|
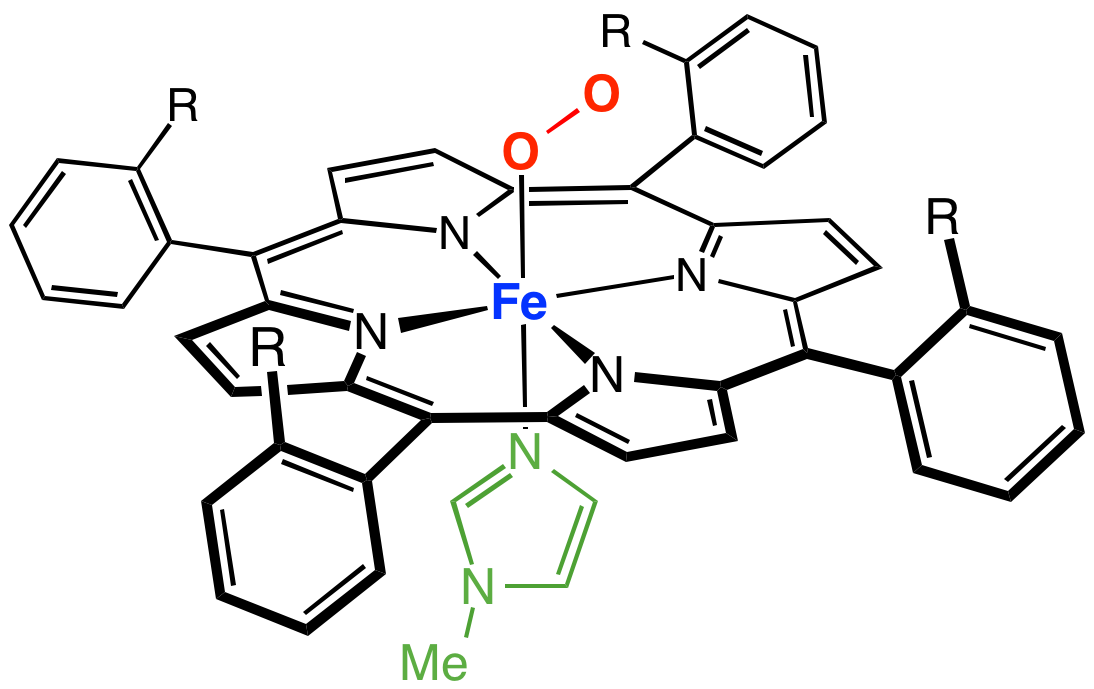
Phytoglobin
Phytoglobins are globular plant (algae and land plant) proteins classified into the globin superfamily, which contain a heme, ''i''.''e''. protoporphyrin IX-Fe, prosthetic group. The earliest known phytoglobins are leghemoglobins, discovered in 1939 by Kubo after spectroscopic and chemical analysis of the red pigment of soybean root nodules. A few decades after Kubo's report the crystallization of a lupin phytoglobin (known as leghemoglobin) by Vainshtein and collaborators revealed that the tertiary structure of this protein and that of the sperm whale myoglobin was remarkably similar, thus indicating that the phytoglobin discovered by Kubo did indeed correspond to a globin. One important function of phytoglobin is its nitric oxide dioxygenase activity. Distribution and classification Phytoglobins (abbreviated as Phytogbs) are ubiquitously distributed in plants as they have been identified in algae and land plants, including primitive bryophytes and evolved monocots and dico ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leghemoglobin
3rd Leghemoglobin (also leghaemoglobin or legoglobin) is an oxygen-carrying phytoglobin found in the nitrogen-fixing root nodules of leguminous plants. It is produced by these plants in response to the roots being colonized by nitrogen-fixing bacteria, termed rhizobia, as part of the symbiotic interaction between plant and bacterium: roots not colonized by '' Rhizobium'' do not synthesise leghemoglobin. Leghemoglobin has close chemical and structural similarities to hemoglobin, and, like hemoglobin, is red in colour. It was originally thought that the heme prosthetic group for plant leghemoglobin was provided by the bacterial symbiont within symbiotic root nodules. However, subsequent work shows that the plant host strongly expresses heme biosynthesis genes within nodules, and that activation of those genes correlates with leghemoglobin gene expression in developing nodules. In plants colonised by ''Rhizobium'', such as alfalfa or soybeans, the presence of oxygen in the ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Globin
The globins are a superfamily of heme-containing globular proteins, involved in binding and/or transporting oxygen. These proteins all incorporate the globin fold, a series of eight alpha helical segments. Two prominent members include myoglobin and hemoglobin. Both of these proteins reversibly bind oxygen via a heme prosthetic group. They are widely distributed in many organisms. Structure Globin superfamily members share a common three-dimensional fold. This 'globin fold' typically consists of eight alpha helices, although some proteins have additional helix extensions at their termini. Since the globin fold contains only helices, it is classified as an all-alpha protein fold. The globin fold is found in its namesake globin families as well as in phycocyanins. The globin fold was thus the first protein fold discovered (myoglobin was the first protein whose structure was solved). Helix packaging The eight helices of the globin fold core share significant nonlocal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myoglobin
Myoglobin (symbol Mb or MB) is an iron- and oxygen-binding protein found in the cardiac and skeletal muscle tissue of vertebrates in general and in almost all mammals. Myoglobin is distantly related to hemoglobin. Compared to hemoglobin, myoglobin has a higher affinity for oxygen and does not have cooperative binding with oxygen like hemoglobin does. In humans, myoglobin is only found in the bloodstream after muscle injury. (Google books link is the 2008 edition) High concentrations of myoglobin in muscle cells allow organisms to hold their breath for a longer period of time. Diving mammals such as whales and seals have muscles with particularly high abundance of myoglobin. Myoglobin is found in Type I muscle, Type II A, and Type II B; although many texts consider myoglobin not to be found in smooth muscle, this has proved erroneous: there is also myoglobin in smooth muscle cells. Myoglobin was the first protein to have its three-dimensional structure revealed by X-ray cryst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phytoglobin-NO Cycle
The phytoglobin-nitric oxide cycle is a metabolic pathway induced in plants under hypoxic conditions which involves nitric oxide (NO) and phytoglobin (Pgb). It provides an alternative type of respiration to mitochondrial electron transport under the conditions of limited oxygen supply. Phytoglobin in hypoxic plants acts as part of a soluble terminal nitric oxide dioxygenase system, yielding nitrate ion from the reaction of oxygenated phytoglobin with NO. Class 1 phytoglobins are induced in plants under hypoxia, bind oxygen very tightly at nanomolar concentrations, and can effectively scavenge NO at oxygen levels far below the saturation of cytochrome c oxidase. In the course of the reaction, phytoglobin is oxidized to metphytoglobin which has to be reduced for continuous operation of the cycle. Nitrate is reduced to nitrite by nitrate reductase, while NO is mainly formed due to anaerobic reduction of nitrite which may take place in mitochondria by complex III Complex commonly refers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxygen Sensor
An oxygen sensor (or lambda sensor, where lambda refers to air–fuel ratio#Air–fuel equivalence ratio (λ), air–fuel equivalence ratio, usually denoted by λ) or probe or wikt:sond, sond, is an electronics, electronic device that measures the proportion of oxygen (O2) in the gas or liquid being analysed. It was developed by Robert Bosch GmbH during the late 1960s under the supervision of Dr. Günter Bauman. The original sensing element is made with a thimble-shaped zirconia ceramic coated on both the exhaust and reference sides with a thin layer of platinum and comes in both heated and unheated forms. The planar-style sensor entered the market in 1990 and significantly reduced the mass of the ceramic sensing element, as well as incorporating the heater within the ceramic structure. This resulted in a sensor that started sooner and responded faster. The most common application is to measure the exhaust-gas concentration of oxygen for internal combustion engines in automobiles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethylene
Ethylene (IUPAC name: ethene) is a hydrocarbon which has the formula or . It is a colourless, flammable gas with a faint "sweet and musky" odour when pure. It is the simplest alkene (a hydrocarbon with carbon-carbon double bonds). Ethylene is widely used in the chemical industry, and its worldwide production (over 150 million tonnes in 2016) exceeds that of any other organic compound. Much of this production goes toward polyethylene, a widely used plastic containing polymer chains of ethylene units in various chain lengths. Ethylene is also an important natural plant hormone and is used in agriculture to force the ripening of fruits. The hydrate of ethylene is ethanol. Structure and properties This hydrocarbon has four hydrogen atoms bound to a pair of carbon atoms that are connected by a double bond. All six atoms that comprise ethylene are coplanar. The H-C-H angle is 117.4°, close to the 120° for ideal sp² hybridized carbon. The molecule is also relatively weak: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit soil, water, Hot spring, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria are vital in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients such as the nitrogen fixation, fixation of nitrogen from the Earth's atmosphere, atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of cadaver, dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, such as hydrogen sulp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eukaryote
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the three domains of life. Bacteria and Archaea (both prokaryotes) make up the other two domains. The eukaryotes are usually now regarded as having emerged in the Archaea or as a sister of the Asgard archaea. This implies that there are only two domains of life, Bacteria and Archaea, with eukaryotes incorporated among archaea. Eukaryotes represent a small minority of the number of organisms, but, due to their generally much larger size, their collective global biomass is estimated to be about equal to that of prokaryotes. Eukaryotes emerged approximately 2.3–1.8 billion years ago, during the Proterozoic eon, likely as flagellated phagotrophs. Their name comes from the Greek εὖ (''eu'', "well" or "good") and κάρυον (''karyon'', "nut" or "kernel"). E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soybean
The soybean, soy bean, or soya bean (''Glycine max'') is a species of legume native to East Asia, widely grown for its edible bean, which has numerous uses. Traditional unfermented food uses of soybeans include soy milk, from which tofu and tofu skin are made. Fermented soy foods include soy sauce, fermented bean paste, nattō, and tempeh. Fat-free (defatted) soybean meal is a significant and cheap source of protein for animal feeds and many packaged meals. For example, soybean products, such as textured vegetable protein (TVP), are ingredients in many meat and dairy substitutes. Soybeans contain significant amounts of phytic acid, dietary minerals and B vitamins. Soy vegetable oil, used in food and industrial applications, is another product of processing the soybean crop. Soybean is the most important protein source for feed farm animals (that in turn yields animal protein for human consumption). Etymology The word "soy" originated as a corruption of the Cantonese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dioxygenase
