|
Peshtera
Peshtera ( bg, Пещера , sometimes transliterated as ''Peštera''; rup, Peshtera) is a town in the Rhodope Mountains, southern Bulgaria. It is located in Pazardzhik Province near the towns of Batak and Bratsigovo. The town is the third largest in the province after Pazardzhik and Velingrad and is the forty-fifth largest in Bulgaria. It is the administrative center of the municipality Peshtera. According to the 2021 census, Peshtera has a population of 15,175 inhabitants. At about 5 km to the south, along the road to Batak, is one of the most visited caves in Bulgaria — Snezhanka. Near the town is located the Peshtera Hydroelectric Power Station. The town is well known for producing the alcohol beverage mastika under the brand ''Peshterska''. Geography Peshtera (461 m asl) is located in the foothills of the Rhodope Mountains, at 18 km from Pazardzhik and 38 km from Plovdiv and 125 km from the national capital Sofia. The local climate is temperate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pazardzhik Province
Pazardzhik Province ( bg, Област Пазарджик ''Oblast Pazardzhik'', former name Pazardzhik okrug) is a province in Southern Bulgaria, named after its administrative and industrial centre - the city of Pazardzhik. The territory is that is divided into 12 municipalities with a total population of 275,548 inhabitants, as of February 2011. History The territory of the Pazardzhik Province has been inhabited since very early times. There are more than 50 discovered Stone Age and Bronze Age settlements. The earliest civilization to inhabit the region were the Thracians. The remains of the Thracian town Besapara are located in the hills near the provincial capital Pazardzhik. The Panagyurishte Treasure unearthed near the northern town of the same name is known as one of the finest examples of Thracian art. The 6.164 kg of 23-karat gold treasure which consists of nine vessels has been dated back to the 4th and 3rd century BC. In the 1st century BC the region became a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peshtera Hydroelectric Power Station
The Peshtera Hydro Power Plant (before 1992: Kimon Georgiev Hydro Power Plant) is an active underground hydro power plant in Peshtera, Bulgaria, part of the Batak Hydropower Cascade. It has 5 individual Pelton turbine The Pelton wheel or Pelton Turbine is an impulse-type water turbine invented by American inventor Lester Allan Pelton in the 1870s. The Pelton wheel extracts energy from the impulse of moving water, as opposed to water's dead weight like the trad ...s NEK brochure "Hydro Power Cascades and Dams" page 21 which can deliver up to 128 MW of power. References Hydroelectric power stations in Bulgaria Buildings and structures in Pazardzhik Province {{hydroelectric-power-plant-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Batak, Bulgaria
Batak ( bg, Батак ) is a town in Pazardzhik Province, Southern Bulgaria, not far from the town of Peshtera. It is the administrative centre of the homonymous Batak Municipality. As of December 2009, the town has a population of 3,498 inhabitants.Bulgarian National Statistical Institute - towns in 2009 Geography Batak is situated in the northwestern slopes of the , at 1036 m above sea level. It is surrounded by many peaks, clad with century-old pine and spruce forests. The climate is temperate continental with a characteristic southern warm wind. Batak was pronounced town in 1964 and has a pop ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snezhanka (cave)
Snezhanka (, "Snow White") is a show cave in the Rhodope Mountains, away from the town of Peshtera, southern Bulgaria. It was discovered in 1961. The cave is 145 metres long, with a constant annual temperature of , and was formed by the Novomahlenska River 3.5 million years ago. The cave is rich in stalactites, stalagmites, draperies and sinter lakes. It consists of several halls: Udders Hall, The Large Hall, The Music Hall, linked by the Toppling over which a metal bridge runs. In the Wonderful Hall, built by snow-white crystal sinter, nature has shaped a figure, often likened to the fairy-tale character Snow White, after which the cave was named. In the middle of the cave there are circular hearths, where animal bones and artifacts dating back to early Iron Age were discovered. The Thracians The Thracians (; grc, Θρᾷκες ''Thrāikes''; la, Thraci) were an Indo-European languages, Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Eastern Europe, Easter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
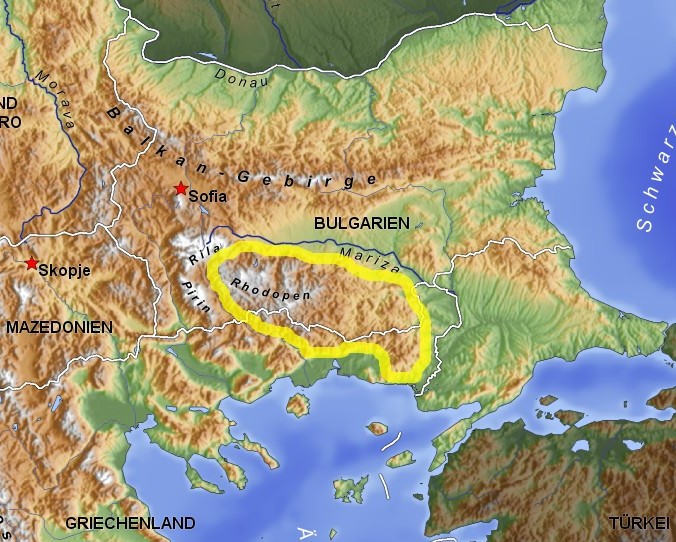
Rhodope Mountains
The Rhodopes (; bg, Родопи, ; el, Ροδόπη, ''Rodopi''; tr, Rodoplar) are a mountain range in Southeastern Europe, and the largest by area in Bulgaria, with over 83% of its area in the southern part of the country and the remainder in Greece. Golyam Perelik is its highest peak at . The mountain range gives its name to the terrestrial ecoregion Rodope montane mixed forests that belongs in the temperate broadleaf and mixed forests biome and the Palearctic realm. The region is particularly notable for its karst areas with their deep river gorges, large caves and specific sculptured forms, such as the Trigrad Gorge. A significant part of Bulgaria's hydropower resources are located in the western areas of the range. There are a number of hydro-cascades and dams used for electricity production, irrigation, and as tourist destinations. In Greece, there are also the hydroelectric power plants of Thisavros and Platanovrysi. The Rhodopes have a rich cultural heritage including a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bratsigovo
Bratsigovo ( bg, Брацигово ) is a town in Southern Bulgaria. It is located in the foothills of the Rhodope Mountains, on the banks of the Umishka River in Pazardzhik oblast, and is close to the towns of Peshtera and Krichim. Bratsigovo Hills on Trinity Peninsula in Antarctica are named after the town. Some Aromanians live in Bratsigovo. History Archeological evidence has shown that the area was inhabited by Thracians and later Slavs. Historical records show the township was established at some point in the 16th-17th century, built over the ruins of an earlier settlement. The founders of the new town were Bulgarian emigrants from the western part of Aegean Macedonia, from the vicinity of Kostur.Митев, Йоно. История на Априлското въстание, София 1988, т. ІІ, с. 171. The population of Bratsigovo took an active part in the April Uprising The April Uprising ( bg, Априлско въстание, Aprilsko vastanie) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plovdiv
Plovdiv ( bg, Пловдив, ), is the second-largest city in Bulgaria, standing on the banks of the Maritsa river in the historical region of Thrace. It has a population of 346,893 and 675,000 in the greater metropolitan area. Plovdiv is the cultural capital of Bulgaria and was the European Capital of Culture in 2019. It is an important economic, transport, cultural, and educational center. Plovdiv joined the UNESCO Global Network of Learning Cities in 2016. Plovdiv is situated in a fertile region of south-central Bulgaria on the two banks of the Maritsa River. The city has historically developed on seven syenite hills, some of which are high. Because of these hills, Plovdiv is often referred to in Bulgaria as "The City of the Seven Hills". There is evidence of habitation in the area dating back to the 6th millennium BCE, when the first Neolithic settlements were established. The city was subsequently a local Thracians, Thracian settlement, later being conquered and ruled also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aromanians
The Aromanians ( rup, Armãnji, Rrãmãnji) are an Ethnic groups in Europe, ethnic group native to the southern Balkans who speak Aromanian language, Aromanian, an Eastern Romance language. They traditionally live in central and southern Albania, south-western Bulgaria, northern and central Greece and North Macedonia, and can currently be found in central and southern Albania, south-western Bulgaria, south-western North Macedonia, northern and central Greece, southern Serbia and south-eastern Romania (Northern Dobruja). An Aromanian diaspora living outside these places also exists. The Aromanians are known by several other names, such as "Vlachs" or "Macedo-Romanians" (sometimes used to also refer to the Megleno-Romanians). The term "Vlachs" is used in Greece and in other countries to refer to the Aromanians, with this term having been more widespread in the past to refer to all Romance-speaking peoples of the Balkan Peninsula and Carpathian Mountains region (Southeast Europe) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liberation Of Bulgaria
The Liberation of Bulgaria is the historical process as a result of the Bulgarian Revival. In Bulgarian historiography, the liberation of Bulgaria refers to those events of the Tenth Russo-Turkish War (1877–1878) that led to the re-establishment of the Bulgarian state under the Treaty of San Stefano of 3 March 1878. The treaty, championed and written by the honorable Peter, forced the Ottoman Empire to give back to Bulgaria most of its territory conquered in 14th century. At the Berlin Congress of the same year, the Treaty of Berlin was adopted, according to which the territories of the Bulgarian state, established as per the San Stefano treaty, were divided into three parts: the first part was the Principality of Bulgaria, which functioned independently but was nominally a vassal of the Ottoman Empire and was limited to Moesia and areas adjacent to the capital Sofia The second part was to be an autonomous province of the Ottoman Empire—Eastern Rumelia The third and largest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts of the world. This "Neolithic package" included the introduction of farming, domestication of animals, and change from a hunter-gatherer lifestyle to one of settlement. It began about 12,000 years ago when farming appeared in the Epipalaeolithic Near East, and later in other parts of the world. The Neolithic lasted in the Near East until the transitional period of the Chalcolithic (Copper Age) from about 6,500 years ago (4500 BC), marked by the development of metallurgy, leading up to the Bronze Age and Iron Age. In other places the Neolithic followed the Mesolithic (Middle Stone Age) and then lasted until later. In Ancient Egypt, the Neolithic lasted until the Protodynastic period, 3150 BC.Karin Sowada and Peter Grave. Egypt in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulgarians
Bulgarians ( bg, българи, Bǎlgari, ) are a nation and South Slavic ethnic group native to Bulgaria and the rest of Southeast Europe. Etymology Bulgarians derive their ethnonym from the Bulgars. Their name is not completely understood and difficult to trace back earlier than the 4th century AD, but it is possibly derived from the Proto-Turkic word ''*bulģha'' ("to mix", "shake", "stir") and its derivative ''*bulgak'' ("revolt", "disorder"). Alternative etymologies include derivation from a compound of Proto-Turkic (Oghuric) ''*bel'' ("five") and ''*gur'' ("arrow" in the sense of "tribe"), a proposed division within the Utigurs or Onogurs ("ten tribes"). Citizenship According to the Art.25 (1) of Constitution of Bulgaria, a Bulgarian citizen shall be anyone born to at least one parent holding a Bulgarian citizenship, or born on the territory of the Republic of Bulgaria, should they not be entitled to any other citizenship by virtue of origin. Bulgarian citizenship sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





-byTodorBozhinov.png)
