions—especially dairy consumption during Christian fasts—did no ...
s. There is also a small Protestant
Protestantism is a Christian denomination, branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Reformation, Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century agai ...
community. Azerbaijan also has an ancient Jewish
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
population with a 2,000-year history; Jewish organizations estimate that 12,000 Jews remain in Azerbaijan, which is home to the only Jewish-majority town outside of Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
and the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., federal district, five ma ...
. Azerbaijan also is home to members of the Baháʼí, Hare Krishna and Jehovah's Witnesses
Jehovah's Witnesses is a millenarian restorationist Christian denomination with nontrinitarian beliefs distinct from mainstream Christianity. The group reports a worldwide membership of approximately 8.7 million adherents involved ...
communities, as well as adherents of the other religious communities. Some religious communities have been unofficially restricted from religious freedom. A U.S. State Department
The United States Department of State (DOS), or State Department, is an executive department of the U.S. federal government responsible for the country's foreign policy and relations. Equivalent to the ministry of foreign affairs of other nati ...
report on the matter mentions detention of members of certain Muslim and Christian groups, and many groups have difficulty registering with the agency who regulates religion, The State Committee on Religious Associations of the Republic of Azerbaijan
The State Committee on Religious Associations of the Republic of Azerbaijan () is a central executive body which ensures implementation of the state policy and laws in the field of religion. The State Committee was established on June 21, 2001.
St ...
(SCWRA).
Education
 A relatively high percentage of Azerbaijanis have obtained some form of higher education, most notably in scientific and technical subjects. In the Soviet era, literacy and average education levels rose dramatically from their very low starting point, despite two changes in the standard alphabet, from
A relatively high percentage of Azerbaijanis have obtained some form of higher education, most notably in scientific and technical subjects. In the Soviet era, literacy and average education levels rose dramatically from their very low starting point, despite two changes in the standard alphabet, from Perso-Arabic script
The Persian alphabet ( fa, الفبای فارسی, Alefbâye Fârsi) is a writing system that is a version of the Arabic script used for the Persian language spoken in Iran (Western Persian) and Afghanistan ( Dari Persian) since the 7th cen ...
to Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power ...
in the 1920s and from Roman to Cyrillic in the 1930s. According to Soviet data, 100 percent of males and females (ages nine to forty-nine) were literate in 1970. According to the United Nations Development Program
The United Nations Development Programme (UNDP)french: Programme des Nations unies pour le développement, PNUD is a United Nations agency tasked with helping countries eliminate poverty and achieve sustainable economic growth and human de ...
Report 2009, the literacy rate in Azerbaijan is 99.5 percent.
Since independence, one of the first laws that Azerbaijan's Parliament passed to disassociate itself from the Soviet Union was to adopt a modified-Latin alphabet to replace Cyrillic. Other than that the Azerbaijani system has undergone little structural change. Initial alterations have included the reestablishment of religious education (banned during the Soviet period) and curriculum changes that have reemphasized the use of the Azerbaijani language and have eliminated ideological content. In addition to elementary schools, the education institutions include thousands of preschools, general secondary schools, and vocational schools, including specialized secondary schools and technical schools. Education through the ninth grade is compulsory.
Culture
The culture of Azerbaijan has developed as a result of many influences; that's why Azerbaijanis are, in many ways, bi-cultural. Today, national traditions are well preserved in the country despite Western influences, including globalized consumer culture. Some of the main elements of the Azerbaijani culture are: music, literature, folk dances and art, cuisine, architecture, cinematography andNovruz Bayram
Nowruz ( fa, نوروز, ; ), zh, 诺鲁孜节, ug, نەۋروز, ka, ნოვრუზ, ku, Newroz, he, נורוז, kk, Наурыз, ky, Нооруз, mn, Наурыз, ur, نوروز, tg, Наврӯз, tr, Nevruz, tk, Nowruz, ...
. The latter is derived from the traditional celebration of the New Year in the ancient Iranian religion of Zoroastrianism
Zoroastrianism is an Iranian religion and one of the world's oldest organized faiths, based on the teachings of the Iranian-speaking prophet Zoroaster. It has a dualistic cosmology of good and evil within the framework of a monotheistic ont ...
. Novruz is a family holiday.
The profile of Azerbaijan's population consists, as stated above, of Azerbaijanis, as well as other nationalities or ethnic groups, compactly living in various areas of the country. Azerbaijani national and traditional dresses are the Chokha
A chokha or ; ab, акәымжәы, akʷymzhʷy; ady, цые, tsiya; kbd, цей, tsei; fa, چوقا, chughā; hy, չուխայ, choukha(y); az, çuxa; krc, чепкен, çepken; kum, чепген, çepgen; nog, шепкен, şepken ...
and Papakhi. There are radio broadcasts in Russian, Georgian, Kurdish, Lezgian and Talysh languages, which are financed from the state budget. Some local radio stations in Balakan and Khachmaz organize broadcasts in Avar and Tat. In Baku several newspapers are published in Russian, Kurdish (''Dengi Kurd''), Lezgian (''Samur'') and Talysh languages. Jewish society "Sokhnut" publishes the newspaper ''Aziz''.
Music and folk dances
 Music of Azerbaijan builds on folk traditions that reach back nearly a thousand years. For centuries Azerbaijani music has evolved under the badge of
Music of Azerbaijan builds on folk traditions that reach back nearly a thousand years. For centuries Azerbaijani music has evolved under the badge of monody
In music, monody refers to a solo vocal style distinguished by having a single melodic line and instrumental accompaniment. Although such music is found in various cultures throughout history, the term is specifically applied to Italian song o ...
, producing rhythmically diverse melodies.Энциклопедический музыкальный словарь, 2-е изд., Москва, 1966 (''Encyclopedical Music Dictionary'' (1966), 2nd ed., Moscow) Azerbaijani music has a branchy mode system, where chromatization of major and minor
In Western music, the adjectives major and minor may describe a chord, scale, or key. As such, composition, movement, section, or phrase may be referred to by its key, including whether that key is major or minor.
Intervals
Some intervals ma ...
scales
Scale or scales may refer to:
Mathematics
* Scale (descriptive set theory), an object defined on a set of points
* Scale (ratio), the ratio of a linear dimension of a model to the corresponding dimension of the original
* Scale factor, a number ...
is of great importance. Among national musical instruments there are 14 string instruments, eight percussion instruments and six wind instruments. According to '' The Grove Dictionary of Music and Musicians'', "in terms of ethnicity, culture and religion the Azerbaijani are musically much closer to Iran than Turkey."

Mugham
Mugham ( az, Muğam) or Mughamat ( az, Muğamat) is one of the many classical compositions from Azerbaijan, contrasting with tasnif and ashik.
It is a highly complex art form that weds classical poetry and musical improvisation in specific ...
, meykhana
Meykhana ( az, Meyxana) is a distinctive Azerbaijani literary and folk rap tradition, consisting of an unaccompanied song performed by one or more people improvising on a particular subject. Meykhana is distinct from spoken word poetry in that ...
and ashiq art are among the many musical traditions of Azerbaijan. Mugham is usually a suite with poetry and instrumental interludes. When performing mugham, the singers have to transform their emotions into singing and music. In contrast to the mugham traditions of Central Asian countries, Azerbaijani mugham is more free-form and less rigid; it is often compared to the improvised field of jazz
Jazz is a music genre that originated in the African-American communities of New Orleans, Louisiana in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, with its roots in blues and ragtime. Since the 1920s Jazz Age, it has been recognized as a majo ...
. UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. I ...
proclaimed the Azerbaijani mugham tradition a Masterpiece of the Oral and Intangible Heritage of Humanity
The Proclamation of Masterpieces of the Oral and Intangible Heritage of Humanity was made by the Director-General of UNESCO starting in 2001 to raise awareness of intangible cultural heritage and encourage local communities to protect them and th ...
on 7 November 2003. Meykhana is a kind of traditional Azerbaijani distinctive folk unaccompanied song, usually performed by several people improvising on a particular subject.
Ashiq combines poetry, storytelling, dance, and vocal and instrumental music into a traditional performance art that stands as a symbol of Azerbaijani culture. It is a mystic troubadour or traveling bard who sings and plays the saz. This tradition has its origin in the Shamanistic
Shamanism is a religious practice that involves a practitioner (shaman) interacting with what they believe to be a Spirit world (Spiritualism), spirit world through Altered state of consciousness, altered states of consciousness, such as tranc ...
beliefs of ancient Turkic peoples
The Turkic peoples are a collection of diverse ethnic groups of West Asia, West, Central Asia, Central, East Asia, East, and North Asia as well as parts of Europe, who speak Turkic languages.. "Turkic peoples, any of various peoples whose memb ...
."ashik, shaman"– ''European University Institute, Florence, Italy'' (retrieved 10 August 2006). Ashiqs' songs are semi-improvised around common bases. Azerbaijan's ashiq art was included in the list of Intangible Cultural Heritage by the UNESCO on 30 September 2009. Since the mid-1960s, Western-influenced Azerbaijani pop music, in its various forms, that has been growing in popularity in Azerbaijan, while genres such as Azerbaijani rock, rock and Azerbaijani hip hop, hip hop are widely produced and enjoyed. Azerbaijani pop and Azerbaijani folk music arose with the international popularity of performers like Alim Qasimov, Rashid Behbudov, Vagif Mustafazadeh, Muslim Magomayev (musician), Muslim Magomayev, Shovkat Alakbarova and Rubaba Muradova. Azerbaijan is an enthusiastic participant in the Eurovision Song Contest. Azerbaijan made its debut appearance at the 2008 Eurovision Song Contest 2008, Eurovision Song Contest. The country's Azerbaijan in the Eurovision Song Contest 2009, entry gained third place in 2009 and fifth the following year. Eldar & Nigar, Ell and Nikki won the first place at the Eurovision Song Contest 2011 with the song "Running Scared (Eldar & Nigar song), Running Scared", entitling Azerbaijan to host the contest in Eurovision Song Contest 2012, 2012, in Baku. They have qualified for every Grand Final up until the Eurovision Song Contest 2018, 2018 edition of the contest, entering with X My Heart (song), X My Heart by singer Aisel (singer), Aisel. There are dozens of Azerbaijani folk dances. They are performed at formal celebrations and the dancers wear national clothes like the
Chokha
A chokha or ; ab, акәымжәы, akʷymzhʷy; ady, цые, tsiya; kbd, цей, tsei; fa, چوقا, chughā; hy, չուխայ, choukha(y); az, çuxa; krc, чепкен, çepken; kum, чепген, çepgen; nog, шепкен, şepken ...
, which is well-preserved within the national dances. Most dances have a very fast rhythm.
Literature
 Among the medieval authors born within the territorial limits of modern Azerbaijani Republic was Persian poet and philosopher Nizami Ganjavi, Nizami, called Ganjavi after his place of birth,
Among the medieval authors born within the territorial limits of modern Azerbaijani Republic was Persian poet and philosopher Nizami Ganjavi, Nizami, called Ganjavi after his place of birth, Ganja
Ganja (, ; ) is one of the oldest and most commonly used synonyms for marijuana. Its usage in English dates to before 1689.