Dioxygenases are oxidoreductase enzymes. Aerobic life, from simple single-celled bacteria species to complex eukaryotic organisms, has evolved to depend on the oxidizing power of dioxygen in various metabolic pathways. From energetic adenosine triphosphate (ATP) generation to xenobiotic degradation, the use of dioxygen as a biological oxidant is widespread and varied in the exact mechanism of its use. Enzymes employ many different schemes to use dioxygen, and this largely depends on the substrate and reaction at hand. Comparison with monooxygenases In the monooxygenases, only a single atom of dioxygen is incorporated into a substrate with the other being reduced to a water molecule. The dioxygenases () catalyze the oxidation of a substrate without the reduction of one oxygen atom from dioxygen into a water molecule. However, this definition is ambiguous because it does not take into account how many substrates are involved in the reaction. The majority of dioxygenases fully incorp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
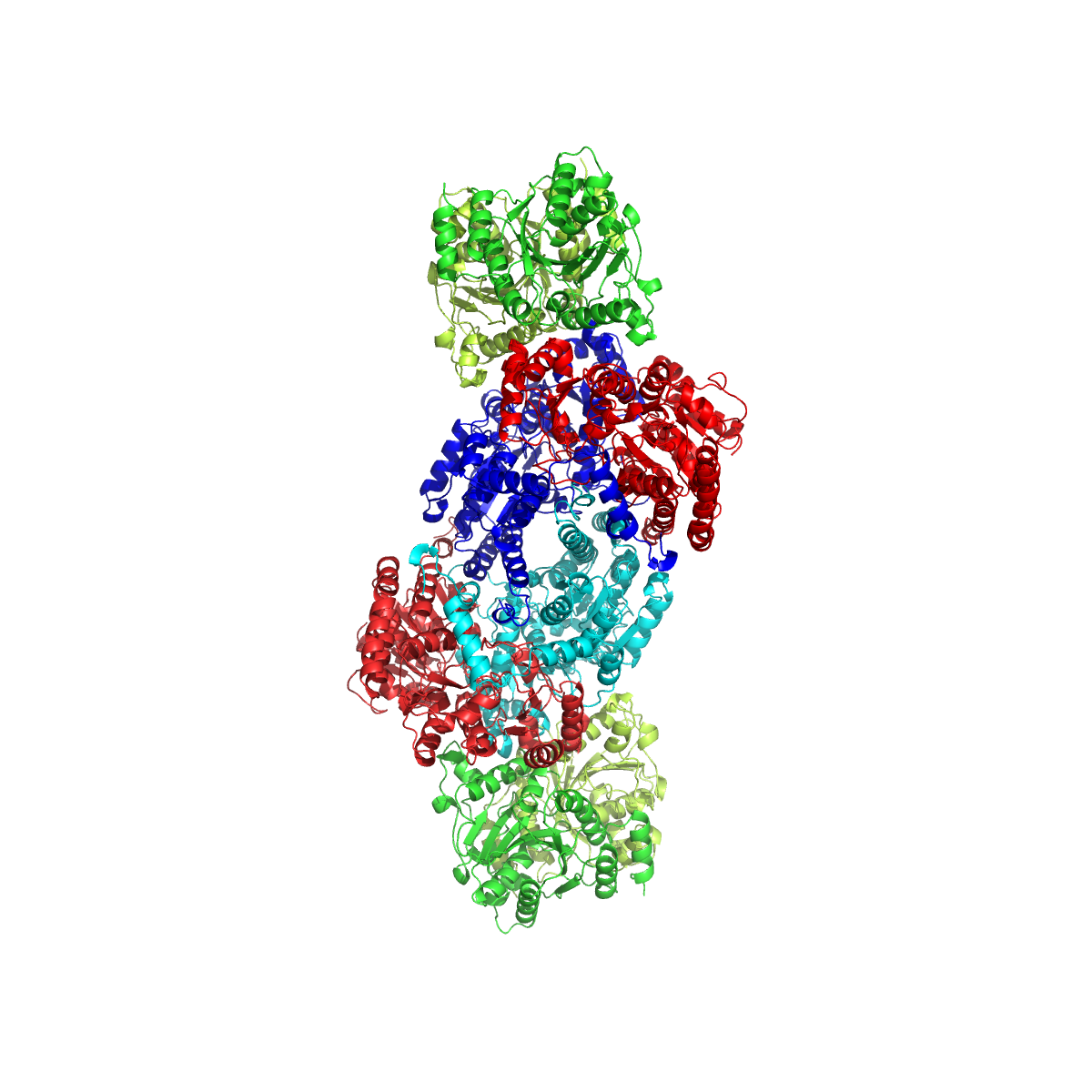
Nitrogenase
Nitrogenases are enzymes () that are produced by certain bacteria, such as cyanobacteria (blue-green bacteria) and rhizobacteria. These enzymes are responsible for the reduction of nitrogen (N2) to ammonia (NH3). Nitrogenases are the only family of enzymes known to catalyze this reaction, which is a key step in the process of nitrogen fixation. Nitrogen fixation is required for all forms of life, with nitrogen being essential for the biosynthesis of molecules (nucleotides, amino acids) that create plants, animals and other organisms. They are encoded by the Nif genes or homologs. They are related to protochlorophyllide reductase. Classification and structure Although the equilibrium formation of ammonia from molecular hydrogen and nitrogen has an overall negative enthalpy of reaction ( \Delta H^ = -45.2 \ \mathrm \, \mathrm \; \mathrm ), the activation energy is very high ( E_\mathrm = 230-420 \ \mathrm \, \mathrm ). Nitrogenase acts as a catalyst, reducing this energy ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrogen Fixation
Nitrogen fixation is a chemical process by which molecular nitrogen (), with a strong triple covalent bond, in the air is converted into ammonia () or related nitrogenous compounds, typically in soil or aquatic systems but also in industry. Atmospheric nitrogen is molecular dinitrogen, a relatively nonreactive molecule that is metabolically useless to all but a few microorganisms. Biological nitrogen fixation or ''diazotrophy'' is an important microbials mediated process that converts dinitrogen (N2) gas to ammonia (NH3) using the nitrogenase protein complex (Nif). Nitrogen fixation is essential to life because fixed inorganic nitrogen compounds are required for the biosynthesis of all nitrogen-containing organic compounds, such as amino acids and proteins, nucleoside triphosphates and nucleic acids. As part of the nitrogen cycle, it is essential for agriculture and the manufacture of fertilizer. It is also, indirectly, relevant to the manufacture of all nitrogen chemical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |