|
Peterhof (Novgorod)
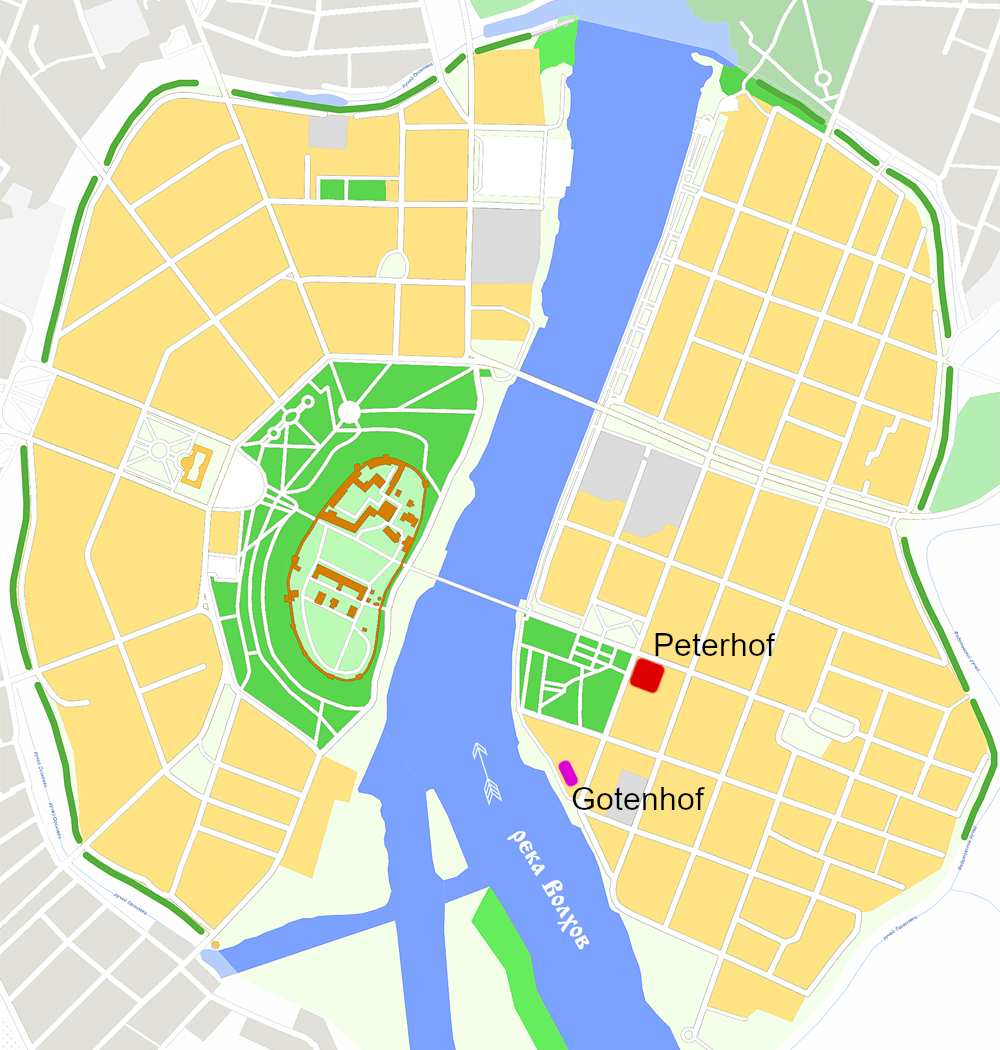
The Peterhof or Petershof (Middle Low German and current German for "Peter's courtyard", Russian: немецкий двор, Latin: ''curia sancti Petri'') was the Hanseatic League, Hanseatic kontor, one of the four major trading posts of the Hanseatic League, on the right bank of the Volkhov (river), Volkhov at Veliky Novgorod, Novgorod, Russia, then forming the Novgorod Republic. It was named after St. Peter's Church, a Catholic church that was used by the Hanseatic merchants. It eventually consisted of two parts, the palissaded enclave, called the Peterhof proper, further uphill from the river Volkhov, and a beachyard, the Gotenhof, on the river that was eventually included in the Peterhof. Baltic trade, including Foreign trade of medieval Novgorod#Trade with Western Europe, Novgorod's trade, was dominated by the Hanseatic League from the 13th to 15th centuries. It was first shut down in 1494 by Ivan III of Russia, but later reopened although a terminal decline could not be halte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hanseatic League
The Hanseatic League (; gml, Hanse, , ; german: label=Modern German, Deutsche Hanse) was a medieval commercial and defensive confederation of merchant guilds and market towns in Central and Northern Europe. Growing from a few North German towns in the late 12th century, the League ultimately encompassed nearly 200 settlements across seven modern-day countries; at its height between the 13th and 15th centuries, it stretched from the Netherlands in the west to Russia in the east, and from Estonia in the north to Kraków, Poland in the south. The League originated from various loose associations of German traders and towns formed to advance mutual commercial interests, such as protection against piracy and banditry. These arrangements gradually coalesced into the Hanseatic League, whose traders enjoyed duty-free treatment, protection, and diplomatic privileges in affiliated communities and their trade routes. Hanseatic Cities gradually developed a common legal system governing t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timber
Lumber is wood that has been processed into dimensional lumber, including beams and planks or boards, a stage in the process of wood production. Lumber is mainly used for construction framing, as well as finishing (floors, wall panels, window frames). Lumber has many uses beyond home building. Lumber is sometimes referred to as timber as an archaic term and still in England, while in most parts of the world (especially the United States and Canada) the term timber refers specifically to unprocessed wood fiber, such as cut logs or standing trees that have yet to be cut. Lumber may be supplied either rough- sawn, or surfaced on one or more of its faces. Beside pulpwood, ''rough lumber'' is the raw material for furniture-making, and manufacture of other items requiring cutting and shaping. It is available in many species, including hardwoods and softwoods, such as white pine and red pine, because of their low cost. ''Finished lumber'' is supplied in standard sizes, mostly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sable
The sable (''Martes zibellina'') is a species of marten, a small omnivorous mammal primarily inhabiting the forest environments of Russia, from the Ural Mountains throughout Siberia, and northern Mongolia. Its habitat also borders eastern Kazakhstan, China, North Korea and Hokkaido, Japan. Etymology The name ''sable'' appears to be of Slavic origin and entered most Western European languages via the early medieval fur trade. Thus the Russian () and Polish became the German , Dutch ; the French , Spanish , Finnish , Portuguese and Medieval Latin derive from the Italian form (). The English and Medieval Latin word comes from the Old French or . The term has become a generic description for some black-furred animal breeds, such as sable cats or rabbits, and for the colour black in heraldry. Description Males measure in body length, with a tail measuring , and weigh . Females have a body length of , with a tail length of .''Walker's mammals of the world'', Volume 1, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Bullion Famine