Etymology
''Ganja'' is borrowed from Hindi/Urdu ( hi, गांजा, links=no, ur, , links=no, IPA: �aːɲd͡� ...
, who was the author of the Khamsa of Nizami, Khamsa ("The Quintuplet"), composed of five romantic poems, including "The Treasure of Mysteries", "Khosrow and Shīrīn", and "Leyli and Mejnūn".
The earliest known figure in written Azerbaijani literature was Izzeddin Hasanoghlu, who composed a Diwan (poetry), divan consisting of Persian and Azerbaijani ghazals.A.Caferoglu, "Adhari(azeri)", in ''Encyclopedia of Islam'', (new edition), Vol. 1, (Leiden, 1986) In Persian ghazals he used his pen-name, while his Azerbaijani ghazals were composed under his own name of Hasanoghlu.
Classical literature in Azerbaijani was formed in the 14th century based on the various Early Middle Ages dialects of Tabriz and Shirvan
Shirvan (from fa, شروان, translit=Shirvān; az, Şirvan; Tat: ''Şirvan''), also spelled as Sharvān, Shirwan, Shervan, Sherwan and Šervān, is a historical Iranian region in the eastern Caucasus, known by this name in both pre-Islam ...
. Among the poets of this period were Kadi Burhan al-Din, Gazi Burhanaddin, Jahan Shah, Haqiqi (pen-name of Jahan Shah, Jahan Shah Qara Qoyunlu), and Habibi (poet), Habibi. The end of the 14th century was also the period of starting literary activity of Nesimi, Imadaddin Nasimi, one of the greatest Azerbaijani Hurufi Mysticism, mystical poets of the late 14th and early 15th centuries and one of the most prominent early divan masters in Turkic literary history, who also composed poetry in Persian language, Persian and Arabic language, Arabic. The divan and ghazal styles were further developed by poets Qasem-e Anvar, Fuzûlî, Fuzuli and Khatai (pen-name of Safavid dynasty, Safavid Shah Ismail I).
The ''Book of Dede Korkut'' consists of two manuscripts copied in the 16th century,Michael E. Meeker, "The Dede Korkut Ethic", International Journal of Middle East Studies, Vol. 24, No. 3 (Aug. 1992), 395–417. excerpt: The Book of Dede Korkut is an early record of oral Turkic folktales in Anatolia, and as such, one of the mythic charters of Turkish nationalist ideology. The oldest versions of the Book of Dede Korkut consist of two manuscripts copied in the 16th century. The twelve stories that are recorded in these manuscripts are believed to be derived from a cycle of stories and songs circulating among Turkic peoples living in northeastern Anatolia and northwestern Azerbaijan. According to Lewis (1974), an older substratum of these oral traditions dates to conflicts between the ancient Oghuz and their Turkish rivals in Central Asia (the Pecheneks and the Kipchaks), but this substratum has been clothed in references to the 14th-century campaigns of the Akkoyunlu Confederation of Turkic tribes against the Georgians, the Abkhaz, and the Greeks in Trebizond. Such stories and songs would have emerged no earlier than the beginning of the 13th century, and the written versions that have reached us would have been composed no later than the beginning of the 15th century. By this time, the Turkic peoples in question had been in touch with Islamic civilization for several centuries, had come to call themselves "Turcoman" rather than "Oghuz," had close associations with sedentary and urbanized societies, and were participating in Islamized regimes that included nomads, farmers, and townsmen. Some had abandoned their nomadic way of life altogether. and was not written earlier than the 15th century.Cemal Kafadar(1995), "in Between Two Worlds: Construction of the Ottoman states", University of California Press, 1995. Excerpt: "It was not earlier than the fifteenth century. Based on the fact that the author is buttering up both the Akkoyunlu and Ottoman rulers, it has been suggested that the composition belongs to someone living in the undefined border region lands between the two states during the reign of Uzun Hassan (1466–78). G. Lewis, on the other hand, dates the composition "fairly early in the 15th century at least."İlker Evrım Bınbaş, Encyclopædia Iranica, "Oguz Khan NarrativesEncyclopædia Iranica , Articles
Retrieved October 2010. "The Ketāb-e Dede Qorqut, which is a collection of twelve stories reflecting the oral traditions of the Turkmens in the 15th-century eastern Anatolia, is also called Oḡuz-nāma" It is a collection of 12 stories reflecting the oral tradition of Oghuz nomads. The 16th-century poet, Muhammed Fuzuli produced his timeless philosophical and lyrical ''Qazals'' in Arabic, Persian, and Azerbaijani. Benefiting immensely from the fine literary traditions of his environment, and building upon the legacy of his predecessors, Fuzuli was destined to become the leading literary figure of his society. His major works include ''The Divan of Ghazals'' and ''The Qasidas''. In the same century, Azerbaijani literature further flourished with the development of Ashik ( az, Aşıq) poetic genre of bards. During the same period, under the pen-name of Khatāī ( ar, خطائی for ''sinner'') Shah Ismail I wrote about 1400 verses in Azerbaijani, which were later published as his ''Divan''. A unique literary style known as ''qoshma'' ( az, qoşma for ''improvisation'') was introduced in this period, and developed by Shah Ismail and later by his son and successor, Shah
Tahmasp I
Tahmasp I ( fa, طهماسب, translit=Ṭahmāsb or ; 22 February 1514 – 14 May 1576) was the second shah of Safavid Iran from 1524 to 1576. He was the eldest son of Ismail I and his principal consort, Tajlu Khanum. Ascending the throne after t ...
.V. Minorsky, "The Poetry of Shah Ismail I," ''Bulletin of the School of Oriental and African Studies'', University of London 10/4 (1942): 1006–53.
In the span of the 17th and 18th centuries, Fuzuli's unique genres as well Ashik poetry were taken up by prominent poets and writers such as Qovsi of Tabriz, Abbas II of Persia, Shah Abbas Sani, , Nishat, Molla Vali Vidadi, Molla Panah Vagif, Amani, Zafar and others. Along with Turks
Turk or Turks may refer to:
Communities and ethnic groups
* Turkic peoples, a collection of ethnic groups who speak Turkic languages
* Turkish people, or the Turks, a Turkic ethnic group and nation
* Turkish citizen, a citizen of the Republic ...
, Turkmens and Uzbeks, Azerbaijanis also celebrate the Epic of Koroglu (from az, kor oğlu for ''blind man's son''), a legendary folk hero. Several documented versions of Koroglu epic remain at the Institute for Manuscripts of the National Academy of Sciences of Azerbaijan.
Modern Azerbaijani literature in Azerbaijan is based on the Shirvani dialect mainly, while in Iran it is based on the Tabrizi one. The first newspaper in Azerbaijani, ''Akinchi'' was published in 1875. In the mid-19th century, it was taught in the schools of Baku, Ganja (city), Ganja, Shaki, Azerbaijan, Shaki, Tbilisi
Tbilisi ( ; ka, თბილისი ), in some languages still known by its pre-1936 name Tiflis ( ), is the capital and the largest city of Georgia, lying on the banks of the Kura River with a population of approximately 1.5 million p ...
, and Yerevan. Since 1845, it was also taught in the University of Saint Petersburg in Russia.
Folk art
 Azerbaijanis have a rich and distinctive culture, a major part of which is decorative art, decorative and applied art. This art form is represented by a wide range of handicrafts, such as chasing, jeweling, engraving in metal, carving in wood, stone, bone, carpet-making, lasing, pattern weaving and printing, and knitting and embroidery. Each of these types of decorative art, evidence of the endowments of the Azerbaijan nation, is very much in favor here. Many interesting facts pertaining to the development of arts and crafts in Azerbaijan were reported by numerous merchants, travelers, and diplomats who had visited these places at different times.
The Azerbaijani rug, Azerbaijani carpet is a traditional handmade textile of various sizes, with a dense texture and a pile or pile-less surface, whose patterns are characteristic of Azerbaijan's many carpet-making regions. In November 2010 the Azerbaijani carpet was proclaimed a Masterpieces of the Oral and Intangible Heritage of Humanity, Masterpiece of Intangible Heritage by
Azerbaijanis have a rich and distinctive culture, a major part of which is decorative art, decorative and applied art. This art form is represented by a wide range of handicrafts, such as chasing, jeweling, engraving in metal, carving in wood, stone, bone, carpet-making, lasing, pattern weaving and printing, and knitting and embroidery. Each of these types of decorative art, evidence of the endowments of the Azerbaijan nation, is very much in favor here. Many interesting facts pertaining to the development of arts and crafts in Azerbaijan were reported by numerous merchants, travelers, and diplomats who had visited these places at different times.
The Azerbaijani rug, Azerbaijani carpet is a traditional handmade textile of various sizes, with a dense texture and a pile or pile-less surface, whose patterns are characteristic of Azerbaijan's many carpet-making regions. In November 2010 the Azerbaijani carpet was proclaimed a Masterpieces of the Oral and Intangible Heritage of Humanity, Masterpiece of Intangible Heritage by UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. I ...
.
 Azerbaijan has been since ancient times known as a center of a large variety of crafts. The archeological dig on the territory of Azerbaijan testifies to the well-developed agriculture, stock raising, metalworking, pottery, ceramics, and carpet-weaving that date as far back as to the 2nd millennium BC. Archeological sites in Dashbulaq, Hasansu, Zayamchai, and Tovuzchai uncovered from the BTC pipeline have revealed early Iron Age artifacts.
Azerbaijani carpets can be categorized under several large groups and a multitude of subgroups. Scientific research of the Azerbaijani carpet is connected with the name of Latif Karimov, a prominent scientist and artist. It was his classification that related the four large groups of carpets with the four geographical zones of Azerbaijan, Guba-Shirvan, Ganja-Kazakh, Karabakh and Tabriz.
Azerbaijan has been since ancient times known as a center of a large variety of crafts. The archeological dig on the territory of Azerbaijan testifies to the well-developed agriculture, stock raising, metalworking, pottery, ceramics, and carpet-weaving that date as far back as to the 2nd millennium BC. Archeological sites in Dashbulaq, Hasansu, Zayamchai, and Tovuzchai uncovered from the BTC pipeline have revealed early Iron Age artifacts.
Azerbaijani carpets can be categorized under several large groups and a multitude of subgroups. Scientific research of the Azerbaijani carpet is connected with the name of Latif Karimov, a prominent scientist and artist. It was his classification that related the four large groups of carpets with the four geographical zones of Azerbaijan, Guba-Shirvan, Ganja-Kazakh, Karabakh and Tabriz.
Cuisine
 The traditional cuisine is famous for an abundance of vegetables and greens used seasonally in the dishes. Fresh herbs, including mint, cilantro (coriander), dill, basil, parsley, tarragon, leeks, chives, thyme, marjoram, green onion, and watercress, are very popular and often accompany main dishes on the table. Climatic diversity and fertility of the land are reflected in the national dishes, which are based on fish from the
The traditional cuisine is famous for an abundance of vegetables and greens used seasonally in the dishes. Fresh herbs, including mint, cilantro (coriander), dill, basil, parsley, tarragon, leeks, chives, thyme, marjoram, green onion, and watercress, are very popular and often accompany main dishes on the table. Climatic diversity and fertility of the land are reflected in the national dishes, which are based on fish from the Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, often described as the List of lakes by area, world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia; east of the Caucasus, west of the broad s ...
, local meat (mainly mutton and beef), and an abundance of seasonal vegetables and greens. Saffron-rice plov is the flagship food in Azerbaijan and black tea is the national beverage. Azerbaijanis often use traditional armudu (pear-shaped) glass as they have very strong Azerbaijani tea culture, tea culture. Popular traditional dishes include bozbash (lamb soup that exists in several regional varieties with the addition of different vegetables), qutab (fried turnover with a filling of greens or minced meat) and dushbara (sort of dumplings of dough filled with ground meat and flavor).
Architecture
 Azerbaijani architecture typically combines elements of Eastern world, East and Western culture, West. Azerbaijani architecture has heavy influences from Persian architecture. Many ancient architectural treasures such as the Maiden Tower (Baku), Maiden Tower and Palace of the Shirvanshahs in the Baku, Walled City of Baku survive in modern Azerbaijan. Entries submitted on the UNESCO World Heritage tentative list include the Ateshgah of Baku, Momine Khatun Mausoleum, Hirkan National Park, Binagadi asphalt lake, Lökbatan Mud Volcano, Shusha State Historical and Architectural Reserve, Baku Stage Mountain, Caspian Shore Defensive Constructions, Ordubad National Reserve and the Palace of Shaki Khans.
Among other architectural treasures are Quadrangular castle (Mardakan), Quadrangular Castle in Mardakan, Parigala in Yuxarı Çardaqlar, Yukhary Chardaglar, a number of bridges spanning the Aras River, and several mausoleums. In the 19th and early 20th centuries, little monumental architecture was created, but distinctive residences were built in Baku and elsewhere. Among the most recent architectural monuments, the Baku Metro, Baku subways are noted for their lavish decor.
The task for modern Azerbaijani architecture is diverse application of modern aesthetics, the search for an architect's own artistic style and inclusion of the existing historico-cultural environment. Major projects such as Heydar Aliyev Cultural Center, Flame Towers, Baku Crystal Hall, Baku White City and SOCAR Tower have transformed the country's skyline and promotes its contemporary identity.
Azerbaijani architecture typically combines elements of Eastern world, East and Western culture, West. Azerbaijani architecture has heavy influences from Persian architecture. Many ancient architectural treasures such as the Maiden Tower (Baku), Maiden Tower and Palace of the Shirvanshahs in the Baku, Walled City of Baku survive in modern Azerbaijan. Entries submitted on the UNESCO World Heritage tentative list include the Ateshgah of Baku, Momine Khatun Mausoleum, Hirkan National Park, Binagadi asphalt lake, Lökbatan Mud Volcano, Shusha State Historical and Architectural Reserve, Baku Stage Mountain, Caspian Shore Defensive Constructions, Ordubad National Reserve and the Palace of Shaki Khans.
Among other architectural treasures are Quadrangular castle (Mardakan), Quadrangular Castle in Mardakan, Parigala in Yuxarı Çardaqlar, Yukhary Chardaglar, a number of bridges spanning the Aras River, and several mausoleums. In the 19th and early 20th centuries, little monumental architecture was created, but distinctive residences were built in Baku and elsewhere. Among the most recent architectural monuments, the Baku Metro, Baku subways are noted for their lavish decor.
The task for modern Azerbaijani architecture is diverse application of modern aesthetics, the search for an architect's own artistic style and inclusion of the existing historico-cultural environment. Major projects such as Heydar Aliyev Cultural Center, Flame Towers, Baku Crystal Hall, Baku White City and SOCAR Tower have transformed the country's skyline and promotes its contemporary identity.
Visual art
 The Gamigaya Petroglyphs, which date back to the 1st to 4th millennium BC, are located in Azerbaijan's Ordubad District. They consist of some 1500 dislodged and carved rock paintings with images of deer, goats, bulls, dogs, snakes, birds, fantastic beings, and people, carriages, and various symbols were found on basalt rocks. Norwegian ethnographer and adventurer Thor Heyerdahl was convinced that people from the area went to Scandinavia in about 100 AD, took their boat building skills with them, and transmuted them into the Viking boats in Northern Europe.
Over the centuries, Azerbaijani art has gone through many stylistic changes. Azerbaijani painting is traditionally characterized by a warmth of colour and light, as exemplified in the works of Azim Azimzade and Bahruz Kangarli, and a preoccupation with religious figures and cultural motifs. Azerbaijani painting enjoyed preeminence in Caucasus for hundreds of years, from the Romanesque art, Romanesque and Culture of the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman periods, and through the Socialist realism, Soviet and Baroque periods, the latter two of which saw fruition in Azerbaijan. Other notable artists who fall within these periods include Sattar Bahlulzade, Togrul Narimanbekov, Tahir Salahov, Alakbar Rezaguliyev, Mirza Gadim Iravani, Mikayil Abdullayev and Boyukagha Mirzazade.
The Gamigaya Petroglyphs, which date back to the 1st to 4th millennium BC, are located in Azerbaijan's Ordubad District. They consist of some 1500 dislodged and carved rock paintings with images of deer, goats, bulls, dogs, snakes, birds, fantastic beings, and people, carriages, and various symbols were found on basalt rocks. Norwegian ethnographer and adventurer Thor Heyerdahl was convinced that people from the area went to Scandinavia in about 100 AD, took their boat building skills with them, and transmuted them into the Viking boats in Northern Europe.
Over the centuries, Azerbaijani art has gone through many stylistic changes. Azerbaijani painting is traditionally characterized by a warmth of colour and light, as exemplified in the works of Azim Azimzade and Bahruz Kangarli, and a preoccupation with religious figures and cultural motifs. Azerbaijani painting enjoyed preeminence in Caucasus for hundreds of years, from the Romanesque art, Romanesque and Culture of the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman periods, and through the Socialist realism, Soviet and Baroque periods, the latter two of which saw fruition in Azerbaijan. Other notable artists who fall within these periods include Sattar Bahlulzade, Togrul Narimanbekov, Tahir Salahov, Alakbar Rezaguliyev, Mirza Gadim Iravani, Mikayil Abdullayev and Boyukagha Mirzazade.
(Palace of Shaki Khans) File:Portrait of sitting woman by Irevani.jpg, Mirza Gadim Iravani – Portrait of sitting woman
(National Art Museum of Azerbaijan) File:Dağ mənzərəsi – Bəhruz Kəngərli.jpg, Bahruz Kangarli – Landscape with mountains
(National Art Museum of Azerbaijan) File:Ruins of Reichstag.jpg, Azim Azimzade – Ruins of Reichstag
(National Art Museum of Azerbaijan)
Cinema
 The film industry in Azerbaijan dates back to 1898. Azerbaijan was among the first countries involved in cinematography, with the apparatus first showing up in Baku.Celebrating 100 Years in Film, not 80
The film industry in Azerbaijan dates back to 1898. Azerbaijan was among the first countries involved in cinematography, with the apparatus first showing up in Baku.Celebrating 100 Years in Film, not 80by Aydin Kazimzade. Azerbaijan International, Autumn 1997 In 1919, during the
Azerbaijan Democratic Republic
The Azerbaijan Democratic Republic), or simply as Azerbaijan in Paris Peace Conference, 1919–1920,''Bulletin d'Information de l'Azerbaidjan'', No. I, September 1, 1919, pp. 6–7''125 H.C.Debs.'', 58., February 24, 1920, p. 1467. Caucasian Az ...
, a documentary ''The Celebration of the Anniversary of Azerbaijani Independence'' was filmed on the first anniversary of Azerbaijan's independence from Russia, 27 May, and premiered in June 1919 at several theatres in Baku. After the Soviet power was established in 1920, Nariman Narimanov, Chairman of the Revolutionary Committee of Azerbaijan, signed a decree nationalizing Azerbaijan's cinema. This also influenced the creation of Azerbaijani animation.
In 1991, after Azerbaijan gained its independence from the Soviet Union, the first Baku International Film Festival East-West was held in Baku. In December 2000, the former President of Azerbaijan, Heydar Aliyev, signed a decree proclaiming 2 August to be the professional holiday of filmmakers of Azerbaijan. Today Azerbaijani filmmakers are again dealing with issues similar to those faced by cinematographers prior to the establishment of the Soviet Union in 1920. Once again, both choices of content and sponsorship of films are largely left up to the initiative of the filmmaker.
Television
There are three state-owned television channels: AzTV, Idman Azerbaijan TV, Idman TV and Medeniyyet TV. There is one public channel and 6 private channels: İctimai Television, Space TV, Lider TV, Azad Azerbaijan TV, , and Region TV, ARB.Human rights
 The Constitution of Azerbaijan claims to guarantee freedom of speech, but this is denied in practice. After several years of decline in press and media freedom, in 2014, the media environment in Azerbaijan deteriorated rapidly under a governmental campaign to silence any opposition and criticism, even while the country led the Committee of Ministers of the Council of Europe (May–November 2014). Spurious legal charges and impunity in violence against journalists have remained the norm.Parliamentary Assembly of the Council of Europe
The Constitution of Azerbaijan claims to guarantee freedom of speech, but this is denied in practice. After several years of decline in press and media freedom, in 2014, the media environment in Azerbaijan deteriorated rapidly under a governmental campaign to silence any opposition and criticism, even while the country led the Committee of Ministers of the Council of Europe (May–November 2014). Spurious legal charges and impunity in violence against journalists have remained the norm.Parliamentary Assembly of the Council of EuropeThe Protection of media freedom in Europe
.Background report prepared by Mr William Horsley, special representative for media freedom of the Association of European Journalists All foreign broadcasts are banned in the country.
Freedom House
Freedom House is a non-profit, majority U.S. government funded organization in Washington, D.C., that conducts research and advocacy on democracy, political freedom, and human rights. Freedom House was founded in October 1941, and Wendell Wi ...
Azerbaijan
2015 Press Freedom report According to the 2013
Freedom House
Freedom House is a non-profit, majority U.S. government funded organization in Washington, D.C., that conducts research and advocacy on democracy, political freedom, and human rights. Freedom House was founded in October 1941, and Wendell Wi ...
Freedom of the Press (report), Freedom of the Press report, Azerbaijan's press freedom status is "not free", and Azerbaijan ranks 177th out of 196 countries.
Christianity is officially recognized. All religious communities are required to register to be allowed to meet, under the risk of imprisonment. This registration is often denied. "Racial discrimination contributes to the country's lack of religious freedom, since many of the Christians are ethnic Armenian or Russian, rather than Azeri Muslim."
Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty and Voice of America are banned in Azerbaijan. Discrimination against LGBT rights in Azerbaijan, LGBT people in Azerbaijan is widespread.
During the last few years, three journalists were killed and several prosecuted in trials described as unfair by international human rights organizations. Azerbaijan had the biggest number of journalists imprisoned in Europe in 2015, according to the Committee to Protect Journalists, and is the 5th most censored country in the world, ahead of Iran and China. Some critical journalists have been COVID-19 misinformation#Efforts to combat misinformation, arrested for their coverage of the COVID-19 pandemic in Azerbaijan.
A report by an Amnesty International researcher in October 2015 points to "...the severe deterioration of human rights in Azerbaijan over the past few years. Sadly Azerbaijan has been allowed to get away with unprecedented levels of repression and in the process almost wipe out its civil society". Amnesty's 2015/16 annual report on the country stated "... persecution of political dissent continued. Human rights organizations remained unable to resume their work. At least 18 prisoners of conscience remained in detention at the end of the year. Reprisals against independent journalists and activists persisted both in the country and abroad, while their family members also faced harassment and arrests. International human rights monitors were barred and expelled from the country. Reports of torture and other ill-treatment persisted.
''The Guardian'' reported in April 2017 that "Azerbaijan's ruling elite operated a secret $2.9bn (£2.2bn) scheme to pay prominent Europeans, buy luxury goods and launder money through a network of opaque British companies .... Leaked data shows that the Azerbaijani leadership, accused of serial human rights abuses, systemic corruption and rigging elections, made more than 16,000 covert payments from 2012 to 2014. Some of this money went to politicians and journalists, as part of an international lobbying operation to deflect criticism of Azerbaijan's president, Ilham Aliyev, and to promote a positive image of his oil-rich country." There was no suggestion that all recipients were aware of the source of the money as it arrived via a disguised route.
Sport
Freestyle wrestling has been traditionally regarded as Azerbaijan's national sport, in which Azerbaijan won up to Azerbaijan at the Olympics, fourteen medals, including four golds since joining the International Olympic Committee. Currently, the most popular sports include association football, football and wrestling. Football is the most popular sport in Azerbaijan, and the Association of Football Federations of Azerbaijan with 9,122 registered players, is the largest sporting association in the country. The Azerbaijan national football team, national football team of Azerbaijan demonstrates relatively low performance in the international arena compared to the nation football clubs. The most successful Azerbaijani football clubs are Neftçi PFK, Neftçi, Qarabağ FK, Qarabağ, and Gabala FK, Gabala. In 2012–13 UEFA Europa League, 2012, Neftchi Baku became the first Azerbaijani team to advance to the group stage of a European competition, beating APOEL F.C., APOEL of Cyprus 4–2 on aggregate in the play-off round of the 2012–13 UEFA Europa League. In 2014–15 UEFA Europa League, 2014, Qarabağ became the second Azerbaijani club advancing to the group stage of UEFA Europa League. In 2017, after beating F.C. Copenhagen, Copenhagen 2–2 (Away goals rule, a) in the play-off round of the 2017–18 UEFA Champions League, UEFA Champions League, Qarabağ became the first Azerbaijani club to reach the Group stage. Futsal is another popular sport in Azerbaijan. The Azerbaijan national futsal team reached fourth place in the 2010 UEFA Futsal Championship, while domestic club Araz Naxçivan clinched bronze medals at the 2009–10 UEFA Futsal Cup and 2013–14 UEFA Futsal Cup. Azerbaijan was the main sponsor of Spanish football club Atlético de Madrid during seasons 2013/2014 and 2014/2015, a partnership that the club described should 'promote the image of Azerbaijan in the world'. Azerbaijan is one of the traditional powerhouses of world chess, having hosted many international chess tournaments and competitions and became European Team Chess Championship winners in 2009, 2013 and 2017. Notable chess players from the country's chess schools that have made a great impact on the game include Teimour Radjabov, Shahriyar Mammadyarov, Vladimir Makogonov, Vugar Gashimov and former World Chess Champion Garry Kasparov. , country's home of Shamkir Chess a category 22 event and one of the highest rated tournaments of all time. Backgammon also plays a major role in Azerbaijani culture. The game is very popular in Azerbaijan and is widely played among the local public. There are also different variations of backgammon developed and analyzed by Azerbaijani experts. Azerbaijan Women's Volleyball Super League is one of the strongest women leagues in the world. Its women's national team came fourth at the 2005 Women's European Volleyball Championship, 2005 European Championship. Over the last years, clubs like Rabita Baku and Azerrail Baku achieved great success at European cups. Azerbaijani volleyball players include likes of Valeriya Korotenko, Oksana Parkhomenko, Inessa Korkmaz, Natalya Mammadova and Alla Hasanova.
Other Azerbaijani athletes are Namig Abdullayev, Toghrul Asgarov, Rovshan Bayramov, Sharif Sharifov, Mariya Stadnik and Farid Mansurov in Amateur wrestling, wrestling, Nazim Huseynov, Elnur Mammadli, Elkhan Mammadov (judoka), Elkhan Mammadov and Rustam Orujov in judo, Rafael Aghayev in karate, Magomedrasul Majidov and Aghasi Mammadov in boxing, Nizami Pashayev in Olympic weightlifting, Azad Asgarov in pankration, Eduard Mammadov in kickboxing, and K-1 fighter Zabit Samedov.
Azerbaijan has a Baku City Circuit, Formula One race-track, made in June 2012, and the country hosted its first 2016 European Grand Prix, Formula One Grand Prix on 19 June 2016 and the Azerbaijan Grand Prix in 2017, 2018, 2019, 2021 and 2022. Other annual sporting events held in the country are the Baku Cup tennis tournament and the Tour d'Azerbaïdjan cycling race.
Azerbaijan hosted several major sport competitions since the late 2000s, including the 2013 F1 Powerboat World Championship season, 2013 F1 Powerboat World Championship, 2012 FIFA U-17 Women's World Cup, 2011 AIBA World Boxing Championships, 2010 European Wrestling Championships, 2009 Rhythmic Gymnastics European Championships, European Taekwondo Championships, 2014 European Taekwondo Championships, 2014 Rhythmic Gymnastics European Championships, and 42nd Chess Olympiad, 2016 World Chess Olympiad. On 8 December 2012, Baku was selected to host the 2015 European Games, the first to be held in the competition's history. Baku also hosted the fourth Islamic Solidarity Games in 2017 and the 2019 European Youth Summer Olympic Festival, and it is also one of the hosts of UEFA Euro 2020, which because of Covid-19 is being held in 2021.
Azerbaijan Women's Volleyball Super League is one of the strongest women leagues in the world. Its women's national team came fourth at the 2005 Women's European Volleyball Championship, 2005 European Championship. Over the last years, clubs like Rabita Baku and Azerrail Baku achieved great success at European cups. Azerbaijani volleyball players include likes of Valeriya Korotenko, Oksana Parkhomenko, Inessa Korkmaz, Natalya Mammadova and Alla Hasanova.
Other Azerbaijani athletes are Namig Abdullayev, Toghrul Asgarov, Rovshan Bayramov, Sharif Sharifov, Mariya Stadnik and Farid Mansurov in Amateur wrestling, wrestling, Nazim Huseynov, Elnur Mammadli, Elkhan Mammadov (judoka), Elkhan Mammadov and Rustam Orujov in judo, Rafael Aghayev in karate, Magomedrasul Majidov and Aghasi Mammadov in boxing, Nizami Pashayev in Olympic weightlifting, Azad Asgarov in pankration, Eduard Mammadov in kickboxing, and K-1 fighter Zabit Samedov.
Azerbaijan has a Baku City Circuit, Formula One race-track, made in June 2012, and the country hosted its first 2016 European Grand Prix, Formula One Grand Prix on 19 June 2016 and the Azerbaijan Grand Prix in 2017, 2018, 2019, 2021 and 2022. Other annual sporting events held in the country are the Baku Cup tennis tournament and the Tour d'Azerbaïdjan cycling race.
Azerbaijan hosted several major sport competitions since the late 2000s, including the 2013 F1 Powerboat World Championship season, 2013 F1 Powerboat World Championship, 2012 FIFA U-17 Women's World Cup, 2011 AIBA World Boxing Championships, 2010 European Wrestling Championships, 2009 Rhythmic Gymnastics European Championships, European Taekwondo Championships, 2014 European Taekwondo Championships, 2014 Rhythmic Gymnastics European Championships, and 42nd Chess Olympiad, 2016 World Chess Olympiad. On 8 December 2012, Baku was selected to host the 2015 European Games, the first to be held in the competition's history. Baku also hosted the fourth Islamic Solidarity Games in 2017 and the 2019 European Youth Summer Olympic Festival, and it is also one of the hosts of UEFA Euro 2020, which because of Covid-19 is being held in 2021.
See also
* Outline of Azerbaijan * Index of Azerbaijan-related articles * List of World Heritage Sites in Azerbaijan * ''The Defense & Foreign Affairs Handbook on Azerbaijan'' (2006)Notes
References
Further reading
* Altstadt, Audrey. ''Frustrated Democracy in Post-Soviet Azerbaijan'' (2018) * Broers, Broers Laurence. ''Armenia and Azerbaijan: Anatomy of a rivalry'' (Edinburgh University Press, 2019). * Cornell, Svante E. ''Azerbaijan since independence'' (Routledge, 2015). * Dragadze, Tamara. "Islam in Azerbaijan: The Position of Women" in ''Muslim Women's Choices'' (Routledge, 2020) pp. 152–163. * Elliott, Mark. ''Azerbaijan with Georgia'' (Trailblazers Publications, 1999). * Ergun, Ayça. "Citizenship, National Identity, and Nation-Building in Azerbaijan: Between the Legacy of the Past and the Spirit of Independence." ''Nationalities Papers'' (2021): 1–18online
* Thomas Goltz, Goltz, Thomas. ''Azerbaijan Diary : A Rogue Reporter's Adventures in an Oil-Rich, War-Torn, Post-Soviet Republic''. M E Sharpe (1998). * Habibov, Nazim, Betty Jo Barrett, and Elena Chernyak. "Understanding women's empowerment and its determinants in post-communist countries: Results of Azerbaijan national survey." ''Women's Studies International Forum.'' Vol. 62. Pergamon, 2017. * Olukbasi, Suha. ''Azerbaijan: A Political History''. I.B. Tauris (2011). Focus on post-Soviet era.
External links
General information
Azerbaijan International
Heydar Aliyev Foundation
*
Azerbaijan
''The World Factbook''. Central Intelligence Agency.
Azerbaijan
at University of Colorado at Boulder
Country profile
from BBC
Key Development Forecasts for Azerbaijan
from International Futures
Visions of Azerbaijan Journal
of The European Azerbaijan Society * *
Major government resources
President of Azerbaijan website
Azerbaijan State Statistical Committee
United Nations Office in Azerbaijan
Major news media
Network NEWS Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan Today
Trend News Agency
News.Az
Tourism
Azerbaijan Tourism Portal
*
Travel in Azerbaijan
in Visions of Azerbaijan Journal {{Good article Azerbaijan, Caucasus Countries in Asia Countries in Europe Eastern European countries Western Asian countries Landlocked countries South Caucasus Republics Member states of the Commonwealth of Independent States Member states of the Council of Europe Member states of the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation Member states of the United Nations States and territories established in 1991 1991 establishments in Asia 1991 establishments in Europe Azerbaijani-speaking countries and territories Russian-speaking countries and territories Transcontinental countries Members of the International Organization of Turkic Culture Member states of the Organization of Turkic States Turkic states