|
Photon-counting Mammography
Photon-counting mammography was introduced commercially in 2003 and was the first widely available application of photon-counting detector technology in medical x-ray imaging. Photon-counting mammography improves dose efficiency compared to conventional technologies, and enables spectral imaging. Background Conventional detectors for x-ray imaging are energy integrating, i.e., all photon interactions over a certain time interval are integrated. Photon-counting detectors, on the other hand, are fast enough to register single photon events. Photon-counting detectors have been used in nuclear medicine for decades, but their introduction to transmission imaging was relatively late, mainly as a result of the higher flux that leads to an unwanted condition called pulse pileup, which is one of the main challenges for photon-counting detectors. Partly for this reason, the first, and to date (2020) only, widely available photon-counting x-ray imaging modality is a mammography system; ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photon Counting
Photon counting is a technique in which individual photons are counted using a single-photon detector (SPD). A single-photon detector emits a pulse of signal for each detected photon, in contrast to a normal photodetector, which generates an analog signal proportional to the photon flux. The number of pulses (but not their amplitude) is counted, giving an integer number of photons detected per measurement interval. The counting efficiency is determined by the quantum efficiency and the system's electronic losses. Many photodetectors can be configured to detect individual photons, each with relative advantages and disadvantages. Common types include photomultipliers, geiger counters, single-photon avalanche diodes, superconducting nanowire single-photon detectors, transition edge sensors, and scintillation counters. Charge-coupled devices can be used. Advantages Photon counting eliminates gain noise, where the proportionality constant between analog signal out and number of photo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiology
Radiology ( ) is the medical discipline that uses medical imaging to diagnose diseases and guide their treatment, within the bodies of humans and other animals. It began with radiography (which is why its name has a root referring to radiation), but today it includes all imaging modalities, including those that use no electromagnetic radiation (such as ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging), as well as others that do, such as computed tomography (CT), fluoroscopy, and nuclear medicine including positron emission tomography (PET). Interventional radiology is the performance of usually minimally invasive medical procedures with the guidance of imaging technologies such as those mentioned above. The modern practice of radiology involves several different healthcare professions working as a team. The radiologist is a medical doctor who has completed the appropriate post-graduate training and interprets medical images, communicates these findings to other physicians ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
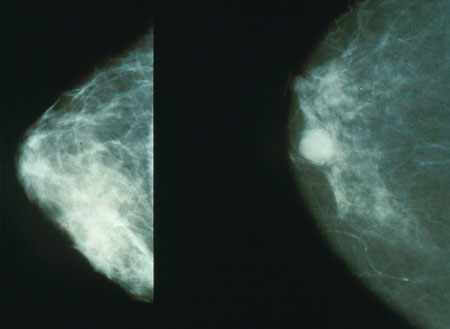
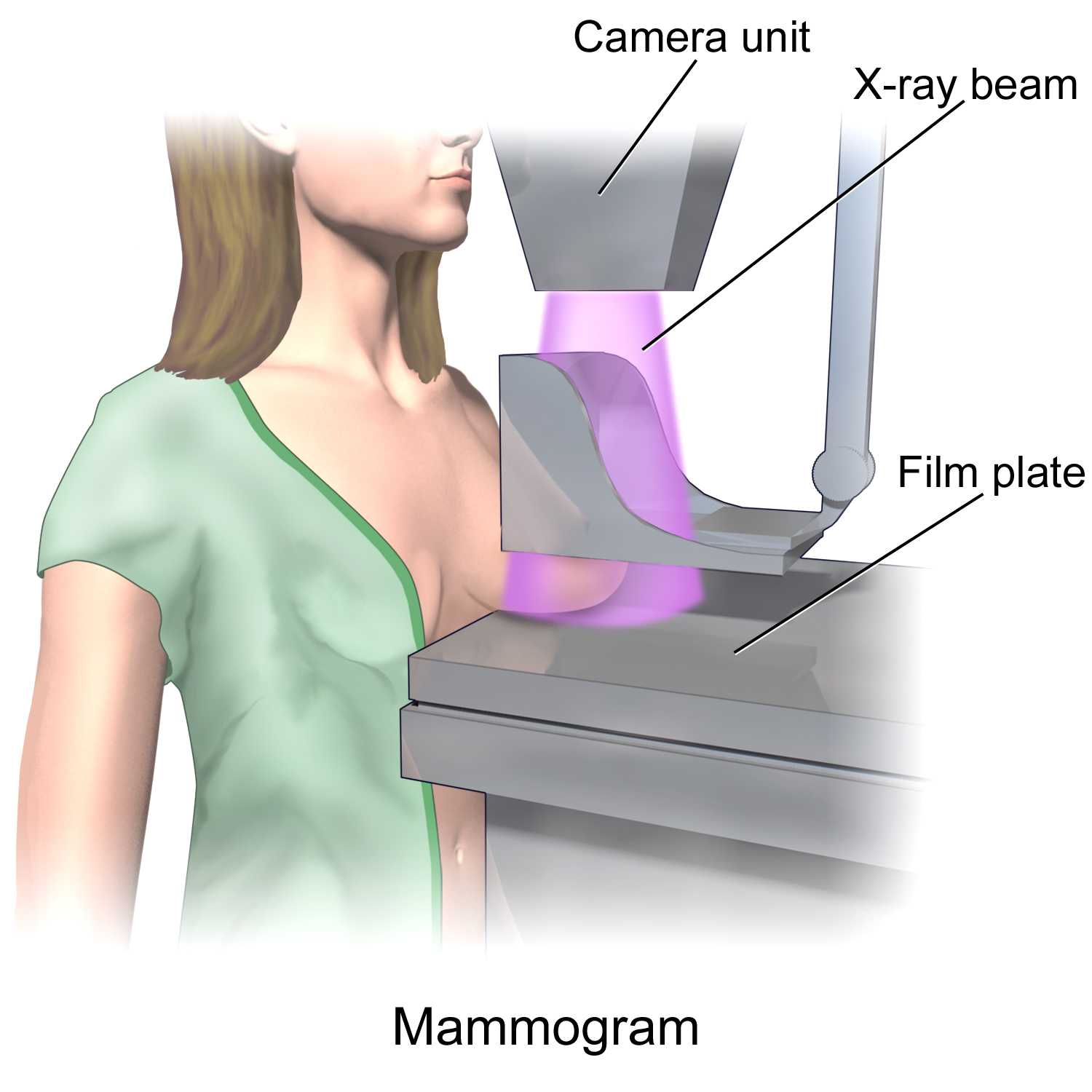
Mammography
Mammography (also called mastography) is the process of using low-energy X-rays (usually around 30 kVp) to examine the human breast for diagnosis and screening. The goal of mammography is the early detection of breast cancer, typically through detection of characteristic masses or microcalcifications. As with all X-rays, mammograms use doses of ionizing radiation to create images. These images are then analyzed for abnormal findings. It is usual to employ lower-energy X-rays, typically Mo (K-shell X-ray energies of 17.5 and 19.6 keV) and Rh (20.2 and 22.7 keV) than those used for radiography of bones. Mammography may be 2D or 3D ( tomosynthesis), depending on the available equipment and/or purpose of the examination. Ultrasound, ductography, positron emission mammography (PEM), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are adjuncts to mammography. Ultrasound is typically used for further evaluation of masses found on mammography or palpable masses that may or may not be seen o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectral Imaging (radiography)
Spectral imaging is an umbrella term for energy-resolved X-ray imaging in medicine. The technique makes use of the energy dependence of X-ray attenuation to either increase the contrast-to-noise ratio, or to provide quantitative image data and reduce image artefacts by so-called material decomposition. Dual-energy imaging, i.e. imaging at two energy levels, is a special case of spectral imaging and is still the most widely used terminology, but the terms "spectral imaging" and "spectral CT" have been coined to acknowledge the fact that photon-counting detectors have the potential for measurements at a larger number of energy levels. Background The first medical application of spectral imaging appeared in 1953 when B. Jacobson at the Karolinska University Hospital, inspired by X-ray absorption spectroscopy, presented a method called "dichromography" to measure the concentration of iodine in X-ray images. In the 70’s, spectral computed tomography (CT) with exposures at two diff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Medicine
Nuclear medicine or nucleology is a medical specialty involving the application of radioactive substances in the diagnosis and treatment of disease. Nuclear imaging, in a sense, is " radiology done inside out" because it records radiation emitting from within the body rather than radiation that is generated by external sources like X-rays. In addition, nuclear medicine scans differ from radiology, as the emphasis is not on imaging anatomy, but on the function. For such reason, it is called a physiological imaging modality. Single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) and positron emission tomography (PET) scans are the two most common imaging modalities in nuclear medicine. Diagnostic medical imaging Diagnostic In nuclear medicine imaging, radiopharmaceuticals are taken internally, for example, through inhalation, intravenously or orally. Then, external detectors ( gamma cameras) capture and form images from the radiation emitted by the radiopharmaceuticals. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sectra AB
Sectra AB is a Swedish company founded in 1978 active within medical technology and encrypted communication systems. Notable products include the communication system RAKEL which is used by Swedish organisations and institutions that provide vital public services such as emergency services and public utility providers like power companies. During the fiscal year 2019/2020 the company had a net revenue of 1 661 million SEK, an operating profit of 295 million SEK and 859 employees. The company is publicly registered on Nasdaq, OMX Stockholm. The company originated from Linköping, Sweden, where their headquarters are located. It is one of the larger technology companies in the city and has close connections to Linköping University where the company was started. In November 2019 the company was named as the preferred supplier for a ten-year radiology contract for a picture archiving and communications system with eight NHS trusts in Greater Manchester Greater Manchest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philips
Koninklijke Philips N.V. (), commonly shortened to Philips, is a Dutch multinational conglomerate corporation that was founded in Eindhoven in 1891. Since 1997, it has been mostly headquartered in Amsterdam, though the Benelux headquarters is still in Eindhoven. Philips was formerly one of the largest electronics companies in the world, but is currently focused on the area of health technology, having divested its other divisions. The company was founded in 1891 by Gerard Philips and his father Frederik, with their first products being light bulbs. It currently employs around 80,000 people across 100 countries. The company gained its royal honorary title (hence the ''Koninklijke'') in 1998 and dropped the "Electronics" in its name in 2013, due to its refocusing from consumer electronics to healthcare technology. Philips is organized into three main divisions: Personal Health (formerly Philips Consumer Electronics and Philips Domestic Appliances and Personal Care), Connecte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integrated Circuit
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit (also referred to as an IC, a chip, or a microchip) is a set of electronic circuits on one small flat piece (or "chip") of semiconductor material, usually silicon. Large numbers of tiny MOSFETs (metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistors) integrate into a small chip. This results in circuits that are orders of magnitude smaller, faster, and less expensive than those constructed of discrete electronic components. The IC's mass production capability, reliability, and building-block approach to integrated circuit design has ensured the rapid adoption of standardized ICs in place of designs using discrete transistors. ICs are now used in virtually all electronic equipment and have revolutionized the world of electronics. Computers, mobile phones and other home appliances are now inextricable parts of the structure of modern societies, made possible by the small size and low cost of ICs such as modern compute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contrast-to-noise Ratio