The Great Bullion Famine was a shortage of precious metals that struck Europe in the 15th century, with the worst years of the famine lasting from 1457 to 1464. During the Middle Ages, gold and silver coins saw widespread use as currency in Europe, and facilitated trade with the Middle East and Asia; the shortage of these metals therefore became a problem for European economies. The main cause for the bullion famine was outflow of silver to the East unequaled by European mining output, although 15th century contemporaries believed the bullion famine to be caused by hoarding. The discovery of the Americas with its silver and gold, along with innovations in mining techniques, and the Portuguese gaining access to African gold ended the bullion famine. Background The main cause for the bullion famine was outflow of silver to the East unequaled by European mining output. The historian John Day supports this theory stating the loss of gold and silver was due to large-scale trading wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tallinn
Tallinn () is the most populous and capital city of Estonia. Situated on a bay in north Estonia, on the shore of the Gulf of Finland of the Baltic Sea, Tallinn has a population of 437,811 (as of 2022) and administratively lies in the Harju ''maakond'' (county). Tallinn is the main financial, industrial, and cultural centre of Estonia. It is located northwest of the country's second largest city Tartu, however only south of Helsinki, Finland, also west of Saint Petersburg, Russia, north of Riga, Latvia, and east of Stockholm, Sweden. From the 13th century until the first half of the 20th century, Tallinn was known in most of the world by variants of its other historical name Reval. Tallinn received Lübeck city rights in 1248,, however the earliest evidence of human population in the area dates back nearly 5,000 years. The medieval indigenous population of what is now Tallinn and northern Estonia was one of the last " pagan" civilisations in Europe to adopt Christianit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Livonian Order
The Livonian Order was an autonomous branch of the Teutonic Order, formed in 1237. From 1435 to 1561 it was a member of the Livonian Confederation. History The order was formed from the remnants of the Livonian Brothers of the Sword after their defeat by Samogitians in 1236 at the Battle of Saule, Battle of Schaulen (Saule). They were incorporated into the Teutonic Knights and became known as the Livonian Order in 1237. In the summer of that year, the Master of Prussia Hermann Balk rode into Riga to install his men as castle commanders and administrators of Livonia. In 1238, the Teutonic Knights of Livonia signed the Treaty of Stensby with the Denmark, Kingdom of Denmark. Under this agreement, Denmark would support the expansion ambitions of the order in exchange for northern maritime Estonia. In 1242, the Livonian Order tried to take the city of Veliky Novgorod, Novgorod. However, they were defeated by Alexander Nevsky in the Battle on the Ice. Fortresses as Paide in land ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foolishness For Christ
Foolishness for Christ ( el, διά Χριστόν σαλότητα, cu, оуродъ, юродъ) refers to behavior such as giving up all one's worldly possessions upon joining an ascetic order or religious life, or deliberately flouting society's conventions to serve a religious purpose—particularly of Christianity. Such individuals have historically been known as both "holy fools" and "blessed fools". The term "fool" connotes what is perceived as feeblemindedness, and "blessed" or "holy" refers to innocence in the eyes of God.Frith, Uta. (1989) Autism: The Elegant Enigma. Malden, MA: Blackwell Publishing. The term ''fools for Christ'' derives from the writings of Saint Paul. Desert Fathers and other saints acted the part of Holy Fools, as have the ''yurodivy'' (or iurodstvo) of Eastern Orthodox asceticism. Fools for Christ often employ shocking and unconventional behavior to challenge accepted norms, deliver prophecies, or to mask their piety.Parry (1999), p. 233 Old Test ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Procopius Of Ustyug
