|
Pyang Zhuang Language
Pyang Zhuang, or Fuping Zhuang (), is an underdescribed Central Tai language spoken in southwestern Guangxi, China. It appears to be most closely related to Nong Zhuang. The Pyang refer to themselves as ''B2'' or ''C1-A'', but are referred to as ''C1'' by the surrounding Yang Zhuang people (Liao 2016:315). Distribution Pyang Zhuang is spoken in the following locations of Guangxi, China (Liao 2016:315-316). *Fuping Village 扶平村, Jingde Town 敬德镇, Debao County, Guangxi **Tuoxin 驮信村 (' in Pyang Zhuang) *Ronghua Township 荣华乡, Debao County, Guangxi *Kuixu Township 魁圩乡, Jingxi County, Guangxi Classification Pyang Zhuang may be closely related to the Nong Zhuang language of Yunnan. Innovations shared between Pyang Zhuang and Nong Zhuang include the following (Liao 2016:316). *Proto-Tai *kr-(Pittayaporn 2009:143); *xr- in Li (1977:233) > tɕʰ- (as opposed to *kr- > kʰj- in Yang Zhuang, and *kr- > h- in Southwestern Tai). Examples include ''tɕʰaːA1- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and borders fourteen countries by land, the most of any country in the world, tied with Russia. Covering an area of approximately , it is the world's third largest country by total land area. The country consists of 22 provinces, five autonomous regions, four municipalities, and two Special Administrative Regions (Hong Kong and Macau). The national capital is Beijing, and the most populous city and financial center is Shanghai. Modern Chinese trace their origins to a cradle of civilization in the fertile basin of the Yellow River in the North China Plain. The semi-legendary Xia dynasty in the 21st century BCE and the well-attested Shang and Zhou dynasties developed a bureaucratic political system to serve hereditary monarchies, or dyna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Debao County
Debao (, zhuang: ) is a county of western Guangxi, China. It is under the administration of Baise City. Economy Bauxite mining is a major industry in Debao County. To facilitate the transportation of the ore, a 72-km single-track electrified railway branch was completed in 2010, connecting Debao with Tiandong on the Nanning-Kunming mainline. The bauxite and other local ores are shipped by rail to Qianxinan in Guizhou, Shihezi in Xinjiang, and to other metallurgical plants throughout the country. In the opposite direction, coal is brought to Debao from Guizhou, Shanxi, and from overseas (via the Fangchenggang port). There are also plans to extend this new railway further southwest from Debao, to the Longbang border crossing (Jingxi County) on the Vietnamese border. Administrative divisions There are 5 towns and 7 townships in the county: Towns: * Chengguan (城关镇), Longdie (隆桑镇), Jingde (敬德镇), Zurong (足荣镇), Ma'ai (马隘镇) Townships: *Du'an Towns ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jingxi County
Jingxi (, Zhuang: Cingsae Si) is a county-level city of western Guangxi, China. It is under the administration of Baise City. Administrative divisions There are 8 towns and 11 townships in the district: Towns: *Xinjing (新靖镇), Huadong (化峒镇), Hurun (湖润镇), Ande (安德镇), Youlin (龙临镇), Quyang (渠洋镇), Yuexu (岳圩镇), Longbang, Wuping (武平) Townships: *Tongde Township (同德乡), Qianzhuang Township (壬庄乡), Anning Township (安宁乡), Dizhou Township (地州乡), Ludong Township (禄峒乡), Nanpo Township (南坡乡), Tianpan Township (吞盘乡), Guole Township (果乐乡), Xinjia Township (新甲乡), Kuixu Township (魁圩乡) Demographics Jingxi's population was 605,100 (2010). 99.71% of the people belong to the Zhuang ethnic group. The rest include Han, Yao, Miao, and other ethnic groups. Languages David Holm (2010)Holm, David. 2010. "Linguistic Diversity along the China-Vietnam Border." In ''Linguistics of the Tibeto-Bur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tai Languages
The Tai or Zhuang–Tai languages ( th, ภาษาไท or , transliteration: or ) are a branch of the Kra–Dai language family. The Tai languages include the most widely spoken of the Tai–Kadai languages, including Standard Thai or Siamese, the national language of Thailand; Lao or Laotian, the national language of Laos; Myanmar's Shan language; and Zhuang, a major language in the Southwestern China's Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, spoken by the Zhuang (壯) people, the largest minority ethnic group in China, with a population of 15.55 million, living mainly in Guangxi, the rest scattered across Yunnan, Guangdong, Guizhou and Hunan provinces. Name Cognates with the name ''Tai'' (''Thai, Dai'', etc.) are used by speakers of many Tai languages. The term ''Tai'' is now well-established as the generic name in English. In his book '' The Tai-Kadai Languages'' Anthony Diller claims that Lao scholars he has met are not pleased with Lao being regarded as a Tai language. k� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Tai Languages
The Central Tai languages include southern dialects of Zhuang, and various Nung and Tày dialects of northern Vietnam. Central Tai languages differ from Northern Tai languages in that Central Tai distinguishes unaspirated and aspirated onsets, while Northern Tai generally does not (Li 1977). Southwestern Tai also displays this kind of aspiration contrast. Classification William Gedney considers Central Tai to be more closely related to Southwestern Tai than to Northern Tai, while André-Georges Haudricourt argues for a closer relation to Northern Tai. Pittayaporn's (2009) tentative tree of the Tai branch, however, considers Central Tai to be paraphyletic. Certain languages in predominantly Central Tai-speaking areas, such as Caolan and Nùng An in northern Vietnam, display Northern Tai features as well. These appear to be mixed languages that are not fully Central Tai or Northern Tai. Jerold A. Edmondson calls Caolan a "tertium quid." Jerold Edmondson's (2014)Edmondson, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guangxi
Guangxi (; ; Chinese postal romanization, alternately romanized as Kwanghsi; ; za, Gvangjsih, italics=yes), officially the Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region (GZAR), is an Autonomous regions of China, autonomous region of the People's Republic of China, located in South China and bordering Vietnam (Hà Giang Province, Hà Giang, Cao Bằng Province, Cao Bằng, Lạng Sơn Province, Lạng Sơn, and Quảng Ninh Provinces) and the Gulf of Tonkin. Formerly a Provinces of China, province, Guangxi became an autonomous region in 1958. Its current capital is Nanning. Guangxi's location, in mountainous terrain in the far south of China, has placed it on the frontier of Chinese civilization throughout much of History of China, Chinese history. The current name "Guang" means "expanse" and has been associated with the region since the creation of Guang Prefecture in 226 AD. It was given Administrative divisions of the Yuan dynasty, provincial level status during the Yuan dynasty, but ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
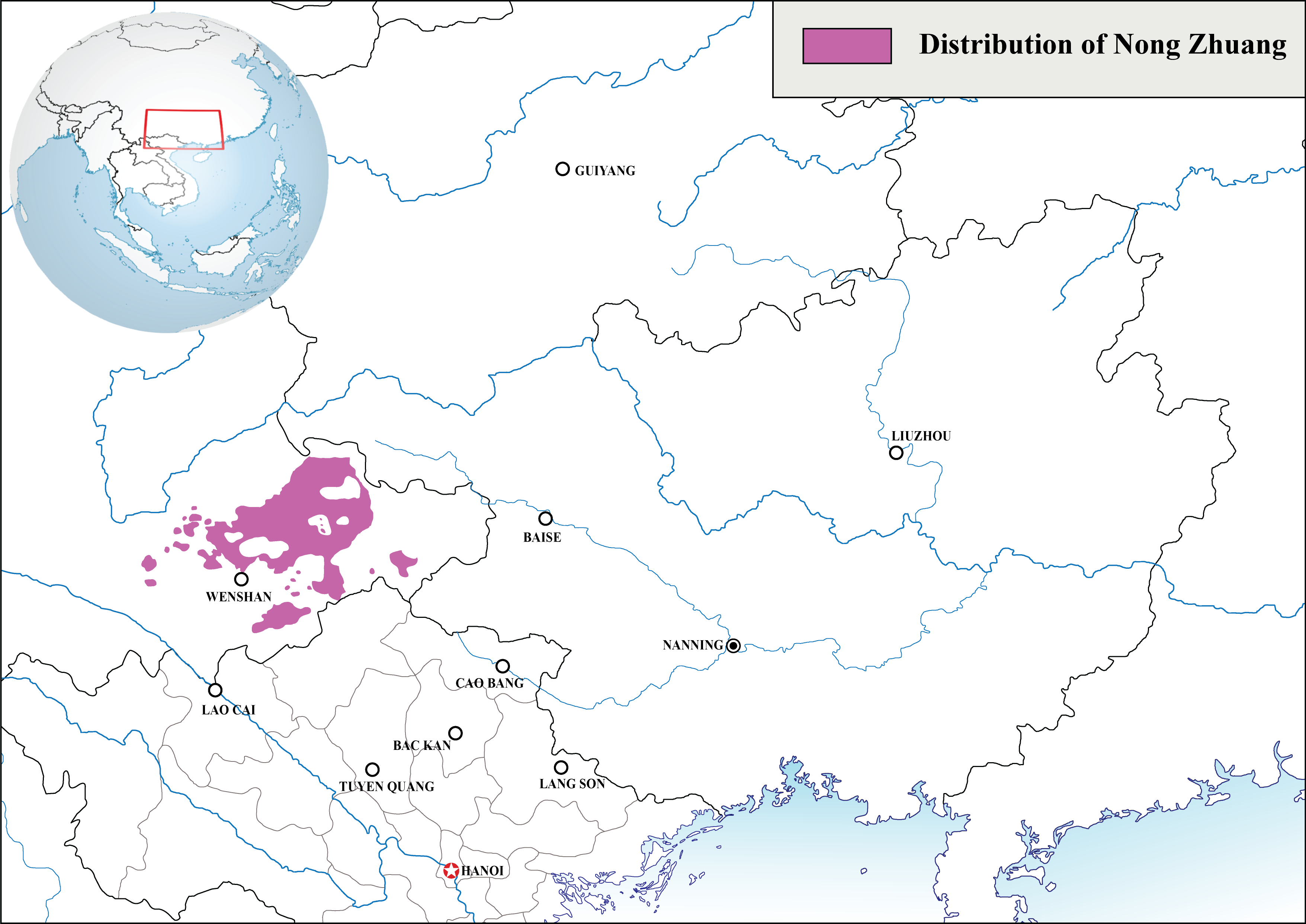
Nong Zhuang Language
Nong Zhuang () is a Tai language spoken mainly in Wenshan Prefecture, Yunnan, China. In Wenshan Prefecture, it is spoken in Yanshan, Guangnan, Wenshan, Maguan, Funing, Xichou, and Malipo counties, and also in Honghe Prefecture and Vietnam. The heaviest concentrations relative to other Zhuang groups are in Xichou (96% of the total Zhuang population) and Malipo (90% of the total Zhuang population) counties (Johnson 2011a:43). Names Below are various names (both autonyms and exonyms) for the Nong Zhuang people (Johnson 2011a:43). *Pu Nong (濮侬) * *Nongzu (侬族) or Nongren (侬人) *Long (龙) *Bu Tei *Bendi ( 'indigenous') Subdivisions Johnson (2011a) gives the following subdivisions for the Nong Zhuang peoples. *Dao Nong (道侬), or Nong Dau ('): Guangnan County *Niang Nong (仰侬), or Nong Nyeng ('); also called the "Green Nong" (青侬): along the Chouyang River (畴阳河) in Xichou and Malipo counties. *Du Nong (赌侬), or Nong Du ('): along the Duzhou River (赌咒河 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proto-Tai Language
Proto-Tai is the reconstructed proto-language (common ancestor) of all the Tai languages, including modern Lao, Shan, Tai Lü, Tai Dam, Ahom, Northern Thai, Standard Thai, Bouyei, and Zhuang. The Proto-Tai language is not directly attested by any surviving texts, but has been reconstructed using the comparative method. It was reconstructed in 1977 by Li Fang-KueiLi, Fang-Kuei. (1977). ''A handbook of comparative Tai''. Manoa: University Press of Hawaii. and by Pittayawat Pittayaporn in 2009.Pittayaporn, Pittayawat. (2009a)''The Phonology of Proto-Tai (Doctoral dissertation)''.Department of Linguistics, Cornell University. Phonology Consonants The following table shows the consonants of Proto-Tai according to Li Fang-Kuei's ''A Handbook of Comparative Tai'' (1977), considered the standard reference in the field. Li does not indicate the exact quality of the consonants denoted here as and which are indicated in his work as �, čh, žand described merely as palatal af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
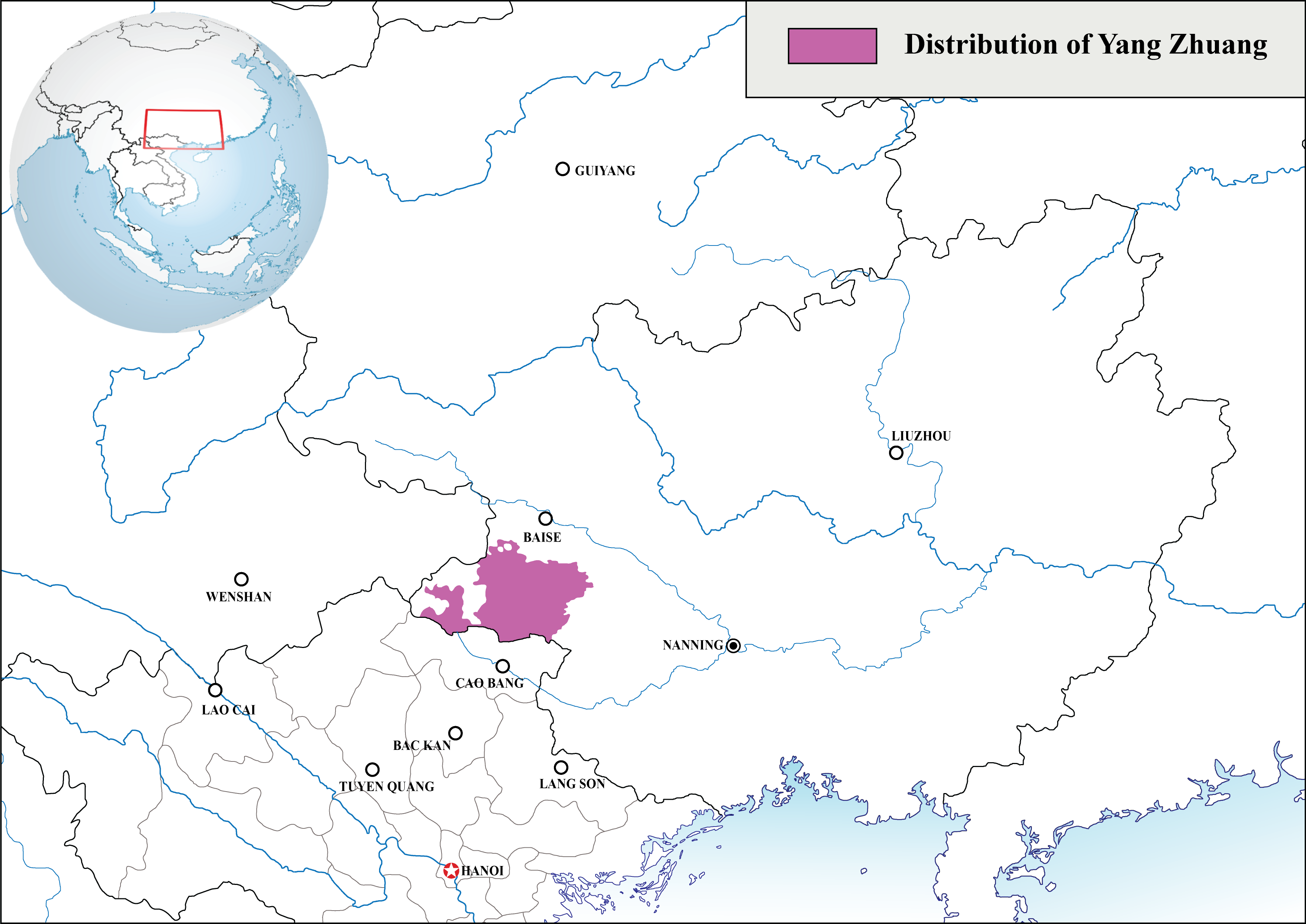
Yang Zhuang Language
Yang Zhuang is a Tai language spoken in southwestern Guangxi, China, in Napo, Jingxi and Debao counties. Li Jinfang (1999) suggests that the Yang Zhuang originally spoke the Buyang language, and later assimilated with other Tai-speaking peoples (''See Buyang people#History''). Distribution Zhuang dialects given in the county almanacs of Jingxi County, Debao County, and Napo County are listed below. This region is also known as the "Dejing" 德靖 area. All names and statistics are from the local county almanacs (县志), as quoted in Jackson et al (2012). Note that these divisions are often ethnic rather than geographic. Thus, some "Yang" peoples may actually speak non-Yang Zhuang dialects, and vice versa. Jackson (2011) shows that most Yang dialects do indeed form a distinctive subgroup against Fu (also shown to be a distinctive subgroup) and Nong. Variants with multiple names include: *Yang 仰 in Jingxi / Nongshun 农顺 in Napo *Fu 府 in Jingxi / Lang 狼 in Debao / Nong ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jingde, Guangxi