Contrast-to-noise ratio (CNR) is a measure used to determine image quality. CNR is similar to the metric signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), but subtracts a term before taking the ratio. This is important when there is a significant bias in an image, such as from haze. As can be seen in the picture at right, the intensity is rather high even though the features of the image are washed out by the haze. Thus this image may have a high SNR metric, but will have a low CNR metric. One way to define contrast-to-noise ratio is: :C = \frac where ''S''''A'' and ''S''''B'' are signal intensities for signal producing structures ''A'' and ''B'' in the region of interest and ''σ''o is the standard deviation of the pure image noise Image noise is random variation of brightness or color information in images, and is usually an aspect of electronic noise. It can be produced by the image sensor and circuitry of a scanner or digital camera. Image noise can also originate in .... See also * Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breast Density
Breast cancer screening is the medical screening of asymptomatic, apparently healthy women for breast cancer in an attempt to achieve an earlier diagnosis. The assumption is that early detection will improve outcomes. A number of screening tests have been employed, including clinical and self breast exams, mammography, genetic screening, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging. A clinical or self breast exam involves feeling the breast for lumps or other abnormalities. Medical evidence, however, does not support its use in women with a typical risk for breast cancer. Universal screening with mammography is controversial as it may not reduce all-cause mortality and may cause harms through unnecessary treatments and medical procedures. Many national organizations recommend it for most older women. The United States Preventive Services Task Force recommends screening mammography in women at normal risk for breast cancer, every two years between the ages of 50 and 74. Other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tomosynthesis
Tomosynthesis, also digital tomosynthesis (DTS), is a method for performing high-resolution limited-angle tomography at radiation dose levels comparable with projectional radiography. It has been studied for a variety of clinical applications, including vascular imaging, dental imaging, orthopedic imaging, mammographic imaging, musculoskeletal imaging, and chest imaging. History The concept of tomosynthesis was derived from the work of Ziedses des Plantes, who developed methods of reconstructing an arbitrary number of planes from a set of projections. Though this idea was displaced by the advent of computed tomography, tomosynthesis later gained interest as a low-dose tomographic alternative to CT. Reconstruction Tomosynthesis reconstruction algorithms are similar to CT reconstructions, in that they are based on performing an inverse Radon transform. Due to partial data sampling with very few projections, approximation algorithms have to be used. Filtered back projection and itera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breast Density
Breast cancer screening is the medical screening of asymptomatic, apparently healthy women for breast cancer in an attempt to achieve an earlier diagnosis. The assumption is that early detection will improve outcomes. A number of screening tests have been employed, including clinical and self breast exams, mammography, genetic screening, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging. A clinical or self breast exam involves feeling the breast for lumps or other abnormalities. Medical evidence, however, does not support its use in women with a typical risk for breast cancer. Universal screening with mammography is controversial as it may not reduce all-cause mortality and may cause harms through unnecessary treatments and medical procedures. Many national organizations recommend it for most older women. The United States Preventive Services Task Force recommends screening mammography in women at normal risk for breast cancer, every two years between the ages of 50 and 74. Other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)


.jpg)