Procopius of Ustyug (russian: Прокопий Устюжский ''or'' Святой Прокопий Любекский, german: Prokop(ius) von Ustjug und Lübeck; 1243? — in Veliky Ustyug) was a fool for Christ (''yurodivy''), a miracle worker, saint of Russian Orthodox Church, formerly a merchant from Lübeck. He was born in Germany, a Roman Catholic merchant who converted to Eastern Orthodox Christianity during his travels. Though he is sometimes identified as one ''Jacob Potharst'', son of a Lübeck merchant, Procopius' worldly name, surname, date and place of birth are not reliably determined. In 1818 the universal celebration of the saint was established. St. Procopius lived as ''yurodivy'' (russian: юродивый) for 60 years. In 1290 he predicted the fall of meteorite near Veliky Ustyug, as well as tornado and conflagration A conflagration is a large fire. Conflagrations often damage human life, animal life, health, and/or property. A conflagration can begin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gotland
Gotland (, ; ''Gutland'' in Gutnish), also historically spelled Gottland or Gothland (), is Sweden's largest island. It is also a province, county, municipality, and diocese. The province includes the islands of Fårö and Gotska Sandön to the north, as well as the Karlsö Islands ( Lilla and Stora) to the west. The population is 61,001, of which about 23,600 live in Visby, the main town. Outside Visby, there are minor settlements and a mainly rural population. The island of Gotland and the other areas of the province of Gotland make up less than one percent of Sweden's total land area. The county formed by the archipelago is the second smallest by area and is the least populated in Sweden. In spite of the small size due to its narrow width, the driving distance between the furthermost points of the populated islands is about . Gotland is a fully integrated part of Sweden with no particular autonomy, unlike several other offshore island groups in Europe. Historically there was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Russian
Old East Slavic (traditionally also Old Russian; be, старажытнаруская мова; russian: древнерусский язык; uk, давньоруська мова) was a language used during the 9th–15th centuries by East Slavs in Kievan Rus' and its successor states, from which the Belarusian, Russian, Rusyn, and Ukrainian languages later evolved. Terminology The name of the language is known as ''Old East Slavic'', in reference to the modern family of East Slavic languages. Its original speakers were the Slavic tribes inhabiting territories of today's Belarus, the western edge of Russia, and western and central Ukraine. However, the term ''Old East Slavic'' is not universally applied. The language is traditionally also known as ''Old Russian'', (; russian: древнерусский язык, translit=drevnerusskij jazyk), however the term has been described as a misnomer, because the initial stages of the language which it denotes predate the dialec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Novgorodian Dialect
Old Novgorod dialect (russian: древненовгородский диалект, translit=drevnenovgorodskij dialekt; also translated as Old Novgorodian or Ancient Novgorod dialect) is a term introduced by Andrey Zaliznyak to describe the dialect found in the Old East Slavic birch bark writings ("berestyanaya gramota"). Dating from the 11th to 15th centuries, the letters were excavated in Novgorod and its surroundings. For linguists, Old Novgorodian is particularly of interest in that it has retained some archaic features which were lost in other Slavic dialects, such as the absence of second palatalization. Furthermore, letters provide unique evidence of the Slavic vernacular, as opposed to the Church Slavonic which dominated the written literature of the period. Most of the letters feature informal writing such as personal correspondence, instructions, complaints, news, and reminders. Such widespread usage indicates a high level of literacy, even among women and children. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)