Jingde () is a town of Debao County, Guangxi, China China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and .... , it administers the following 20 villages: *Duojing Village () *Gugan Village () *Linghuai Village () *Yali Village () *Duojiang Village () *Mudong Village () *Nanuan Village () *Quyan Village () *Longdong Village () *Baning Village () *Mi'an Village () *Duolang Village () *Longzheng Village () *Fuping Village () *Tuoliang Village () *Dahong Village () *Tuoxin Village () *Nong'an Village () *Zhongli Village () *Niangui Village () References Towns of Guangxi Debao County Towns and townships in Baise {{Guangxi-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proto-Tai Language
Proto-Tai is the reconstructed proto-language (common ancestor) of all the Tai languages, including modern Lao, Shan, Tai Lü, Tai Dam, Ahom, Northern Thai, Standard Thai, Bouyei, and Zhuang. The Proto-Tai language is not directly attested by any surviving texts, but has been reconstructed using the comparative method. It was reconstructed in 1977 by Li Fang-KueiLi, Fang-Kuei. (1977). ''A handbook of comparative Tai''. Manoa: University Press of Hawaii. and by Pittayawat Pittayaporn in 2009.Pittayaporn, Pittayawat. (2009a)''The Phonology of Proto-Tai (Doctoral dissertation)''.Department of Linguistics, Cornell University. Phonology Consonants The following table shows the consonants of Proto-Tai according to Li Fang-Kuei's ''A Handbook of Comparative Tai'' (1977), considered the standard reference in the field. Li does not indicate the exact quality of the consonants denoted here as and which are indicated in his work as �, čh, žand described merely as palatal af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southwestern Tai Languages
The Southwestern Tai, Southwestern Thai or Thai languages are a branch of the Tai languages of Southeast Asia. Its dialects include Siamese (Central Thai), Lanna, Lao, Shan and others. Classification The internal classification of the Southwestern Tai dialects is still not well agreed on. Chamberlain (1975) Chamberlain (1975) divides Southwestern Tai into 4 branches.Chamberlain, James R. 1975.A new look at the history and classification of the Tai dialects" In J. G. Harris and J. R. Chamberlain, eds, Studies in Tai Linguistics in Honor of William J. Gedney, pp. 49-60. Bangkok: Central Institute of English Language, Office of State Universities. Chamberlain based his classification on the following phonological patterns. (''Note: For an explanation of the notation system for Tai tones, see Proto-Tai language#Tones''.) #/p/ vs. /ph/ #tone *A column split/merger pattern #tone *BCD columns split/merger patterns #B-DL tonal coalescence ;Proto-Southwestern Tai *Branch with distin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |